【每日一题】1971. 寻找图中是否存在路径
有一个具有 n 个顶点的 双向 图,其中每个顶点标记从 0 到 n - 1(包含 0 和 n -1)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示顶点 ui 和顶点 vi之间的双向边。 每个顶点对由 最多一条 边连接,并且没有顶点存在与自身相连的边。
请你确定是否存在从顶点 source 开始,到顶点 destination 结束的 有效路径 。
给你数组 edges 和整数 n、source 和 destination,如果从 source 到 destination 存在 有效路径,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
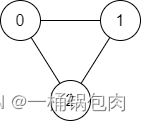
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:true
解释:存在由顶点 0 到顶点 2 的路径:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
题目解析
【广度优先搜索】:从顶点出发,找到该点所能到达的其他顶点,并存入到队列中。之后每次从队列中取出队头顶点,将该点所能到达的其他顶点压入到队列中。
class Solution {
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
if(source == destination) return true;
// 使用邻接表存储
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] e : edges){
List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(e[0], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(e[1]);
map.put(e[0], list);
list = map.getOrDefault(e[1], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(e[0]);
map.put(e[1], list);
}
// 广度优先
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] flag = new boolean[n];
//顶点
flag[source] = true;
if(map.get(source) == null) return false;
for(Integer i : map.get(source)){
queue.addLast(i);
flag[i] = true;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int node = queue.removeFirst();
if(node == destination) return true;
if(map.get(node) == null) continue;
for(Integer i : map.get(node)){
if(flag[i]) continue;
queue.addLast(i);
flag[i] = true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
【深度优先搜索】:使用递归,每遇到一个顶点,一直向下搜索。
class Solution {
boolean[] flag;
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
if(source == destination) return true;
flag = new boolean[n];
// 使用邻接表存储
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] e : edges){
List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(e[0], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(e[1]);
map.put(e[0], list);
list = map.getOrDefault(e[1], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(e[0]);
map.put(e[1], list);
}
// 递归
return dfs(map, source, destination);
}
public boolean dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map, int source, int destination){
if(source == destination) return true;
if(map.get(source) == null) return false;
for(Integer i : map.get(source)){
if(flag[i]) continue;
flag[i] = true;
if(dfs(map, i, destination)) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
【并查集】
class Solution {
// 并查集模版!
class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (x != parent[x]) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
parent[find(x)] = parent[find(y)];
}
}
public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
// 一条边的两个点 属于一个集合
for (int[] edge : edges) {
uf.union(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
return uf.find(source) == uf.find(destination);
}
}
【leetcode hot 100】739. 每日温度
题目描述
给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
题目描述
【单调栈】:该题可以使用单调栈。从后向前遍历,栈从上到下存放温度递增的顺序。
【入栈】:将当前温度压入栈
【出栈】:如果栈顶温度小于当前温度,则将栈顶出栈。
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
// 单调栈
// 栈中存放的是 温度递增的顺序
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int[] re = new int[temperatures.length];
stack.push(temperatures.length - 1);
for(int i = temperatures.length - 2; i >= 0; i--){
while(!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[stack.peek()] <= temperatures[i]){
stack.pop();
}
if(stack.isEmpty()){
re[i] = 0;
}else{
re[i] = stack.peek() - i;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return re;
}
}
【代码随想录】 860. 柠檬水找零
题目描述
在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元。顾客排队购买你的产品,(按账单 bills 支付的顺序)一次购买一杯。
每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元、10 美元或 20 美元。你必须给每个顾客正确找零,也就是说净交易是每位顾客向你支付 5美元。
注意,一开始你手头没有任何零钱。
给你一个整数数组 bills ,其中 bills[i] 是第 i 位顾客付的账。如果你能给每位顾客正确找零,返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
输入:bills = [5,5,5,10,20]
输出:true
解释:
前 3 位顾客那里,我们按顺序收取 3 张 5 美元的钞票。
第 4 位顾客那里,我们收取一张 10 美元的钞票,并返还 5 美元。
第 5 位顾客那里,我们找还一张 10 美元的钞票和一张 5 美元的钞票。
由于所有客户都得到了正确的找零,所以我们输出 true。
题目解析
class Solution {
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
int[] b = new int[3];
for(int i : bills){
if(i == 5){
b[0]++;
}else if(i == 10){
if(b[0] > 0){
b[0]--;
b[1]++;
}else{
return false;
}
}else{
if(b[1] > 0 && b[0] > 0){
b[0]--;
b[1]--;
}else if(b[0] >= 3){
b[0] -= 3;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}