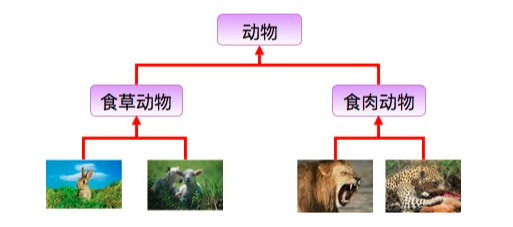
题目一:
77. 组合

思路:
思路:回溯算法。使用回溯三部曲进行解题:
1.递归函数的返回值以及参数:n,k,startIndex(记录每次循环集合从哪里开始遍历的位置),其中startIndex 就是防止出现重复的组合。比如从1开始了循环,则使用startindex=2,让startindex作为下次循环的开始。
还有全局变量:一个是用来存放一个符合条件的结果path,一个用来存放所有符合条件的结果集合result。
2.回溯函数终止条件:path这个数组的大小如果达到k,说明我们找到了一个子集大小为k的组合,在图中path存的就是根节点到叶子节点的路径
3.单层搜索的过程:for循环用来横向遍历,递归的过程是纵向遍历。
代码:
class Solution {
// 存放单个结果path, 存放所有结果res
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
combineHelper(n, k, 1);
return res;
}
// startindex就是循环开始位置
private void combineHelper(int n, int k, int startindex) {
// 终止条件
if (path.size() == k){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 单层逻辑
for (int i = startindex; i <= n ; i++ ){
path.add(i);
combineHelper(n, k, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}题目二:
17. 电话号码的字母组合

思路:同组合。不过换成了对字符串的使用,细节见代码。
代码:
class Solution {
// 存储结果的集合
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 存储结果,类似组合问题中的path
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits){
// 初始判断
if (digits.length() == 0 || digits == null) return res;
// 先设置好电话号码对应的字母
String[] numString = {"","","abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
zimuzuhe(digits, numString, 0);
return res;
}
// s代表输入的数字,
private void zimuzuhe(String s, String[] numString, int num) {
// temp.length 也可以换成 num,我习惯比较path.size与k的使用, temp.length等同于path.size,k等同于s.length
if (temp.length() == s.length()){
res.add(temp.toString());
return;
}
// num指代的是字符串中数字的位置索引,比如“23”,num会分别等于0,1。因为是使用charAt去获取的str
String str = numString[s.charAt(num) - '0'];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
temp.append(str.charAt(i));
zimuzuhe(s, numString, num + 1);
temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1);
}
}
}题目三;
39. 组合总和

思路:回溯。但因为本题区别普通组合问题可以重复使用数字,需要对startIndex进行调整
代码:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target){
if (candidates.length == 0) return res;
// 排序,以防重复,因为每个数字可以多次取
Arrays.sort(candidates);
// 用于判断总和
int sum = 0;
// 每次循环的起始位置
int startIndex = 0;
sum_zuhe(candidates, target, sum, startIndex);
return res;
}
private void sum_zuhe(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {
// 总和判断
if (sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 虽然可以重复使用数字,但仍然是组合问题,只是每次的起始点不再+1
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) break;
path.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
// 使用i为起始点,不再i+1,因为可重复使用
sum_zuhe(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}