本文作者为 360 奇舞团前端开发工程师
前言
本文中使用的
React版本为18,在摘取代码的过程中删减了部分代码,具体以源代码为准。
在React 18里,通过ReactDOM.createRoot创建根节点。并且通过调用原型链上的render来渲染。 本文主要是从以下两个方法来介绍展开。
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App.tsx';
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);一、createRoot()
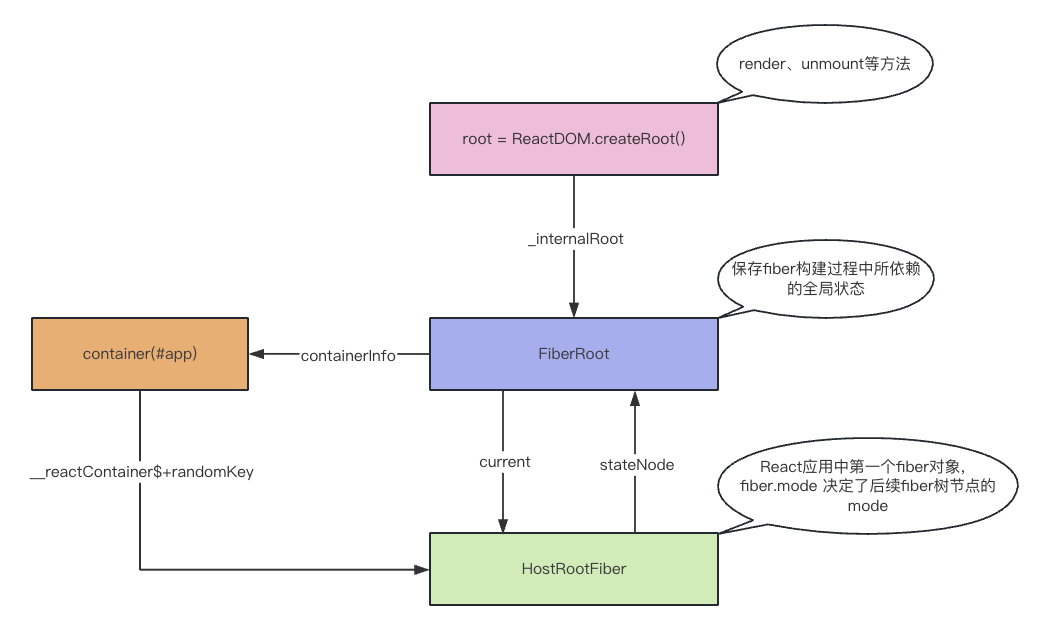
createRoot这个方法主要是用来创建FiberRoot(全局唯一,保存全局状态)和RootFiber(是应用里的第一个fiber对象),并将其关系关联起来。主要有以下过程:
校验
container有效性,以及处理options参数创建
FiberRoot和rootFiber,并关联起来事件代理
返回
ReactDOMRoot实例
function createRoot(
container: Element | Document | DocumentFragment,
options?: CreateRootOptions,
): RootType {
// 校验合法性,以及处理options参数,此处省略
if (!isValidContainer(container)) {
//...
}
// 调用 createFiberRoot,创建FiberRoot和rootFiber,并关联关系,最终返回FiberRoot。FiberRoot.current = rootFiber; rootFiber.stateNode = FiberRoot;
const root = createContainer(
container,
ConcurrentRoot,
null,
isStrictMode,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride,
identifierPrefix,
onRecoverableError,
transitionCallbacks,
);
// 标记container和rootFiber关系 container['__reactContainer$' + randomKey] = root.current
markContainerAsRoot(root.current, container);
const rootContainerElement: Document | Element | DocumentFragment =
container.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE
? (container.parentNode: any)
: container;
listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement); // 事件代理
// 实例化,挂载render,unmount方法
return new ReactDOMRoot(root); // this._internalRoot = root;
}关系结构示意图
二、render()
render主要是通过调用updateContainer,将组件渲染在页面上。
ReactDOMHydrationRoot.prototype.render = ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render = function(
children: ReactNodeList,
): void {
const root = this._internalRoot;
if (root === null) {
throw new Error('Cannot update an unmounted root.');
}
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
};updateContainer
updateContainer主要执行了以下步骤:
获取当前时间
eventTime和任务优先级lane,调用createUpdate生成update;执行
enqueueUpdate将更新添加到更新队列里,并返回FiberRoot;scheduleUpdateOnFiber调度更新;
function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
callback: ?Function,
): Lane {
const current = container.current; // rootFiber
const eventTime = requestEventTime(); // 更新触发时间
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current); // 获取任务优先级
// ... context 处理
// 创建update:{eventTime, lane, tag: UpdateState // 更新类型, payload: null, callback: null, next: null, // 下一个更新}
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
update.payload = {element}; // element首次渲染时为App
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
update.callback = callback;
}
const root = enqueueUpdate(current, update, lane); // 将update添加到concurrentQueues队列里,返回 FiberRoot
if (root !== null) {
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, current, lane, eventTime); // 调度
entangleTransitions(root, current, lane);
}
return lane;
}调度阶段
调度入口:scheduleUpdateOnFiber
主要有以下过程:
在
root上标记更新通过执行
ensureRootIsScheduled来调度任务
function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
root: FiberRoot,
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
) {
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime); // 在root上标记更新
// root.pendingLanes |= lane; 将update的lane放到root.pendingLanes
// 设置lane对应事件时间 root.eventTimes[laneToIndex(lane)] = eventTime;
if (
(executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoLanes &&
root === workInProgressRoot
) {
// 更新是在渲染阶段调度提示错误 ...
} else { // 正常更新
// ...
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime); // 调度任务
// ...
}
}调度优先级:ensureRootIsScheduled
该函数用于调度任务,一个root只能有一个任务在执行
设置任务的过期时间,有过期任务加入到
expiredLanes中获取下一个要处理的优先级,没有要执行的则退出
判断优先级相等则复用,否则取消当前执行的任务,重新调度。
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode; // 正在执行的任务
// 遍历root.pendingLanes,没有过期时间设置root.expirationTimes,有过期时间判断是否过期,是则加入到root.expiredLanes中
markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime);
// 过期时间设置 root.expirationTimes = currentTime+t(普通任务5000ms,用户输入250ms);
// 获取要处理的下一个lanes
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
);
// 没有要执行的lanes
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
// 取消正在执行的任务
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
return;
}
const newCallbackPriority = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes); // 获取最高优先级的lane
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority;
// 优先级相等复用已有的任务
if (
existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority &&
!(
__DEV__ &&
ReactCurrentActQueue.current !== null &&
existingCallbackNode !== fakeActCallbackNode
)
) {
return;
}
// 优先级变化,取消正在执行的任务,重新调度
if (existingCallbackNode != null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
let newCallbackNode; // 注册调度任务
// 同步任务,不可中断
// 1. 调用scheduleSyncCallback将任务添加到队列syncQueue里;
// 2. 创建微任务,调用flushSyncCallbacks,遍历syncQueue队列执行performSyncWorkOnRoot,清空队列;
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot) {
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
} else {
scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
if (supportsMicrotasks) {
// 支持微任务
scheduleMicrotask(() => {
if (
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) ===
NoContext
) {
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
});
} else {
scheduleCallback(ImmediateSchedulerPriority, flushSyncCallbacks);
}
newCallbackNode = null;
} else {
let schedulerPriorityLevel;
switch (lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)) {
// ...
case DefaultEventPriority:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
default:
schedulerPriorityLevel = NormalSchedulerPriority;
break;
}
// 非同步任务,可中断
// 1. 维护了两个队列 timerQueue taskQueue
// 2. 通过requestHostCallback开启宏任务执行任务
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
);
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}调度任务 scheduleSyncCallback or scheduleCallback
scheduleSyncCallback只有一个队列,将任务添加到队列里。按照顺序同步执行,不能中断。
function scheduleSyncCallback(callback: SchedulerCallback) { // callback =》performSyncWorkOnRoot
if (syncQueue === null) {
syncQueue = [callback];
} else {
syncQueue.push(callback);
}
}scheduleCallback有两个队列(小顶堆),timerQueue存放未就绪的任务,taskQueue存放已就绪任务。每次循环,判断timerQueue里是否有可执行任务,并将其移动到taskQueue中,然后从taskQueue中取出任务执行。
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
// ... startTime timeout expirationTime 等初始化
var newTask = { // 新的调度任务
id: taskIdCounter++,
callback, // render时为performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
priorityLevel,
startTime, // getCurrentTime()
expirationTime, // startTime + timeout(根据priorityLevel,-1、250、1073741823、10000、5000、)
sortIndex: -1, // startTime > currentTime ? startTime: expirationTime,
};
// 按照是否过期将任务推到队列timerQueue或者taskQueue里
if (startTime > currentTime) {
newTask.sortIndex = startTime;
push(timerQueue, newTask);
if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {
if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {
cancelHostTimeout(); // 取消当前的timeout
} else {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;
}
// 本质上是从timerQueue去取可以执行的任务放到taskQueue里,然后执行requestHostCallback
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
}
} else {
newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime;
push(taskQueue, newTask);
// 调度任务
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork); // 设置isMessageLoopRunning,开启宏任务【schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline】(优先级:setImmediate > MessageChannel > setTimeout)执行 performWorkUntilDeadline()
}
}
return newTask;
}这里要注意下,一直以来都认为是
MessageChannel优先级大于setTimeout,但在浏览器打印之后发现事实相反。这个原因是chrome在某次更新里修改了二者的优先级顺序。想了解更多可以查看这篇文章:聊聊浏览器宏任务的优先级 - 掘金
执行任务 performWorkUntilDeadline
当监听到MessageChannel message的时候,执行该方法。通过调用scheduledHostCallback(即flushWork->workLoop返回的)结果,判断是否还有任务,若有则开启下一个宏任务。
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {
const currentTime = getCurrentTime();
startTime = currentTime;
const hasTimeRemaining = true;
let hasMoreWork = true;
try {
hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime); // scheduledHostCallback = flushWork ->workLoop
} finally {
if (hasMoreWork) {
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline(); // 开启下一个宏任务MessageChannel,执行 performWorkUntilDeadline()
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
scheduledHostCallback = null;
}
}
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
}
needsPaint = false;
};workLoop
从taskQueue取出任务执行task.callback即(performConcurrentWorkOnRoot)。如果callback返回的是函数,则表示任务被中断。否则任务执行完毕,则弹出该任务。
function workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
let currentTime = initialTime;
advanceTimers(currentTime); // 将 timerQueue里到时间执行的定时任务移动到 taskQueue 里
currentTask = peek(taskQueue); // 从 taskQueue 取任务
while (
currentTask !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
) {
// 任务未过期并且任务被中断
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
break;
}
const callback = currentTask.callback; // 在scheduleCallback接受的第二个参数:performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
currentTask.callback = null;
currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;
const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;
// 如果返回是函数,则代表要重新执行;
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {
// 任务暂停重新赋值callback
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
} else {
// 任务完成弹出
if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {
pop(taskQueue);
}
}
advanceTimers(currentTime); // 每次执行完,去timerQueue查看有没有到时间的任务
} else {
pop(taskQueue); // 弹出该任务
}
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
}
// 返回给外部判断是否还有任务需要执行,即performWorkUntilDeadline里面的hasMoreWork
if (currentTask !== null) {
return true;
} else {
// taskQueue里面没有任务了,从timerQueue取任务
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
// 目的将timerQueue里的任务,移动到taskQueue里执行
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
return false;
}
}Render 阶段
这里render不是实际的dom render,而是fiber树的构建阶段。
Render入口
performSyncWorkOnRoot: 同步更新 =》 renderRootSync =》 workLoopSync
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot: 异步更新 =》 renderRootConcurrent =》 workLoopConcurrent
二者的区别主要是是否调用shouldYield,判断是否中断循环。
render之后就进入了commit阶段。
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
currentEventTime = NoTimestamp;
currentEventTransitionLane = NoLanes;
const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
const didFlushPassiveEffects = flushPassiveEffects();
if (didFlushPassiveEffects) {
// ...
}
let lanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
);
if (lanes === NoLanes) {
return null;
}
// 判断是否有用户输入、过期任务打断,需要同步渲染
const shouldTimeSlice =
!includesBlockingLane(root, lanes) &&
!includesExpiredLane(root, lanes) &&
(disableSchedulerTimeoutInWorkLoop || !didTimeout);
// renderRootConcurrent|renderRootSync里都会调用prepareFreshStack:构建新的workInProgress树
let exitStatus = shouldTimeSlice
? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes)
: renderRootSync(root, lanes);
// render执行完成或抛出异常
if (exitStatus !== RootInProgress) {
if (exitStatus === RootErrored) {
}
if (exitStatus === RootFatalErrored) {
}
if (exitStatus === RootDidNotComplete) {
markRootSuspended(root, lanes);
} else {
// render完成
const renderWasConcurrent = !includesBlockingLane(root, lanes);
const finishedWork: Fiber = (root.current.alternate: any);
if (
renderWasConcurrent &&
!isRenderConsistentWithExternalStores(finishedWork)
) {
exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (exitStatus === RootErrored) {
}
if (exitStatus === RootFatalErrored) {
}
}
// 将新的fiber树赋值给root.finishedWork
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
// 进入commit阶段->调用 commitRoot-> commitRootImpl;
// commitRootImpl 执行完成之后会清空重置root.callbackNode和root.callbackPriority;以及重置workInProgressRoot、workInProgress、workInProgressRootRenderLanes。
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
}
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now()); // 退出前检测,是否有其他更新,需要发起调度
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) { // 没有改变,说明任务被中断,返回function,等待调用
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
return null;
}是否可中断循环
workLoopSync 和 workLoopConcurrent
共同点:用于构建fiber树,
workInProgress从根开始,遍历创建fiber节点。区别是:
workLoopConcurrent里面增加了shouldYield判断。
function workLoopSync() {
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}
function workLoopConcurrent() {
while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}递归阶段 performUnitOfWork
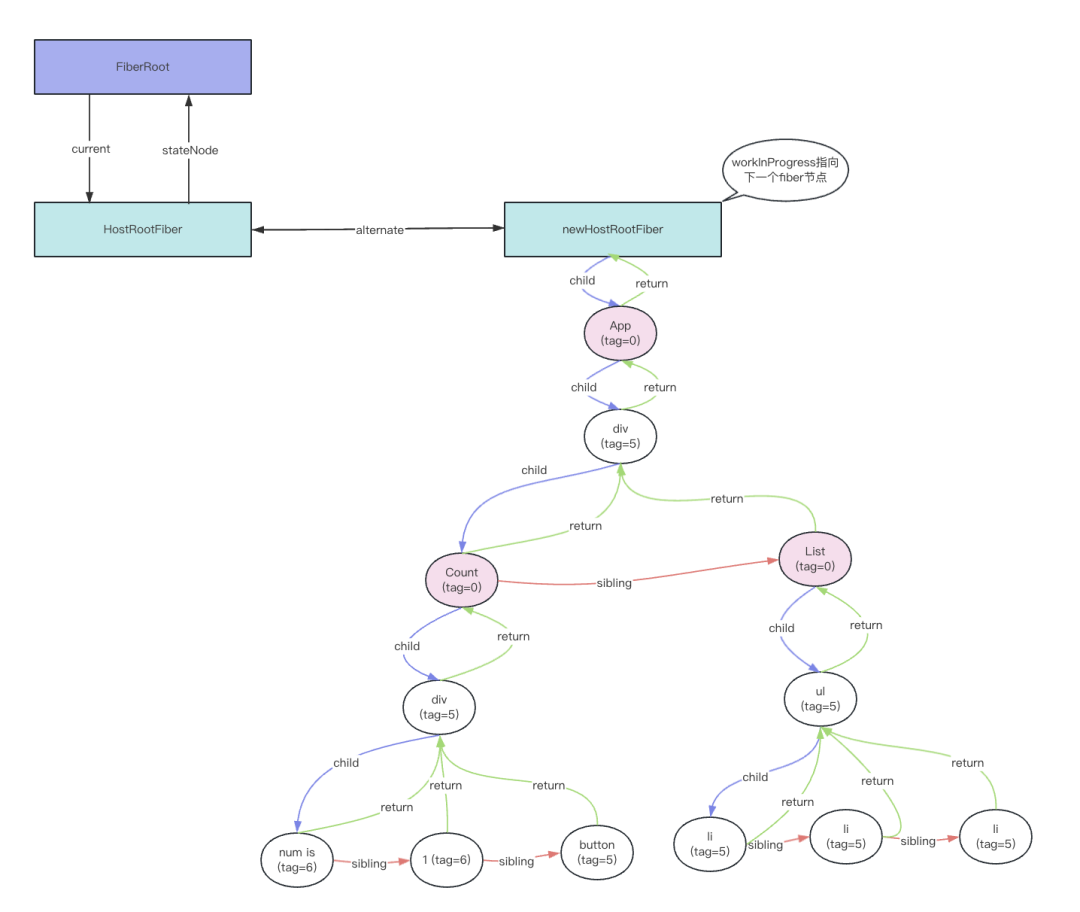
遍历过程:从rootFiber向下采用深度优先遍历,当遍历到叶子节点时(递),然后会进入到归阶段,即遍历该节点的兄弟节点,如果没有兄弟节点则返回父节点。然后进行递归的交错执行。
递阶段
beginWork: 创建或复用fiber节点。diff过程在此发生;归阶段
completeWork: 由下至上根据fiber创建或复用真实节点,并赋值给fiber.stateNode;
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void { // unitOfWork即workInProgress,指向下一个节点
const current = unitOfWork.alternate;
let next;
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, renderLanes);
unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps;
if (next === null) {
// 遍历到叶子节点后,开始归阶段,并创建dom节点
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
} else {
workInProgress = next; // workInProgress指向next
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null;
}递归后的新的fiber树
Commit 阶段
通过commitRoot进入commit阶段。此阶段是同步执行的,不可中断。接下来经历了三个过程:
before mutation阶段(执行DOM操作前):处理DOM节点渲染/删除后的focus、blur逻辑;调用getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期钩子;调度useEffect。
mutation阶段(执行DOM操作):DOM 插入、更新、删除
layout阶段(执行DOM操作后):调用类组件的
componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate、setState的回调函数;或函数组件的useLayoutEffect的create函数;更新ref。
页面渲染结果
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Count() {
const [num, setNum] = useState(1);
const onClick = () => {
setNum(num + 1);
};
return (
<div>
num is {num}
<button onClick={onClick}>点击+1</button>
</div>
);
}
function List() {
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
return (
<ul>
{arr.map((item) => (
<li key={item}>{item}</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Count />
<List />
</div>
);
}
export default App;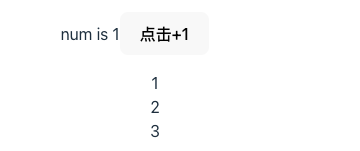
参考文章
[1] React https://github.com/facebook/react
[2] React技术揭秘 https://react.iamkasong.com/
[3] 图解React https://7km.top/main/macro-structure/
[4] 聊聊浏览器宏任务的优先级 https://juejin.cn/post/7202211586676064315
- END -
关于奇舞团
奇舞团是 360 集团最大的大前端团队,代表集团参与 W3C 和 ECMA 会员(TC39)工作。奇舞团非常重视人才培养,有工程师、讲师、翻译官、业务接口人、团队 Leader 等多种发展方向供员工选择,并辅以提供相应的技术力、专业力、通用力、领导力等培训课程。奇舞团以开放和求贤的心态欢迎各种优秀人才关注和加入奇舞团。






![[python 刷题] 42 Trapping Rain Water](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6974ce2533274defb76be788aea3c1d5.png)