点云分割是根据空间、几何和纹理等特征对点云进行划分,使得同一划分区域内的点云拥有相似的特征 。点云的有效分割往往是许多应用的前提。例如,在逆向工程CAD/CAM 领域,对零件的不同扫描表面进行分割,然后才能更好地进行孔洞修复、曲面重建、特征描述和提取,进而进行基于3D内容的检索、组合重用等。在激光遥感领域,同样需要对地面、物体首先进行分类处理,然后才能进行后期地物的识别、重建 。
总之,分割采用分而治之的思想,在点云处理中和滤波一样属于重要的基础操作,在PCL 中目前实现了进行分割的基础架构,为后期更多的扩展奠定了基础,现有实现的分割算法是鲁棒性比较好的Cluster聚类分割和RANSAC基于随机采样一致性的分割。
PCL分割库包含多种算法,这些算法用于将点云分割为不同簇。适合处理由多个隔离区域空间组成的点云。将点云分解成其组成部分,然后可以对其进行独立处理。 可以在集群提取教程中找到理论入门,以解释集群方法的工作原理。这两个图说明了平面模型分割(左)和圆柱模型分割(右)的结果。

平面模型分割
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
/***
* 生成20个无序点云,x,y为随机数,z为1.0
* 将points中0、3、6、9、12、15索引位置的z值进行修改,将之作为离群值
*/
cloud->width = 20;
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->points.resize(cloud->width * cloud->height);
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i) {
cloud->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].z = 1.0;
}
// 设置离群点
cloud->points[0].z = 2.0;
cloud->points[3].z = -2.0;
cloud->points[6].z = 4.0;
cloud->points[9].z = 3.0;
cloud->points[12].z = -3.0;
cloud->points[15].z = -4.0;
std::cerr << "Point cloud data: " << cloud->points.size() << " points" << std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud->points[i].z << std::endl;
/**
* 创建分割时所需要的模型系数对象 coefficients 及存储内点的点索引集合对象 inliers .
* 这也是我们指定“阈值距离DistanceThreshold”的地方,该距离阈值确定点必须与模型有多远才能被视为离群点。
* 这里距离阔值是 0.01m ,即只要点到 z=1 平面距离小于该阈值的点都作为内部点看待,而大于该阈值的则看做离群点。
* 我们将使用RANSAC方法(`pcl::SAC_RANSAC`)作为可靠的估计器。因为RANSAC比较简单(其他强大的估算工具也以此为基础,并添加了其他更复杂的概念)。
*/
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
// 创建分割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
// 可选配置:是否优化模型系数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
// 必选配置:设置分割的模型类型、分割算法、距离阈值、输入点云
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.01);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud);
// 执行分割操作,并存储分割结果保存到点集合 inliers 及存储平面模型系数 coefficients
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) {
PCL_ERROR("Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset.");
return (-1);
}
// 此段代码用来打印出估算的平面模型的参数(以 ax+by+ca+d=0 形式),详见RANSAC采样一致性算法的SACMODEL_PLANE平面模型
std::cerr << "Model coefficients: " << coefficients->values[0] << " "
<< coefficients->values[1] << " "
<< coefficients->values[2] << " "
<< coefficients->values[3] << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Model inliers: " << inliers->indices.size() << std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < inliers->indices.size(); ++i)
std::cerr << inliers->indices[i] << " " << cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].x << " "
<< cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].y << " "
<< cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].z << std::endl;
return 0;
}输出结果
Point cloud data: 20 points
1.28125 577.094 2
197.938 828.125 1
599.031 491.375 1
358.688 917.438 -2
842.562 764.5 1
178.281 879.531 1
727.531 525.844 4
311.281 15.3438 1
93.5938 373.188 1
150.844 169.875 3
1012.22 456.375 1
121.938 4.78125 1
9.125 386.938 -3
544.406 584.875 1
616.188 621.719 1
170.219 678.938 -4
461.594 360.562 1
58.4062 622.25 1
802.094 821.844 1
532.344 309.188 1
Model coefficients: 0 0 1 -1
Model inliers: 14
1 197.938 828.125 1
2 599.031 491.375 1
4 842.562 764.5 1
5 178.281 879.531 1
7 311.281 15.3438 1
8 93.5938 373.188 1
10 1012.22 456.375 1
11 121.938 4.78125 1
13 544.406 584.875 1
14 616.188 621.719 1
16 461.594 360.562 1
17 58.4062 622.25 1
18 802.094 821.844 1
19 532.344 309.188 1圆柱体模型分割
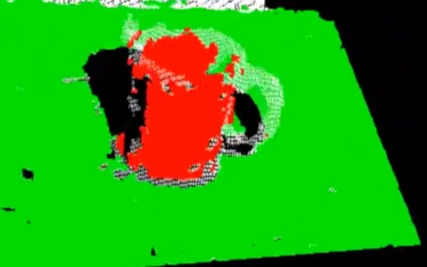
本节举例说明了如何采用随机采样一致性估计从带有噪声的点云中提取一个圆柱体模型,整个程序处理流程如下 :
- 过滤掉远于 1. 5 m 的数据点
- 估计每个点的表面法线
- 分割出平面模型 (数据集中的桌面)并保存到磁盘中。
- 分割圆出柱体模型(数据集中的杯子)并保存到磁盘中。
注:由于数据中包含噪声,圆柱体模型并不十分严格 。
代码实现
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// 需要的所有对象
pcl::PCDReader reader; // PCD文件读取对象
pcl::PassThrough<PointT> pass; // 直通滤波器
pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, pcl::Normal> ne; // 法线估算对象
pcl::SACSegmentationFromNormals<PointT, pcl::Normal> seg; // 分割器
pcl::PCDWriter writer; // PCD文件写出对象
pcl::ExtractIndices<PointT> extract; // 点提取对象
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::Normal> extract_normals; // 法线提取对象
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>());
// 数据
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_filtered2(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals2(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients_plane(new pcl::ModelCoefficients), coefficients_cylinder(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers_plane(new pcl::PointIndices), inliers_cylinder(new pcl::PointIndices);
// 读取点云数据
reader.read("G:/vsdata/PCLlearn/PCDdata/table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "PointCloud has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 构建一个直通过滤器以删除虚假的NaNs
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0, 1.5);
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl;
// 估计点法线
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
ne.setKSearch(50);
ne.compute(*cloud_normals);
// 为平面模型创建分割对象并设置所有参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.03);
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals);
// 获得平面内点和系数
seg.segment(*inliers_plane, *coefficients_plane);
std::cerr << "Plane coefficients: " << *coefficients_plane << std::endl;
// 从输入云中提取平面内联
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 将平面点云保存
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd", *cloud_plane, false);
// 移除平面inliers, 提取其余部分
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered2);
extract_normals.setNegative(true);
extract_normals.setInputCloud(cloud_normals);
extract_normals.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract_normals.filter(*cloud_normals2);
// 设置圆柱体分割对象参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER); // 设置分割模型为圆柱体
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); // 设置采用RANSAC算法进行参数估计
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1); // 设置表面法线权重系数
seg.setMaxIterations(10000); // 设置最大迭代次数10000
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.05); // 设置内点到模型的最大距离 0.05m
seg.setRadiusLimits(0, 0.1); // 设置圆柱体的半径范围0 -> 0.1m
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals2);
// 获取cylinder inliers
seg.segment(*inliers_cylinder, *coefficients_cylinder);
std::cerr << "Cylinder coefficients: " << *coefficients_cylinder << std::endl;
// 将cylinder inliers保存
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
extract.setIndices(inliers_cylinder);
extract.setNegative(false);
pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud_cylinder(new pcl::PointCloud<PointT>());
extract.filter(*cloud_cylinder);
if (cloud_cylinder->points.empty())
std::cerr << "Can't find the cylindrical component." << std::endl;
else {
std::cerr << "PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: " << cloud_cylinder->points.size()
<< " data points." << std::endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd", *cloud_cylinder, false);
}
return (0);
}输出结果
PointCloud has: 307200 data points.
PointCloud after filtering has: 139897 data points.
Plane coefficients: header:
seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
values[]
values[0]: 0.016223
values[1]: -0.83761
values[2]: -0.546028
values[3]: 0.528923
PointCloud representing the planar component: 116054 data points.
Cylinder coefficients: header:
seq: 0 stamp: 0 frame_id:
values[]
values[0]: 0.0519707
values[1]: 0.172656
values[2]: 0.834861
values[3]: 0.0229013
values[4]: -0.836744
values[5]: -0.547116
values[6]: 0.0387646
PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: 11479 data points.欧式聚类提取
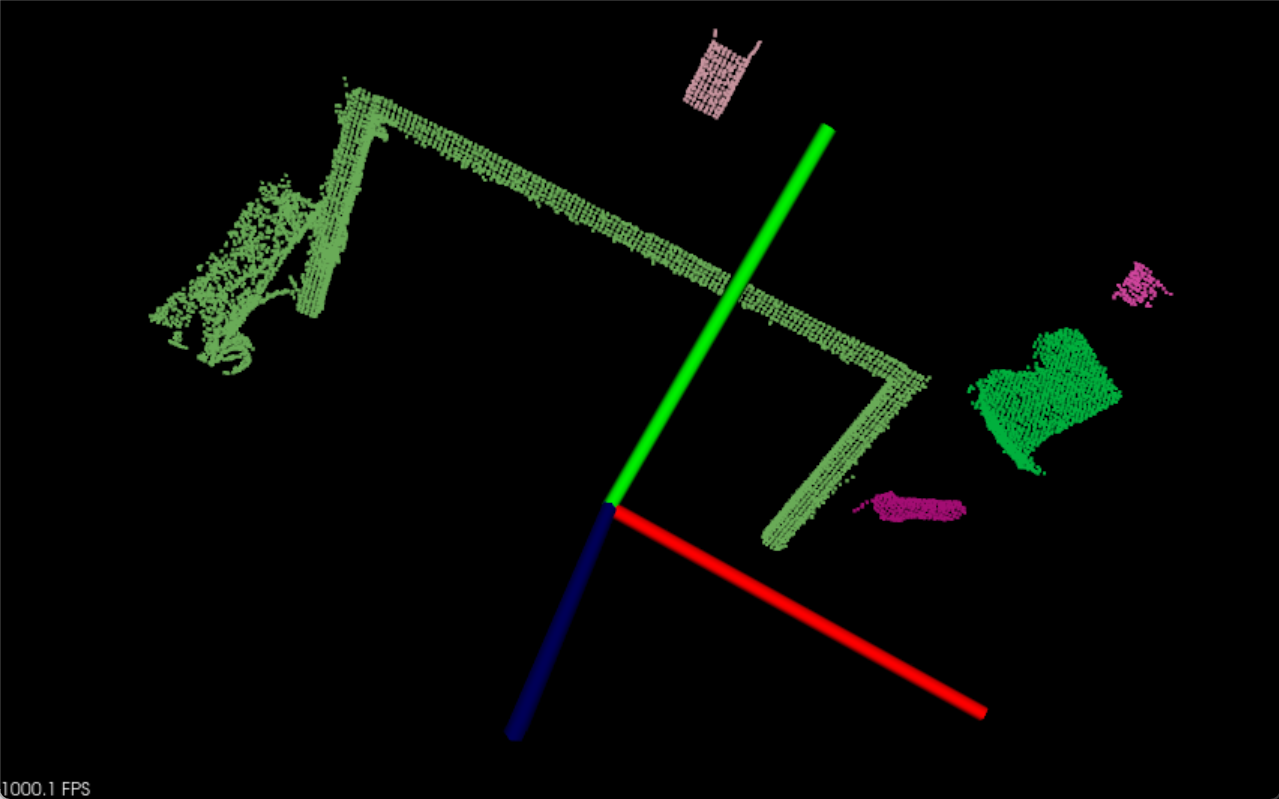
基于欧式距离的分割和基于区域生长的分割本质上都是用区分邻里关系远近来完成的。由于点云数据提供了更高维度的数据,故有很多信息可以提取获得。欧几里得算法使用邻居之间距离作为判定标准,而区域生长算法则利用了法线,曲率,颜色等信息来判断点云是否应该聚成一类。
欧几里德算法
具体的实现方法大致是:
- 找到空间中某点p10,有kdTree找到离他最近的n个点,判断这n个点到p的距离。将距离小于阈值r的点p12,p13,p14....放在类Q里
- 在 Q\p10 里找到一点p12,重复1
- 在 Q\p10,p12 找到一点,重复1,找到p22,p23,p24....全部放进Q里
- 当 Q 再也不能有新点加入了,则完成搜索了
因为点云总是连成片的,很少有什么东西会浮在空中来区分。但是如果结合此算法可以应用很多东西。比如
- 半径滤波删除离群点
- 采样一致找到桌面或者除去滤波
当然,一旦桌面被剔除,桌上的物体就自然成了一个个的浮空点云团。就能够直接用欧几里德算法进行分割了,这样就可以提取出我们想要识别的东西。
代码实现
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_f(
new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
reader.read("G:/vsdata/PCLlearn/PCDdata/table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// 执行降采样滤波,叶子大小1cm
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
vg.setInputCloud(cloud);
vg.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl; //*
// 创建平面模型分割器并初始化参数
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);
int i = 0, nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->points.size();
while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points) {
// 移除剩余点云中最大的平面
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
// 执行分割,将分割出来的平面点云索引保存到inliers中
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) {
std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
break;
}
// 从输入点云中取出平面内点
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 得到与平面相关的点cloud_plane
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl;
// 从点云中剔除这些平面内点,提取出剩下的点保存到cloud_f中,并重新赋值给cloud_filtered。
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_f);
*cloud_filtered = *cloud_f;
}
// 为提取算法的搜索方法创建一个KdTree对象
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
/**
* 在这里,我们创建一个PointIndices的vector,该vector在vector <int>中包含实际的索引信息。
* 每个检测到的簇的索引都保存在这里-请注意,cluster_indices是一个vector,包含多个检测到的簇的PointIndices的实例。
* 因此,cluster_indices[0]包含我们点云中第一个 cluster(簇)的所有索引。
*
* 从点云中提取簇(集群),并将点云索引保存在 cluster_indices 中。
*/
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> cluster_indices;
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction<pcl::PointXYZ> ec;//因为点云是PointXYZ类型的,所以这里用PointXYZ创建一个欧氏聚类对象,并设置提取的参数和变量
ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 设置一个合适的聚类搜索半径 ClusterTolerance,如果搜索半径取一个非常小的值,那么一个实际独立的对象就会被分割为多个聚类;如果将值设置得太高,那么多个对象就会被分割为一个聚类,所以需要进行测试找出最合适的ClusterTolerance
ec.setMinClusterSize(100); // 每个簇(集群)的最小大小
ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000); // 每个簇(集群)的最大大小
ec.setSearchMethod(tree); // 设置点云搜索算法
ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); // 设置输入点云
ec.extract(cluster_indices); // 设置提取到的簇,将每个簇以索引的形式保存到cluster_indices;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
// 为了从点云索引向量中分割出每个簇,必须迭代访问点云索引,
int j = 0;
for (std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin();
it != cluster_indices.end(); ++it) {
// 每次创建一个新的点云数据集,并且将所有当前簇的点写入到点云数据集中。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
const std::vector<int>& indices = it->indices;
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator pit = indices.begin(); pit != indices.end(); ++pit)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_filtered->points[*pit]);
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
std::cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size() << " data points."
<< std::endl;
/*
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>(ss.str(), *cloud_cluster, false); //
*/
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j;
// Generate a random (bright) color
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerRandom<pcl::PointXYZ> single_color(cloud_cluster);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_cluster, single_color, ss.str());
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, ss.str());
j++;
}
std::cout << "cloud size: " << cluster_indices.size() << std::endl;
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(0.5);
while (!viewer->wasStopped()) {
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}输出结果
PointCloud before filtering has: 460400 data points.
PointCloud after filtering has: 41049 data points.
PointCloud representing the planar component: 20536 data points.
PointCloud representing the planar component: 12442 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 4857 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 1386 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 321 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 291 data points.
PointCloud representing the Cluster: 123 data points.
cloud size: 5实现效果