Netty
在此非常感谢尚硅谷学院以及韩顺平老师在B站公开课
Netty视频教程
Netty demo代码文件
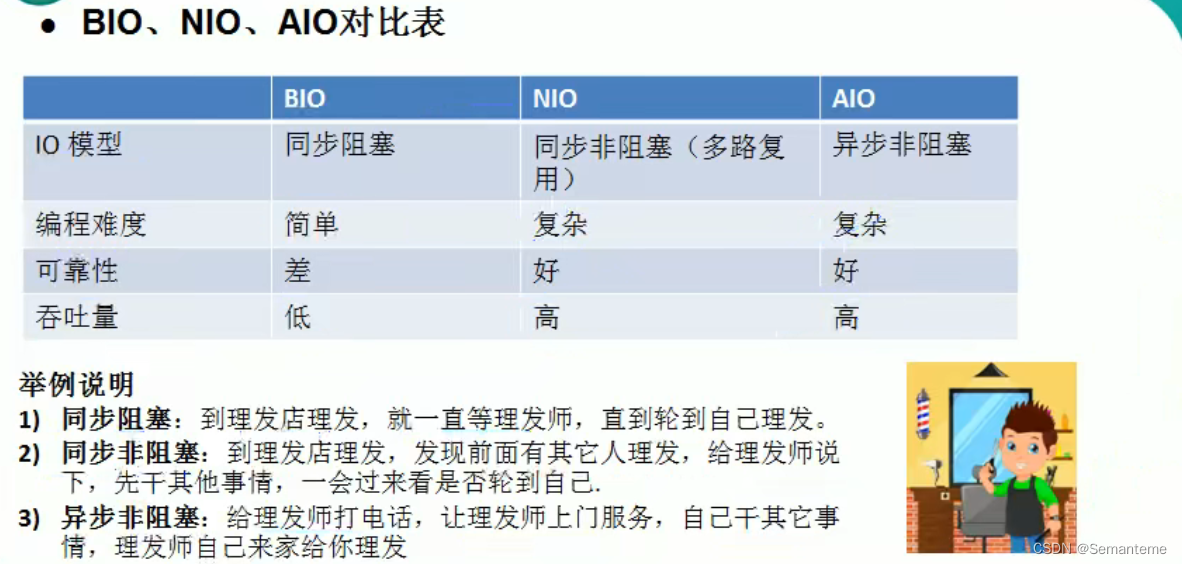
I/O
说NIO之前先说一下BIO(Blocking IO),如何理解这个Blocking呢?客户端监听(Listen)时,Accept是阻塞的,只有新连接来了,Accept才会返回,主线程才能继读写socket时,Read是阻塞的,只有请求消息来了,Read才能返回,子线程才能继续处理读写socket时,Write是阻塞的,只有客户端把消息收了,Write才能返回,子线程才能继续读取下一个请求
BIO
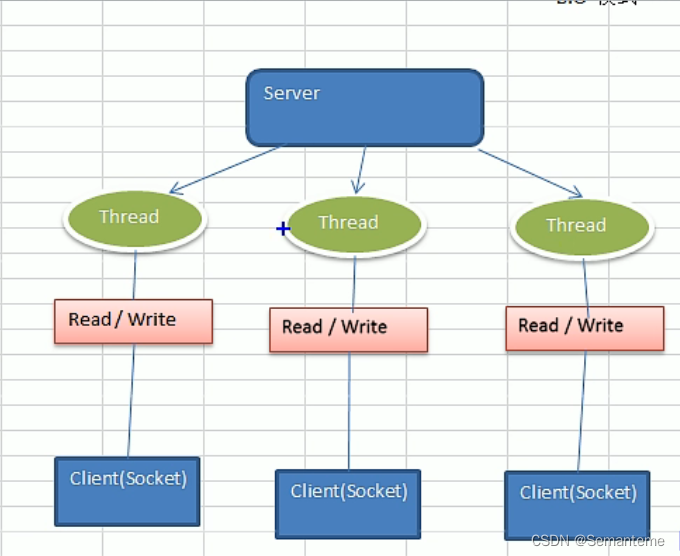
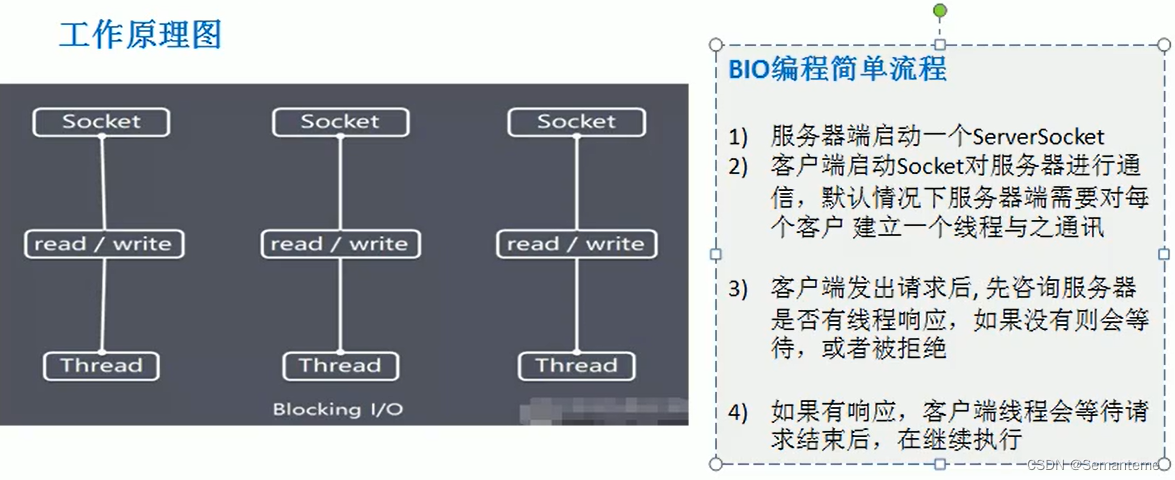
- 适用连接数目少且固定的服务
package com.example.demo01.netty;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class BIODemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功。。。");
while(true){
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 等待连接正在阻塞。。。。。。");
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
executorService.submit(() -> {
socketHandler(socket);
});
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private static void socketHandler(Socket socket) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取数据正在阻塞。。。");
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
if(read != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
NIO

- 适用连接数目多且连接比较短的服务
- jdk1.4开始支持
AIO
- 适用连接数目多且连接比较长的服务
- jdk7开始支持
NIO原理



FIleBuffer
package com.example.demo01.netty.nio;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NioFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = new String("测试文档");
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
allocate.put(str.getBytes());
allocate.flip();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\test.txt");
FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
channel.write(allocate);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
package com.example.demo01.netty.nio;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NioFileChannelInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\test.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
channel.read(allocate);
System.out.println(new String(allocate.array()));
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
package com.example.demo01.netty.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NioTrancfer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\1.jpeg");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\2.jpeg");
FileChannel sourceChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
destChannel.transferFrom(sourceChannel, 0, sourceChannel.size());
sourceChannel.close();
destChannel.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
selector


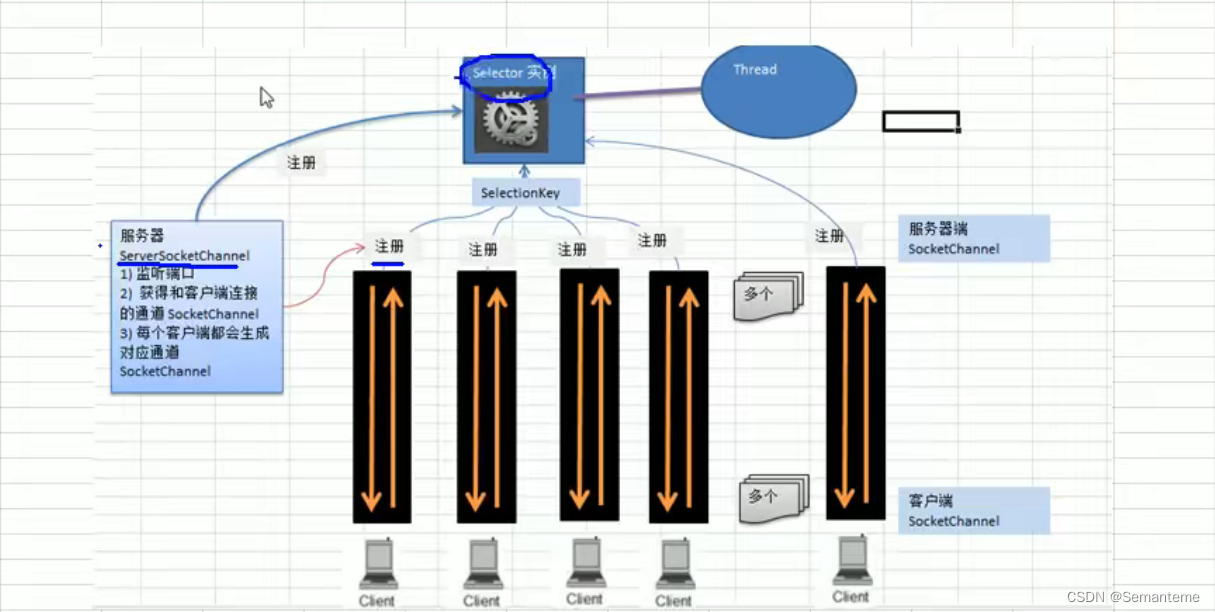
selectionKey

零拷贝


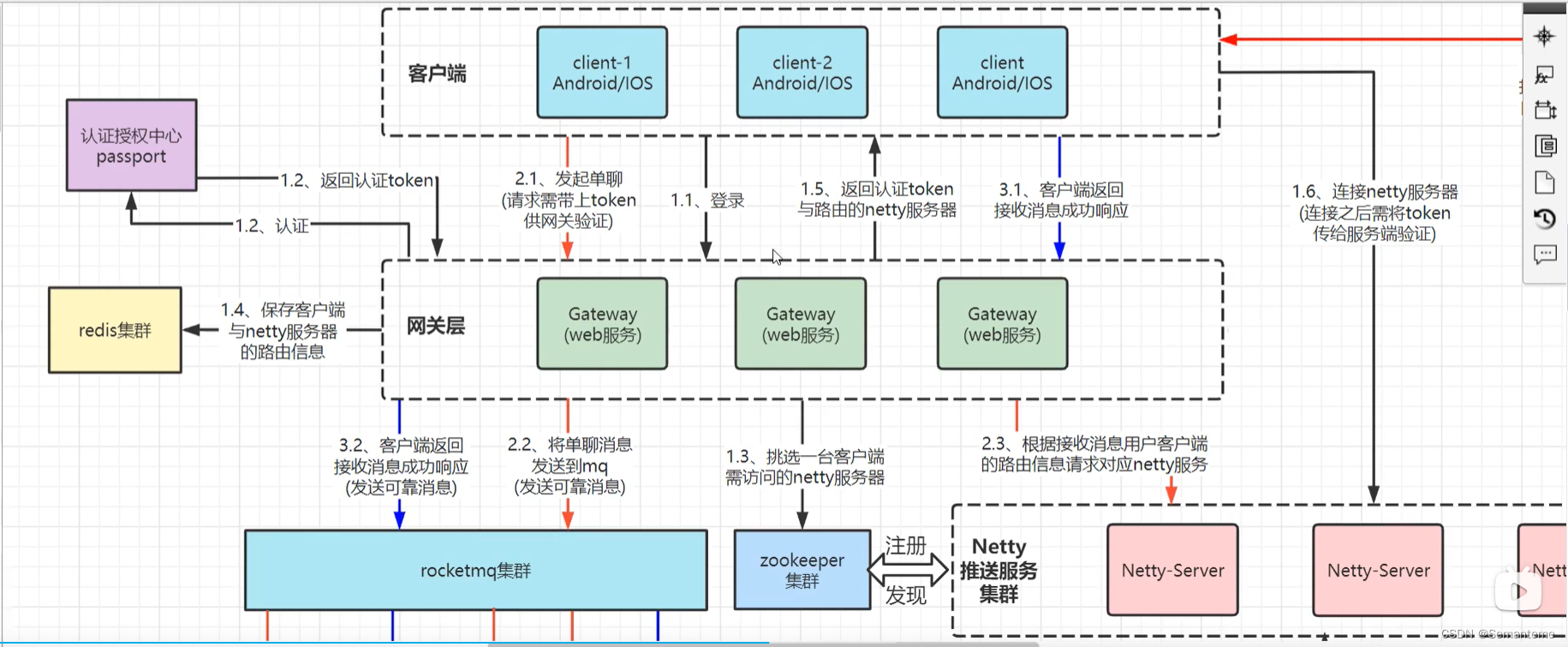
Reactor
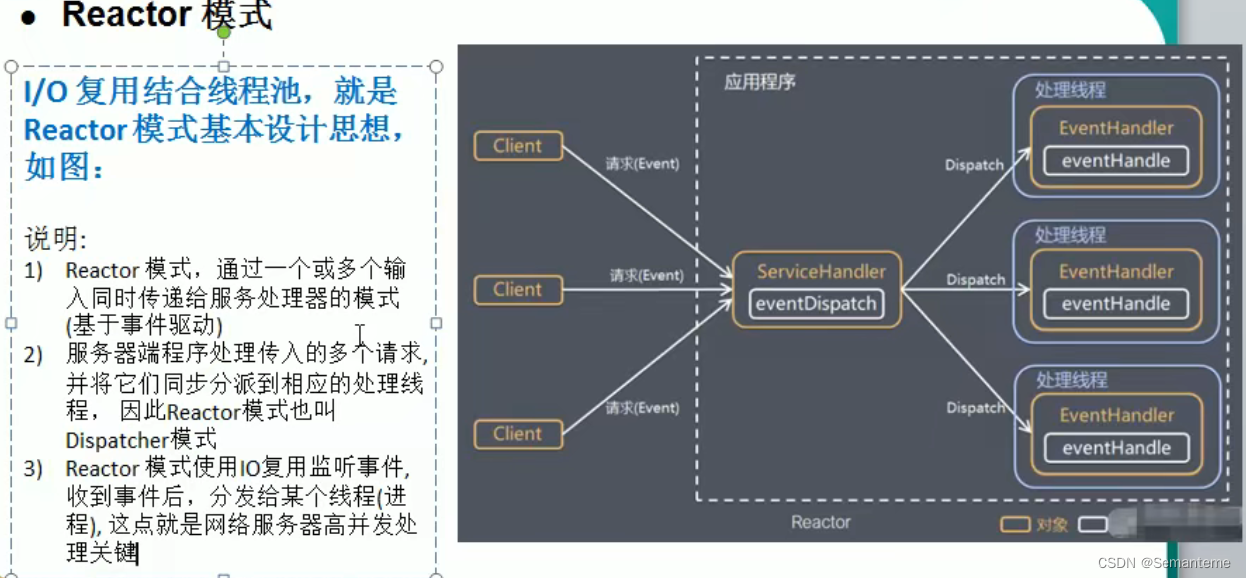
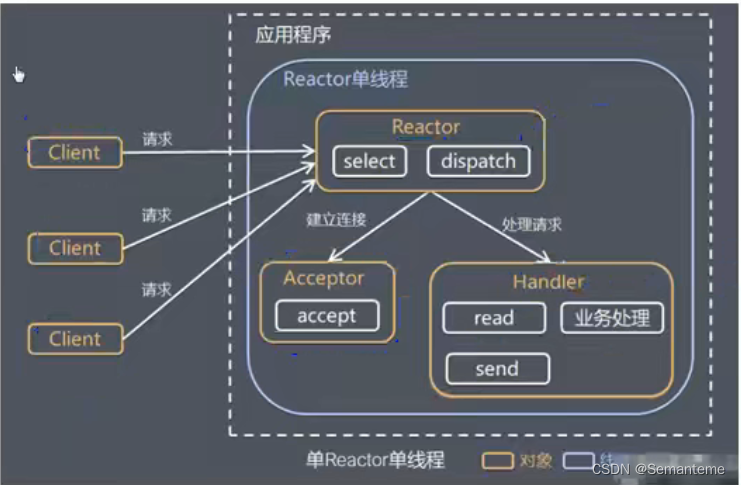
单Reactor单线程
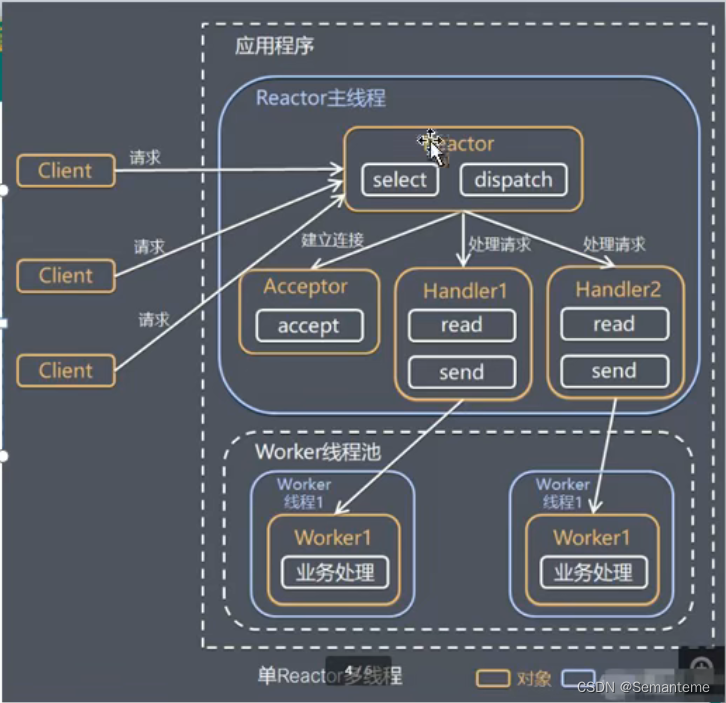
单Reactor多线程
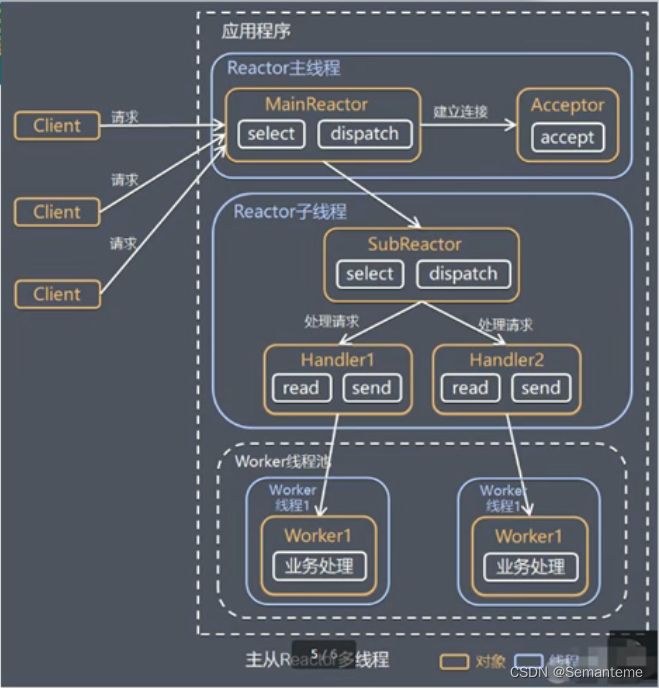
主从Reactor多线程
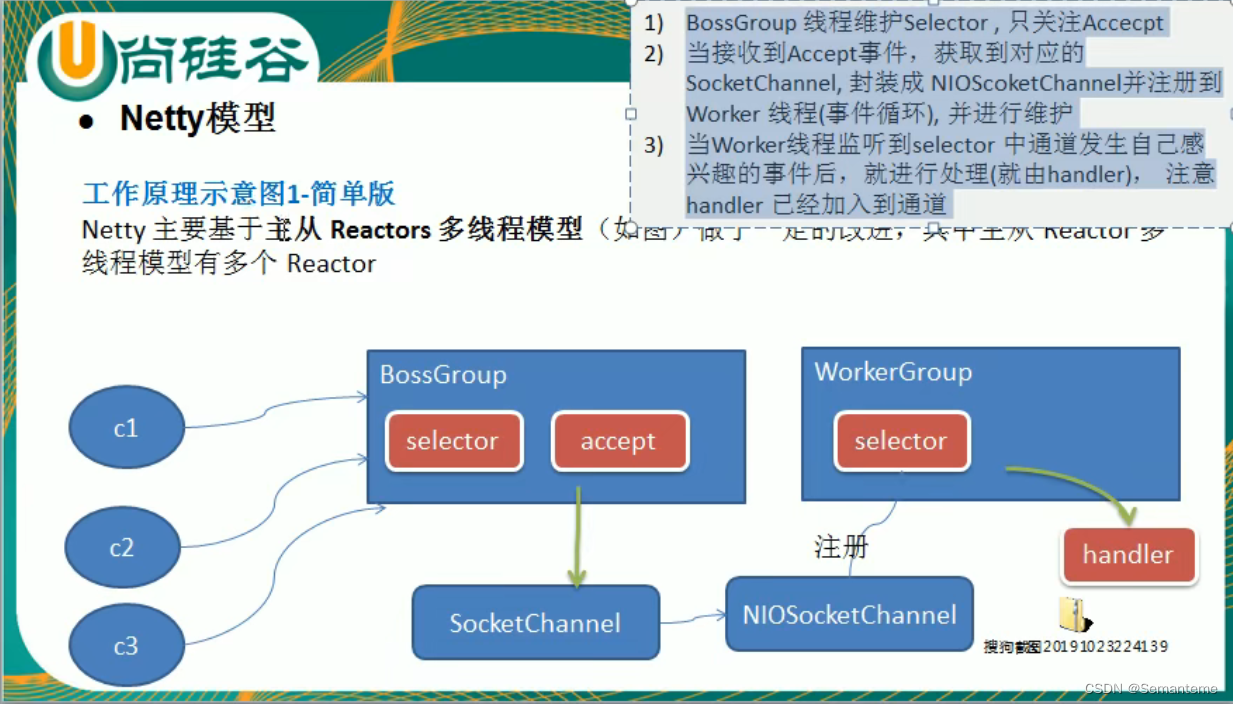
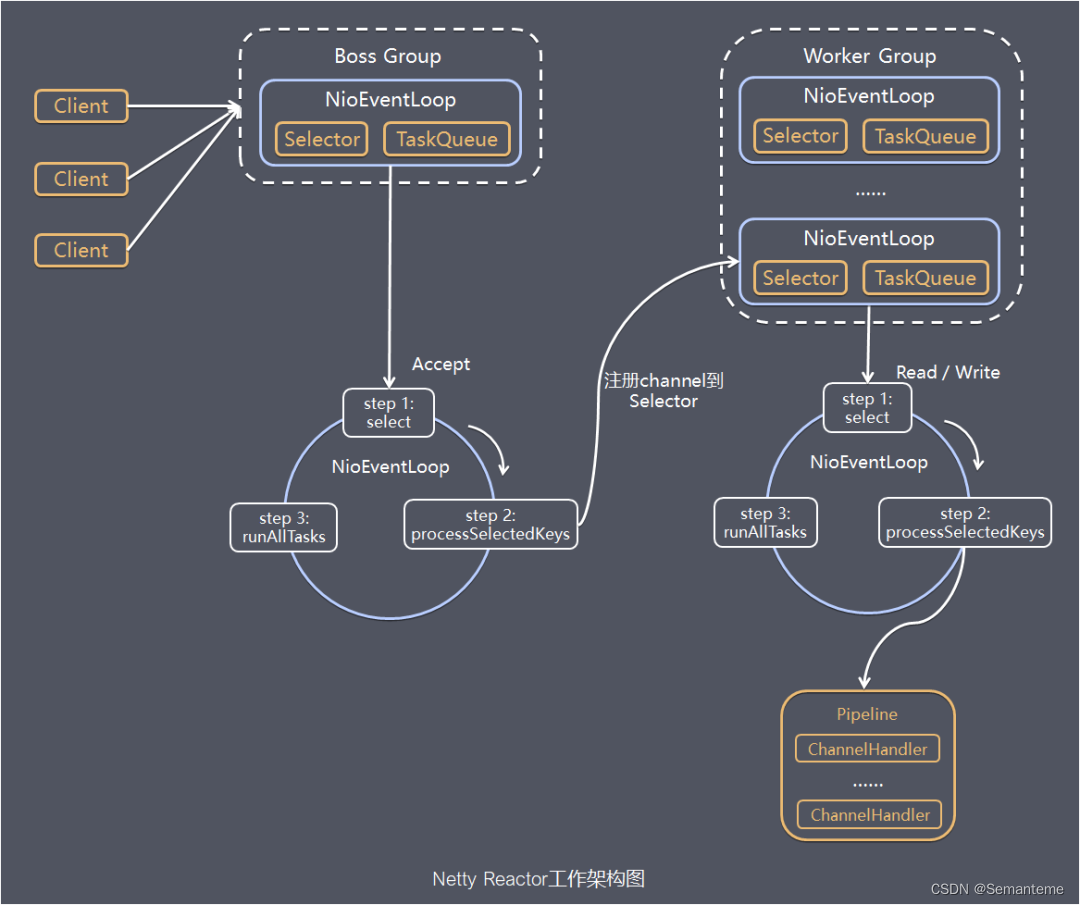
Netty线程模型
- 简单版
- 详细版


![[FineReport]安装与使用(连接Hive3.1.2)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f9fc1b418f2f451ba15fb6f60432cf66.png)