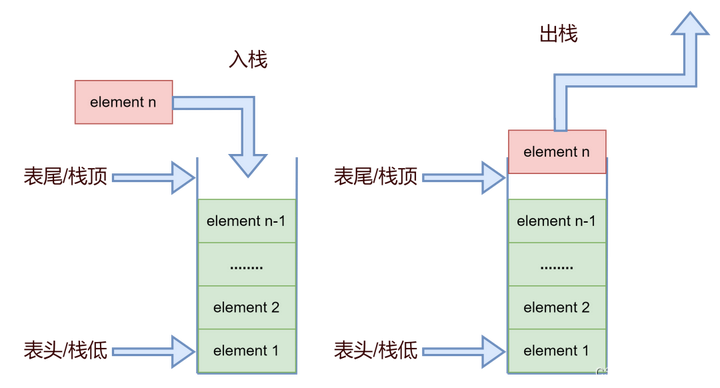
一、栈 Stack(存取O(1))
先进后出,进去123,出来321。
基于数组:最后一位为栈尾,用于取操作。
基于链表:第一位为栈尾,用于取操作。
1.1、数组栈
/**
* 基于数组实现的顺序栈; items[0]:表头/栈底; items[size-1]:表尾/栈顶;
*/
public class MyArrayStack {
// 存储元素的 数组
private String items[];
// 栈实际大小
private int size =0;
// 栈的容量
private int capacity = 0;
public MyArrayStack(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.items = new String[capacity];
}
/**
* 入栈
*/
public boolean push(String item) {
if(size >= capacity){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyArrayStack 栈的内存满了");
}
items[size] = item;
size++;
return true;
}
/**
* 出栈
*/
public String pop() {
if(size<=0){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyArrayStack 栈的内存空了");
}
String item = items[size-1];
items[size-1] = null;
size--;
return item;
}
}1.2、链表栈
/**
* 基于链表实现的链式栈 top: 表尾/栈顶;
*/
public class MyLinkedStack {
// 表尾/栈顶;
private Node top = null;
/**
* 入栈
*/
public void push(String value) {
Node node = new Node(value,null);
if(top != null){
node.nextNode = top;
}
top = node;
}
/**
* 出栈
*/
public String pop() {
if(top==null){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyLinkedStack 栈的内存空了");
}
String retValue = top.getValue();
top = top.nextNode;
return retValue;
}
/**
* 节点
*/
private static class Node{
// 存储数据
private String value;
// 下个节点
private Node nextNode;
public Node(String value, Node nextNode) {
this.value = value;
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}二、队列 Queue (存取O(1))
先进先出(FIFO)的有序列表
2.1、数组单向队列 (存取O(1))
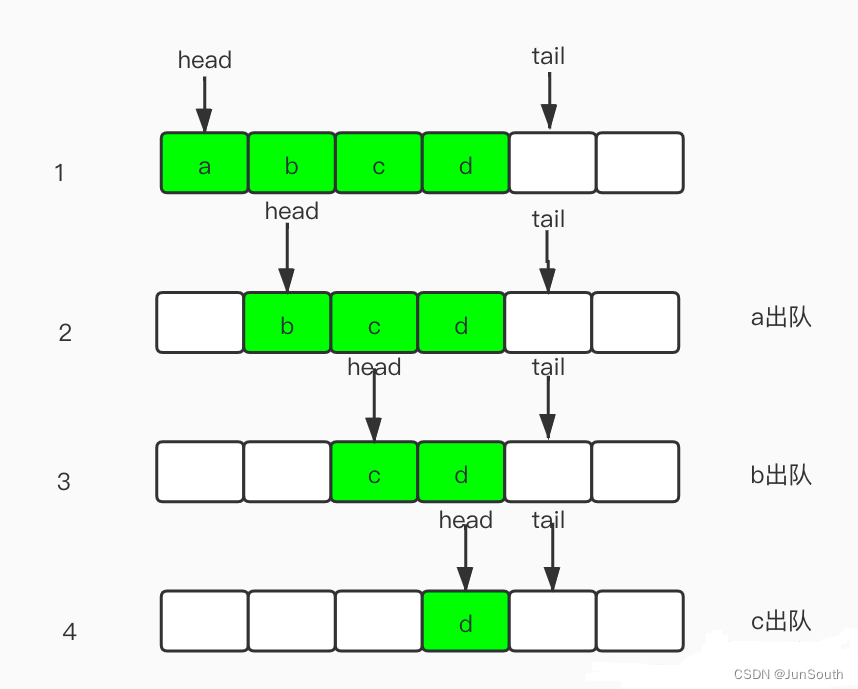
/**
* 基于数组实现的顺序队列
*/
public class MyArrayQueue {
private String [] items;
// 容量
private int capacity = 0;
// 队头下标
private int head = 0;
// 队尾下标
private int tail = 0;
public MyArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.items = new String [capacity];
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/**
* 入队
*/
public boolean enqueue(String item) {
if(capacity == tail){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyArrayQueue 容量满了");
}
items[tail] = item;
tail++;
return true;
}
/**
* 出队
*/
public String dequeue() {
if(head==tail){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyArrayQueue 容量空了");
}
String retValue = items[head];
head++;
return retValue;
}
}2.2、链表单向队列
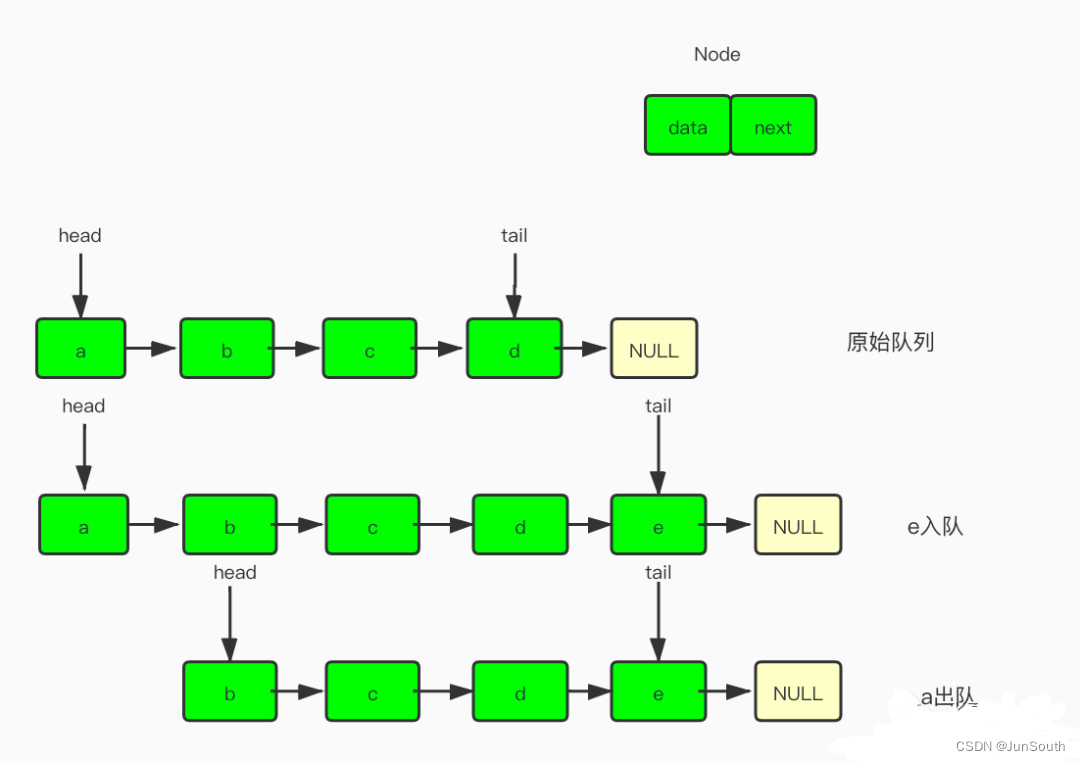
/**
* 基于链表实现的链式队列
*/
public class MyLinkedListQueue {
// 队头
private Node head = null;
// 队尾
private Node tail = null;
/**
* 入队
*/
public void enqueue(String value) {
Node node = new Node(value,null);
if(tail==null){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else {
tail.next=node;
tail=node;
}
}
/**
* 出队
*/
public String dequeue() {
if(head==null){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyLinkedListQueue 队列空了");
}
String retValue = head.getValue();
head = head.next;
if (head == null) {
tail = null;
}
return retValue;
}
private static class Node{
private String value;
private Node next;
public Node(String value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}三、链表 LinkedList
3.1、单向链表
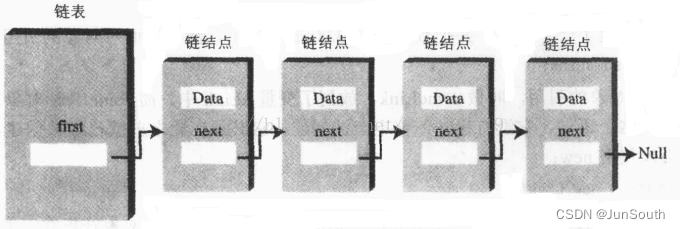
/**
* 单向普通链表
*/
public class MyLinkedList {
// 链表大小
private int size;
// 表头
private Node head;
/**
* 插入
*/
public void insert(int index, String value) {
if(index<0){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyLinkedList 下标越界了");
} else {
if(head==null){
head = new Node(value,null);
}else {
if(index>=size){
index = size-1;
}
Node prev = head;
for(int i=0;i<index;i++){
prev = prev.next;
}
Node node = new Node(value,prev);
prev.next =node;
}
size++;
}
}
/**
* 获取
*/
public String get(int index){
if(size<=0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("MyLinkedList 空链表");
}
if(index<0 || index>=size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("MyLinkedList 下标越界了");
}
Node prev = head;
for (int i=0;i<index;i++){
prev = prev.next;
}
return prev.getValue();
}
private class Node{
private String value;
private Node next;
public Node(String value, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}3.2、双向链表
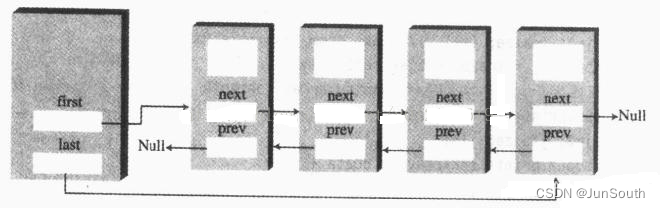
public class MyDoubleLinkedList {
// 链表大小
private int size;
// 表头
private Node head;
// 表尾
private Node tail;
/**
* 插入
*/
public void insert(int index,String data) {
if(index < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyDoubleLinkedList insert 下标越界");
}
Node node = new Node(data,null,null);
if(index == 0) {
head.next = node.next;
head= node;
return;
}
if(index >= size) {
tail.prev = node.prev;
tail= node;
return;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while(index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
public String get(int index){
if(index<0||index>size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("MyDoubleLinkedList get 下标越界了");
}
if(index<=(size/2)){
Node cur = head;
for(int i = 0;i<index-1;i++){
cur = head.next;
}
return cur.getValue();
}else {
index = size-index;
Node cur = tail;
for (int i=size;i>index;i--){
cur = cur.prev;
}
return cur.getValue();
}
}
private class Node{
public String value;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node(String value, Node prev, Node next) {
this.value = value;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}3.3、跳表
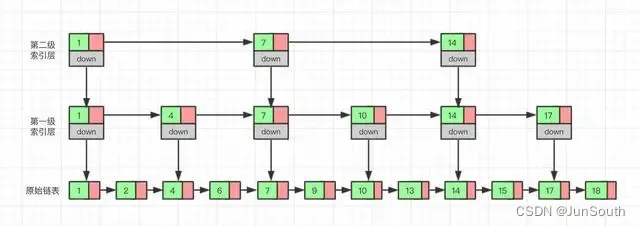
1.跳表由很多层结构组成,level是通过一定的概率随机产生的;
2.每一层都是一个有序的链表,默认是升序 ;
3.最底层(Level 1)的链表包含所有元素;
4.如果一个元素出现在Level i 的链表中,则它在Level i 之下的链表也都会出现;
5.每个节点包含两个指针,一个指向同一链表中的下一个元素,一个指向下面一层的元素。
import java.util.Random;
public class SkipList {
// 跳表中存储的是正整数,并且存储的数据是不重复的
private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16;
// 结点的个数
private int levelCount = 1;
// 索引的层级数
private final Node head = new Node();
// 头结点
private final Random random = new Random();
// 查找操作
public Node find(int value) {
Node p = head;
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (p.next[i] != null && p.next[i].data < value) {
p = p.next[i];
}
}
if (p.next[0] != null && p.next[0].data == value) {
return p.next[0]; // 找到,则返回原始链表中的结点
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 插入操作
public void insert(int value) {
int level = randomLevel();
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.data = value;
newNode.maxLevel = level; // 通过随机函数改变索引层的结点布置
Node[] update = new Node[level];
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
update[i] = head;
}
Node p = head;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (p.next[i] != null && p.next[i].data < value) {
p = p.next[i];
}
update[i] = p;
}
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
newNode.next[i] = update[i].next[i];
update[i].next[i] = newNode;
}
if (levelCount < level) {
levelCount = level;
}
}
// 删除操作
public void delete(int value) {
Node[] update = new Node[levelCount];
Node p = head;
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (p.next[i] != null && p.next[i].data < value) {
p = p.next[i];
}
update[i] = p;
}
if (p.next[0] != null && p.next[0].data == value) {
for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (update[i].next[i] != null && update[i].next[i].data == value) {
update[i].next[i] = update[i].next[i].next[i];
}
}
}
}
// 随机函数
private int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i) {
if (random.nextInt() % 2 == 1) {
level++;
}
}
return level;
}
// Node内部类
public static class Node {
private int data = -1;
private final Node[] next = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
private int maxLevel = 0;
// 重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{data:" +
data +
"; levels: " +
maxLevel +
" }";
}
}
// 显示跳表中的结点
public void display() {
Node p = head;
while (p.next[0] != null) {
System.out.println(p.next[0] + " ");
p = p.next[0];
}
System.out.println();
}
}