目录
2251. 花期内花的数目
题目描述:
实现代码与解析:
离散化差分
原理思路:
2251. 花期内花的数目
题目描述:
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 flowers ,其中 flowers[i] = [starti, endi] 表示第 i 朵花的 花期 从 starti 到 endi (都 包含)。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始大小为 n 的整数数组 people ,people[i] 是第 i 个人来看花的时间。
请你返回一个大小为 n 的整数数组 answer ,其中 answer[i]是第 i 个人到达时在花期内花的 数目 。
示例 1:
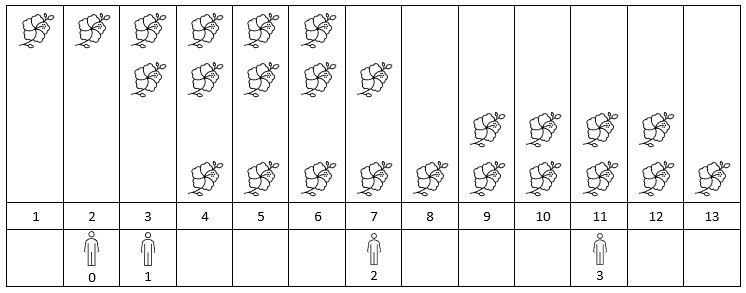
输入:flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], people = [2,3,7,11] 输出:[1,2,2,2] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
示例 2:
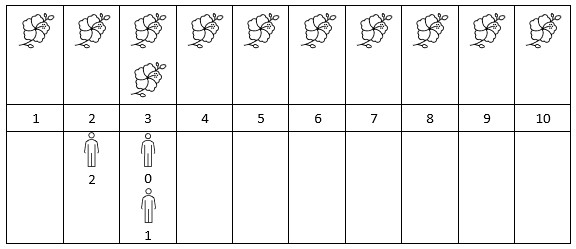
输入:flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], people = [3,3,2] 输出:[2,2,1] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
提示:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 1091 <= people.length <= 5 * 1041 <= people[i] <= 109
实现代码与解析:
离散化差分
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& people) {
map<int, int> diff; // 差分
for (auto &t: flowers) { // 计算差分
diff[t[0]]++;
diff[t[1] + 1]--;
}
vector<int> pidx(people.size());
for (int i = 0; i < pidx.size(); i++) // 记录下标
pidx[i] = i;
sort(pidx.begin(), pidx.end(), [&](int a, int b) { // 用 & 别用 = 会超时
return people[a] < people[b]; // 根据到达时间对于下标排序
});
vector<int> res(people.size());
int cur = 0;
auto it = diff.begin(); // iter
for (int t: pidx) {
while (it != diff.end() && it->first <= people[t]) {
cur += it->second;
it++;
}
res[t] = cur;
}
return res;
}
};原理思路:
根据题目,差分一定是最先想到的,但是数据量比较大,我们也没必要每个时间的数量都查询到,只需要查询有人去的时间的结果。
所以,这里用map来代替数组,由于结果要按查询顺序返回,我们记录people下标并且按到达时间排序,为了后面按顺序求前缀和,这样求前缀时,就不用每次都返回开头再求。
然后开始遍历,对于小于等于现在遍历的人的时间,进行前缀和并且记录结果,最终得到结果数组,返回,完成。




![[chrome devtools]Console面板](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7fc258f2f95b472a9bb8ee6bad41db49.png)