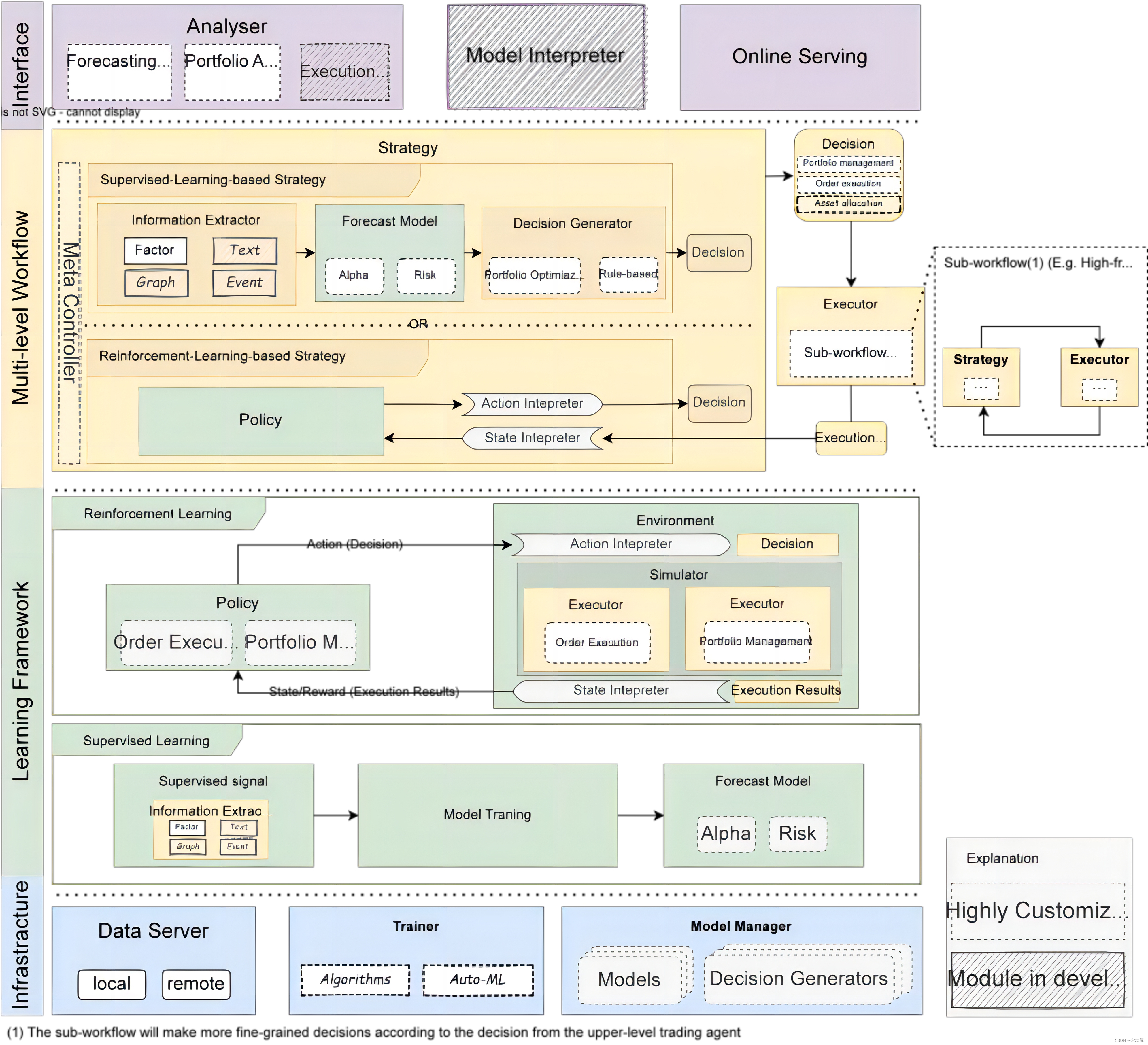
MPU6050 是一款集成了六轴加速度计和陀螺仪的微电子机械系统(MEMS)传感器。它由 InvenSense(现为 TDK) 公司开发,是一种广泛应用于姿态估计、运动追踪和稳定控制等领域的常用传感器。
MPU6050 具有以下主要特点和技术规格:
-
6轴测量能力:MPU6050 集成了三轴加速度计和三轴陀螺仪,能够同时测量物体的加速度和角速度,从而获得姿态信息。
-
高精度:MPU6050 提供高精度的测量性能,能够在多种环境条件下稳定工作,并具有较低的噪声和漂移。
-
低功耗:MPU6050 设计优化了功耗,适用于移动设备和电池供电的应用场景。
-
数字输出:MPU6050 输出的数据以数字形式呈现,通过 I2C 接口与微控制器或其他处理器通信,简化了数据获取和处理过程。
-
可编程寄存器:MPU6050 提供一些可编程寄存器,允许用户配置传感器的工作模式和测量范围,以满足不同应用需求。
-
姿态估计支持:由于同时具备加速度计和陀螺仪,MPU6050 能够用于姿态估计和导航,例如通过融合算法计算物体的俯仰角、滚转角和航向角。
-
应用广泛:MPU6050 可广泛应用于各种领域,如智能手机、游戏控制器、无人机、机器人、虚拟现实设备等。
在之前的文章 esp32连接mpu6050 中演示了esp32通过i2c连接mpu6050,并获取了mpu6050的寄存器值;ch347连接mpu6050 中演示了通过ch347连接mpu6050,并获取了mpu6050的寄存器值。今天通过ch347连接mpu6050,读取传感器数据,并显示出来。
首先编写mpu6050模块代码mpu6050.py,对mpu6050的功能进行一些封装,关键代码如下:
import ch347
class MPU6050:
# Global Variables
GRAVITIY_MS2 = 9.80665
address = None
driver = None
# Scale Modifiers
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G = 16384.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_4G = 8192.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_8G = 4096.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_16G = 2048.0
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG = 131.0
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_500DEG = 65.5
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_1000DEG = 32.8
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_2000DEG = 16.4
# Pre-defined ranges
ACCEL_RANGE_2G = 0x00
ACCEL_RANGE_4G = 0x08
ACCEL_RANGE_8G = 0x10
ACCEL_RANGE_16G = 0x18
GYRO_RANGE_250DEG = 0x00
GYRO_RANGE_500DEG = 0x08
GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG = 0x10
GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG = 0x18
FILTER_BW_256=0x00
FILTER_BW_188=0x01
FILTER_BW_98=0x02
FILTER_BW_42=0x03
FILTER_BW_20=0x04
FILTER_BW_10=0x05
FILTER_BW_5=0x06
# MPU-6050 Registers
PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B
PWR_MGMT_2 = 0x6C
ACCEL_XOUT0 = 0x3B
ACCEL_YOUT0 = 0x3D
ACCEL_ZOUT0 = 0x3F
TEMP_OUT0 = 0x41
GYRO_XOUT0 = 0x43
GYRO_YOUT0 = 0x45
GYRO_ZOUT0 = 0x47
ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x1C
GYRO_CONFIG = 0x1B
MPU_CONFIG = 0x1A
def __init__(self, address=0x68, dll="CH347DLLA64.dll", device_index=0):
self.address = address << 1
self.driver = ch347.CH347Driver(dll)
self.device_index = device_index
self.driver.open_device(self.device_index)
# Wake up the MPU-6050 since it starts in sleep mode
self.driver.stream_i2c(self.device_index, [self.address, self.PWR_MGMT_1, 0x00], 0)
# I2C communication methods
def read_byte_data(self, register):
raw_data = self.driver.stream_i2c(self.device_index, [self.address, register], 1)
return raw_data[0]
def write_byte_data(self, register, value):
return self.driver.stream_i2c(self.device_index, [self.address, register, value], 0)
def read_i2c_word(self, register):
"""Read two i2c registers and combine them.
register -- the first register to read from.
Returns the combined read results.
"""
# Read the data from the registers
# high = self.read_byte_data(self.address, register)
# low = self.read_byte_data(self.address, register + 1)
raw_data = self.driver.stream_i2c(self.device_index, [self.address, register], 2)
# value = (high << 8) + low
value = raw_data[0] << 8 | raw_data[1]
if (value >= 0x8000):
return -((65535 - value) + 1)
else:
return value
# MPU-6050 Methods
def get_temp(self):
"""Reads the temperature from the onboard temperature sensor of the MPU-6050.
Returns the temperature in degrees Celcius.
"""
raw_temp = self.read_i2c_word(self.TEMP_OUT0)
# raw_temp = self.driver.stream_i2c(self.device_index, [self.address, self.TEMP_OUT0], 2)
# temp = raw_temp[0] << 8 | raw_temp[1]
# Get the actual temperature using the formule given in the
# MPU-6050 Register Map and Descriptions revision 4.2, page 30
actual_temp = (raw_temp / 340.0) + 36.53
return actual_temp
def set_accel_range(self, accel_range):
"""Sets the range of the accelerometer to range.
accel_range -- the range to set the accelerometer to. Using a
pre-defined range is advised.
"""
# First change it to 0x00 to make sure we write the correct value later
self.write_byte_data(self.ACCEL_CONFIG, 0x00)
# Write the new range to the ACCEL_CONFIG register
self.write_byte_data(self.ACCEL_CONFIG, accel_range)
def read_accel_range(self, raw = False):
"""Reads the range the accelerometer is set to.
If raw is True, it will return the raw value from the ACCEL_CONFIG
register
If raw is False, it will return an integer: -1, 2, 4, 8 or 16. When it
returns -1 something went wrong.
"""
raw_data = self.read_byte_data(self.ACCEL_CONFIG)
if raw is True:
return raw_data
elif raw is False:
if raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_2G:
return 2
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_4G:
return 4
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_8G:
return 8
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_16G:
return 16
else:
return -1
def get_accel_data(self, g = False):
"""Gets and returns the X, Y and Z values from the accelerometer.
If g is True, it will return the data in g
If g is False, it will return the data in m/s^2
Returns a dictionary with the measurement results.
"""
x = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_XOUT0)
y = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_YOUT0)
z = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_ZOUT0)
accel_scale_modifier = None
accel_range = self.read_accel_range(True)
if accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_2G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_4G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_4G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_8G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_8G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_16G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_16G
else:
print("Unkown range - accel_scale_modifier set to self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G")
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G
x = x / accel_scale_modifier
y = y / accel_scale_modifier
z = z / accel_scale_modifier
if g is True:
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
elif g is False:
x = x * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
y = y * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
z = z * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
def set_gyro_range(self, gyro_range):
"""Sets the range of the gyroscope to range.
gyro_range -- the range to set the gyroscope to. Using a pre-defined
range is advised.
"""
# First change it to 0x00 to make sure we write the correct value later
self.write_byte_data(self.GYRO_CONFIG, 0x00)
# Write the new range to the ACCEL_CONFIG register
self.write_byte_data(self.GYRO_CONFIG, gyro_range)
def set_filter_range(self, filter_range=FILTER_BW_256):
"""Sets the low-pass bandpass filter frequency"""
# Keep the current EXT_SYNC_SET configuration in bits 3, 4, 5 in the MPU_CONFIG register
EXT_SYNC_SET = self.read_byte_data(self.MPU_CONFIG) & 0b00111000
return self.write_byte_data(self.MPU_CONFIG, EXT_SYNC_SET | filter_range)
def read_gyro_range(self, raw = False):
"""Reads the range the gyroscope is set to.
If raw is True, it will return the raw value from the GYRO_CONFIG
register.
If raw is False, it will return 250, 500, 1000, 2000 or -1. If the
returned value is equal to -1 something went wrong.
"""
raw_data = self.read_byte_data(self.GYRO_CONFIG)
if raw is True:
return raw_data
elif raw is False:
if raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_250DEG:
return 250
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_500DEG:
return 500
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG:
return 1000
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG:
return 2000
else:
return -1
def get_gyro_data(self):
"""Gets and returns the X, Y and Z values from the gyroscope.
Returns the read values in a dictionary.
"""
x = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_XOUT0)
y = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_YOUT0)
z = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_ZOUT0)
gyro_scale_modifier = None
gyro_range = self.read_gyro_range(True)
if gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_250DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_500DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_500DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_1000DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_2000DEG
else:
print("Unkown range - gyro_scale_modifier set to self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG")
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG
x = x / gyro_scale_modifier
y = y / gyro_scale_modifier
z = z / gyro_scale_modifier
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
def get_all_data(self):
"""Reads and returns all the available data."""
temp = self.get_temp()
accel = self.get_accel_data()
gyro = self.get_gyro_data()
return [accel, gyro, temp]
def close(self):
self.driver.close_device(self.device_index)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mpu = MPU6050()
print(mpu.get_temp())
accel_data = mpu.get_accel_data(True)
print(accel_data['x'])
print(accel_data['y'])
print(accel_data['z'])
gyro_data = mpu.get_gyro_data()
print(gyro_data['x'])
print(gyro_data['y'])
print(gyro_data['z'])
mpu.close()
这个文件放在ch347.py和CH347DLLA64.DLL同级目录下,将CH347与MPU6050模块连接:
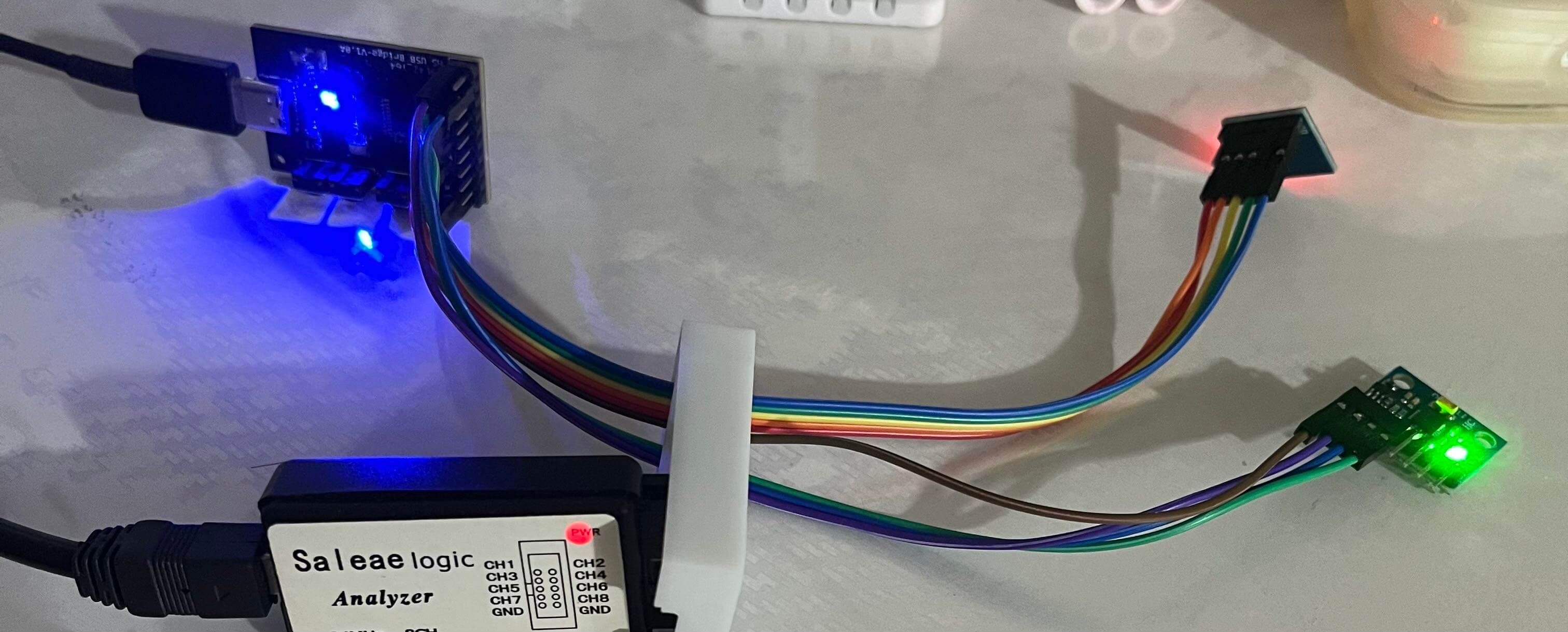

运行上面的代码:
❯ python mpu6050.py
29.659411764705883
-0.044921875
0.016357421875
1.291015625
-2.2977099236641223
0.35877862595419846
-3.4885496183206106
因为MPU6050传感器数据寄存器地址是连续的,获取传感器数据时其实可以快读,理论上会更快,上面的代码还没有优化,先可用。输出数据g值约1.3,没有进行校准。
接下来编写数据显示代码,mpu6050_plot.py:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
from mpu6050 import MPU6050
# Initialize the MPU6050 sensor
mpu6050 = MPU6050()
# Replace these lines with the actual import and initialization of the MPU6050 sensor
# For demonstration purposes, we use dummy functions to generate random data
def read_mpu6050_accel_data():
accel_data = mpu6050.get_accel_data(True)
return [accel_data['x'], accel_data["y"], accel_data["z"]]
def read_mpu6050_gyro_data():
gyro_data = mpu6050.get_gyro_data()
return [gyro_data['x'], gyro_data["y"], gyro_data["z"]]
# Generator function to produce data from the MPU6050 sensor
def generate_mpu6050_data():
data_buffer = []
while True:
accel_data = read_mpu6050_accel_data()
gyro_data = read_mpu6050_gyro_data()
data_buffer.append(accel_data + gyro_data)
yield data_buffer
# Create a figure with 6 subplots for accelerometer and gyroscope data
fig, axs = plt.subplots(6, 1, figsize=(8, 12))
# Initialize empty lines for the accelerometer and gyroscope data plots
lines = [axs[i].plot([], [], lw=2)[0] for i in range(6)]
# Set the number of data points to be displayed on the plot
num_display_points = 50
def init():
for line in lines:
line.set_data([], [])
return lines
def update(frame):
data_buffer = next(data_generator)
# Generate the x-axis values (time steps) based on the number of data points
time_steps = np.arange(len(data_buffer))
# Get the starting index to display a specific number of data points
start_index = max(0, len(data_buffer) - num_display_points)
# Update the plot data for accelerometer and gyroscope
for i in range(6):
lines[i].set_data(time_steps[start_index:], [data[i] for data in data_buffer[start_index:]])
# Adjust the plot limits for better visualization
if i < 3:
axs[i].set_ylim(-2, 2) # Accelerometer data range: -2 to +2
else:
axs[i].set_ylim(-200, 200) # Gyroscope data range: -200 to +200
axs[i].set_xlim(start_index, start_index + num_display_points - 1)
return lines
# Create the generator for MPU6050 sensor data
data_generator = generate_mpu6050_data()
# Create an animation for real-time plotting, update every 100 milliseconds (0.1 seconds)
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=range(100), init_func=init, blit=True, interval=100)
# Add labels and title to each subplot
axis_labels = ['AX', 'AY', 'AZ', 'GX', 'GY', 'GZ']
for i in range(6):
axs[i].set_title(f'{axis_labels[i]} Data')
axs[i].set_xlabel('Time Steps')
axs[i].set_ylabel('MPU6050 Data Value')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
mpu6050.close()
运行效果:
ch347读取mpu6050传感器数据和显示
公众号 | FunIO
微信搜一搜 “funio”,发现更多精彩内容。
个人博客 | blog.boringhex.top