1、我需要读取HTTP消息的整个 body 来填充 MVC 方法参数;
2、HTTP消息的 body 不是 form-data,而是完全的二进制内容。
最简单的方法就是不使用模型绑定,即在MVC方法中直接访问 HttpContext.Request.Body。
var request = HttpContext.Request;
using(StreamReader reader = new(request.Body))
{
……
}
这样很省事。不过这法子是不走模型绑定路线的,不时候我们是不希望这么弄,而是用这样的控制器。
// 魔鬼控制器
[HttpPost("/magic/post")]
public ActionResult PostSomething(Stream data)
{
// 计算个哈希
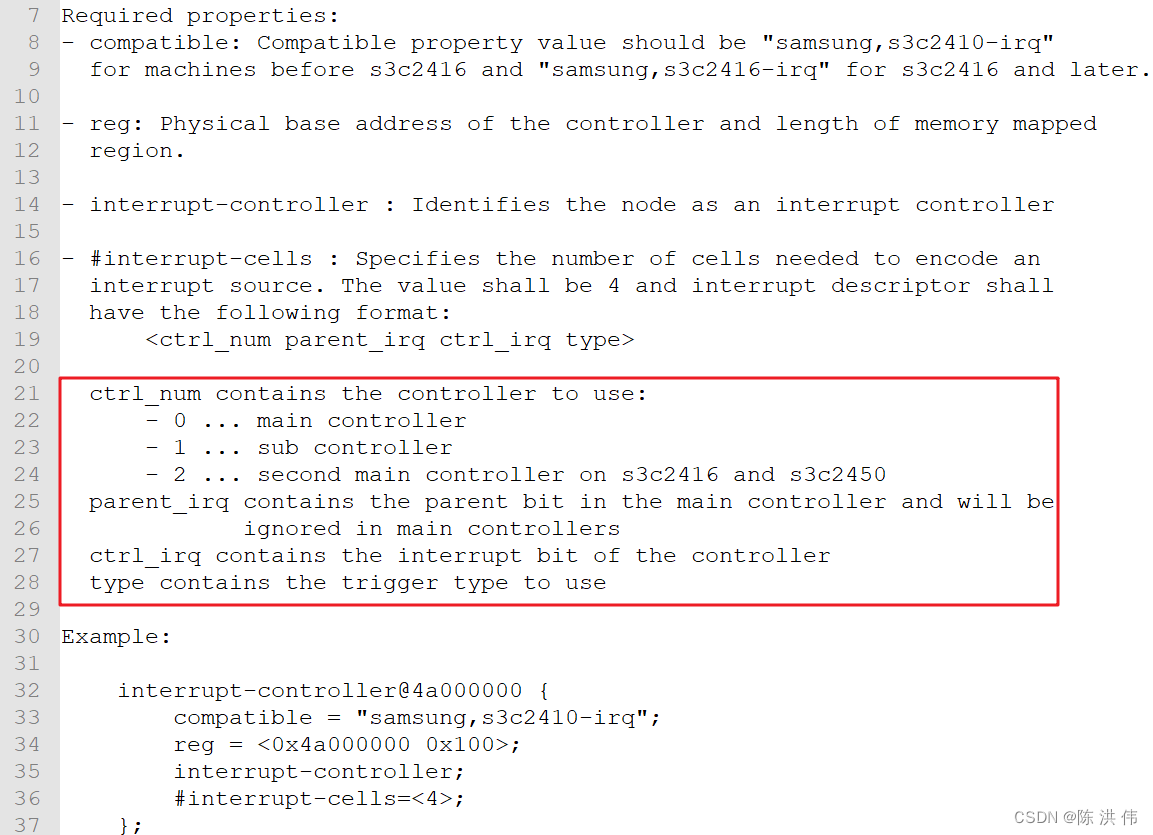
byte[] hash = SHA1.HashData(data);
// 长度
long len = data.Length;
// 响应
return Content($"你提交的数据长度:{len},SHA1:{Convert.ToHexString(hash)}");
}
这里我用单元测试来尝试调用它。
[TestClass]
public class UnitTest1
{
[TestMethod]
public async Task TestMethod1()
{
Uri rootURL = new Uri("https://localhost:7194");
HttpClient client = new();
client.BaseAddress = rootURL;
// 随便弄点数据
byte[] data = new byte[512];
Random.Shared.NextBytes(data);
// 建立流
MemoryStream mmstream = new MemoryStream(data);
// 构建内容
StreamContent content = new StreamContent(mmstream);
// 设置标准头 application/octet-stream
content.Headers.ContentType = MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse(MediaTypeNames.Application.Octet);
// 发输出一下哈希
string sha1 = Convert.ToHexString(SHA1.HashData(data));
Console.WriteLine("SHA1: {0}", sha1);
// 发送POST请求
var response = await client.PostAsync("/magic/post", content);
// 输出结果
Console.WriteLine($"响应代码:{response.StatusCode}");
Console.WriteLine("响应内容:{0}", await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync());
Assert.IsTrue(response.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK);
}
}
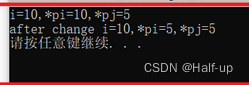
先运行服务器,再运行单元测试。结果:Failed。
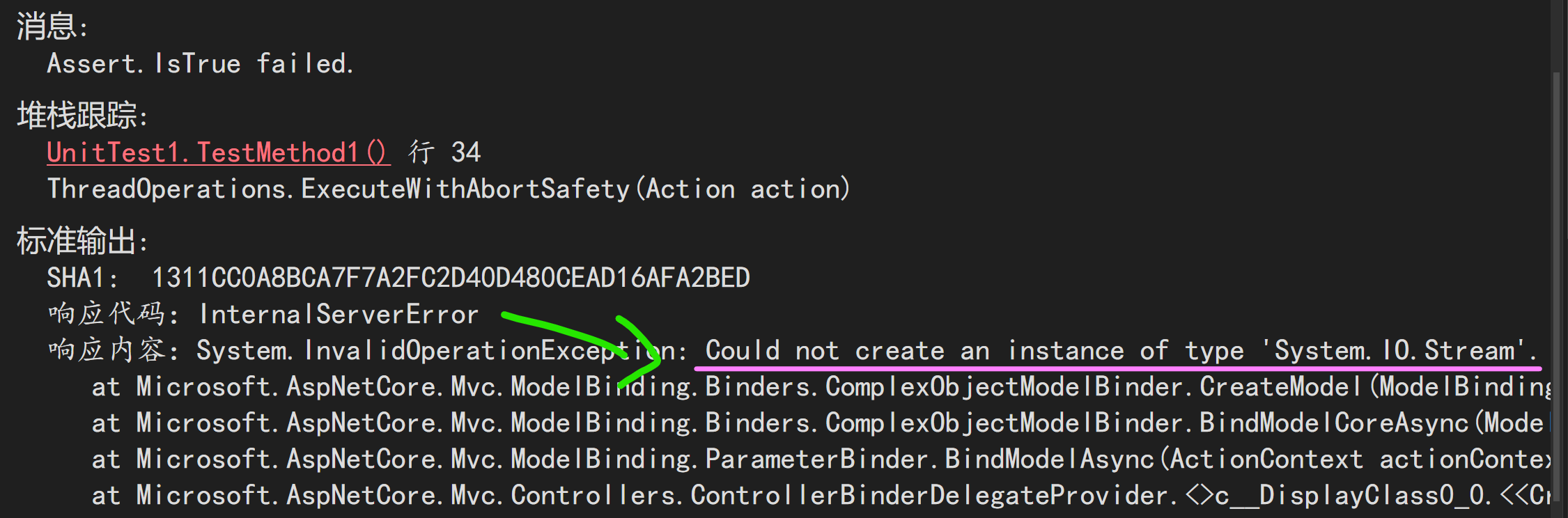
这个提示是说不能创建 Stream 类的实例。是的,因为这厮不是实现类,它很抽象,抽象到连 ComplexObjectModelBinder 都玩不下去了。这同时也说明,对于非基础类型,ASP.NET Core 默认是把参数当成复杂类型来绑定的。
于是咱们又冒出另一个思路:用 BodyModelBinder 试试。就是在参数上加个[FromBody]特性。
[HttpPost("/magic/post")]
public ActionResult PostSomething([FromBody]Stream data)
{
……
}
其实,Web API 说白了就是不用视图的 MVC 控制器。在控制器上应用 [ApiController] 特性后,在方法参数上可以省略 [FromBody] 特性。如果控制器上不应用 [ApiController] 特性,就要手动加 [FromBody] 特性。
再运行一下单元测试。结果还是 Failed。
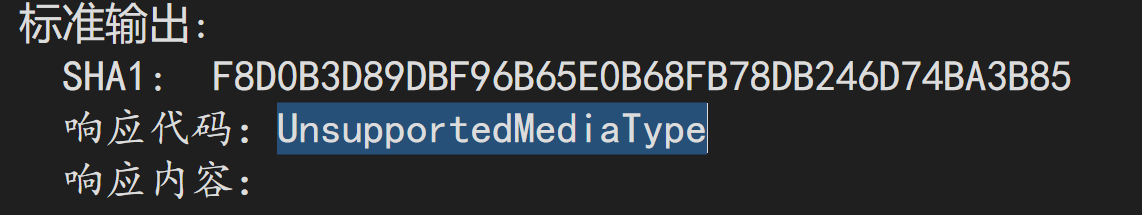
这次返回的状态是 UnsupportedMediaType,即415。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
接下来是无聊的理论知识,请准备好奶茶。
BodyModelBinder 在进行绑定时实际上是使用 IInputFormatter 来读取HTTP消息正文(body)的。允许使用多个 IInputFormatter,只要有一个能解析成功就行。默认情况下,仅支持 application/json、text/json 格式。这个咱们可以从源代码看出来。
// Set up default input formatters.
options.InputFormatters.Add(new SystemTextJsonInputFormatter(_jsonOptions.Value, _loggerFactory.CreateLogger<SystemTextJsonInputFormatter>()));
// Media type formatter mappings for JSON
options.FormatterMappings.SetMediaTypeMappingForFormat("json", MediaTypeHeaderValues.ApplicationJson);
于是,咱们把单元测试的代码改一下。
// 构建内容 //StreamContent content = new StreamContent(mmstream); JsonContent content = JsonContent.Create<Stream>(data); // 设置标准头 application/json content.Headers.ContentType = MediaTypeHeaderValue.Parse(MediaTypeNames.Application.Json);
这样做也是不行的。
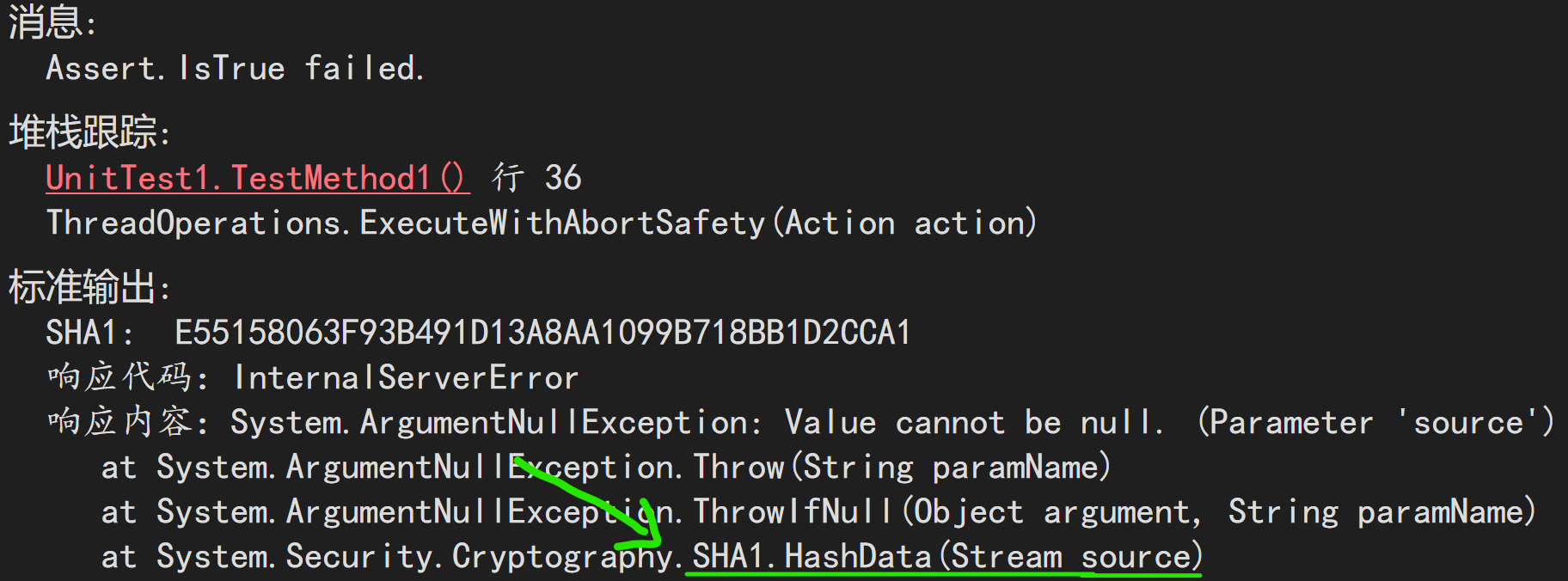
这次是 HashData 方法抛出的异常,问题还是出在 Stream 类型的参数不能实例化。若把操作方法的参数类型改为 byte[] 就没问题了。
public ActionResult PostSomething([FromBody]byte[] data)
可是这样一改,就与我们当初的要求相差太大了,我就喜欢用 Stream 类型啊,咋办?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
那只好自己写 Binder 了,反正也不难。
public class StreamModelBinder : IModelBinder
{
public async Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
if(bindingContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(bindingContext));
}
// 数据源要来自body
Console.WriteLine($"Binding Source: {bindingContext.BindingSource?.Id}");
if(bindingContext.BindingSource == null || bindingContext.BindingSource != BindingSource.Body)
{
return;
}
var request = bindingContext.HttpContext.Request;
// 咱们不关心Content-Type是啥
long? len = request.ContentLength;
// 只关心有没有正文
if(len == null && len == 0L)
{
return;
}
// 由于这个流类型有些成员不支持(比如Length属性),所以复制到内存流中
MemoryStream mstream = new MemoryStream();
await request.Body.CopyToAsync(mstream);
// 回位
mstream.Position = 0L;
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(mstream);
}
}
然后改一下控制器方法,并将上面的 Binder 通过 [ModelBinder] 特性应用到 Stream 类型的参数上。
[HttpPost("/magic/post")]
public async Task<ActionResult> PostSomething([FromBody, ModelBinder(typeof(StreamModelBinder))]Stream data)
{
// 计算个哈希
byte[] hash = await SHA1.HashDataAsync(data);
// 长度
long len = data.Length;
// 响应
return Content($"你提交的数据长度:{len}\nSHA1:{Convert.ToHexString(hash)}");
}
[ModelBinder] 特性可以局部使用自定义的 ModelBinder。此处老周建议不需要全局注册,仅在有 Stream 类型的输入参数时才用,毕竟这货也不是通用型的。
如果要全局应用,你得实现 IModelBinderProvider 接口,让 GetBinder 方法返回 StreamModelBinder 实例。然后把这个实现 IModelBinderProvider 的类型添加到 MvcOptions 选项类的 ModelBinderProviders 列表中。
经过这么一弄,嘿,有门!
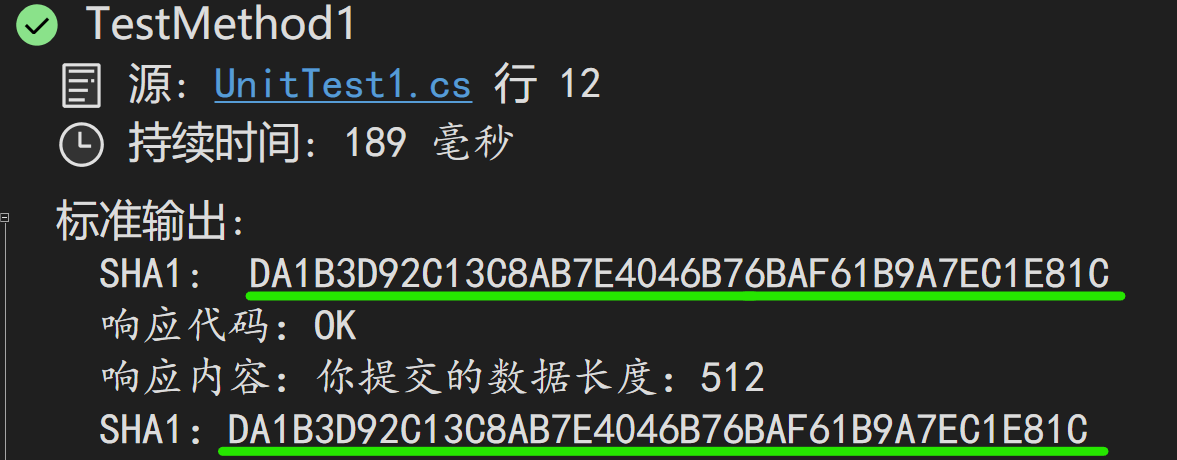
只有两个哈希值相同才表明数据被正确传输。
有大伙伴肯定又有疑问了:在 StreamModelBinder 中把 Body 复制到内存流,再用内存流来为模型赋值。这……这……这不闲得肛门疼吗?在注释里老周写明了,因为 Body 那个是 HttpRequest 网络流,像 Length 属性等成员是不支持的,在控制器方法中访问会抛异常。
你也可以节能一下,直接用 Body 来设置模型值,但在控制器代码中不能用 Length 属性来读取长度了。
public class StreamModelBinder : IModelBinder
{
public Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
if(bindingContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(bindingContext));
}
// 数据源要来自body
//Console.WriteLine($"Binding Source: {bindingContext.BindingSource?.Id}");
if(bindingContext.BindingSource == null || bindingContext.BindingSource != BindingSource.Body)
{
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
var request = bindingContext.HttpContext.Request;
// 咱们不关心Content-Type是啥
long? len = request.ContentLength;
// 只关心有没有正文
if(len == null && len == 0L)
{
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// 直接赋值
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(request.Body);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
控制器中的代码可以改为绑定 HTTP 消息头来获取长度。
[HttpPost("/magic/post")]
public async Task<ActionResult> PostSomething([FromBody, ModelBinder(typeof(StreamModelBinder))]Stream data, [FromHeader(Name = "Content-Length")]long len)
{
// 计算个哈希
byte[] hash = await SHA1.HashDataAsync(data);
// 响应
return Content($"你提交的数据长度:{len}\nSHA1:{Convert.ToHexString(hash)}");
}
len 参数的值来自 Content-Length 消息头。
运行服务器,再执行一下单元测试,结果是有效的。
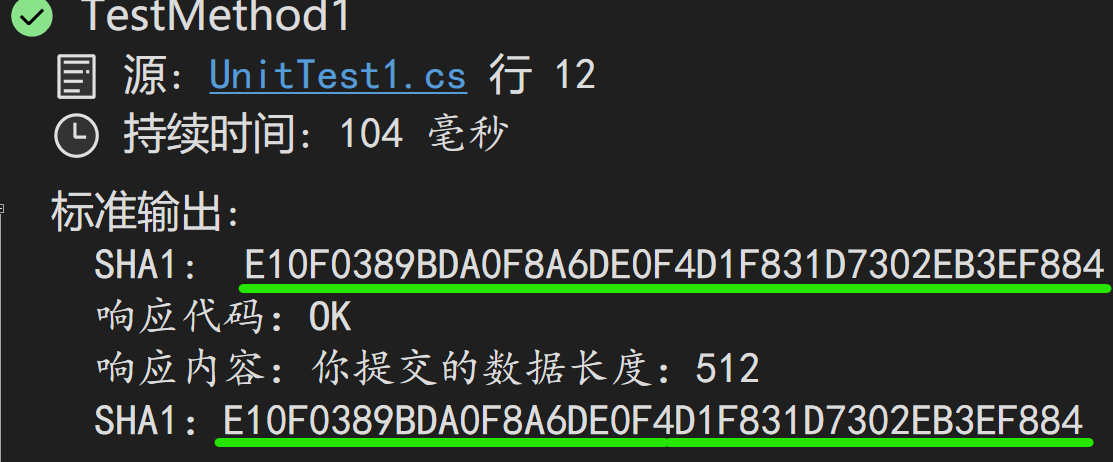
最后,补充一下,Mini-API 方式是支持使用 Stream 类型的参数的,不用自定义写代码。
app.MapPost("/dowork", async (Stream data) =>
{
byte[] hash = await SHA1.HashDataAsync(data);
string hashstr = Convert.ToHexString(hash);
return Results.Content($"接收的数据的哈希:{hashstr}");
});
结果是 Success 的。
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计Python的物品交换平台(程序+源码+LW文档)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0debc74d2bec4a17ad5ee521cdd62c22.png)