之前了解过语义分割的内容,感觉可以做好多东西,然后就抽空学习了一下,这里记录一下方便以后查阅,这篇文章可能也会随着学习的深入不断更新。
语义分割 Semantic Segmentation
- 一些基本概念
- 几种语义分割算法
- Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN)
- 全卷积网络(FCN)的基本信息
- FCN的优缺点
- 语义分割VS图像分类
- 分类 -> 分割 的变化
- 上采样方法
- 上采——双线性插值
- 上采样——Un-pooling
- 上采样——Transpose Conv
- FCN网络结构
- FCN代码实现
- U-Net
- U-Net网络结构
- skip-connect机制
- U-Net输出层
- U-Net代码实现
- Pyramid Scene Parsing Network(PSP)分割网络
- 三个分割问题
- PSPNet的主要贡献
- PSP针对的问题
- 感受野(RF)作用的理解
- RF -> PSP
- Pyramid Pooling 模块
- Adaptive Pool 自适应池化的维度计算
- PSP网络结构
- Dilated Convolution 空洞卷积
- PSP网的辅助模块
- PSPNet代码实现
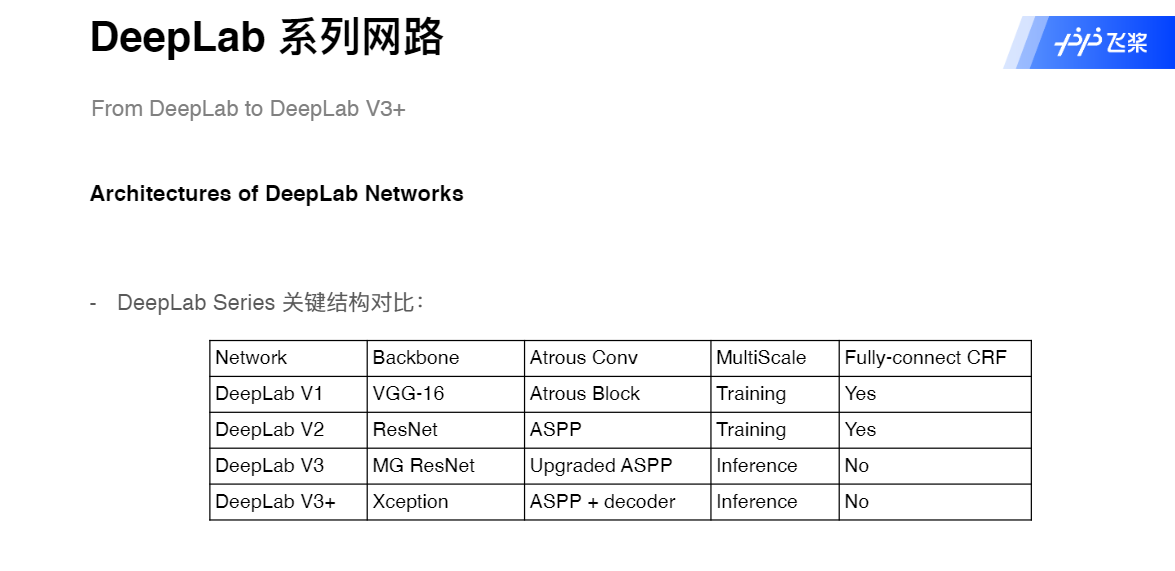
- DeepLab
- DeepLab V1
- DeepLab V1 网络结构
- DeepLab V1 代码实现
- DeepLab V2
- DeepLab V2 网络结构
- DeepLab V2 ASPP模块
- DeepLab V2 代码实现
- DeepLab V3
- DeepLab V3 网络结构
- DeepLab V3 ASPP升级模块
- DeepLab V3 Multi-Grid
- 代码实现
- DeepLab V3+
一些基本概念
图像分割
图像分割指的是使用边界、色彩梯度等特征对图像进行划分,此时比较火的算法有Ostu、FCM、分水岭、N-Cut等,这些算法一般是非监督学习,分割出来的结果并没有语义的标注,换句话说,分割出来的东西并不知道是什么。
语义分割(semantic segmentation)
是将输入图像中的每个像素点预测为不同的语义类别。更注重类别之间的区分,会重点将前景里的车辆和背景里的房屋、天空、地面分割开,但是不区分重叠车辆。主要有FCN,DeepLab,PSPNet等方法。
实例分割(instance segmentation)
是目标检测和语义分割的结合,将输入图像中的目标检测出来,对目标包含的每个像素分配类别标签。更注重前景中目标个体之间的分割,背景的房屋、天空、地面均为一类。主要有DeepMask,Mask R-CNN,PANet等方法。
全景分割(panoptic segmentation)
是语义分割和实例分割的综合,旨在同时分割实例层面的目标(thing)和语义层面的背景内容(stuff),将输入图像中的每个像素点赋予类别标签和实例ID,生成全局的,统一的分割图像。

语义分割和图像分割的区别
实例与全景分割PPT
「自行科技」一文带你读懂全景分割
CNN图像语义分割基本上是这个套路:
下采样+上采样:Convlution + Deconvlution/Resize
多尺度特征融合:特征逐点相加/特征channel维度拼接
获得像素级别的segement map:对每一个像素点进行判断类别
语义分割网络在特征融合时也有2种办法:
FCN式的逐点相加,对应caffe的EltwiseLayer层,对应tensorflow的tf.add()
U-Net式的channel维度拼接融合,对应caffe的ConcatLayer层,对应tensorflow的tf.concat()
图像分割综述【深度学习方法】
几种语义分割算法
Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN)
Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation,简称FCN。这篇论文是第一篇成功使用深度学习做图像语义分割的论文。论文的主要贡献有两点:
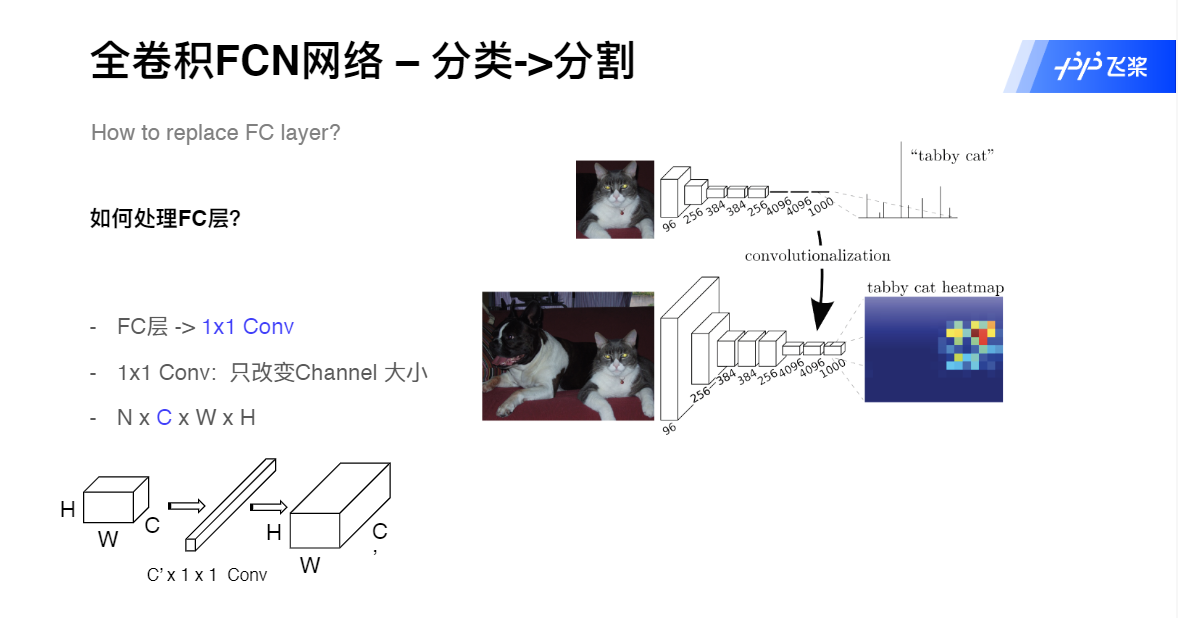
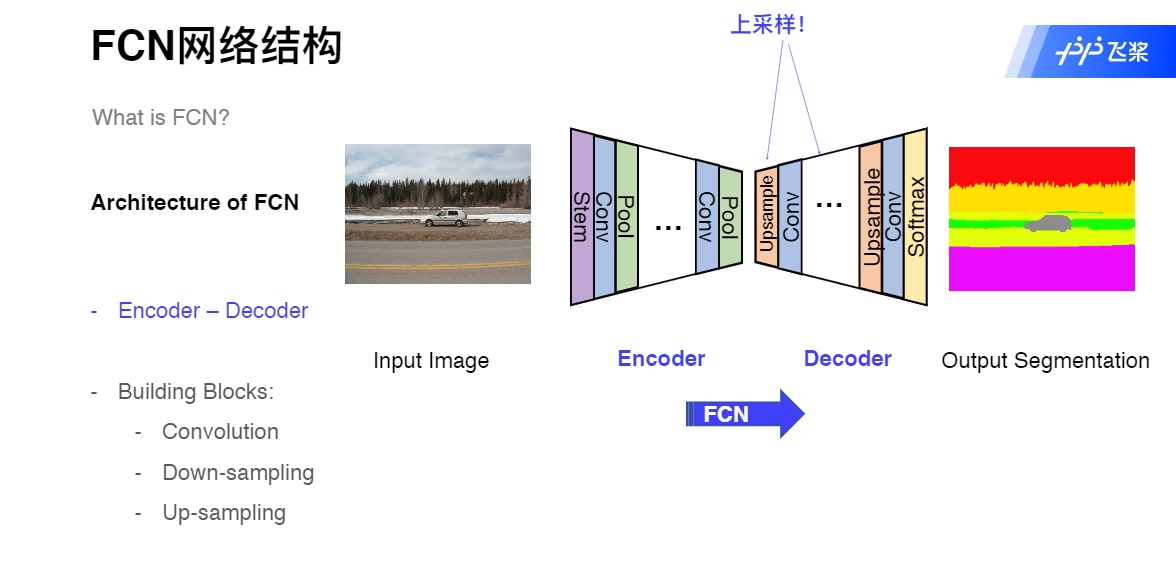
提出了全卷积网络。将全连接网络替换成了卷积网络,使得网络可以接受任意大小的图片,并输出和原图一样大小的分割图。只有这样,才能为每个像素做分类。
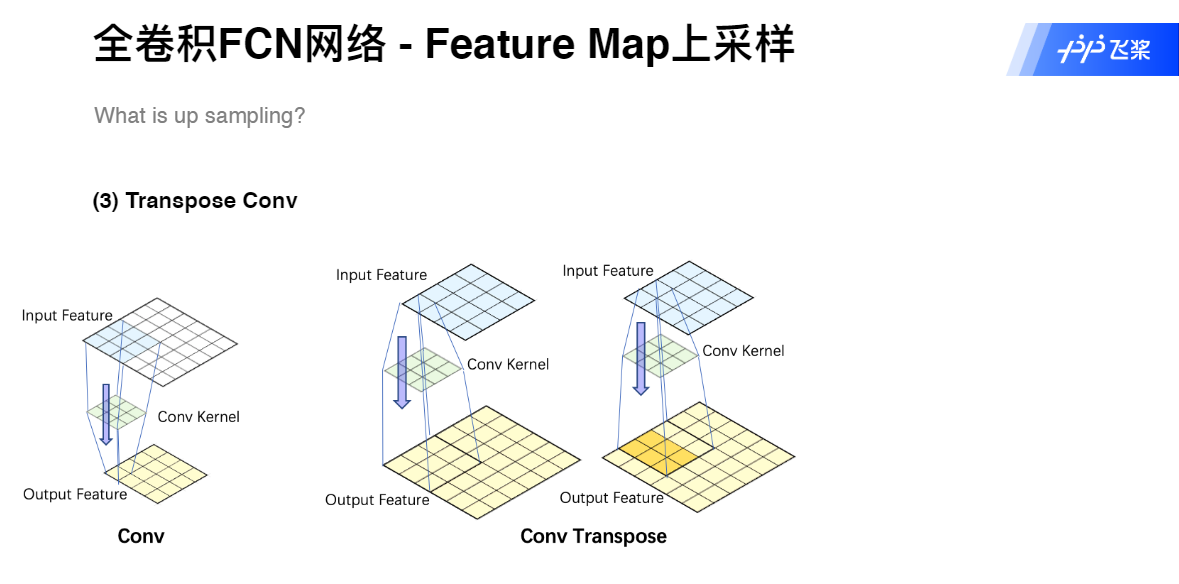
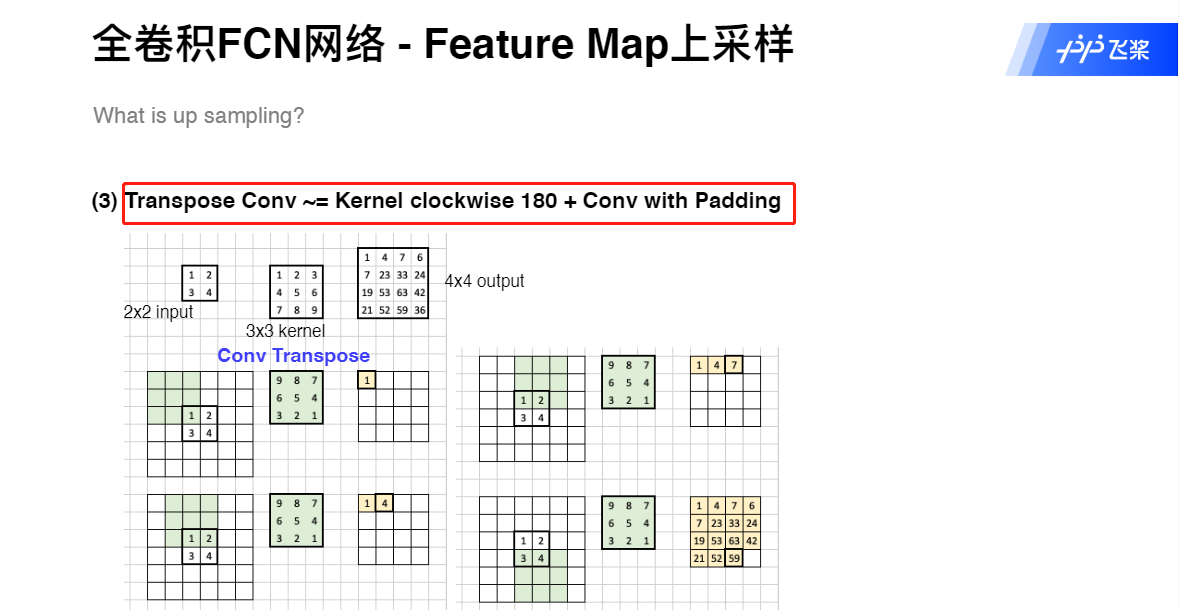
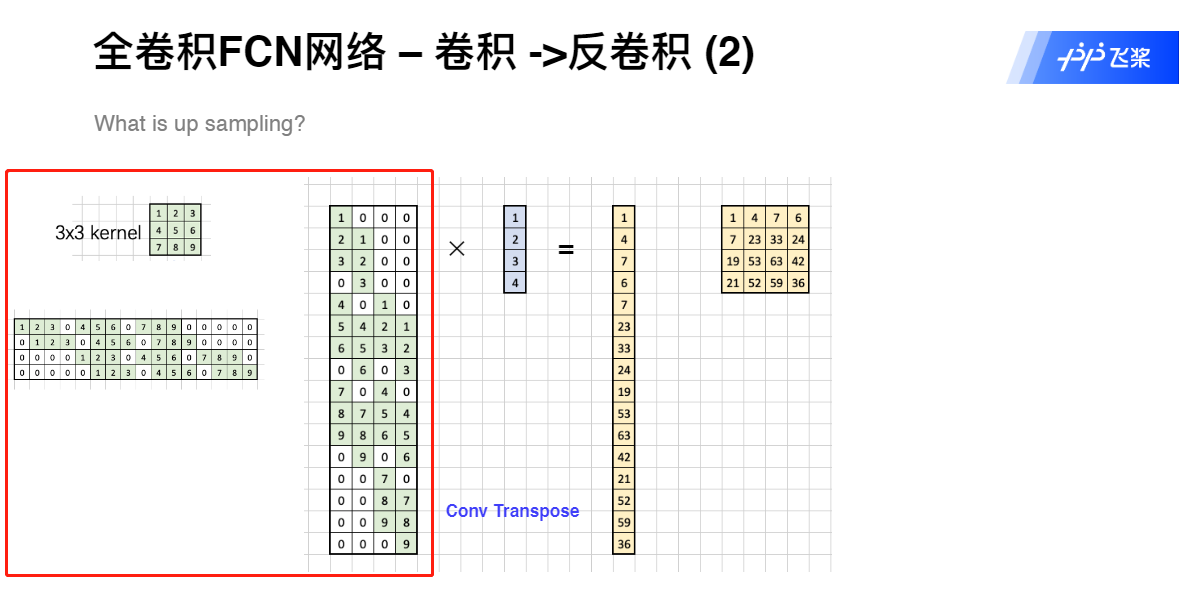
使用了反卷积层(Deconvolution)。分类神经网络的特征图一般只有原图的几分之一大小。想要映射回原图大小必须对特征图进行上采样,这就是反卷积层的作用。虽然名字叫反卷积层,但其实它并不是卷积的逆操作,更合适的名字叫做转置卷积(Transposed Convolution),作用是从小的特征图卷出大的特征图。
全卷积网络(FCN)的基本信息


FCN的优缺点
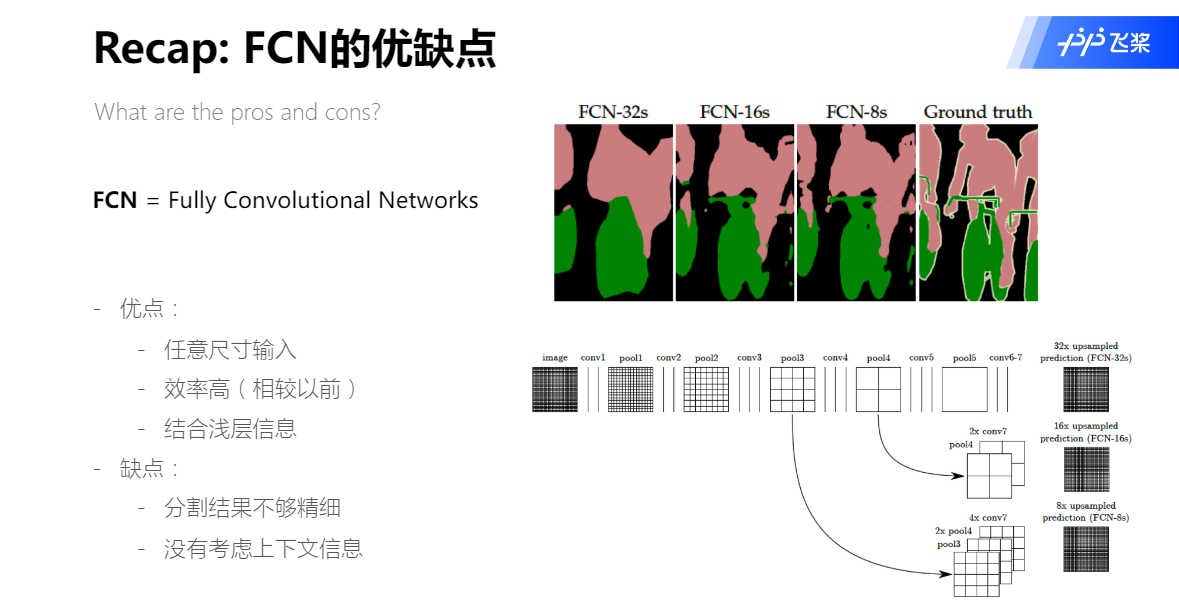
语义分割VS图像分类


分类 -> 分割 的变化
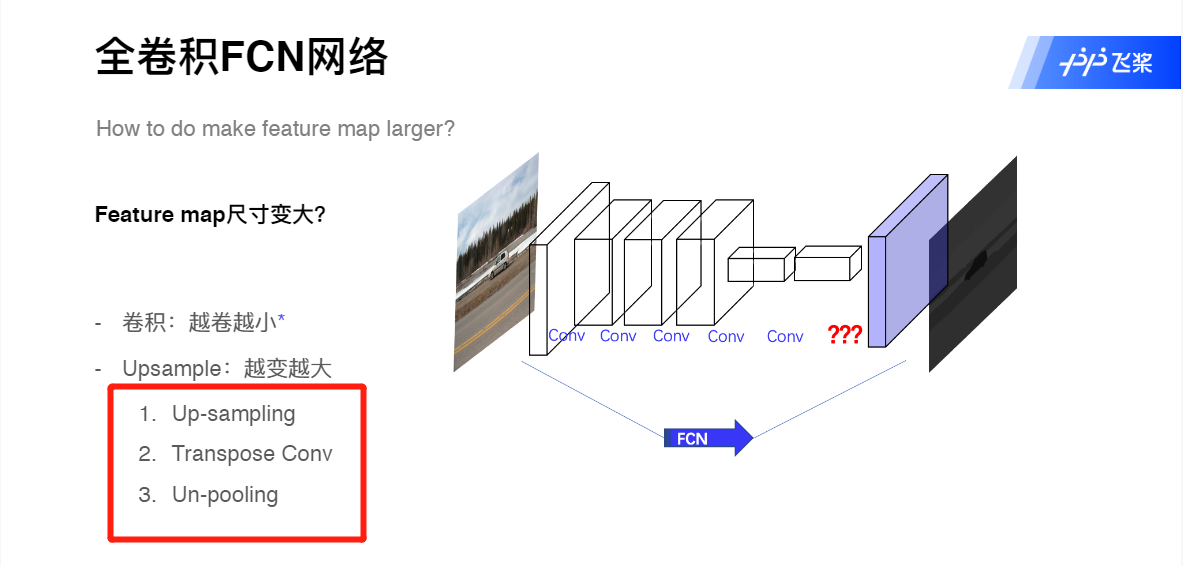
上采样方法
上采——双线性插值


上采样——Un-pooling
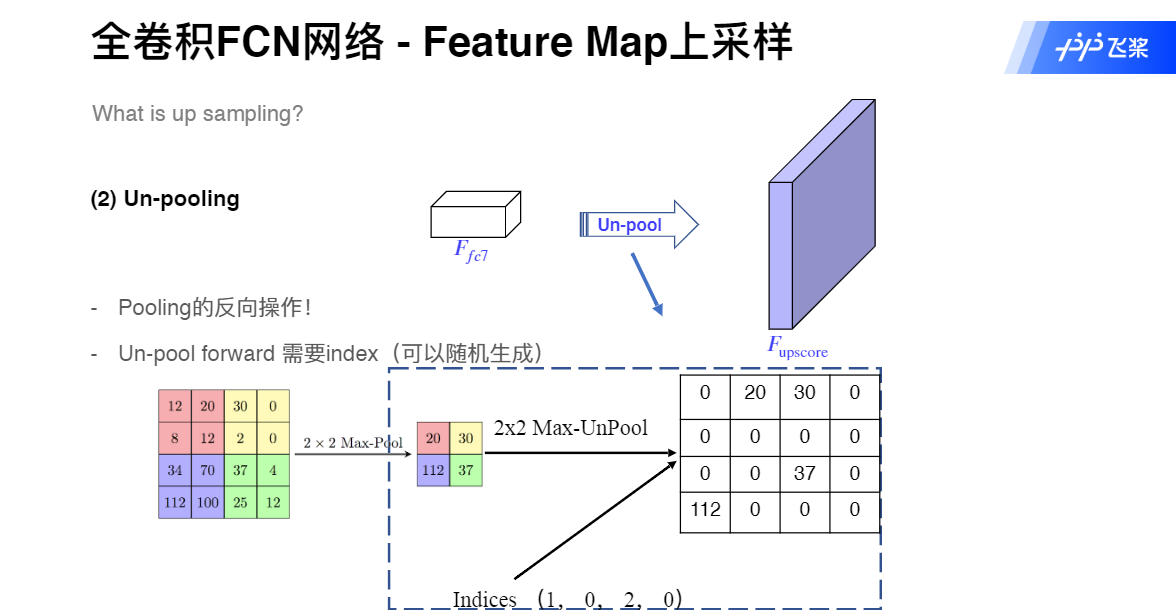
上采样——Transpose Conv
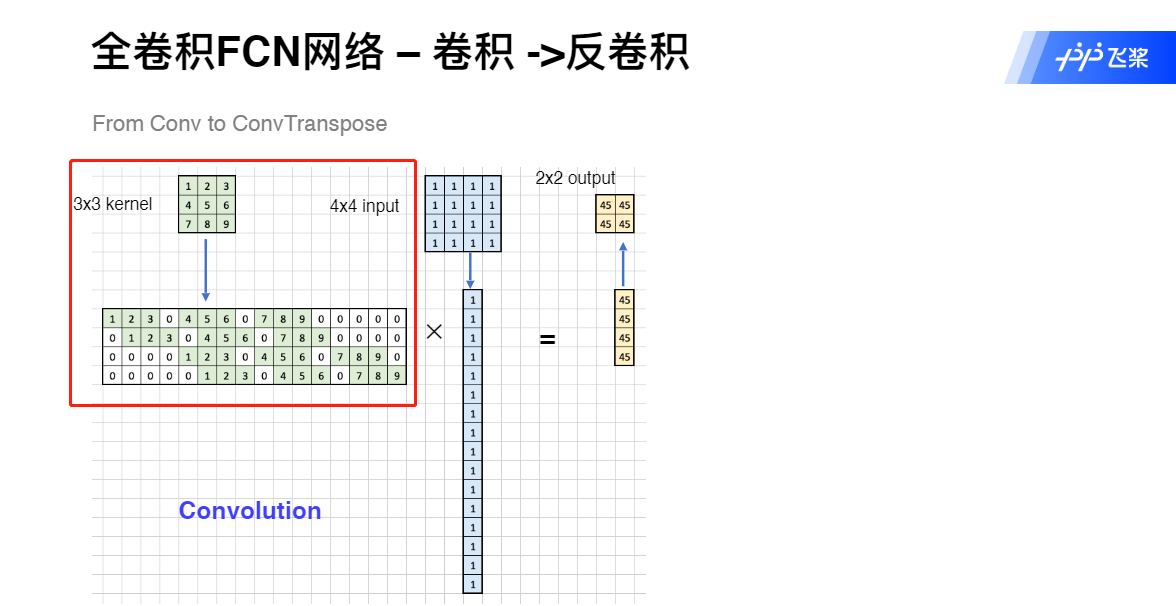
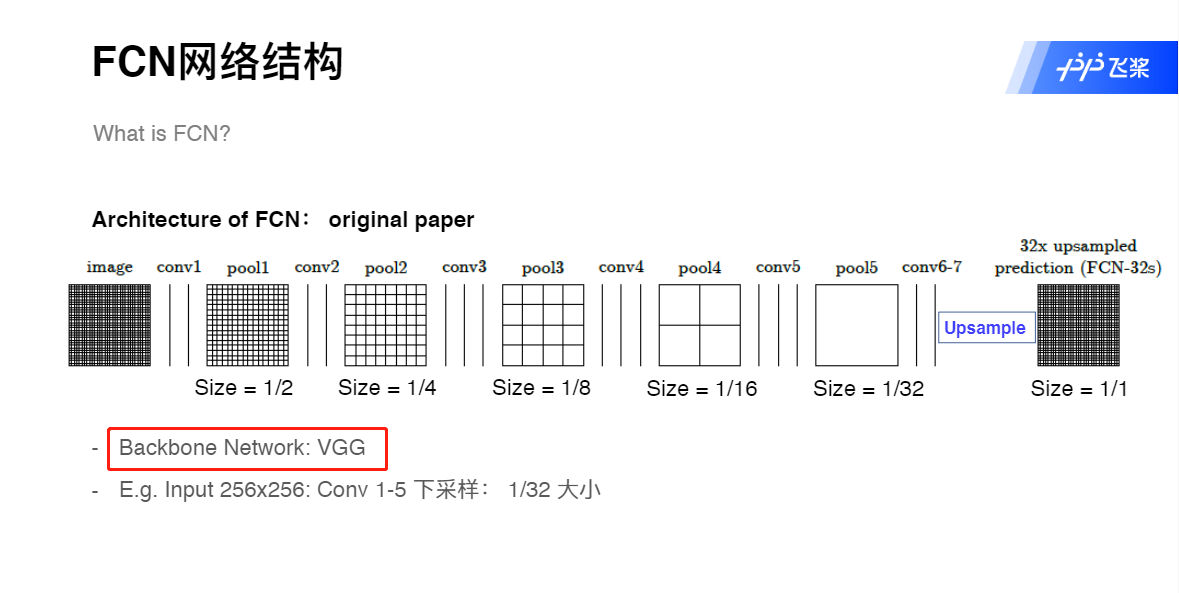
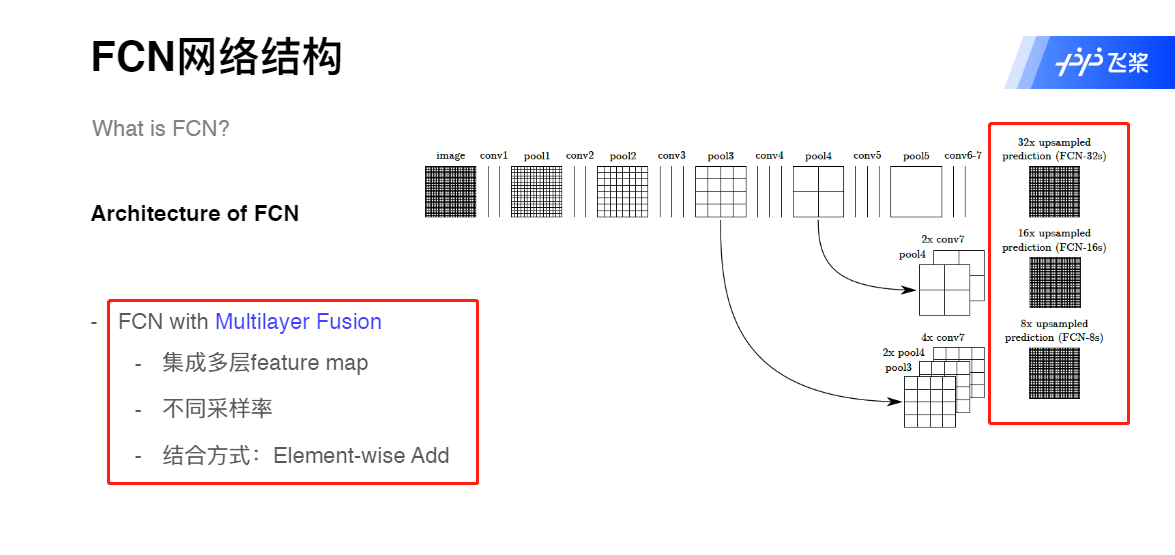
FCN网络结构
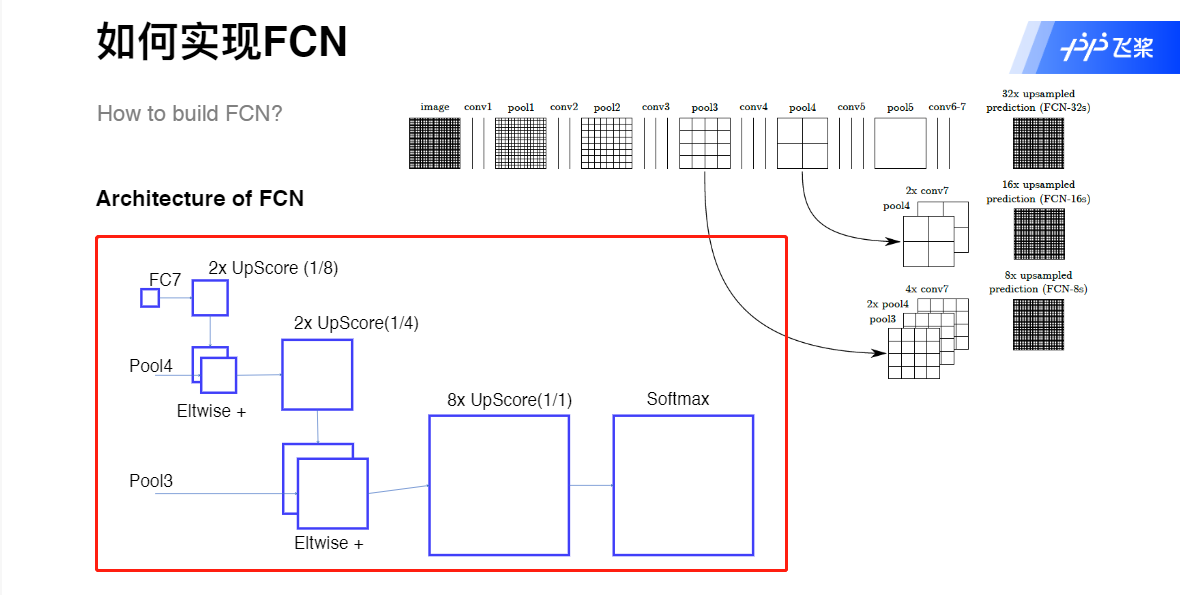
FCN代码实现
class FCN8s(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 512, 4096, 4096], n_class=21):
super(FCN8s, self).__init__()
# conv1
self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding=100)
self.relu1_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv1_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=out_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu1_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 覆盖掉原来的变量
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # 向上取整, 1/2
# conv2
self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=out_channels[1], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu2_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[1], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu2_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 覆盖掉原来的变量
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # 向上取整, 1/4
# conv3
self.conv3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu3_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu3_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv3_3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu3_3 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 覆盖掉原来的变量
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # 向上取整, 1/8
# conv4
self.conv4_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu4_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu4_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv4_3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu4_3 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 覆盖掉原来的变量
self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # 向上取整, 1/16
# conv5
self.conv5_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu5_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv5_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[4], out_channels=out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu5_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv5_3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[4], out_channels=out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, padding='same')
self.relu5_3 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 覆盖掉原来的变量
self.pool5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True) # 向上取整, 1/32
# fc6
self.fc6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[4], out_channels=out_channels[5], kernel_size=7) # 由padding=100得此处的最小尺寸为7!
self.relu6 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.drop6 = nn.Dropout2d()
# fc7
self.fc7 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[5], out_channels=out_channels[6], kernel_size=1)
self.relu7 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.drop7 = nn.Dropout2d()
self.score_fr = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[5], out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=1)
self.scoer_pool3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=1)
self.score_pool4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=1)
self.upscore2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=n_class, out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=4, stride=2, bias=False)
self.upscore8 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=n_class, out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=16, stride=8, bias=False)
self.upscore_pool4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels=n_class, out_channels=n_class, kernel_size=4, stride=2, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
shape = x.shape
if len(shape) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1)
x = self.relu1_1(self.conv1_1(x)) # [n, c, h-2+200, w-2+200]
x = self.relu1_2(self.conv1_2(x))
x = self.pool1(x) # [n, 64, (h-2+200)/2, (w-2+200)/2]
x = self.relu2_1(self.conv2_1(x))
x = self.relu2_2(self.conv2_2(x))
x = self.pool2(x) # [n, 128, (h-2+200)/4, (w-2+200)/4]
x = self.relu3_1(self.conv3_1(x))
x = self.relu3_2(self.conv3_2(x))
x = self.relu3_3(self.conv3_3(x))
x = self.pool3(x) # [n, 256, (h-2+200)/8, (w-2+200)/8]
pool3 = x
x = self.relu4_1(self.conv4_1(x))
x = self.relu4_2(self.conv4_2(x))
x = self.relu4_3(self.conv4_3(x))
x = self.pool4(x) # [n, 256, (h-2+200)/16, (w-2+200)/16]
pool4 = x
x = self.relu5_1(self.conv5_1(x))
x = self.relu5_2(self.conv5_2(x))
x = self.relu5_3(self.conv5_3(x))
x = self.pool5(x) # [n, 512, (h-2+200)/32, (w-2+200)/32]
x = self.relu6(self.fc6(x)) # [n, 4096, (h-2+200)/32-6, (w-2+200)/32-6]
x = self.drop6(x)
x = self.relu7(self.fc7(x)) # [n, 4096, (h-2+200)/32-6, (w-2+200)/32-6]
x = self.drop7(x)
x = self.score_fr(x) # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/32-6, (w-2+200)/32-6]
x = self.upscore2(x) # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/16-10, (w-2+200)/16-10]
score_pool4 = self.score_pool4(pool4) # [n, n_class, (w-2+200)/16, (w-2+200)/16]
score_pool4 = score_pool4[:, :, 5:5+x.size()[2], 5:5+x.size()[3]] # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/16-10, (w-2+200)/16-10]
x = x + score_pool4 # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/16-10, (w-2+200)/16-10]
x = self.upscore_pool4(x) # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/8-18, (w-2+200)/8-18]
score_pool3 = self.scoer_pool3(pool3) # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/8, (w-2+200)/8]
score_pool3 = score_pool3[:, :, 9:9+x.size()[2], 9:9+x.size()[3]] # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/8-18, (w-2+200)/8-18]
x = x + score_pool3 # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)/8-18, (w-2+200)/8-18]
x = self.upscore8(x) # [n, n_class, (h-2+200)-17*8, (w-2+200)-17*8] -> [n, n_class, h+62, w+62]
x = x[:, :, 31:31+shape[1], 31:31+shape[2]].contiguous() # [n, n_class, h, w]
return x
FCN全卷积网络详解PPT
U-Net
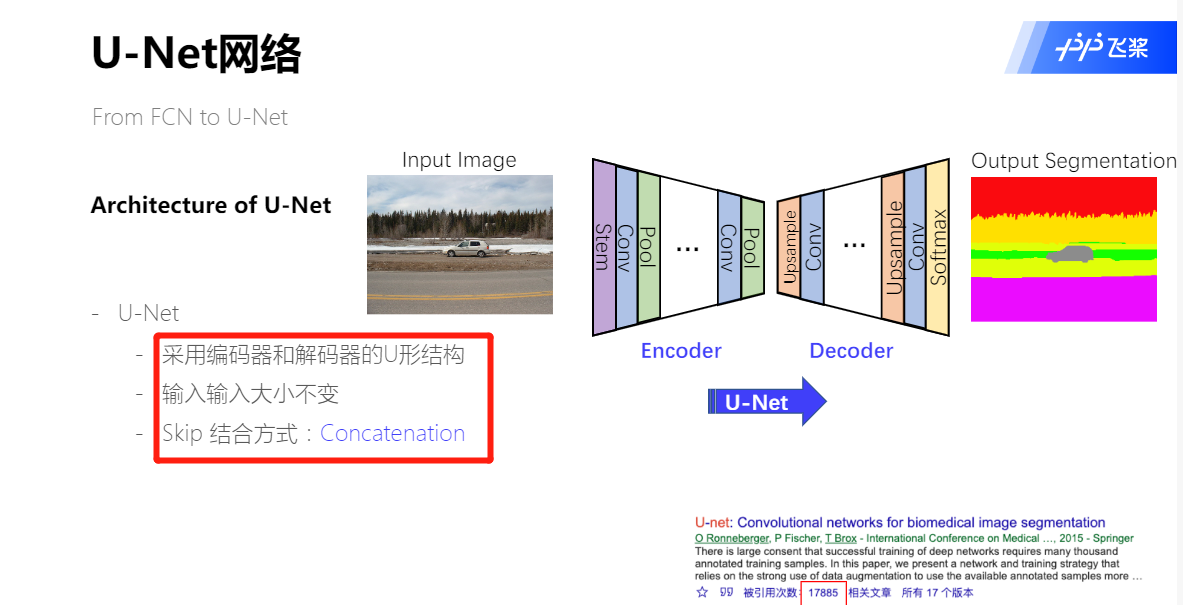
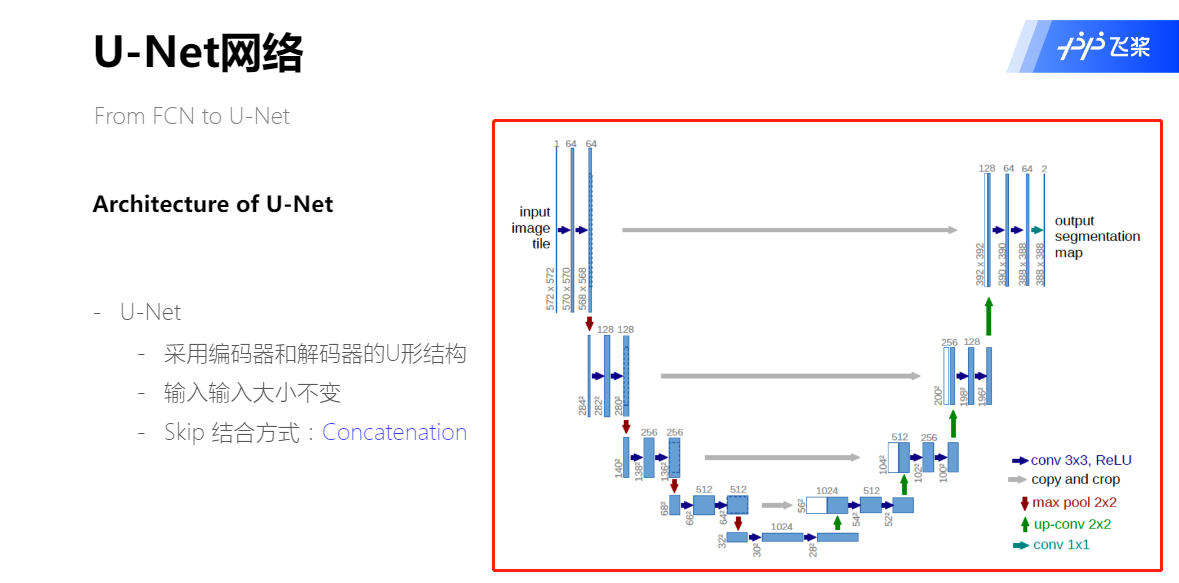
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation,U-Net是原作者参加ISBI Challenge提出的一种分割网络,能够适应很小的训练集(大约30张图)。U-Net与FCN都是很小的分割网络,既没有使用空洞卷积,也没有后接CRF,结构简单。
U-Net类似于一个大大的U字母:首先进行Conv+Pooling下采样;然后Deconv反卷积进行上采样,crop之前的低层feature map,进行融合;然后再次上采样。重复这个过程,直到获得输出388x388x2的feature map,最后经过softmax获得output segment map。总体来说与FCN思路非常类似。
U-Net网络结构
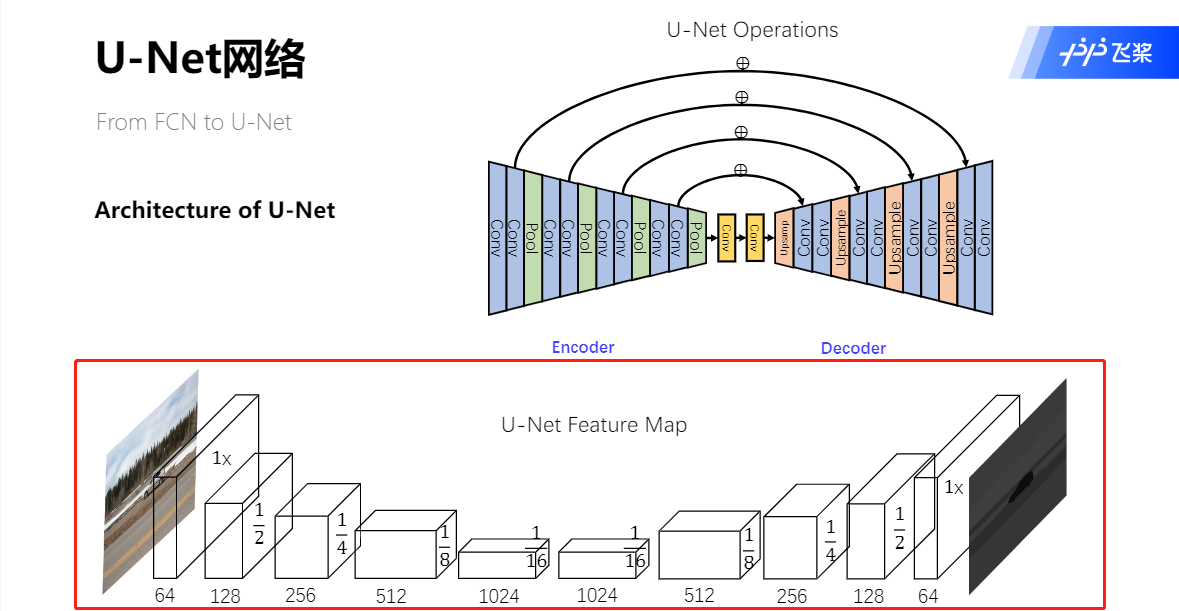
skip-connect机制
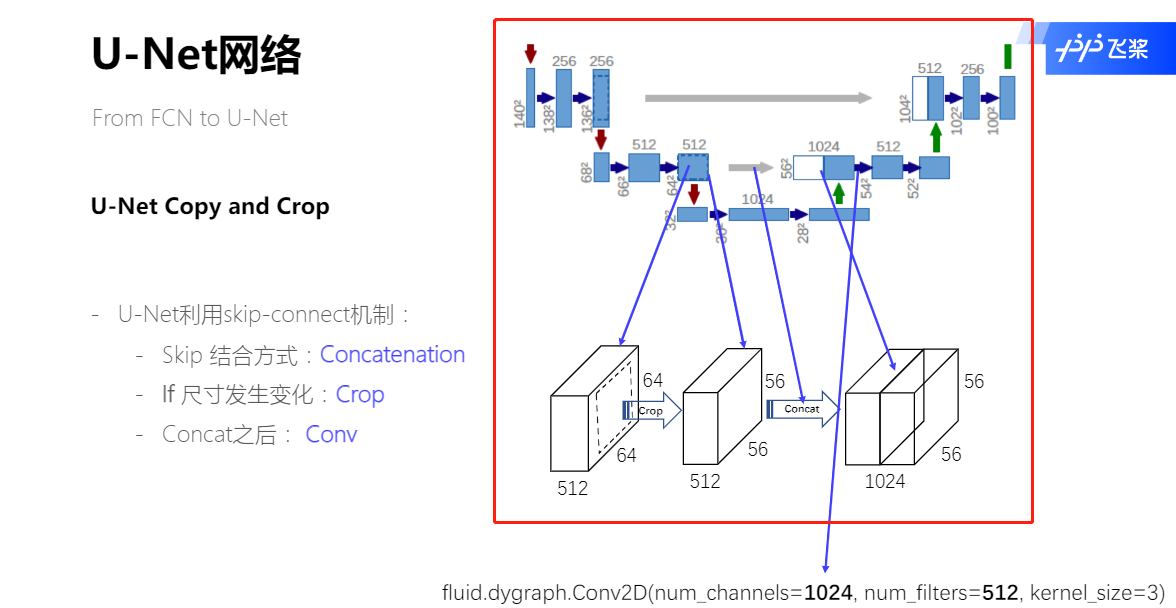
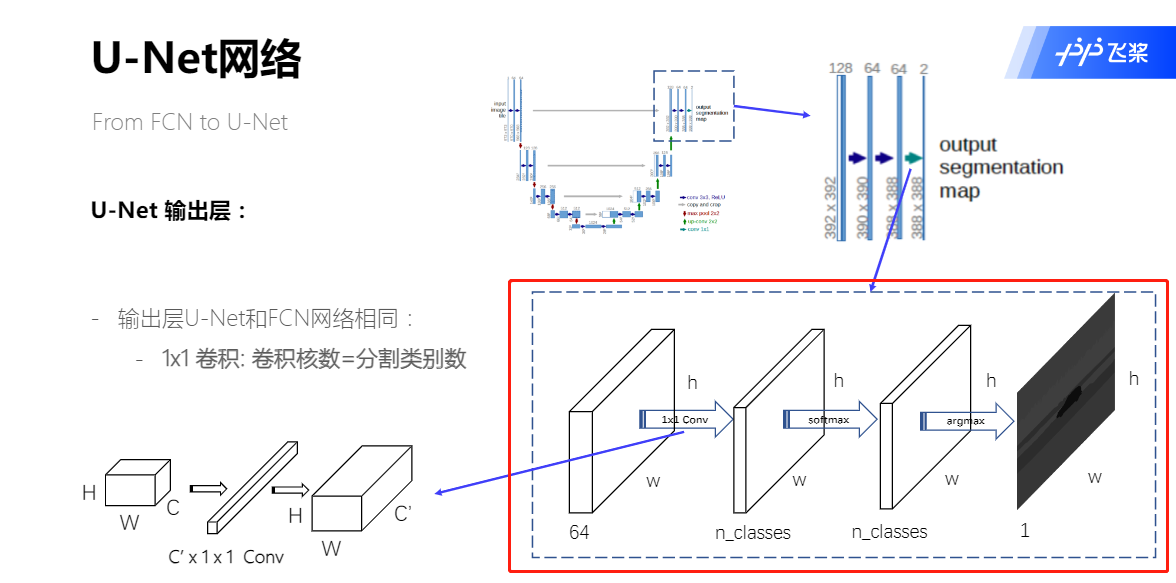
U-Net输出层
U-Net代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
from torchstat import stat
#%%
class DoubleConv(nn.Module):
'''(convolution => [BN] => ReLU) * 2'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, mid_channels=None):
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__()
if not mid_channels:
mid_channels = out_channels
self.double_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.double_conv(x)
#%%
class DownSample(nn.Module):
"""Downscaling with maxpool then double conv"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(DownSample, self).__init__()
self.doubleConv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
def forward(self, x):
res = self.doubleConv(x)
out = self.maxpool(res)
return res, out
#%%
class UpSample(nn.Module):
"""Upscaling then double conv"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, bilinear=False):
super().__init__()
# if bilinear, use the normal convolutions to reduce the number of channels
if bilinear:
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels, in_channels//2)
else:
self.up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, in_channels//2, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x1, x2):
x1 = self.up(x1)
# input is CHW
diffY = x2.size()[2] - x1.size()[2]
diffX = x2.size()[3] - x1.size()[3]
x1 = F.pad(x1, [diffX//2, diffX-diffX//2,
diffY//2, diffY-diffY//2]) # 补齐维度
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
return self.conv(x)
#%%
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 1024], n_classes=5, bilinear=False):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.down1 = DownSample(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels[0])
self.down2 = DownSample(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=out_channels[1])
self.down3 = DownSample(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[2])
self.down4 = DownSample(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[3])
factor = 2 if bilinear else 1
self.center = DoubleConv(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[4]//factor)
self.up1 = UpSample(in_channels=out_channels[4], out_channels=out_channels[3]//factor, bilinear=bilinear)
self.up2 = UpSample(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[2]//factor, bilinear=bilinear)
self.up3 = UpSample(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[1]//factor, bilinear=bilinear)
self.up4 = UpSample(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[0])
self.outConv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=n_classes, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
if len(x.shape) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1)
res1, x = self.down1(x)
res2, x = self.down2(x)
res3, x = self.down3(x)
res4, x = self.down4(x)
x = self.center(x)
x = self.up1(x, res4)
x = self.up2(x, res3)
x = self.up3(x, res2)
x = self.up4(x, res1)
x = self.outConv(x)
return x
U-Net/PSP网络PPT
Pyramid Scene Parsing Network(PSP)分割网络
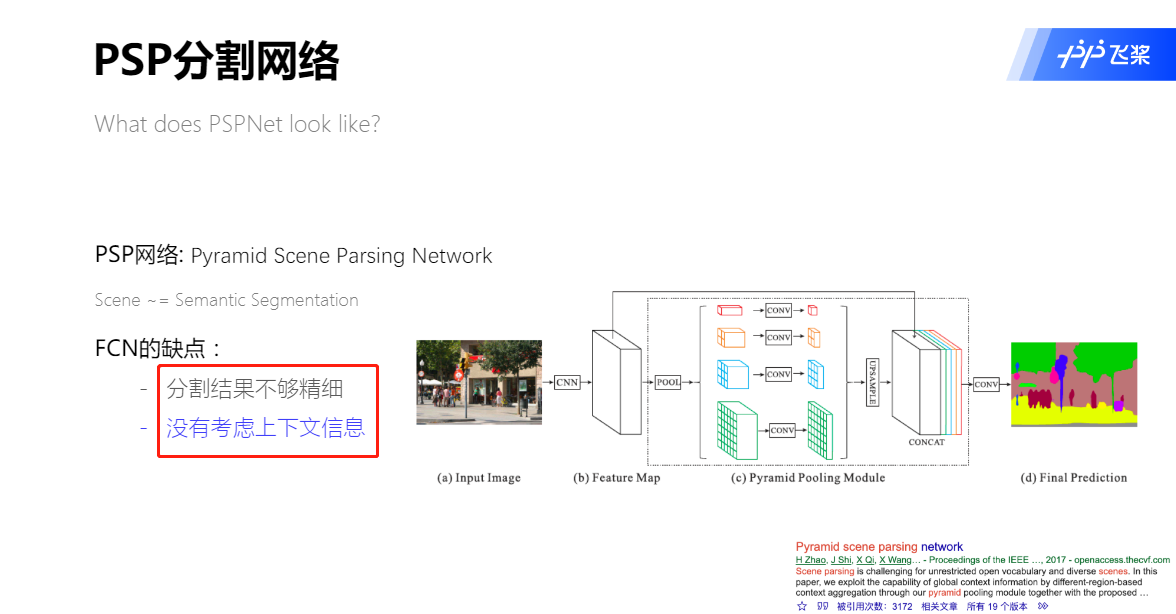
Pyramid Scene Parsing Network,提出的金字塔池化模块( pyramid pooling module)能够聚合不同区域的上下文信息,从而提高获取全局信息的能力。
三个分割问题
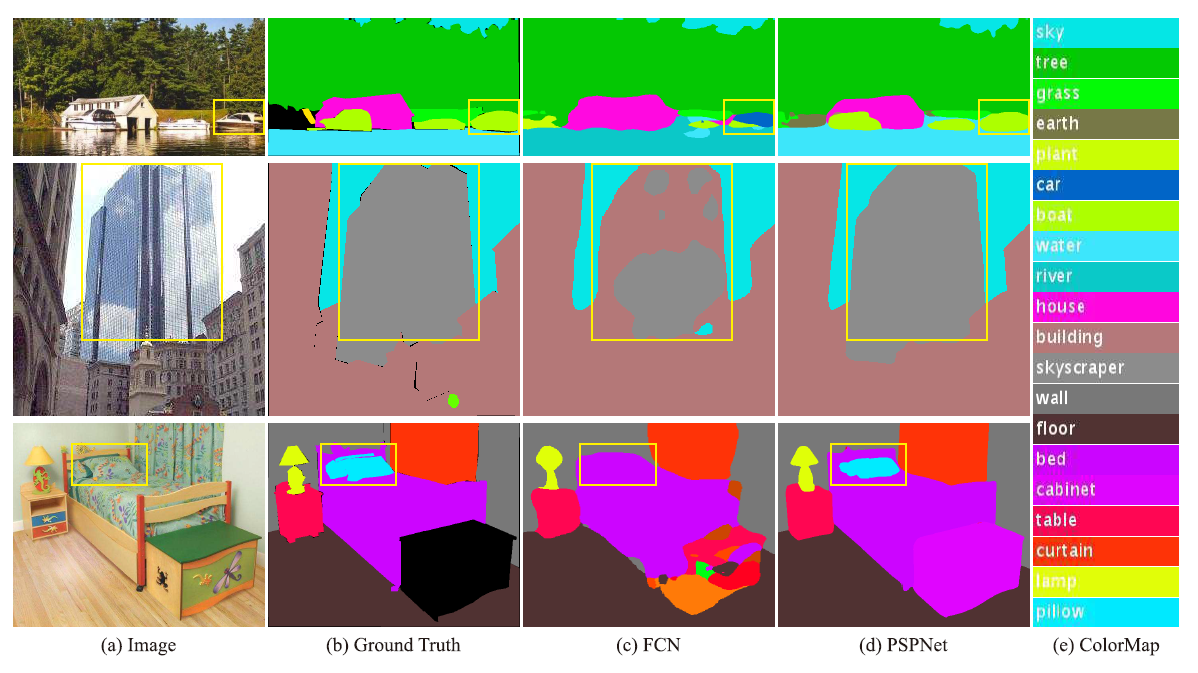
基于CNN的分割模型取得了很大的成果,但是在面对场景分析这一任务中遇到了困难。场景分析有两个特点:目标种类繁多;多个目标交叠在一起。这共同导致分割难度增大,分割效果不尽如人意。由此产生了三个问题:
Mismatched Relationship(不匹配联系)
上下文关系匹配对理解复杂场景很重要。对于一个物体其存在的位置是有其规律的,比如上图第一行中所示的,FCN网络错将“船”分类成“汽车”,但是汽车很少会出现在河面上的,这是因为FCN缺乏依据上下文推断的能力。
Confusion Categories(类别混乱)
对于一些具有相似属性的目标会在分割网络结果中存在混淆的现象,如上图中第二行所示,FCN对于building和skyscaper这两个相似目标的分类出现了混淆,许多标签之间存在关联,可以通过标签之间的关系弥补分割网络这一缺陷。
Inconspicuous Classes(不连续类别)
对于一些较小的目标在分割任务中难以找到,大目标超出了网络感受野而导致不连续分割的情况,如上图第三行所示。床和枕头因为颜色和材质一致,而且枕头被包含在床里面,因此FCN缺失对枕头的分割。为了提高网络对非常小或非常大的对象的性能,应该特别注意包含不显著类别(过大或者过小)的不同子区域。
PSPNet的主要贡献
分割网络的许多问题出在FCN不能有效的处理场景之间的关系和全局信息。论文提出了能够获取全局场景的深度网络PSPNet,能够融合合适的全局特征,将局部和全局信息融合到一起。并提出了一个适度监督损失的优化策略,在多个数据集上表现优异。
PSP针对的问题
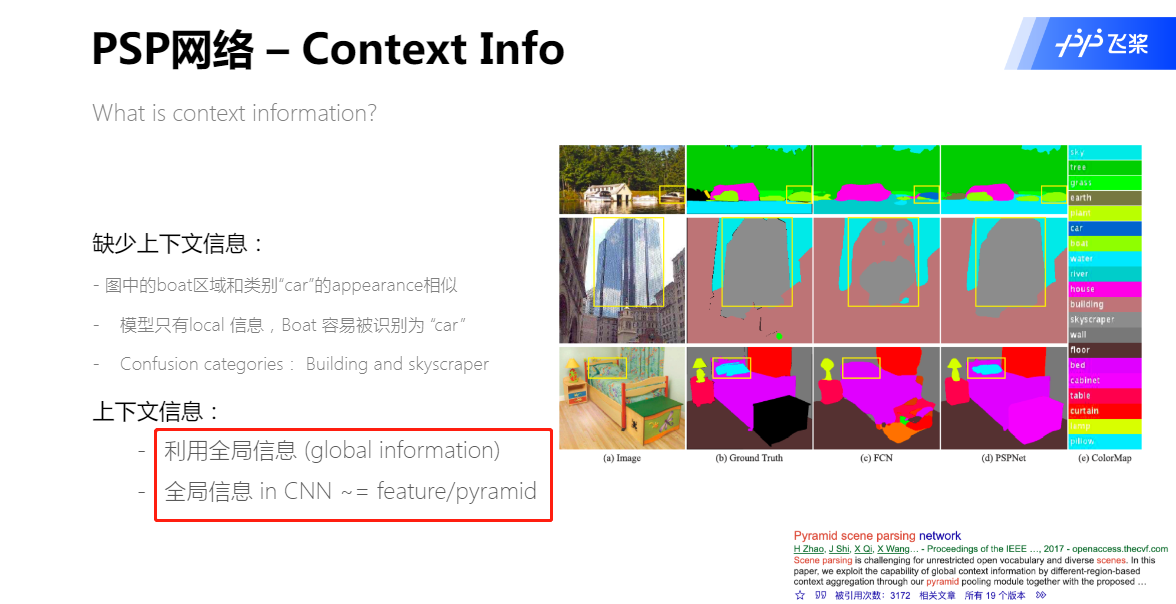
感受野(RF)作用的理解

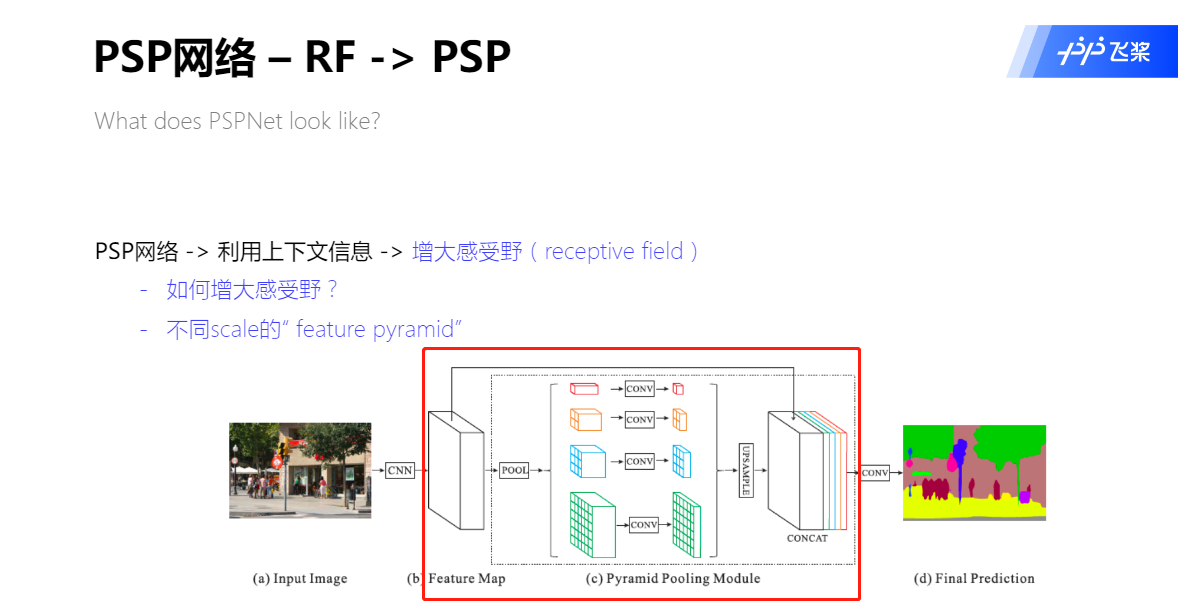
RF -> PSP
Pyramid Pooling 模块
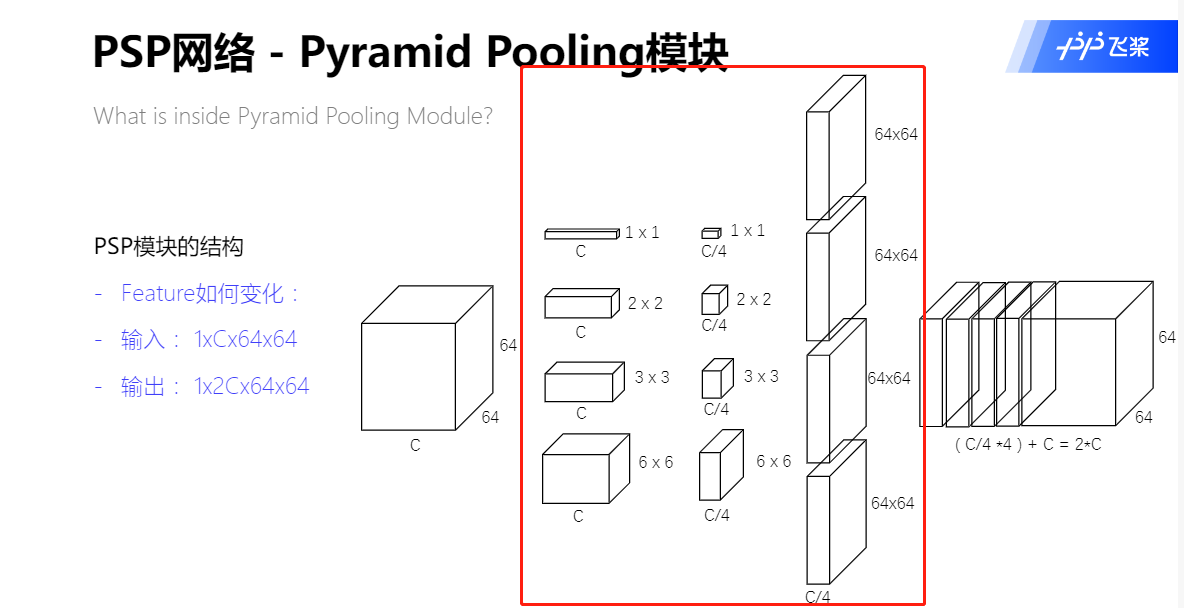
在一般CNN中感受野可以粗略的认为是使用上下文信息的大小,论文指出在许多网络中没有充分的获取全局信息,所以效果不好。要解决这一问题,常用的方法是:
- 用Global Average Pooling处理。但这可能会失去空间关系导致模糊。
- 由金字塔池化产生不同层次的特征最后被平滑的连接成一个FC层做分类。这样可以去除CNN固定大小的图像分类约束,减少不同区域之间的信息损失。
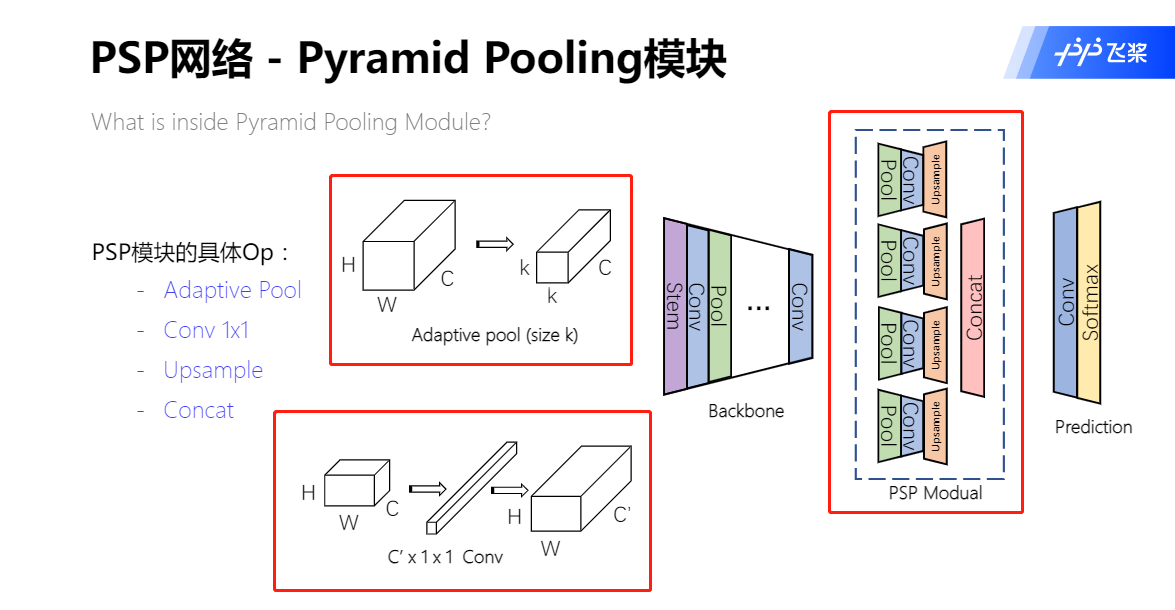
Adaptive Pool 自适应池化的维度计算
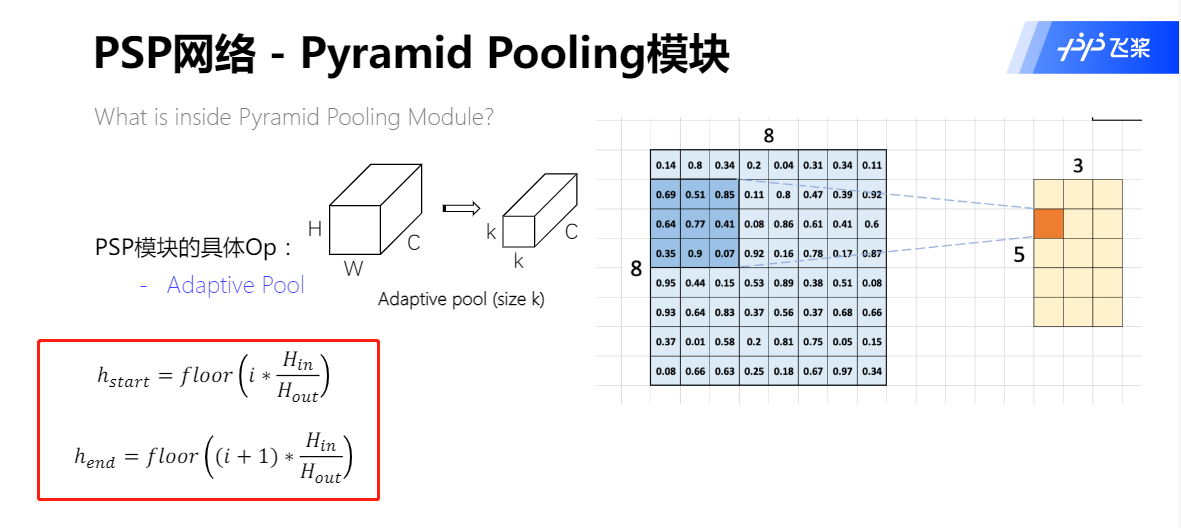
PSP网络结构
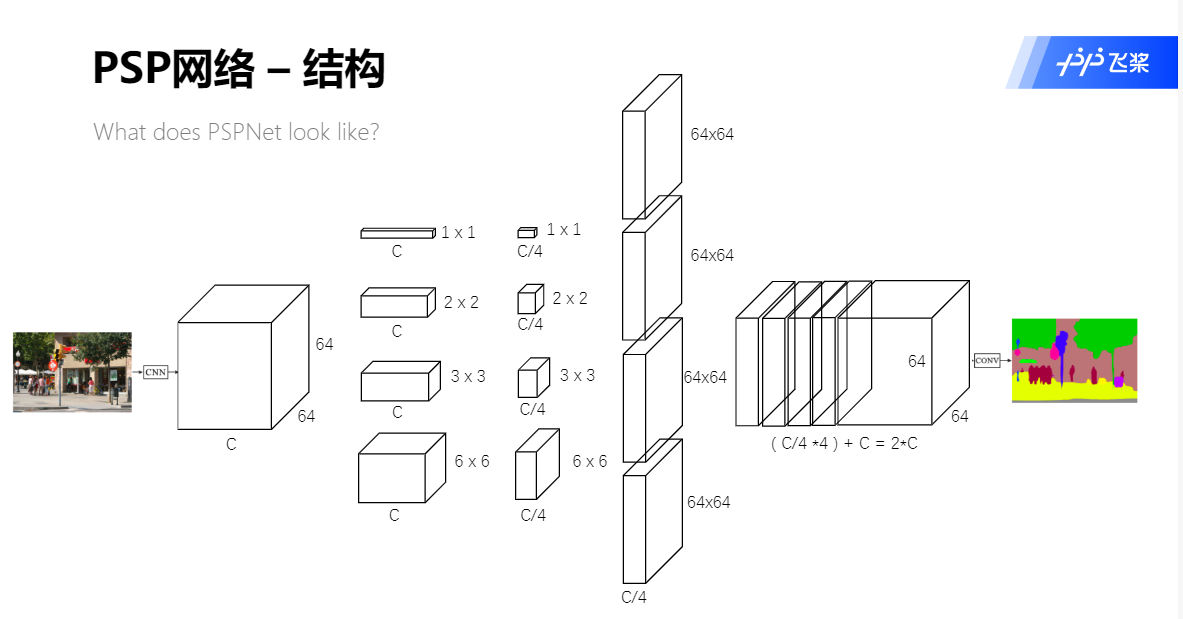
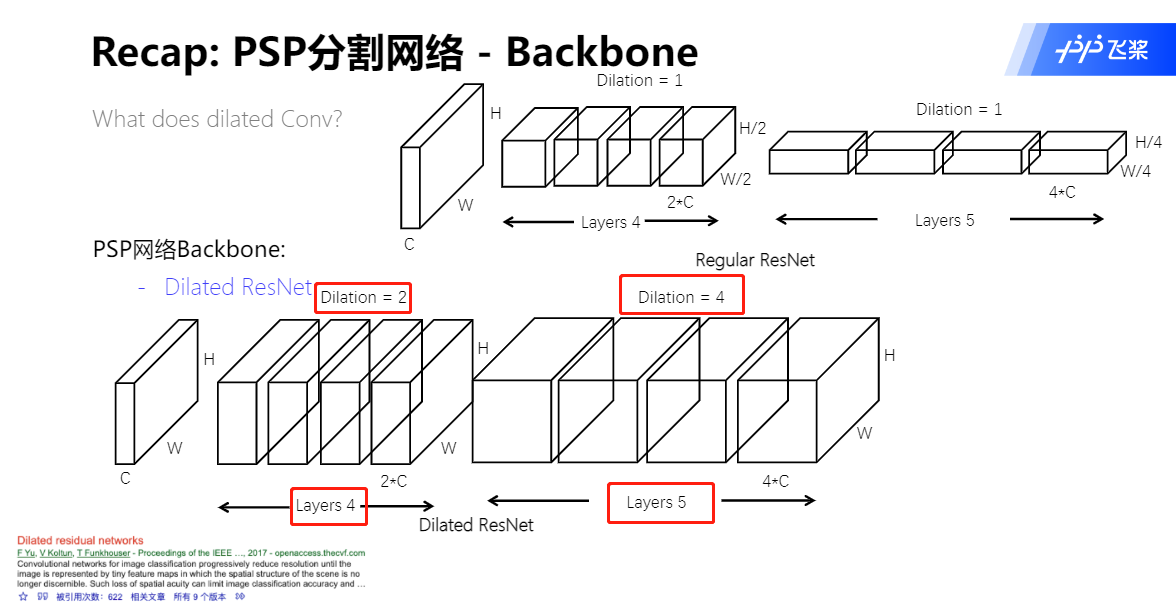
- 输入图像经过预训练的模型(ResNet101)和 空洞卷积(dilated) 策略提取feature map,提取后的feature map是原始输入图像的1/8。
- feature map经过Pyramid Pooling Module得到融合的带有整体信息的feature map,在池化前的feature map拼接到一起。
- 最后过一个卷积层得到最终输出。
Dilated Convolution 空洞卷积
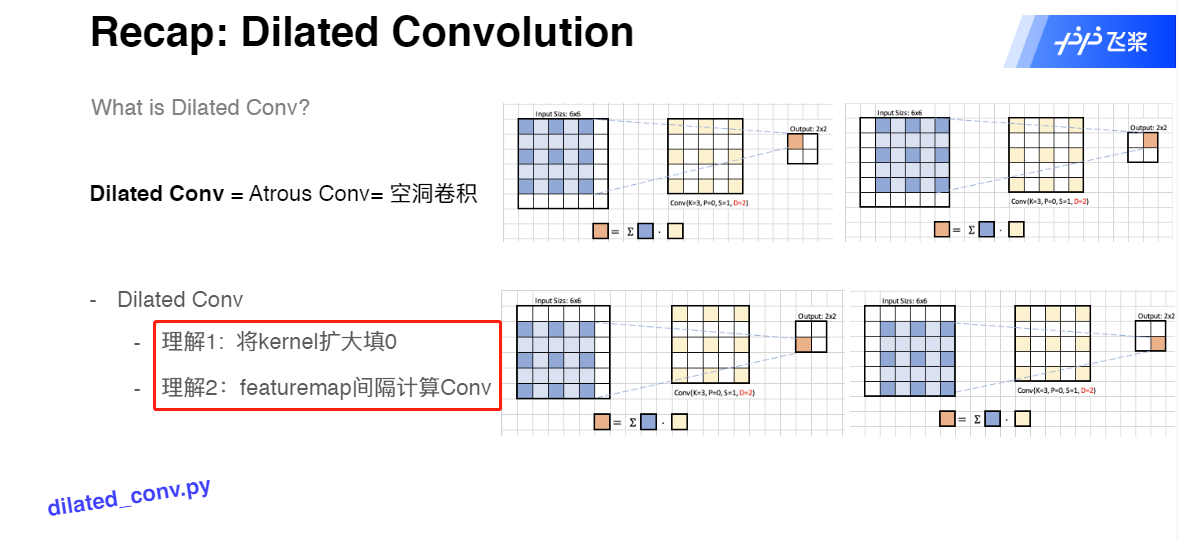
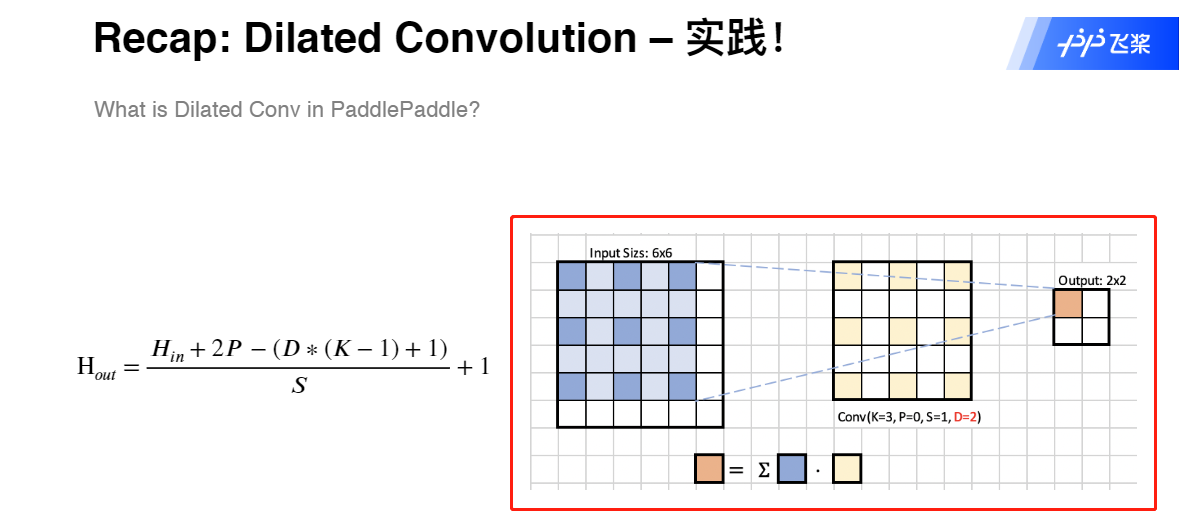
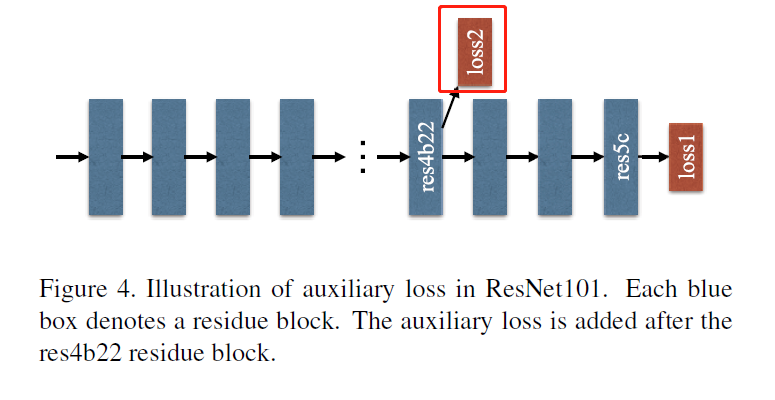
PSP网的辅助模块
PSPNet代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import models
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
from torchstat import stat
#%%
def initialize_weights(*models):
for model in models:
for module in model.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
nn.init.kaiming_normal(module.weight)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
module.weight.data.fill_(1)
module.bias.data.zero_()
#%%
class PyramidPoolingModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, reduction_dim, setting):
super(PyramidPoolingModule, self).__init__()
self.features = []
for s in setting:
self.features.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=s),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=reduction_dim, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=reduction_dim, momentum=.95),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
))
self.features = nn.ModuleList(self.features)
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
out = [x]
for f in self.features:
out.append(F.upsample(f(x), x_size[2:], mode='bilinear'))
out = torch.cat(out, 1)
return out
#%%
class PSPNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, n_classes=5, pretrained=False, use_aux=False):
super(PSPNet, self).__init__()
self.use_aux = use_aux
resnet = models.resnet101()
if pretrained:
resnet = models.resnet101(pretrained=pretrained)
self.layer0 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
) # out_channel=64
self.layer1 = resnet.layer1 # out_channel=256
self.layer2 = resnet.layer2 # out_channel=512
self.layer3 = resnet.layer3 # out_channel=1024
self.layer4 = resnet.layer4 # out_channel=2048
for n, m in self.layer3.named_modules():
if 'conv2' in n:
m.dilation, m.padding, m.stride = (2, 2), (2, 2), (1, 1)
elif 'downsample.0' in n:
m.stride = (1, 1)
for n, m in self.layer4.named_modules():
if 'conv2' in n:
m.dilation, m.padding, m.stride = (4, 4), (4, 4), (1, 1)
elif 'downsample.0' in n:
m.stride = (1, 1)
self.ppm = PyramidPoolingModule(in_dim=2048, reduction_dim=512, setting=[1, 2, 3, 6])
self.final = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=4096, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=512, momentum=.95),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=n_classes, kernel_size=1)
)
if use_aux: # auxiliary loss
self.aux_logits = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=n_classes, kernel_size=1)
initialize_weights(self.aux_logits)
initialize_weights(self.ppm, self.final)
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
if len(x_size) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # [n, c, h, w]
x = self.layer0(x) # [n, 64, h//4, w//4]
x = self.layer1(x) # [n, 256, h//4, w//4]
x = self.layer2(x) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
x = self.layer3(x) # [n, 1024, h//8, w//8]
if self.training and self.use_aux:
aux = self.aux_logits(x)
x = self.layer4(x) # [n, 2048, h//8, w//8]
x = self.ppm(x) # [n, 4096, h//8, w//8]
x = self.final(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
if self.training and self.use_aux:
return F.upsample(x, x_size[1:], mode='bilinear'), F.upsample(aux, x_size[1:], mode='bilinear')
return F.upsample(x, x_size[1:], mode='bilinear')
U-Net/PSP网络PPT
图像分割2(U-Net/V-Net/PSPNet)
DeepLab
DeepLab V1
Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets and Fully Connected CRFs
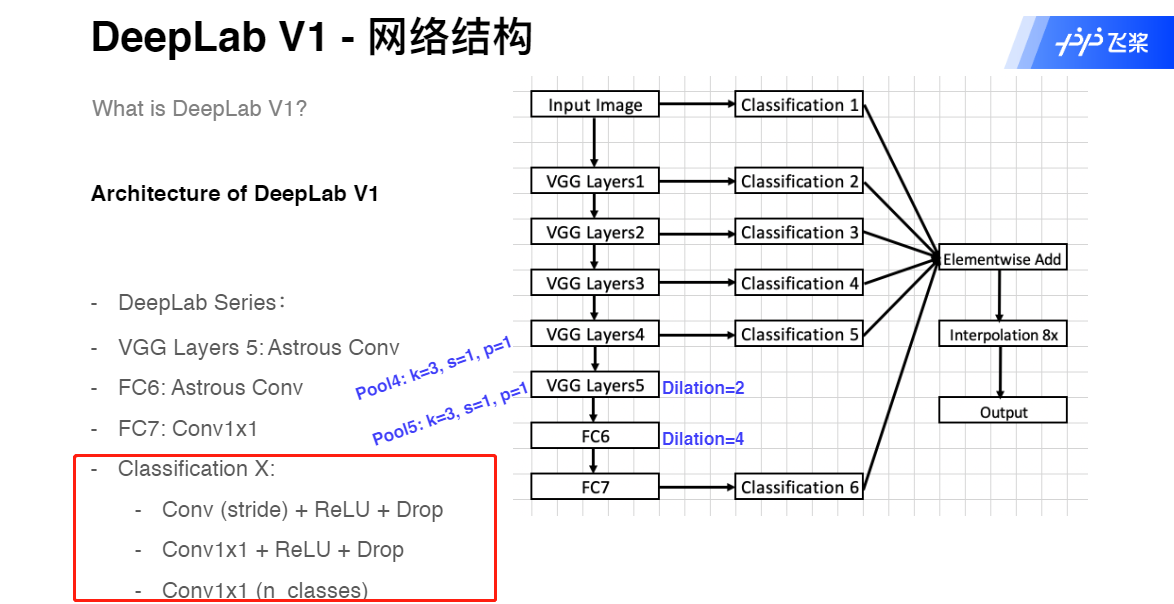
DeepLab V1 网络结构
DeepLab V1 代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
from torchstat import stat
#%%
class classification(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, n_classes):
super(classification, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(p=0.3)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(p=0.3)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=n_classes, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.relu2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
return x
#%%
class DeepLab_V1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 512, 512, 512], n_classes=5):
super(DeepLab_V1, self).__init__()
self.classification0 = classification(
in_channels, out_channels[0], stride=8, n_classes=n_classes
) # 下采样八倍所以里面的第一个卷积的stride = 8
self.vggLayer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=out_channels[0], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.classification1 = classification(
out_channels[0], out_channels[1], stride=4, n_classes=n_classes
) #接受Layer1的输出所以下采样4倍
self.vggLayer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[0], out_channels=out_channels[1], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[1], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.classification2 = classification(
out_channels[1], out_channels[2], stride=2, n_classes=n_classes
) #接受Layer1的输出所以下采样2倍
self.vggLayer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[1], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[2], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.classification3 = classification(
out_channels[2], out_channels[3], stride=1, n_classes=n_classes
) #接受Layer3的输出相对于原图已经下采样8倍所以不用下采样
self.vggLayer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[2], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels[3], out_channels=out_channels[3], kernel_size=3, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.classification4 = classification(
out_channels[3], out_channels[4], stride=1, n_classes=n_classes
) #接受Layer4的输出相对于原图已经下采样8倍所以不用下采样
self.vggLayer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels[3], out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, dilation=2, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels[4], out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, dilation=2, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels[4], out_channels[4], kernel_size=3, dilation=2, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.fc6 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels[4], out_channels[5], kernel_size=3, dilation=4, padding='same'),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout()
)
self.fc7 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(out_channels[5], out_channels[6], kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout()
)
self.classification7 = classification(
out_channels[6], out_channels[6], stride=1, n_classes=n_classes
) #接受fc7的输出相对于原图已经下采样8倍所以不用下采样
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
if len(x_size) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # [n, c, h, w]
cla0 = self.classification0(x) # [n, 64, h//8, w//8]
x = self.vggLayer1(x) # [n, 64, h//2, w//2]
cla1 = self.classification1(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = self.vggLayer2(x) # [n, 128, h//4, w//4]
cla2 = self.classification2(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = self.vggLayer3(x) # [n, 256, h//8, w//8]
cla3 = self.classification3(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = self.vggLayer4(x) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
cla4 = self.classification4(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = self.vggLayer5(x) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
x = self.fc6(x) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
x = self.fc7(x) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
cla7 = self.classification7(x) # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = cla0+cla1+cla2+cla3+cla4+cla7 # [n, n_classes, h//8, w//8]
x = F.upsample(x, size=x_size[1:], mode='bilinear')
return x
DeepLab V2
DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs
DeepLab V2 网络结构

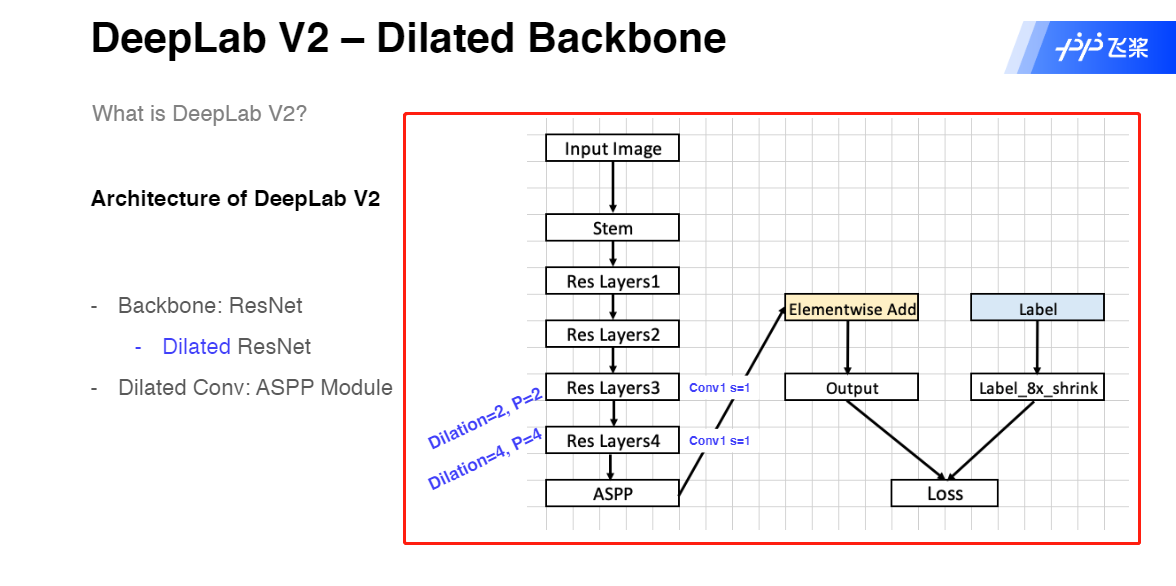
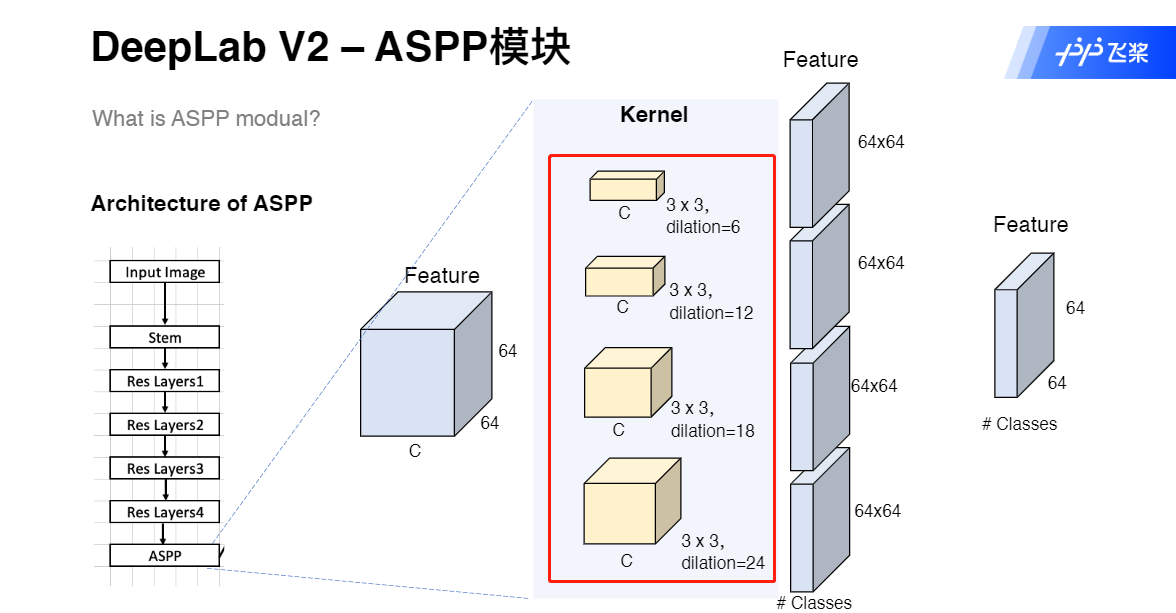
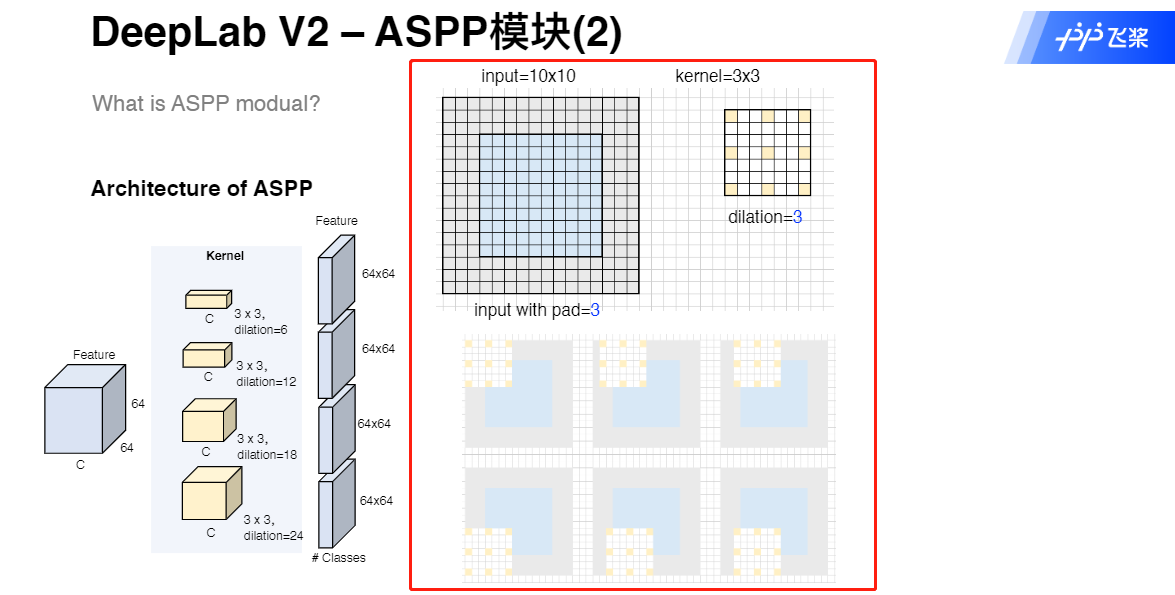
DeepLab V2 ASPP模块
DeepLab V2 代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
from torchstat import stat
#%%
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, padding, dilation):
super(ResBlock, self).__init__()
self.downsample = False
self.mid_channels = out_channels//4
self.reduce = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, self.mid_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=self.mid_channels)
)
self.conv3x3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.mid_channels, self.mid_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=self.mid_channels)
)
self.increase = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
if in_channels != out_channels:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels)
)
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
res = x
x = self.reduce(x)
x = self.conv3x3(x)
x = self.increase(x)
res = self.shortcut(res)
x = x+res
return x
#%%
class ResLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, n_layers, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1):
super(ResLayer, self).__init__()
resLayer = []
for i in range(n_layers):
resLayer.append(
ResBlock(in_channels=(in_channels if i==0 else out_channels),
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=(stride if i==0 else 1),
padding=padding,
dilation=dilation)
)
self.resLayers = nn.Sequential(*resLayer)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.resLayers(x)
return x
#%%
class ASPP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channesls, out_channels, dilatopns):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
self.aspp1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[0], padding=dilatopns[0]),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[1], padding=dilatopns[1]),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[2], padding=dilatopns[2]),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[3], padding=dilatopns[3]),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
aspp1 = self.aspp1(x)
aspp2 = self.aspp2(x)
aspp3 = self.aspp3(x)
aspp4 = self.aspp4(x)
out = aspp1+aspp2+aspp3+aspp4
return out
#%%
class DeepLab_V2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=[64, 256, 512, 1024, 2048], n_layers=[3, 4, 23, 3], n_classes=5):
super(DeepLab_V2, self).__init__()
self.stem = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels[0], kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, dilation=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels[0]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.res101Layer1 = ResLayer(out_channels[0], out_channels[1], n_layers[0], stride=2)
self.res101Layer2 = ResLayer(out_channels[1], out_channels[2], n_layers[1], stride=2)
self.res101Layer3 = ResLayer(out_channels[2], out_channels[3], n_layers[2], stride=1, padding=2, dilation=2)
self.res101Layer4 = ResLayer(out_channels[3], out_channels[4], n_layers[3], stride=1, padding=4, dilation=4)
self.aspp = ASPP(out_channels[4], n_classes, dilatopns=[6, 12, 18, 24])
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
if len(x_size) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # [n, c, h, w]
x = self.stem(x)
x = self.res101Layer1(x)
x = self.res101Layer2(x)
x = self.res101Layer3(x)
x = self.res101Layer4(x)
x = self.aspp(x)
x = F.upsample(x, size=x_size[1:], mode='bilinear')
return x
DeepLab V3
Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation
DeepLab V3 网络结构
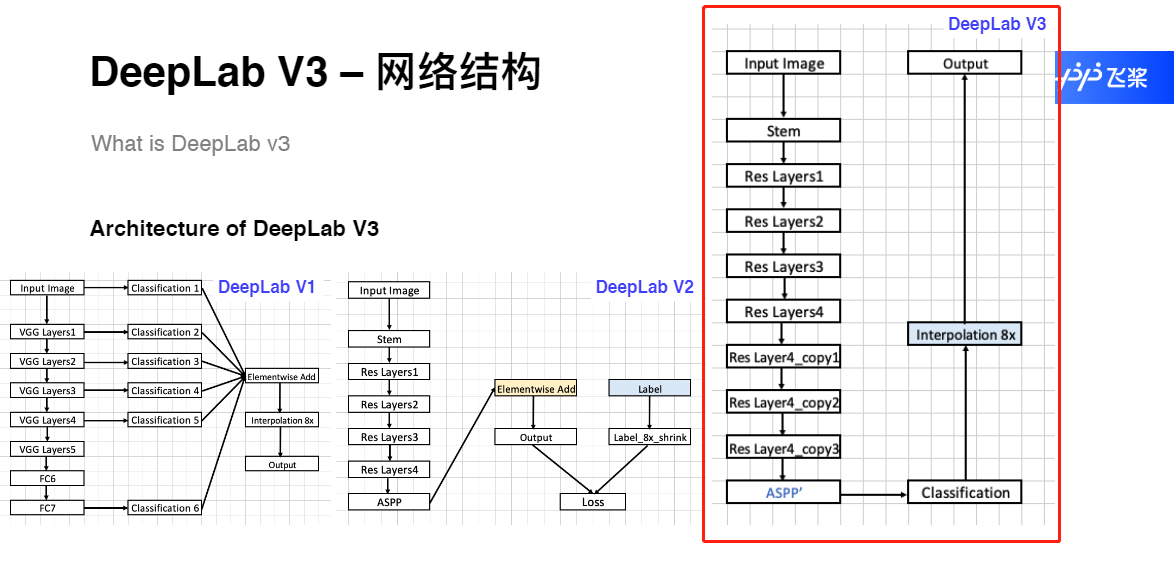
DeepLab V3 ASPP升级模块
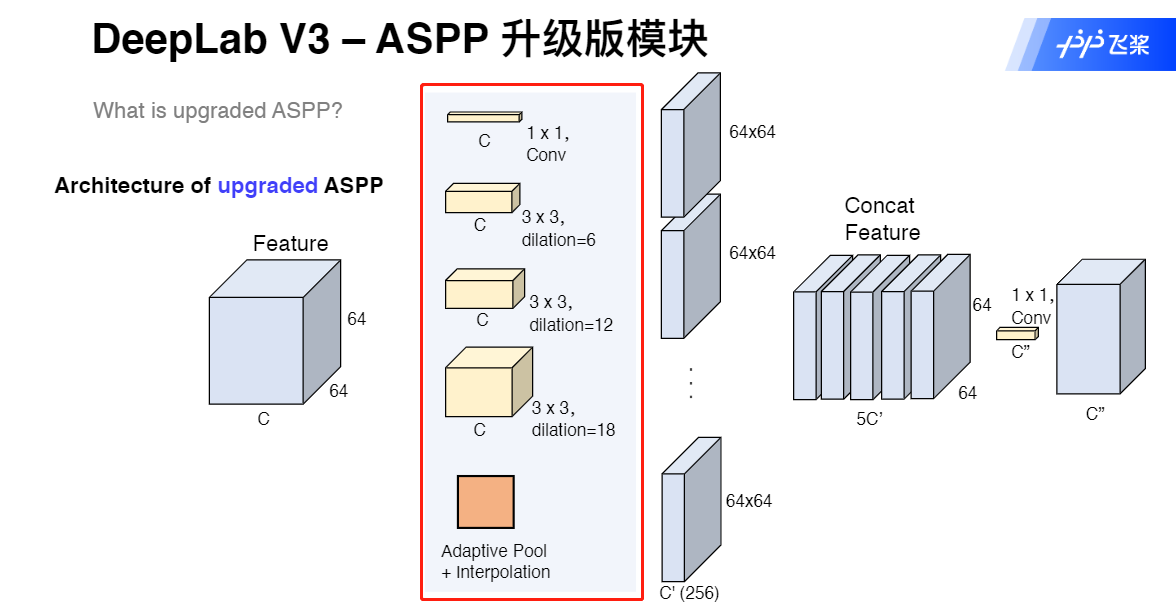
DeepLab V3 Multi-Grid
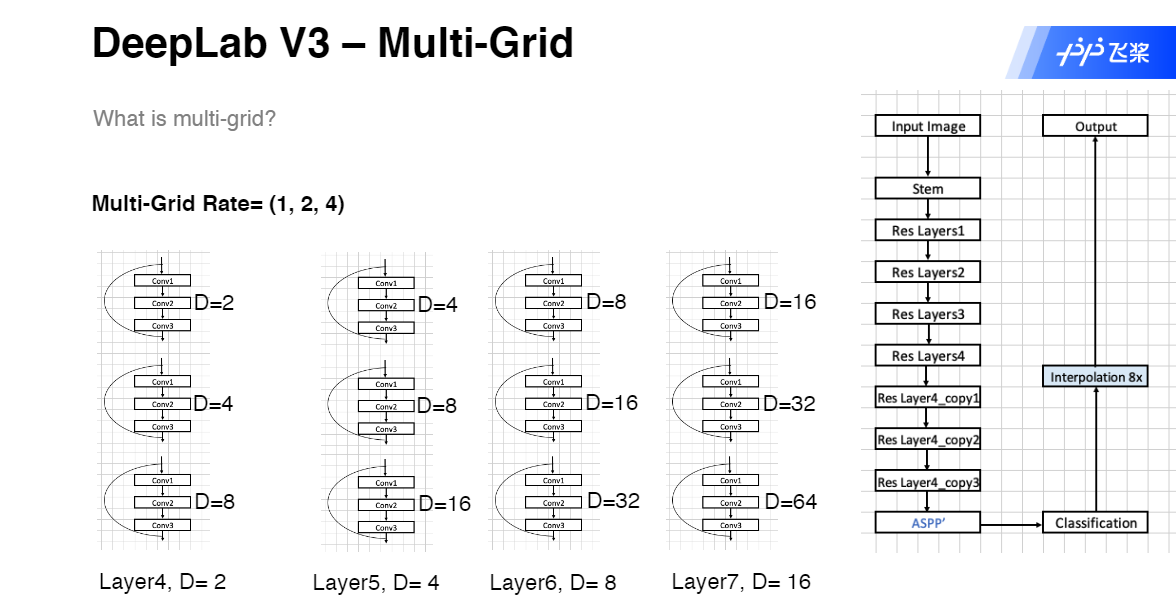
代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchinfo import summary
from torchstat import stat
#%%
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, padding, dilation):
super(ResBlock, self).__init__()
self.downsample = False
self.mid_channels = out_channels//4
self.reduce = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, self.mid_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=self.mid_channels)
)
self.conv3x3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.mid_channels, self.mid_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=self.mid_channels)
)
self.increase = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
if in_channels != out_channels:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels)
)
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
res = x
x = self.reduce(x)
x = self.conv3x3(x)
x = self.increase(x)
res = self.shortcut(res)
x = x+res
return x
#%%
class ResLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, n_layers, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, multi_grids=None):
super(ResLayer, self).__init__()
if multi_grids is None:
multi_grids = [1 for _ in range(n_layers)]
else:
assert n_layers == len(multi_grids)
resLayer = []
for i in range(n_layers):
resLayer.append(
ResBlock(in_channels=(in_channels if i==0 else out_channels),
out_channels=out_channels,
stride=(stride if i==0 else 1),
padding=padding*multi_grids[i],
dilation=dilation*multi_grids[i])
)
self.resLayers = nn.Sequential(*resLayer)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.resLayers(x)
return x
#%%
class ASPP_plus(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channesls, out_channels, dilatopns=[6, 12, 18]):
super(ASPP_plus, self).__init__()
self.aspp0 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[0], padding=dilatopns[0], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[1], padding=dilatopns[1], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilatopns[2], padding=dilatopns[2], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.aspp4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channesls, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
aspp0 = self.aspp0(x)
aspp1 = self.aspp1(x)
aspp2 = self.aspp2(x)
aspp3 = self.aspp3(x)
aspp4 = self.aspp4(x)
aspp4 = F.interpolate(aspp4, x_size[2:], mode='bilinear')
out = aspp0+aspp1+aspp2+aspp3+aspp4
return out
#%%
class DeepLab_V3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, out_channels=[64, 256, 512, 1024, 2048],
n_layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], multi_grids=[1, 2, 4], n_classes=5):
super(DeepLab_V3, self).__init__()
self.stem = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels[0], kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, dilation=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels[0]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, ceil_mode=True)
)
self.res50Layer1 = ResLayer(out_channels[0], out_channels[1], n_layers[0], stride=2)
self.res50Layer2 = ResLayer(out_channels[1], out_channels[2], n_layers[1], stride=2)
self.res50Layer3 = ResLayer(out_channels[2], out_channels[3], n_layers[2], stride=1, padding=2, dilation=2)
self.res50Layer4 = ResLayer(out_channels[3], out_channels[4], n_layers[3],
stride=1, padding=2, dilation=2, multi_grids=multi_grids)
self.res50Layer4_copy1 = ResLayer(out_channels[4], out_channels[4], n_layers[3],
stride=1, padding=4, dilation=4, multi_grids=multi_grids)
self.res50Layer4_copy2 = ResLayer(out_channels[4], out_channels[4], n_layers[3],
stride=1, padding=8, dilation=8, multi_grids=multi_grids)
self.res50Layer4_copy3 = ResLayer(out_channels[4], out_channels[4], n_layers[3],
stride=1, padding=16, dilation=16, multi_grids=multi_grids)
self.aspp = ASPP_plus(out_channels[4], n_classes, dilatopns=[6, 12, 18, 24])
def forward(self, x):
x_size = x.size()
if len(x_size) is not 4:
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # [n, c, h, w]
x = self.stem(x)
x = self.res50Layer1(x)
x = self.res50Layer2(x)
x = self.res50Layer3(x)
x = self.res50Layer4(x)
x = self.res50Layer4_copy1(x)
x = self.res50Layer4_copy2(x)
x = self.res50Layer4_copy3(x)
x = self.aspp(x)
x = F.upsample(x, size=x_size[1:], mode='bilinear')
return x
DeepLab V3+
Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation
DeepLab PPT

![【PWN · ret2shellcode | “jmp esp“】[i春秋]ret2shellcode](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a42315e0f8db44f4903a902d156b5170.png)