一、单端口RAM原理及实现
1.1、概念/原理
在内存空间中开辟出一段固定大小的内存用于存储数据,每一个数据所占的bit位称之为位宽,这段内存空间中数据的总数称之为深度。例如reg [7:0] mem [255:0],这段内存空间中每一个数据的位宽为8bit,深度为256。
在这段内存空间中,每个数据分配给一个地址,如上例深度为256,可以用8bit的地址来表示所有的数据,0000_0000则表示第0个数据,1111_1111则表示第255个数据。
外部信号通过固定的时钟节拍,通过使能信号及地址信号来读取RAM中特定位置的数据或者向RAM中特定位置写入数据。
1.2接口
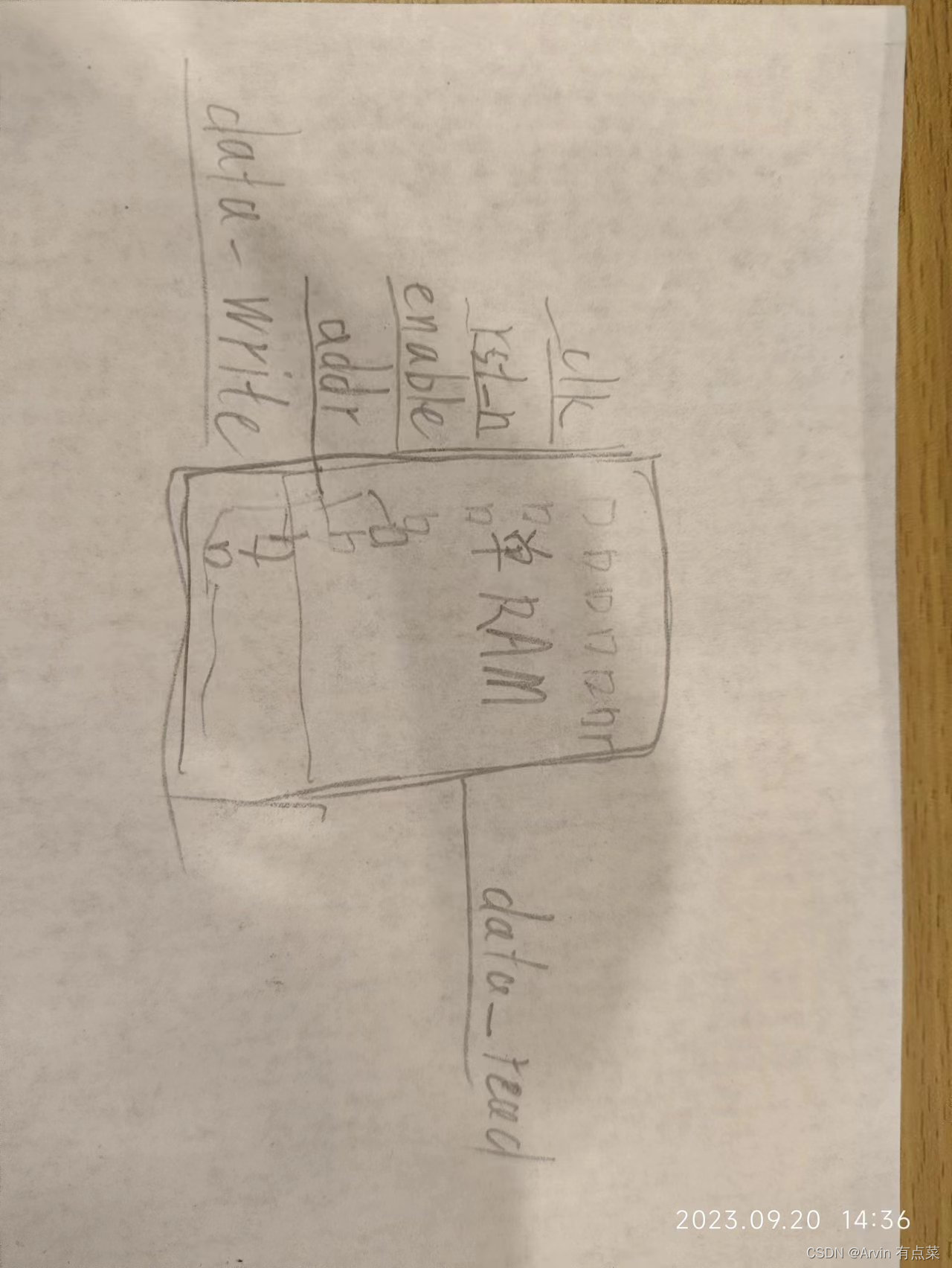
1.3、Verilog实现
module Single_Port_RAM
(
//system input
input clk
,input rst_n
//data input
,input enable_wr //allow the user to read or write the data
//when enable_wr == 0,it means to write the data from RAM
//when enable_wr == 1,it means to read the data from RAM
,input [7:0] data_write
,input [7:0] address
//data output
,output reg [7:0] data_read
);
//setup RAM which has the width of 8 and depth of 256
localparam mem_width = 7;
localparam mem_depth = 255;
reg [mem_width:0] mem [mem_depth:0];
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
data_read <= 8'd0;
else if (!enable_wr)
mem[address] <= data_write;
else if (enable_wr)
data_read <= mem[address];
end
endmodule1.4、优缺点分析
缺点:同一时刻只能对同一地址进行读操作或者写操作,而不能同时进行;地址处的数据为0时也会读取,可能会发生错误。
优点:简单,不需要协调读写操作;
1.5、TB
验证策略: 先写厚读
写: 在enable为低时,从0地址开始,每次地址加1时加到255,每次给/写一个随机数。查看相应地址中的数据和给/写的输出是否相同,相同则写成功。
读: 在enable为高时,从0地址开始,每次地址加1时加到255,每次读一个数。查看读出的数和相应地址中的数据是否相同,相同则读成功。
二、双端口RAM原理及实现
2.1、原理
参考如上的单端口RAM,双端口RAM在单端口RAM的基础上,将使能信号分为读使能信号和写使能信号,将地址信号分为读地址信号和写地址信号。
2.2 接口

2.3、Verilog实现
module Dual_Port_RAM
(
//system input
input clk
,input rst_n
//signal of read
,input read_en //when read_en == 1,read the data from mem according to read_addr
,input [7:0] read_addr
,output reg [7:0] read_data
//signal of write
,input write_en //when write_en ==1,write the data to mem according to write_addr
,input [7:0] write_addr
,input [7:0] write_data
);
//setup RAM which has the width of 8 and depth of 256
localparam mem_width = 7;
localparam mem_depth = 255;
reg [mem_width:0] mem [mem_depth:0];
reg [7:0] i;
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if (~rst_n)
for (i=0;i<=(mem_depth);i=i+1) //ram初始化
mem[i] <= 8'd0;
else if (write_en)
mem[write_addr] <= write_data;
end
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if (~rst_n)
read_data <= 8'd0; //数据初始化
else if (read_en)
read_data <= mem[read_addr];
else
read_data <= read_data; //when read_en is disabled, read_data maintains the data before
end
endmodule2.4、优缺点分析
优点:因为地址分为读地址和写地址,所以可以同时对RAM进行读写操作。
1.5、TB
和单端口类似




![[管理与领导-102]:经营与管理的关系:攻守关系;武将文官关系;开疆拓土与守护城池的关系;战斗与练兵的关系;水涨船高,水落船低的关系。](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/15882cfb98834563a56d0040cff25b15.png)

![[Linux] 2.Linux开发环境的搭建(Ubuntu)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/04c734f9dd24496ab69390b32fe1f8cd.png)