前言
本人是算法小白,甚至也没有做过Leetcode。所以,我相信【同为菜鸡的我更能理解作为菜鸡的你们的痛点】。
题干
1. 题目描述
张兵和王武是五子棋迷,工作之余经常切磋棋艺。走了一会儿,轮到张兵了,他对着一条线思考起来了,这条线上的棋子分布如下:
用数组表示:-1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 -1
棋子分布说明:
- -1代表白子,0代表空位,1代表黑子:
- 数组长度L,满足1<L<40,且L为奇数:
请帮他写一个程序,算出最有利的出子位置。最有利定义如下:
- 找到一个空位(0),用棋子(1/-1)填充该位置,可以使得当前子的最大连续长度变大;
- 如果存在多个位置,返回最靠近中间的较小的那个坐标;
- 如果不存在可行位置,直接返回-1;
- 连续长度不能超过5个(五子棋约束);
2. 输入描述
第一行:当前出子颜色
第二行:当前的棋局状态
3. 输出描述
一个整数,表示出子位置的数组下标
4. 示例
示例1:
输入:
1
-1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 -1 1
输出:
5
说明:当前为黑子(1),放置在下表为5的位置,黑子的最大连续长度由3->5,所以满足条件
示例2:
输入:
-1
-1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 -1 1
输出:
1
说明:当前为白子(-1),唯一可以防止的位置下标为1,婊子的最大长度由1->2,所以满足条件
示例3:
输入:
1
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
输出:
5
说明:可行的位置很多,但是5是最接近中间的位置坐标
解答
遇到的问题
这题整体难度不是很大,但还是遇到了一些问题。
- 如何从控制台输入一个变长的数组(哈,确实不会,没怎么用过
Scanner) - 在实现过程中,其实我还发现,输入多行、不定长数据还存在无法停止输入的情况(只能通过输入非目标类型数据来停止,但我希望的是【回车】停止)
- 虽然脑海里大概能想到一个暴力解题办法,但总觉得怪怪的,应该有更好的方式才对
解题思路
暴力解题版:
根据题目给出的条件,做出如下思考:
- 新增一个方法,用来寻找【下一个空位】。由于是下一个,所以需要一个检索的起始点
- 新增一个方法,用来获取当前数组的中间位置的下标(其实可以不新增一个方法,单纯是个人喜欢这么做,我比较追求语义清晰跟代码可读性)
- 新增一个方法,用来计算给定线上棋子的【最大连续长度】
- 整体思路是,循环遍历每一个可以下子的点,然后记录当前点的位置,以及最大连续长度,还有距离中心点的位置。接着判断最大连续长度是否变大且
<5。最后比较距离中心点的位置是否更近了
但我看了网上答案之后,发现了更好的解题方法。那就是【滑动窗口法】,这应该才是本题真正的考点。
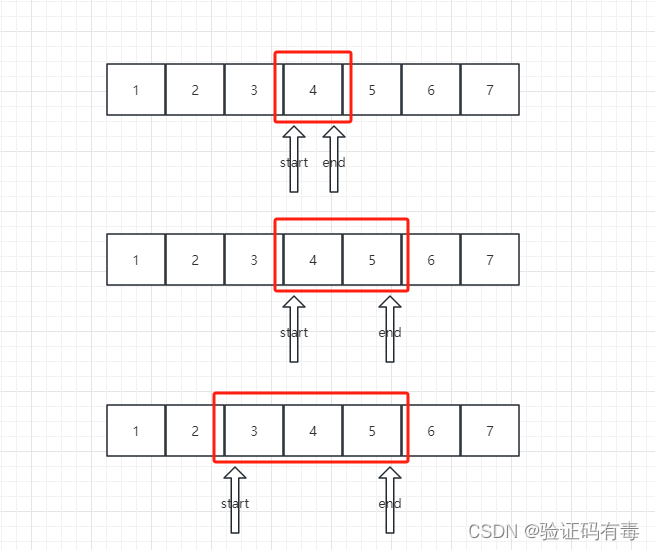
滑动窗口法:
- 滑动窗口在这里的应用,主要是在求落子后新的最大连续长度。而且这个滑动起点跟终点,不是从
0开始,而是从引起变化的【落子节点】开始。怎么理解?这个我们在代码解读中给大家解释一下。
滑动窗口示意图:(随着起点、终点变化,[start, end]区间也在变化)
代码示例
暴力破解版:(但其实我不推荐,我贴出来完全是因为这是我个人自己的努力,所以为了鼓励自己就贴上,哈哈)
public class FiveInRow {
/**
* 白棋
*/
static final int WHITE_CHESS = -1;
/**
* 黑棋
*/
static final int BLACK_CHESS = 1;
/**
* 空白
*/
static final int BLANK_SPACE = 0;
/**
* 最大连续长度
*/
static final int MAX_CONTINOUS_LENGTH = 5;
/**
* 数组长度
*/
static final int MAX_LENGTH = 40;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数据准备
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int currChess = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
String nextLine = scanner.nextLine();
String[] nums = nextLine.split(" ");
List<Integer> chesses = new ArrayList<>();
for (String num : nums) {
chesses.add(Integer.parseInt(num));
}
// 获取最有利下子位置
int bestPlace = getBestPlace(currChess, chesses);
System.out.println("最佳下子位置:" + bestPlace);
}
/**
* 找到最有利的位置
*
* @param currChess 当前棋子颜色
* @param chesses 一条线上棋子分布
* @return -1-找不到可以下的位置;其他-最有利下棋处
*/
private static int getBestPlace(int currChess, List<Integer> chesses) {
int bestPlace = -1;
// 获取当前连续长度
int currContinuous = getCurrContinuous(currChess, chesses);
int midLocation = getMidLocation(chesses.size());
// 获取下一个空白点
int nearest = 99;
int start = 0;
int nextBlankPlace = getNextBlankPlace(start, chesses);
while (nextBlankPlace != -1) {
List<Integer> newChesses = new ArrayList<>(chesses);
newChesses.set(nextBlankPlace, currChess);
int newCurrContinuous = getCurrContinuous(currChess, newChesses);
if (newCurrContinuous > currContinuous && newCurrContinuous <= MAX_CONTINOUS_LENGTH) {
int interval = Math.abs(nextBlankPlace - midLocation);
if (interval < nearest) {
bestPlace = nextBlankPlace;
nearest = interval;
}
}
start = nextBlankPlace + 1;
nextBlankPlace = getNextBlankPlace(start, chesses);
}
return bestPlace;
}
/**
* 获取当前连续度
*
* @param currChess 当前棋子颜色
* @param chesses 一条线上棋子分布
* @return 当前连续长度
*/
private static int getCurrContinuous(int currChess, List<Integer> chesses) {
// 当前棋局下最大连续长度
int curMaxConsecutive = 0;
// 当前连续长度
int consecutiveCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chesses.size(); ++i) {
if (chesses.get(i) == currChess) {
consecutiveCount += 1;
} else {
consecutiveCount = 0;
}
curMaxConsecutive = Math.max(curMaxConsecutive, consecutiveCount);
}
return curMaxConsecutive;
}
/**
* 从指定位置开始检索空白位置
*
* @param start 开始检索位置
* @param chesses 一条线上棋子分布
* @return 下一个空白位置
*/
private static int getNextBlankPlace(int start, List<Integer> chesses) {
if (start >= chesses.size()) {
return -1;
}
for (int i = start; i < chesses.size(); i++) {
Integer chess = chesses.get(i);
if (chess == BLANK_SPACE) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 获取中间位置的索引
*
* @param length 数组长度
* @return 中间位置的索引
*/
private static int getMidLocation(int length) {
return length / 2;
}
}
代码解读:整体来说我还是按照了解题思路完成的
- 多行不定长输入,我是这么完成的。我也不是很理解为什么,没有细看API源码
// 数据准备
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int currChess = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
String nextLine = scanner.nextLine();
String[] nums = nextLine.split(" ");
List<Integer> chesses = new ArrayList<>();
for (String num : nums) {
chesses.add(Integer.parseInt(num));
}
滑动窗口法:(推荐版本)
新增一个方法getBestPlaceUsingSlidingWindows替换旧方法getBestPlace
/**
* 找到最有利的位置,滑动窗口法
*
* @param currChess 当前棋子颜色
* @param chesses 一条线上棋子分布
* @return -1-找不到可以下的位置;其他-最有利下棋处
*/
private static int getBestPlaceUsingSlidingWindows(int currChess, List<Integer> chesses) {
int bestPlace = -1;
// 获取当前连续长度
int currContinuous = getCurrContinuous(currChess, chesses);
int midLocation = getMidLocation(chesses.size());
// 获取下一个空白点
int nearest = 99;
for (int i = 0; i < chesses.size(); i++) {
Integer chess = chesses.get(i);
if (chess != BLANK_SPACE) {
continue;
}
int start = i - 1, end = i + 1;
// 确定窗口真实起点
while (start >= 0 && chesses.get(start).equals(currChess)) {
start--;
}
// 确定窗口真实终点
while (end < chesses.size() && chesses.get(end).equals(currChess)) {
end++;
}
// 由于是开区间(不包含区间范围的两个节点),所以需要-1
int newCurrContinuous = end - start - 1;
if (newCurrContinuous > currContinuous && newCurrContinuous <= MAX_CONTINOUS_LENGTH) {
int interval = Math.abs(i - midLocation);
if (interval < nearest) {
bestPlace = i;
nearest = interval;
}
}
}
return bestPlace;
}
我们解释回解题思路中,所谓【滑动起点跟终点,不是从0开始,而是从引起变化的【落子节点】开始】这段话,我们结合示例3看看,不知道大家发现没有,假设我们落子在0/1/2下标处,再求它的新的最大连续度的时候,其实真正引起连续度变化的点,就是我们落子开始的点。
例如:示例3,落子在2处
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0(落子前)
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0(落子后)
看,如果使用暴力解题的方法,还是会去遍历0/1坐标,有必要吗?其实可以不需要的
代码解读:滑动窗口在这里的应用,重点是里面的两个while循环,这里就不过多解释了



![2023年中国电容炭受益于超级电容器需求及进口替代双重驱动,行业呈快速增长态势[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/29b47d807ba7e3f7674b1ab90ad13d5f.png)


![2023年中国CEM-3型覆铜板市场供需现状、销售收入及行业趋势分析[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/12fa0fcea268f22129d08ab5e69de72e.png)