CoroutineScope 是实现协程结构化并发的关键。使用 CoroutineScope,可以批量管理同一个作用域下面所有的协程。
CoroutineScope 与 结构化并发
launch、async 被定义成了 CoroutineScope 扩展函数。在调用 launch 之前,必须先获取 CoroutineScope。
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {
val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)
LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) else
StandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)
return coroutine
}
public fun <T> CoroutineScope.async(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T
): Deferred<T> {
val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)
LazyDeferredCoroutine(newContext, block) else
DeferredCoroutine<T>(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)
return coroutine
}为何要设计成扩展方法?
fun main() {
testCoroutinueScope()
}
private fun showScopeLog(any: Any?) {
println("""$any Thread:${Thread.currentThread().name}""".trimIndent())
}
private fun testCoroutinueScope() {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {
launch {
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("Inner")
}
showScopeLog("Hello")
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("World") //不执行
}
scope.launch {
launch {
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("Inner!!!")
}
showScopeLog("Hello!!!")
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("World!!!") //不执行
}
Thread.sleep(500L)
scope.cancel()
}
Log:
Hello Thread:DefaultDispatcher-worker-1 @coroutine#1
Hello!!! Thread:DefaultDispatcher-worker-3 @coroutine#2
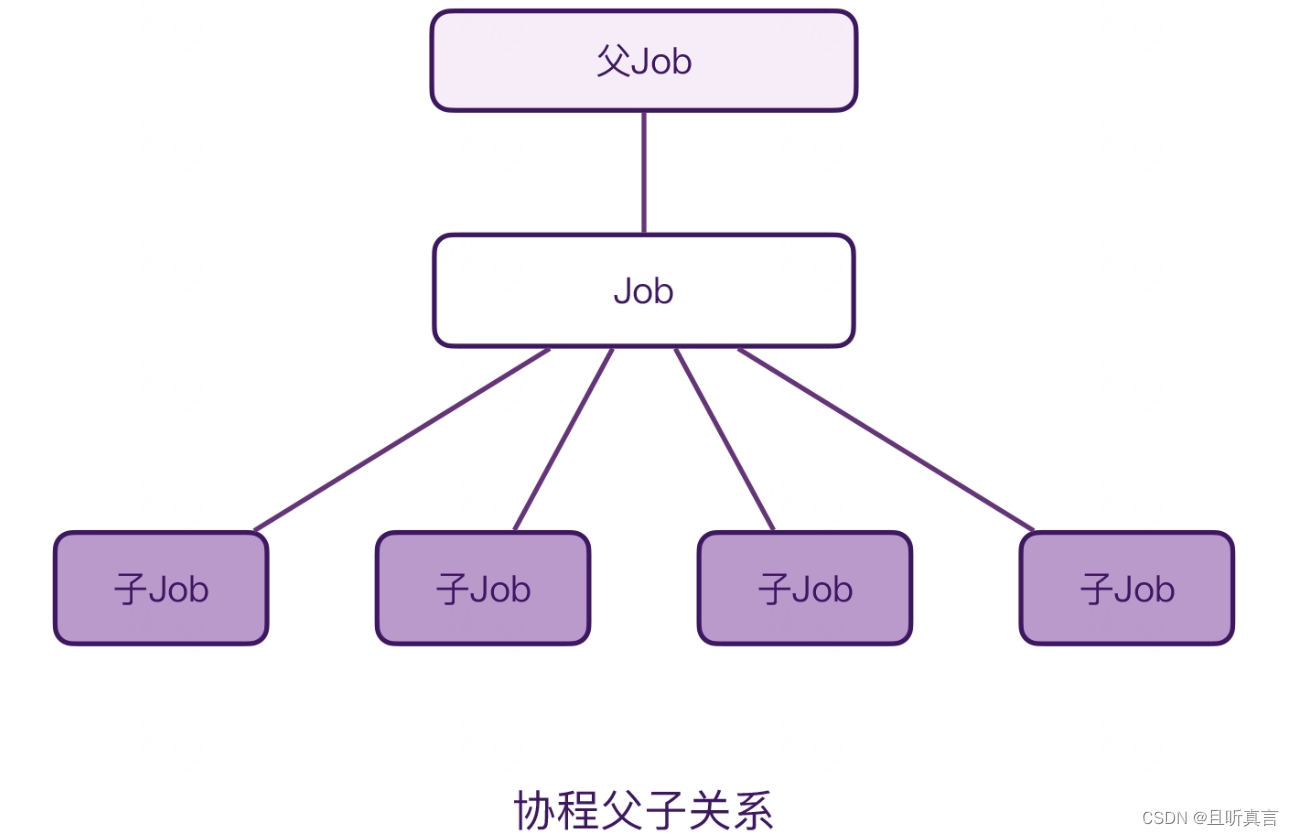
Process finished with exit code 0scope 创建了两个顶层的协程,接着,在协程的内部我们使用 launch 又创建了一个子协程。最后,在协程的外部等待了 500 毫秒,并且调用了 scope.cancel()。结果前面创建的 4 个协程就全部都取消了。
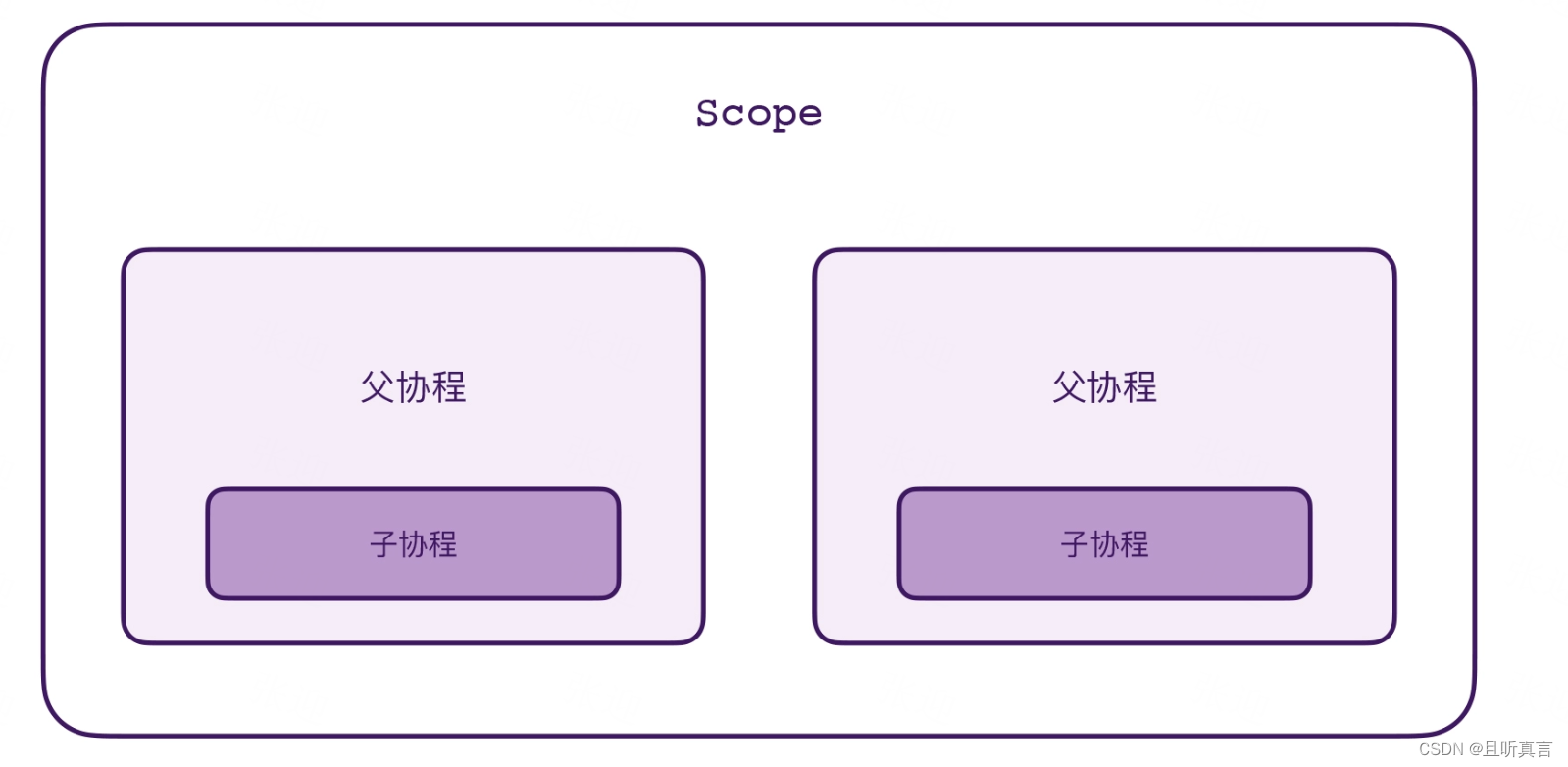
父协程是属于 Scope 的,子协程是属于父协程的,只要调用了 scope.cancel(),这 4 个协程都会被取消。
CoroutineScope 管理协程的能力,源自于 Job。
父子协程关系如何建立?-CoroutineScope 如何通过 Job 来管理协程。
CoroutineScope 是一个接口,为什么可以调用其构造函数,来创建 CoroutineScope 对象?不应该使用 object 关键字创建匿名内部类吗?
调用 CoroutineScope() 并不是构造函数,而是一个顶层函数。
private fun testCoroutinueScope() {
val scope = CoroutineScope(Job())
scope.launch {
launch {
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("Inner")
}
showScopeLog("Hello")
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("World") //不执行
}
scope.launch {
launch {
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("Inner!!!")
}
showScopeLog("Hello!!!")
delay(1000000L)
showScopeLog("World!!!") //不执行
}
Thread.sleep(500L)
scope.cancel()
}public fun CoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineScope =
ContextScope(if (context[Job] != null) context else context + Job())
internal class ContextScope(context: CoroutineContext) : CoroutineScope {
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext = context
// CoroutineScope is used intentionally for user-friendly representation
override fun toString(): String = "CoroutineScope(coroutineContext=$coroutineContext)"
}
public fun Job(parent: Job? = null): CompletableJob = JobImpl(parent)Kotlin 当中的函数名称,在大部分情况下都是遵循“驼峰命名法”的,而在一些特殊情况下则不遵循这种命名法。上面的顶层函数 CoroutineScope(),其实就属于特殊的情况,因为它虽然是一个普通的顶层函数,但它发挥的作用却是“构造函数”。类似的用法,还有 Job() 这个顶层函数。
在 Kotlin 当中,当顶层函数作为构造函数使用的时候,首字母是要大写的。
创建 CoroutineScope 的时候,如果传入的 Context 是包含 Job 的,那就直接用;如果是不包含 Job 的,就会创建一个新的 Job。这就意味着,每一个 CoroutineScope 对象,它的 Context 当中必定存在一个 Job 对象。代码中的 CoroutineScope(Job()),改成 CoroutineScope() 也是完全没问题的。
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {
val newContext = newCoroutineContext(context)
val coroutine = if (start.isLazy)
LazyStandaloneCoroutine(newContext, block) else
StandaloneCoroutine(newContext, active = true)
coroutine.start(start, coroutine, block)
return coroutine
}
private open class StandaloneCoroutine(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
active: Boolean
) : AbstractCoroutine<Unit>(parentContext, initParentJob = true, active = active) {
override fun handleJobException(exception: Throwable): Boolean {
handleCoroutineException(context, exception)
return true
}
}
private class LazyStandaloneCoroutine(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
) : StandaloneCoroutine(parentContext, active = false) {
private val continuation = block.createCoroutineUnintercepted(this, this)
override fun onStart() {
continuation.startCoroutineCancellable(this)
}
}StandaloneCoroutine 是 AbstractCoroutine 的子类,AbstractCoroutine 代表了协程的抽象类。另外这里有一个 initParentJob 参数,它是 true,代表了协程创建了以后,需要初始化协程的父子关系。而 LazyStandaloneCoroutine 则是 StandaloneCoroutine 的子类,它的 active 参数是 false,代表了以懒加载的方式创建协程。
public abstract class AbstractCoroutine<in T>(
parentContext: CoroutineContext,
initParentJob: Boolean,
active: Boolean
) : JobSupport(active), Job, Continuation<T>, CoroutineScope {
... ...
init {
/*
* Setup parent-child relationship between the parent in the context and the current coroutine.
* It may cause this coroutine to become _cancelling_ if the parent is already cancelled.
* It is dangerous to install parent-child relationship here if the coroutine class
* operates its state from within onCancelled or onCancelling
* (with exceptions for rx integrations that can't have any parent)
*/
if (initParentJob) initParentJob(parentContext[Job])
}
}AbstractCoroutine 是 JobSupport 的子类,在 init{} 代码块当中,根据 initParentJob 参数,判断是否需要初始化协程的父子关系。initParentJob 是 true,所以这里的 initParentJob() 方法一定会执行,而它的参数 parentContext[Job]取出来的 Job,其实就是在 Scope 当中的 Job。
initParentJob() 方法,是它的父类 JobSupport 当中的方法。
public open class JobSupport constructor(active: Boolean) : Job, ChildJob, ParentJob, SelectClause0 {
final override val key: CoroutineContext.Key<*> get() = Job
protected fun initParentJob(parent: Job?) {
assert { parentHandle == null }
if (parent == null) {
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandle
return
}
parent.start()
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
val handle = parent.attachChild(this)
parentHandle = handle
if (isCompleted) {
handle.dispose()
parentHandle = NonDisposableHandle
}
}
}
public interface Job : CoroutineContext.Element {
public val children: Sequence<Job>
public fun attachChild(child: ChildJob): ChildHandle
}上面的代码一共有三个地方需要注意,我们来分析一下:
首先判断传入的 parent 是否为空,如果 parent 为空,说明当前的协程不存在父 Job,就不需要创建协程父子关系。
然后确保 parent 对应的 Job 启动了。
parent.attachChild(this)它会将当前的 Job,添加为 parent 的子 Job。这里其实就是建立协程父子关系的关键代码。
协程是如何“结构化取消”的?
协程的结构化取消,本质上是事件的传递。
public fun CoroutineScope.cancel(cause: CancellationException? = null) {
val job = coroutineContext[Job] ?: error("Scope cannot be cancelled because it does not have a job: $this")
job.cancel(cause)
}CoroutineScope 的 cancel() 方法,本质上是调用了它当中的 Job.cancel()。而这个方法的具体实现在 JobSupport 当中
public override fun cancel(cause: CancellationException?) {
cancelInternal(cause ?: defaultCancellationException())
}
public open fun cancelInternal(cause: Throwable) {
cancelImpl(cause)
}
internal fun cancelImpl(cause: Any?): Boolean {
var finalState: Any? = COMPLETING_ALREADY
if (onCancelComplete) {
finalState = cancelMakeCompleting(cause)
if (finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN) return true
}
if (finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY) {
finalState = makeCancelling(cause)
}
return when {
finalState === COMPLETING_ALREADY -> true
finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN -> true
finalState === TOO_LATE_TO_CANCEL -> false
else -> {
afterCompletion(finalState)
true
}
}
}if (onCancelComplete) {
finalState = cancelMakeCompleting(cause)
if (finalState === COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN)
return true
}job.cancel() 最终会调用 JobSupport 的 cancelImpl() 方法。上面的代码中onCancelComplete 是 Boolean 类型的成员属性。代表了当前的 Job,是否有协程体需要执行。另外,由于 CoroutineScope 当中的 Job 是手动创建的,并不需要执行任何协程代码,所以,它会是 true。继续分析 cancelMakeCompleting() 方法:
private fun cancelMakeCompleting(cause: Any?): Any? {
loopOnState { state ->
val finalState = tryMakeCompleting(state, proposedUpdate)
if (finalState !== COMPLETING_RETRY) return finalState
}
}
private fun tryMakeCompleting(state: Any?, proposedUpdate: Any?): Any? {
if (state !is Incomplete)
return COMPLETING_ALREADY
return COMPLETING_RETRY
}
return tryMakeCompletingSlowPath(state, proposedUpdate)
}
private fun tryMakeCompletingSlowPath(state: Incomplete, proposedUpdate: Any?): Any? {
notifyRootCause?.let { notifyCancelling(list, it) }
return finalizeFinishingState(finishing, proposedUpdate)
}cancelMakeCompleting() 会调用 tryMakeCompleting() 方法,最终则会调用 tryMakeCompletingSlowPath() 当中的 notifyCancelling() 方法。所以,它才是最关键的代码。
private fun notifyCancelling(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable) {
onCancelling(cause)
notifyHandlers<JobCancellingNode>(list, cause)
cancelParent(cause)
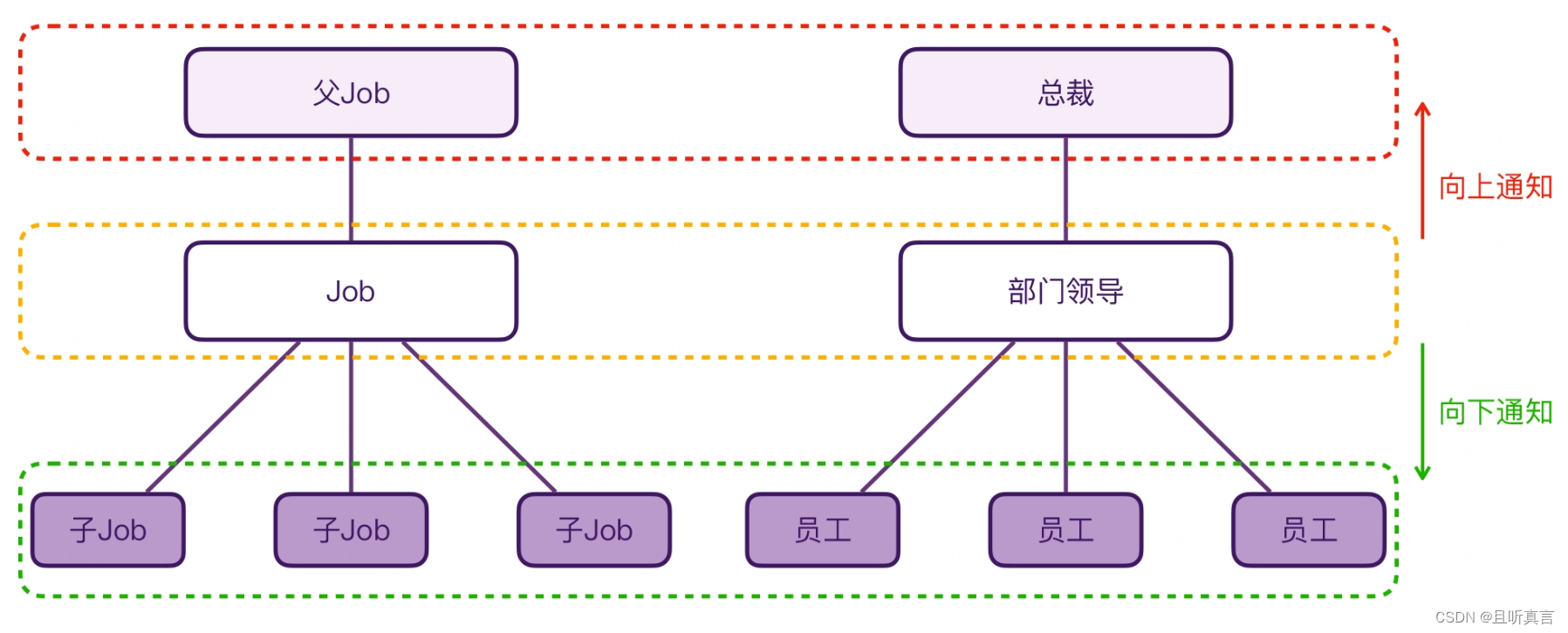
}- 通知子Job
notifyHandlers<JobCancellingNode>(list, cause)- 通知父Job
cancelParent(cause)
通知子Job流程:
private inline fun <reified T: JobNode> notifyHandlers(list: NodeList, cause: Throwable?) {
var exception: Throwable? = null
list.forEach<T> { node ->
try {
node.invoke(cause)
} catch (ex: Throwable) {
exception?.apply { addSuppressedThrowable(ex) } ?: run {
exception = CompletionHandlerException("Exception in completion handler $node for $this", ex)
}
}
}
exception?.let { handleOnCompletionException(it) }
}遍历当前 Job 的子 Job,并将取消的 cause 传递过去,这里的 invoke() 最终会调用 ChildHandleNode 的 invoke() 方法:
internal class ChildHandleNode(
@JvmField val childJob: ChildJob
) : JobCancellingNode(), ChildHandle {
override val parent: Job get() = job
override fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) = childJob.parentCancelled(job)
override fun childCancelled(cause: Throwable): Boolean = job.childCancelled(cause)
}
public final override fun parentCancelled(parentJob: ParentJob) {
cancelImpl(parentJob)
}ChildHandleNode 的 invoke() 方法会调用 parentCancelled() 方法,而它最终会调用 cancelImpl() 方法。 Job 取消的入口函数。这实际上就相当于在做递归调用。
通知父 Job 的流程:
private fun cancelParent(cause: Throwable): Boolean {
if (isScopedCoroutine) return true
val isCancellation = cause is CancellationException
val parent = parentHandle
if (parent === null || parent === NonDisposableHandle) {
return isCancellation
}
return parent.childCancelled(cause) || isCancellation
}这个函数的返回值返回 true 代表父协程处理了异常,而返回 false,代表父协程没有处理异常。这种类似责任链的设计模式。
public open fun childCancelled(cause: Throwable): Boolean {
if (cause is CancellationException) return true
return cancelImpl(cause) && handlesException
}当异常是 CancellationException 的时候,协程是会进行特殊处理的。一般来说,父协程会忽略子协程的取消异常。而如果是其他的异常,那么父协程就会响应子协程的取消了。代码又会继续递归调用cancelImpl() 方法了。