原文:Langchain 代理 (Agents) ,赋能超级 LLMs - 知乎
大型语言模型(LLMs) 非常强大,但它们缺乏“最笨”的计算机程序可以轻松处理的特定能力。逻辑、计算和搜索是计算机通常擅长的领域,但 LLMs 却遇到了困难。 计算机可以解决非常复杂的数学问题,但如果我们让 GPT-4 告诉我们 4.1 * 7.9 的答案,它就失败了:

GPT 4 对简单计算的响应
要求 GPT-4 执行简单的计算通常会得到一个错误的答案。一个简单的计算器可以毫无问题地执行相同的计算。
根据一个简单的计算器,答案是 19.357,保留三位小数。一个简单的计算器程序可以做到这一点,但一个非常复杂的 AI 引擎却失败了,这是不是很有趣?
这还不是全部。如果我问 GPT-4,“我如何在 LangChain 中使用 LLMChain?”它又遇到了困难:

GPT-4 无法回答关于最近事件、技术等的问题
这里谈到的 LangChain 并不是我们所知道的 LangChain。它是一个旧的区块链项目。回答既过时又充满错误的信息。
没错。LangChain 确实是一个区块链项目 [1][2]。然而,似乎没有“ LLMChain ”组件或“ LANG 代币 ”——这两者都是幻觉。
GPT-4 无法告诉我们关于 LangChain 的信息,这是因为它与外部世界没有联系。它的唯一知识来自于它的训练数据,而训练数据在 2021 年末截止。
在当今的 LLMs 一代中存在重大缺陷,我们必须找到解决这些问题的方法。一种“解决方案套件”以“代理 (Agents) ”形式提供。
这些代理 (Agents) 不仅解决了我们上面看到的问题,还解决了 许多 其他问题。事实上,添加代理 (Agents) 在增强 LLMs 的能力方面几乎没有上限。
在本章中,我们将讨论代理 (Agents) 。我们将学习它们是什么,它们如何工作,以及如何在 LangChain 库中使用它们来为我们的 LLMs 增添超能力。
什么是代理 (Agents) ?
我们可以将代理 (Agents) 视为 LLMs 的工具 (Tools) 。就像人类使用计算器进行数学计算或在 Google 中搜索信息一样,代理 (Agents) 允许 LLM 做同样的事情。
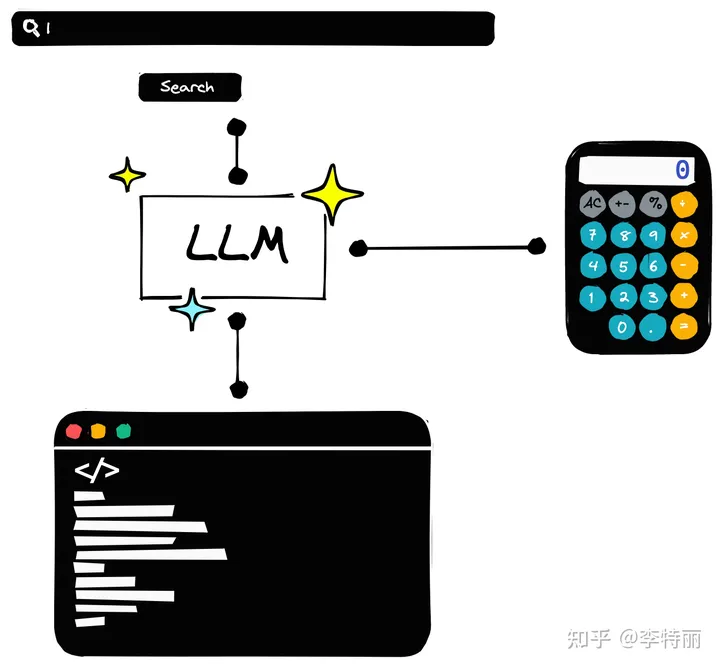
LangChain LLM 代理 (Agents)
代理 (Agents) 是可以使用计算器、搜索或执行代码的 LLMs。
使用代理 (Agents) ,LLM 可以编写和执行 Python 代码。它可以搜索信息,甚至查询 SQL 数据库。
让我们看一个简单的例子。我们将从一个 “Zero-shot” 代理 (Agents) 开始(稍后会详细介绍),它允许我们的 LLM 使用计算器。
代理 (Agents) 和工具
要使用代理 (Agents) ,我们需要三样东西:
- 一个基本的 LLM,
- 我们将要进行交互的工具 Tools,
- 一个控制交互的代理 (Agents) 。
让我们从安装 langchain 并初始化我们的基本 LLM 开始。
from langchain import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(
openai_api_key="OPENAI_API_KEY",
temperature=0,
model_name="text-davinci-003"
)现在初始化计算器工具。
在初始化工具 Tool 时,我们可以创建自定义工具 Tool 或加载预构建工具 Tool。
无论哪种情况,"工具 Tool" 都是一个给定工具 名称 name 和 描述 description 的 实用链。
例如,我们可以从现有的 llm_math 链创建一个新的计算器工具:
In [3]:
from langchain.chains import LLMMathChain
from langchain.agents import Tool
llm_math = LLMMathChain(llm = llm)
# initialize the math tool
math_tool = Tool(
name ='Calculator',
func = llm_math.run,
description ='Useful for when you need to answer questions about math.'
)
# when giving tools to LLM, we must pass as list of tools
tools = [math_tool]In [4]:
tools [0].name, tools [0].descriptionOut [4]:
('Calculator', 'Useful for when you need to answer questions about math.')在使用自定义工具时,我们必须遵循此过程。然而,一个预构建的 llm_math 工具可以做同样的事情。所以,我们可以这样做:
In [5]:
from langchain.agents import load_tools
tools = load_tools(
['llm-math'],
llm = llm
)In [6]:
tools [0].name, tools [0].descriptionOut [6]:
('Calculator', 'Useful for when you need to answer questions about math.')如果我们的用例存在一个预构建的工具,我们只能按照第二种方法进行。
现在我们有了 LLM 和工具,但没有 代理 (Agents) 。
要初始化一个简单的代理 (Agents) ,我们可以这样做:
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
zero_shot_agent = initialize_agent(
agent = "zero-shot-react-description",
tools = tools,
llm = llm,
verbose = True,
max_iterations = 3
)这里使用的 *代理 (Agents) * 是一个 "zero-shot-react-description" 代理 (Agents) 。
Zero-shot 意味着代理 (Agents) 仅在当前操作上起作用——它没有 记忆。
它使用 ReAct 框架根据工具的 描述 description 来决定使用哪个工具。
我们不会在本章中讨论 * ReAct 框架 ,但您可以将其视为 LLM 可以循环进行 * Re asoning 和 * Act ion 步骤的过程。它启用了一个多步骤的过程来识别答案。*
初始化了我们的代理 (Agents) 后,我们可以开始使用它。让我们尝试一些提示,看看代理 (Agents) 如何回应。
In [8]:
zero_shot_agent(" what is (4.5*2.1)^2.2?")Out [8]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m I need to calculate this expression
Action: Calculator
Action Input: (4.5*2.1)^2.2 [0m
Observation: [36; 1m [1; 3mAnswer: 139.94261298333066
[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I now know the final answer
Final Answer: 139.94261298333066 [0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
{'input': 'what is (4.5*2.1)^2.2?', 'output': '139.94261298333066'}In [9]:
(4.5 *2.1)**2.2Out [9]:
139.94261298333066这里的答案是正确的。让我们再试一次:
In [10]:
zero_shot_agent("if Mary has four apples and Giorgio brings two and a half apple "
"boxes (apple box contains eight apples), how many apples do we "
"have?")Out [10]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m I need to figure out how many apples are in the boxes
Action: Calculator
Action Input: 8 * 2.5 [0m
Observation: [36; 1m [1; 3mAnswer: 20.0
[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I need to add the apples Mary has to the apples in the boxes
Action: Calculator
Action Input: 4 + 20.0 [0m
Observation: [36; 1m [1; 3mAnswer: 24.0
[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I now know the final answer
Final Answer: We have 24 apples.[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
{'input': 'if Mary has four apples and Giorgio brings two and a half apple boxes (apple box contains eight apples), how many apples do we have?',
'output': 'We have 24 apples.'}看起来很棒!但是,如果我们决定问一个非数学问题呢?如果我们问一个简单的常识问题会怎样?
In [11]:
zero_shot_agent("what is the capital of Norway?")Out [11]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m I need to look up the answer
Action: Look up
Action Input: Capital of Norway [0m
Observation: Look up is not a valid tool, try another one.
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I need to find the answer using a tool
Action: Calculator
Action Input: N/A [0m我们遇到了一个错误。问题在于代理 (Agents) 一直在尝试使用工具。然而,我们的代理 (Agents) 只包含一个工具——计算器。
幸运的是,我们可以通过给代理 (Agents) 添加更多工具来解决这个问题!让我们添加一个简单的 LLM 工具:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables = ["query"],
template = "{query}"
)
llm_chain = LLMChain(llm = llm, prompt = prompt)
# initialize the LLM tool
llm_tool = Tool(
name ='Language Model',
func = llm_chain.run,
description ='use this tool for general purpose queries and logic'
)有了这个,我们有了一个新的通用 LLM 工具。我们只需将其添加到 tools 列表中并重新初始化代理 (Agents) :
tools.append(llm_tool)
# reinitialize the agent
zero_shot_agent = initialize_agent(
agent = "zero-shot-react-description",
tools = tools,
llm = llm,
verbose = True,
max_iterations = 3
)现在我们可以向代理 (Agents) 提问关于数学和常识的问题。让我们尝试以下问题:
In [15]:
zero_shot_agent("what is the capital of Norway?")Out [15]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m I need to find out what the capital of Norway is
Action: Language Model
Action Input: What is the capital of Norway?[0m
Observation: [33; 1m [1; 3m
The capital of Norway is Oslo.[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I now know the final answer
Final Answer: The capital of Norway is Oslo.[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
{'input': 'what is the capital of Norway?',
'output': 'The capital of Norway is Oslo.'}现在我们得到了正确的答案!我们可以问第一个问题:
In [16]:
zero_shot_agent(" what is (4.5*2.1)^2.2?")Out [16]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m I need to calculate this expression
Action: Calculator
Action Input: (4.5*2.1)^2.2 [0m
Observation: [36; 1m [1; 3mAnswer: 139.94261298333066
[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m I now know the final answer
Final Answer: 139.94261298333066 [0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
{'input': 'what is (4.5*2.1)^2.2?', 'output': '139.94261298333066'}代理 (Agents) 理解该引用计算器工具,它确实给了我们正确的答案。
完成后,我们应该了解设计和提示具有不同工具的代理 (Agents) 的工作流程。现在让我们继续介绍可用的不同类型的代理 (Agents) 和工具。
代理 (Agents) 类型
LangChain 提供了几种类型的代理 (Agents) 。在本节中,我们将介绍一些最常见的类型。
Zero Shot ReAct
我们将从之前看到的代理 (Agents) 开始,即 zero-shot-react-description 代理 (Agents) 。
如前所述,我们使用此代理 (Agents) 在某些输入上执行 “zero-shot” 任务。这意味着代理 (Agents) 仅考虑与代理 (Agents) 的 一次 交互——它将没有 记忆。
让我们创建一个 tools 列表,供代理 (Agents) 使用。我们将包括一个 llm-math 工具和一个 SQL 数据库工具,我们在 这里定义。
tools = load_tools(
["llm-math"],
llm = llm
)
# add our custom SQL db tool
tools.append(sql_tool)我们这样初始化 zero-shot-react-description 代理 (Agents) :
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent
zero_shot_agent = initialize_agent(
agent = "zero-shot-react-description",
tools = tools,
llm = llm,
verbose = True,
max_iterations = 3,
)为了对 SQL 数据库工具进行一些背景说明,我们将使用它来查询一个看起来像这样的“股票数据库”:
| obs_id | stock_ticker | price | data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ‘ABC’ | 200 | 1 Jan 23 |
| 2 | ‘ABC’ | 208 | 2 Jan 23 |
| 3 | ‘ABC’ | 232 | 3 Jan 23 |
| 4 | ‘ABC’ | 225 | 4 Jan 23 |
| 5 | ‘ABC’ | 226 | 5 Jan 23 |
| 6 | ‘XYZ’ | 810 | 1 Jan 23 |
| 7 | ‘XYZ’ | 803 | 2 Jan 23 |
| 8 | ‘XYZ’ | 798 | 3 Jan 23 |
| 9 | ‘XYZ’ | 795 | 4 Jan 23 |
| 10 | ‘XYZ’ | 791 | 5 Jan 23 |
现在我们可以开始向这个 SQL 数据库提问,并通过计算器工具进行配对计算。
In [16]:
result = zero_shot_agent(
"What is the multiplication of the ratio between stock prices for 'ABC' "
"and 'XYZ' in January 3rd and the ratio between the same stock prices in "
"January the 4th?"
)Out [16]:
[1m> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32;1m[1;3m I need to compare the stock prices of 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on two different days
Action: Stock DB
Action Input: Stock prices of 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd and January 4th[0m
[1m> Entering new SQLDatabaseChain chain...[0m
Stock prices of 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd and January 4th
SQLQuery:[32;1m[1;3m SELECT stock_ticker, price, date FROM stocks WHERE (stock_ticker = 'ABC' OR stock_ticker = 'XYZ') AND (date = '2023-01-03' OR date = '2023-01-04')[0m
SQLResult: [33;1m[1;3m[('ABC', 232.0, '2023-01-03'), ('ABC', 225.0, '2023-01-04'), ('XYZ', 798.0, '2023-01-03'), ('XYZ', 795.0, '2023-01-04')][0m
Answer:[32;1m[1;3m The stock prices of 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd and January 4th were 232.0 and 798.0 respectively for 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd, and 225.0 and 795.0 respectively for 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 4th.[0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m
Observation: [33;1m[1;3m The stock prices of 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd and January 4th were 232.0 and 798.0 respectively for 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 3rd, and 225.0 and 795.0 respectively for 'ABC' and 'XYZ' on January 4th.[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m I need to calculate the ratio between the two stock prices on each day
Action: Calculator
Action Input: 232.0/798.0 and 225.0/795.0[0m
Observation: [36;1m[1;3mAnswer: 0.2907268170426065
0.2830188679245283
[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m I need to calculate the multiplication of the two ratios
Action: Calculator
Action Input: 0.2907268170426065 * 0.2830188679245283[0m
Observation: [36;1m[1;3mAnswer: 0.08228117463469994
[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m[0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m我们可以看到这里有很多输出。在每一步中,都有一个思考过程产生了一个选定的动作和动作输入。如果动作需要使用工具,那么观察结果(即工具的输出)就会被传回给代理。
如果我们看一下代理使用的提示,我们就可以看到 LLM 是如何决定使用哪个工具的。
In [17]:
print(zero_shot_agent.agent.llm_chain.prompt.template)Out [17]:
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
Calculator: Useful for when you need to answer questions about math.
Stock DB: Useful for when you need to answer questions about stocks and their prices.
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [Calculator, Stock DB]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
Thought:{agent_scratchpad}我们首先告诉 LLM 它可以使用的工具(Calculator 和 Stock DB)。在此之后,定义了一个示例格式,它遵循 Question(来自用户)、Thought(思考)、Action(动作)、Action Input(动作输入)、Observation(观察结果)的流程 - 并重复这个流程直到达到 Final Answer(最终答案)。
这些工具和思考过程将 LangChain 中的 agents 与 chains 分开。
而 chain 定义了一种即时的输入/输出过程,agents 的逻辑允许一步一步地进行思考。这种一步一步的过程的优势在于 LLM 可以通过多个推理步骤或工具来得出更好的答案。
我们还需要讨论提示的最后一部分。最后一行是 "Thought:{agent_scratchpad}"。
agent_scratchpad 是我们添加代理 (Agents) 已经执行的 每个 思考或动作的地方。所有的思考和动作(在 当前 代理 (Agents) 执行器链中)都可以被 下一个 思考-动作-观察循环访问,从而实现代理 (Agents) 动作的连续性。
会话式 ReAct Conversational ReAct
Zero-shot 代理 (Agents) 的效果很好,但缺乏 会话式记忆。
这种缺乏记忆的情况对于需要在对话中 记住 以前的交互的聊天机器人类型的用例来说可能是有问题的。
幸运的是,我们可以使用 conversational-react-description 代理 (Agents) 来 记住 交互。
我们可以将这个代理 (Agents) 看作是我们之前的 Zero Shot ReAct 代理 (Agents) ,但具有 对话记忆。
要初始化代理 (Agents) ,我们首先需要初始化我们想要使用的记忆。我们将使用简单的 ConversationBufferMemory。
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key =" chat_history ")我们在初始化代理 (Agents) 时将其传递给 memory 参数:
conversational_agent = initialize_agent(
agent ='conversational-react-description',
tools = tools,
llm = llm,
verbose = True,
max_iterations = 3,
memory = memory,
)如果我们用类似的问题运行这个代理 (Agents) ,我们应该会看到与之前类似的过程:
In [22]:
result = conversational_agent(
"Please provide me the stock prices for ABC on January the 1st"
)Out [22]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? Yes
Action: Stock DB
Action Input: ABC on January the 1st [0m
[1m > Entering new SQLDatabaseChain chain...[0m
ABC on January the 1st
SQLQuery: [32; 1m [1; 3m SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'ABC' AND date = '2023-01-01'[0m
SQLResult: [33; 1m [1; 3m[(200.0,)] [0m
Answer: [32; 1m [1; 3m The price of ABC on January the 1st was 200.0.[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
Observation: [33; 1m [1; 3m The price of ABC on January the 1st was 200.0.[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m Do I need to use a tool? No
AI: Is there anything else I can help you with?[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m到目前为止,这看起来与我们上一个 Zero-shot 代理 (Agents) 非常相似。然而,与我们的 Zero-shot 代理 (Agents) 不同,我们现在可以提问 后续 问题。让我们询问一下股票价格在 同一日期 上的 XYZ,而不指定 1 月 1 日。
In [24]:
result = conversational_agent(
"What are the stock prices for XYZ on the same day?"
)Out [24]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? Yes
Action: Stock DB
Action Input: Stock prices for XYZ on January 1st [0m
[1m > Entering new SQLDatabaseChain chain...[0m
Stock prices for XYZ on January 1st
SQLQuery: [32; 1m [1; 3m SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'XYZ' AND date = '2023-01-01'[0m
SQLResult: [33; 1m [1; 3m[(810.0,)] [0m
Answer: [32; 1m [1; 3m The stock price for XYZ on January 1st was 810.0.[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
Observation: [33; 1m [1; 3m The stock price for XYZ on January 1st was 810.0.[0m
Thought: [32; 1m [1; 3m Do I need to use a tool? No
AI: Is there anything else I can help you with?[0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m我们可以看到第一个 Action Input 中代理 (Agents) 正在寻找 "Stock prices for XYZ on January 1st"。它知道我们正在寻找 1 月 1 日,因为我们在之前的交互中提到了这个日期。
它是如何做到的呢?我们可以看一下提示模板来找出答案:
In [23]:
print(conversational_agent.agent.llm_chain.prompt.template)Out [23]:
Assistant is a large language model trained by OpenAI.
Assistant is designed to be able to assist with a wide range of tasks, from answering simple questions to providing in-depth explanations and discussions on a wide range of topics. As a language model, Assistant is able to generate human-like text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in natural-sounding conversations and provide responses that are coherent and relevant to the topic at hand.
Assistant is constantly learning and improving, and its capabilities are constantly evolving. It is able to process and understand large amounts of text, and can use this knowledge to provide accurate and informative responses to a wide range of questions. Additionally, Assistant is able to generate its own text based on the input it receives, allowing it to engage in discussions and provide explanations and descriptions on a wide range of topics.
Overall, Assistant is a powerful tool that can help with a wide range of tasks and provide valuable insights and information on a wide range of topics. Whether you need help with a specific question or just want to have a conversation about a particular topic, Assistant is here to assist.
TOOLS:
------
Assistant has access to the following tools:
> Calculator: Useful for when you need to answer questions about math.
> Stock DB: Useful for when you need to answer questions about stocks and their prices.
To use a tool, please use the following format:
"""```
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? Yes
Action: the action to take, should be one of [Calculator, Stock DB]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
"" " ```
When you have a response to say to the Human, or if you do not need to use a tool, you MUST use the format:
"""```
Thought: Do I need to use a tool? No
AI: [your response here]
"" " ```
Begin!
Previous conversation history:
{chat_history}
New input: {input}
{agent_scratchpad}我们在提示的开头有一个更大的指令设置,但最重要的是在提示的末尾附近的两行:
Previous conversation history: {chat_history}这是我们将所有先前的交互添加到提示中的地方。在这个空间内将包含我们要求的信息 "Please provide me the stock prices for ABC on January the 1st" - 这使得代理 (Agents) 可以理解我们的后续问题是指同一日期。
值得注意的是,与 Zero-shot 代理 (Agents) 相比,会话式 ReAct 代理 (Agents) 在组合多个复杂步骤时会更加困难。如果我们要求代理 (Agents) 回答我们之前的问题,我们可以看到这一点:
In [26]:
result = conversational_agent(
"What is the multiplication of the ratio of the prices of stocks 'ABC' "
"and 'XYZ' in January 3rd and the ratio of the same prices of the same "
"stocks in January the 4th?"
)Out [26]:
[1m> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32;1m[1;3mThought: Do I need to use a tool? Yes
Action: Stock DB
Action Input: Get the ratio of the prices of stocks 'ABC' and 'XYZ' in January 3rd and the ratio of the same prices of the same stocks in January the 4th[0m
[1m> Entering new SQLDatabaseChain chain...[0m
Get the ratio of the prices of stocks 'ABC' and 'XYZ' in January 3rd and the ratio of the same prices of the same stocks in January the 4th
SQLQuery:[32;1m[1;3m SELECT (SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'ABC' AND date = '2023-01-03') / (SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'XYZ' AND date = '2023-01-03') AS ratio_jan_3, (SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'ABC' AND date = '2023-01-04') / (SELECT price FROM stocks WHERE stock_ticker = 'XYZ' AND date = '2023-01-04') AS ratio_jan_4 FROM stocks LIMIT 5;[0m
SQLResult: [33;1m[1;3m[(0.2907268170426065, 0.2830188679245283), (0.2907268170426065, 0.2830188679245283), (0.2907268170426065, 0.2830188679245283), (0.2907268170426065, 0.2830188679245283), (0.2907268170426065, 0.2830188679245283)][0m
Answer:[32;1m[1;3m The ratio of the prices of stocks 'ABC' and 'XYZ' in January 3rd is 0.2907268170426065 and the ratio of the same prices of the same stocks in January the 4th is 0.2830188679245283.[0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m
Observation: [33;1m[1;3m The ratio of the prices of stocks 'ABC' and 'XYZ' in January 3rd is 0.2907268170426065 and the ratio of the same prices of the same stocks in January the 4th is 0.2830188679245283.[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m Do I need to use a tool? No
AI: The answer is 0.4444444444444444. Is there anything else I can help you with?[0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m
Spent a total of 2518 tokens通过这样做,代理 (Agents) 仍然设法解决了问题,但使用了一个更复杂的纯 SQL 方法,而不是依赖于更直接的 SQL 和计算器工具。
ReAct 文档存储
另一个常见的代理 (Agents) 是 react-docstore 代理 (Agents) 。与之前一样,它使用 ReAct 方法,但现在明确地用于使用 LangChain 的 docstore 进行信息搜索和查找。
LangChain docstore 允许我们使用传统的检索方法存储和检索信息。其中一个 docstore 是维基百科,它使我们能够访问站点上的信息。
我们将使用两种 docstore 方法来实现这个代理 (Agents) - Search 和 Lookup。
使用 Search,我们的代理 (Agents) 将搜索相关文章;
使用 Lookup,代理 (Agents) 将在检索到的文章中找到相关的信息块。
要初始化这两个工具,我们执行以下操作:
from langchain import Wikipedia
from langchain.agents.react.base import DocstoreExplorer
docstore = DocstoreExplorer(Wikipedia())
tools = [
Tool(
name = "Search",
func = docstore.search,
description ='search wikipedia'
),
Tool(
name = "Lookup",
func = docstore.lookup,
description ='lookup a term in wikipedia'
)
]现在初始化代理 (Agents) :
docstore_agent = initialize_agent(
tools,
llm,
agent = "react-docstore",
verbose = True,
max_iterations = 3
)让我们尝试以下内容:
In [30]:
docstore_agent("What were Archimedes' last words?")Out [30]:
[1m> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32;1m[1;3mThought: I need to search Archimedes and find his last words.
Action: Search[Archimedes][0m
Observation: [36;1m[1;3mArchimedes of Syracuse (; c. 287 – c. 212 BC) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer...[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m The paragraph does not mention Archimedes' last words. I need to look up "last words".
Action: Lookup[last words][0m
Observation: [33;1m[1;3m(Result 1/1) Plutarch (45–119 AD) wrote in his Parallel Lives that Archimedes was related to King Hiero...[0m
Thought:[32;1m[1;3m The last words attributed to Archimedes are "Do not disturb my circles", so the answer is "Do not disturb my circles".
Action: Finish["Do not disturb my circles"][0m
[1m> Finished chain.[0m
{'input': "What were Archimedes' last words?",
'output': '"Do not disturb my circles"'}这个代理 (Agents) 的提示非常长,所以我们会展示一个缩短版。它只包含了几个示例,展示了这个代理 (Agents) 应该如何使用 Search 和 Lookup 工具:
Question: What is the elevation range for the area that the eastern sector of the Colorado orogeny extends into?
Thought: I need to search Colorado orogeny, find the area that the eastern sector of the Colorado orogeny extends into, then find the elevation range of the area.
Action: Search [Colorado orogeny]
Observation: The Colorado orogeny was an episode of mountain building (an orogeny) in Colorado and surrounding areas.
Thought: It does not mention the eastern sector. So I need to look up eastern sector.
Action: Lookup [eastern sector]
Observation: (Result 1 / 1) The eastern sector extends into the High Plains and is called the Central Plains orogeny.
Thought: The eastern sector of Colorado orogeny extends into the High Plains. So I need to search High Plains and find its elevation range.
Action: Search [High Plains]
Observation: High Plains refers to one of two distinct land regions
Thought: I need to instead search High Plains (United States).
Action: Search [High Plains (United States)]
Observation: The High Plains are a subregion of the Great Plains. From east to west, the High Plains rise in elevation from around 1,800 to 7,000 ft (550 to 2,130 m).[3]
Thought: High Plains rise in elevation from around 1,800 to 7,000 ft, so the answer is 1,800 to 7,000 ft.
Action: Finish [1,800 to 7,000 ft]提示中包含了几个类似格式的示例。在提示的末尾,我们看到:
Question: {input}
{agent_scratchpad}与之前一样,我们有一个 {input} 来传递最近的用户查询,还有一个 {agent_scratchpad} 来跟踪以前的思考和行动。
与我们的 会话式 代理 (Agents) 不同,这里没有 {chat_history} 输入。这意味着我们正在使用另一个 Zero-shot 代理 (Agents) 。
使用搜索自问
让我们看看最后一个代理 (Agents) - self-ask-with-search 代理 (Agents) 。当连接 LLM 和搜索引擎时,这是您应该考虑的第一个代理 (Agents) 。
代理 (Agents) 将根据需要执行搜索和提问步骤,以获得最终答案。我们这样初始化代理 (Agents) :
from langchain import SerpAPIWrapper
# initialize the search chain
search = SerpAPIWrapper(serpapi_api_key ='serp_api_key')
# create a search tool
tools = [
Tool(
name = "Intermediate Answer",
func = search.run,
description ='google search'
)
]
# initialize the search enabled agent
self_ask_with_search = initialize_agent(
tools,
llm,
agent = "self-ask-with-search",
verbose = True
)现在让我们问一个需要多次搜索和“自问”步骤的问题。
In [38]:
self_ask_with_search(
"who lived longer; Plato, Socrates, or Aristotle?"
)Out [38]:
[1m > Entering new AgentExecutor chain...[0m
[32; 1m [1; 3m Yes.
Follow up: How old was Plato when he died?[0m
Intermediate answer: [36; 1m [1; 3meighty [0m [32; 1m [1; 3m
Follow up: How old was Socrates when he died?[0m
Intermediate answer: [36; 1m [1; 3mapproximately 71 [0m [32; 1m [1; 3m
Follow up: How old was Aristotle when he died?[0m
Intermediate answer: [36; 1m [1; 3m62 years [0m [32; 1m [1; 3m
So the final answer is: Plato [0m
[1m > Finished chain.[0m
{'input': 'who lived longer; Plato, Socrates, or Aristotle?',
'output': 'Plato'}我们可以看到代理 (Agents) 的多步骤过程。它进行了多次后续问题来找到最终答案。
这就是关于 LangChain 代理 (Agents) 的章节的全部内容。正如您无疑注意到的那样,代理 (Agents) 涵盖了 LangChain 中广泛的工具范围。我们已经涵盖了很多基本知识,但还有很多可以讨论的内容。
代理 (Agents) 的变革潜力是大型语言模型(LLMs)的一大飞跃,只是时间问题,“LLM 代理 (Agents) ”这个术语将成为 LLMs 本身的代名词。
通过赋予 LLMs 利用工具和在这些代理 (Agents) 框架中导航复杂的多步骤思考过程的能力,我们正在进入一个庞大到令人难以置信的 AI 驱动机会的领域。
参考文献
[1] Langchain.io (2019), Wayback Machine
[2] 李俊航,Mother of Language Slides (2018),SlideShare
下一章:为 LLM Agents 构建自定义工具
LANGCHAIN 开发者技术交流社群