超级聚合,是在group by的基础上,再次进行聚合。
它再次聚合的列,是select中没有用到聚合函数的列。
文章目录
- 例子1
- 解释
- 例子2
- 表以及数据
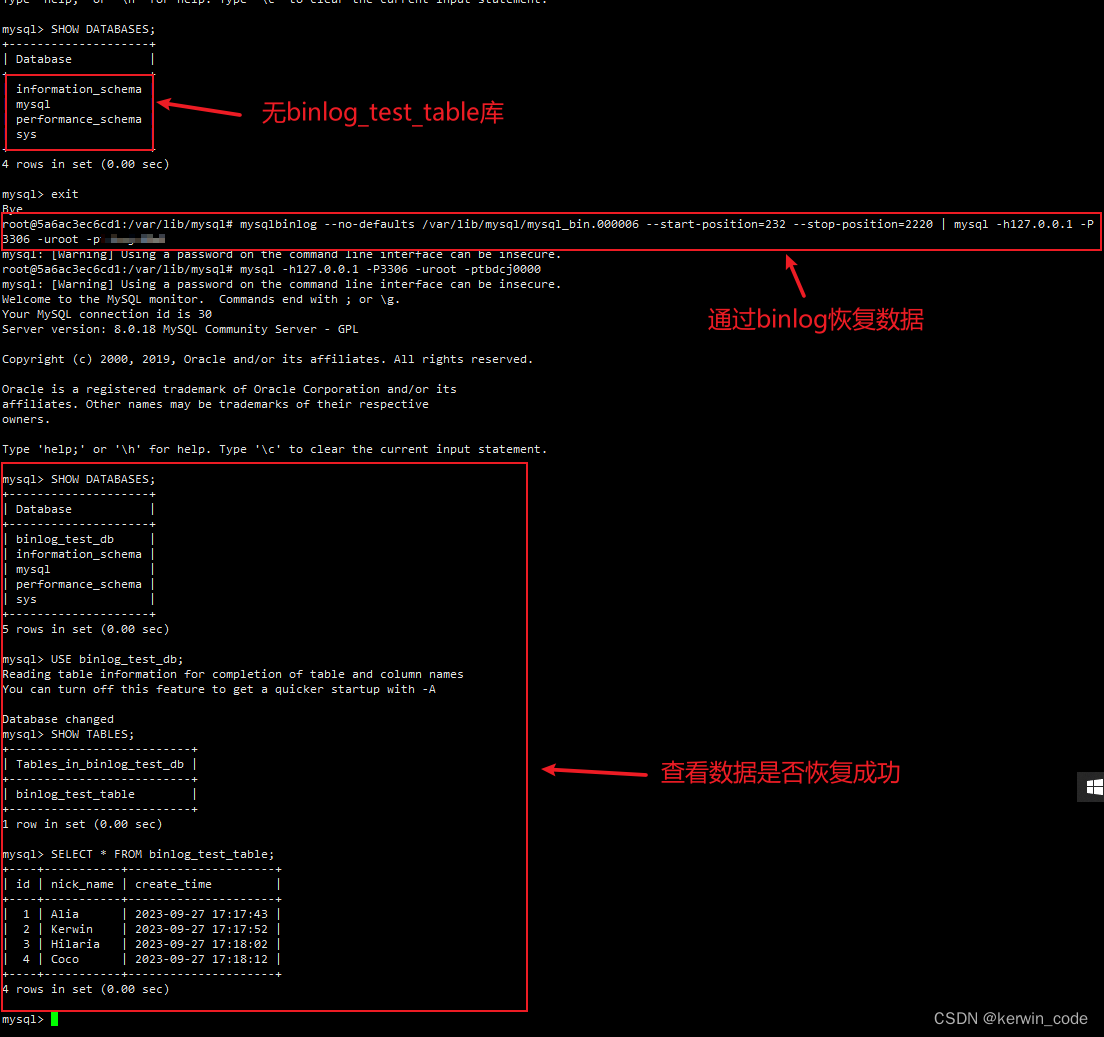
例子1
mysql> SELECT year, country, product, SUM(profit) AS profit
FROM sales
GROUP BY year, country, product;
+------+---------+------------+--------+
| year | country | product | profit |
+------+---------+------------+--------+
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 150 |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 2700 |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 250 |
+------+---------+------------+--------+
mysql> SELECT year, country, product, SUM(profit) AS profit
FROM sales
GROUP BY year, country, product WITH ROLLUP;
+------+---------+------------+--------+
| year | country | product | profit |
+------+---------+------------+--------+
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 |
| 2000 | Finland | NULL | 1600 |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 150 |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 |
| 2000 | India | NULL | 1350 |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 75 |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 |
| 2000 | USA | NULL | 1575 |
| 2000 | NULL | NULL | 4525 |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 |
| 2001 | Finland | NULL | 10 |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 2700 |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 250 |
| 2001 | USA | NULL | 3000 |
| 2001 | NULL | NULL | 3010 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 7535 |
+------+---------+------------+--------+
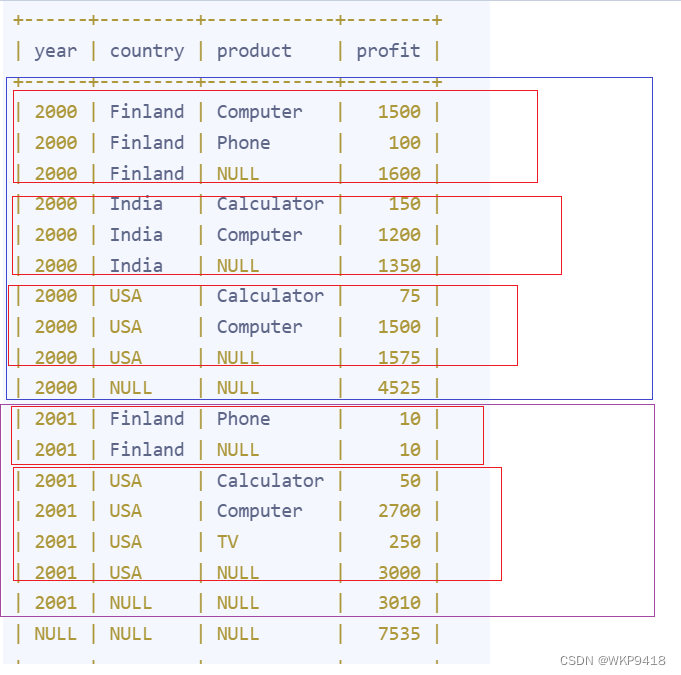
解释
with rollup的工作原理就是在group by分组后,进行超级聚合。
它针对的是在group by后面出现的列,会把他们设置成null,表示不对这一列进行统计。
从最左边开始,找到不同的列值,把他们设置成null
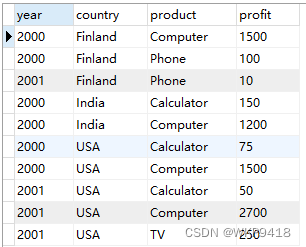
例子2
SELECT year, country, product, SUM(profit) AS profit
FROM sales
GROUP BY country, year, product
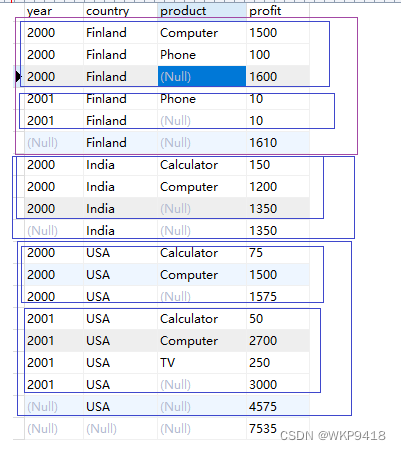
超级聚合 with rollup后,
表以及数据
/*
Navicat MySQL Data Transfer
Source Server : demo
Source Server Version : 50733
Source Host : localhost:3306
Source Database : demo
Target Server Type : MYSQL
Target Server Version : 50733
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 2023-09-27 00:22:21
*/
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `sales`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sales`;
CREATE TABLE `sales` (
`country` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`year` varchar(4) DEFAULT NULL,
`product` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`profit` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of sales
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('Finland', '2000', 'Computer', '1500', '1');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('Finland', '2000', 'Phone', '100', '2');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('India', '2000', 'Calculator', '150', '3');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('India', '2000', 'Computer', '1200', '4');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('USA', '2000', 'Calculator', '75', '5');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('USA', '2000', 'Computer', '1500', '6');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('Finland', '2001', 'Phone', '10', '7');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('USA', '2001', 'Calculator', '50', '8');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('USA', '2001', 'Computer', '2700', '9');
INSERT INTO `sales` VALUES ('USA', '2001', 'TV', '250', '10');