文章目录
- 前言
- 以实现优先队列来描述实现思想
- 基本类型的包装类型
- 比较函数
- 演示
- 总结
前言
最近一段时间在复习数据结构和算法,用的C语言,不得不说,不学个高级语言再回头看C语言根本不知道C语言的强大和完美,不过相比之下也有许多不便利的地方,尤其是以下两个方面:
- 没有异常处理机制
- 没有泛型
其中第一方面之前就解决了,详情请看在C语言中实现类似面向对象语言的异常处理机制,今天下午有空来实现一下泛型。不得不说,通过异常处理机制和泛型的实现,既让我C语言使用的得心应手,又让我对高级语言的设计有了亲身般体验。
以实现优先队列来描述实现思想
首先C语言本身不支持泛型,这意味着实现泛型有以下两个困难(解决这两个困难也就意味着成功):
- ①:类型信息在编译前就已经确定了
- ②:类型信息不能像参数一样传递
有了目标就轻松多了,于是我立刻就想到了函数的可变参数<stdarg.h>,请看下面的DEMO:
PackagingTypeList intBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, int);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
在使用va_arg取可变参数时我们确实直接将int类型作为参数传递了,这就意味着困难②克服了,那么困难①呢?于是我继续研究,我发现函数的参数存储在一个GCC内置的数据结构中:
typedef struct {
void *__stack; /* __stack 记录下一个匿名栈参数的存储位置, 随着va_arg的调用可能变化 */
void *__gr_top; /* __gr_top 记录最后一个匿名通用寄存器参数的尾地址, 其不随va_arg调用变化 */
void *__vr_top; /* __vr_top 记录最后一个匿名浮点寄存器参数的尾地址, 其不随va_arg调用变化 */
int __gr_offs; /* __gr_offs 记录下一个匿名通用寄存器参数到__gr_top的偏移(负数),随着va_arg的调用可能变化 */
int __vr_offs; /* __vr_offs 记录下一个匿名浮点寄存器参数到__vr_top的偏移(负数),随着va_arg的调用可能变化 */
} __builtin_va_list;
这就意味着要想克服困难①就必须得到编译器的支持,显然这是不可能的,于是我果断放弃了,但困难②的克服给我了灵感,va_arg是一个宏定义,强大的预处理器赋予了C语言元编程的能力,这就是我想到的第一种方法:
- 克服困难①:使用宏定义在编译时定义可以存储指定类型的优先队列,
- 克服困难②:使用带参数的宏传递类型信息
于是第一种方案诞生了:
#define PriorityQueueNode(TYPE) \
{ \
typedef struct PriorityQueueNode_##TYPE{ \
TYPE data; \
struct PriorityQueueNode *next; \
struct PriorityQueueNode *prior; \
}PriorityQueueNode_##TYPE; \
}while(false)
#define priorityQueueEnQueue(TYPE) \
{ \
void priorityQueueEnQueue_##TYPE(struct PriorityQueue_##TYPE queue,TYPE data){ \
... \
} \
}while(false)
#define PriorityQueue(TYPE, NAME) \
{ \
PriorityQueueNode(TYPE); \
priorityQueueEnQueue(TYPE) \
PriorityQueueNode_##TYPE head={.next=NULL,.prior=NULL}; \
struct PriorityQueue_##TYPE{ \
PriorityQueueNode *front; \
PriorityQueueNode *rear; \
void (* priorityQueueEnQueue)(struct PriorityQueue_##TYPE,TYPE); \
} NAME={ \
.front=&head, \
.rear=&head \
.priorityQueueEnQueue=priorityQueueEnQueue_##TYPE \
}; \
}while(false)
不过还没等写完我就放弃了,因为这太不优雅了,这其实和单独为每种类型定义一个优先队列没什么区别,于是我又想到了void*指针,这就是我想到的第二个方法,也是最终实现的方法:
- 克服困难①:使用
void*指针存储任意数据类型的指针,实际存储数据的空间由调用者分配 - 克服困难②:在数据结构内部需要类型信息的地方通过传入的函数完成,这个函数也由调用者提供
//PriorityQueue.h
#ifndef INC_2023_PRIORITYQUEUE_H
#define INC_2023_PRIORITYQUEUE_H
#include "../../../util/Util.h"
typedef struct PriorityQueueNode PriorityQueueNode;
typedef struct PriorityQueue *PriorityQueue;
/**
* 构造带头结点的优先队列
* @param compare
* @return
*/
PriorityQueue priorityQueueConstructor(int (*compare)(void *, void *)) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION;
/**
* 销毁优先队列
* @param queue
*/
void priorityQueueFinalize(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION;
/**
* 优先队列是否为空
* @param queue
* @return
*/
bool priorityQueueIsEmpty(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION;
/**
* 入队
* @param queue
* @param element
*/
void priorityQueueEnQueue(PriorityQueue queue, void *element) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION;
/**
* 出队
* @param queue
* @return
*/
void *priorityQueueDeQueue(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION;
#endif //INC_2023_PRIORITYQUEUE_H
//PriorityQueue.c
#include "PriorityQueue.h"
struct PriorityQueueNode {
void *data;
PriorityQueueNode *next;
PriorityQueueNode *prior;
};
struct PriorityQueue {
PriorityQueueNode *front;
PriorityQueueNode *rear;
int (*compare)(void *, void *);
};
/**
* 构造带头结点的优先队列
* @param compare
* @return
*/
PriorityQueue priorityQueueConstructor(int (*compare)(void *, void *)) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION {
if (compare == NULL) {
throw Error(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION, "比较函数不能为空");
}
PriorityQueue queue = malloc(sizeof(struct PriorityQueue));
//头结点
queue->front = queue->rear = malloc(sizeof(PriorityQueueNode));
queue->front->next = NULL;
queue->front->prior = NULL;
queue->compare = compare;
return queue;
}
/**
* 销毁优先队列
* @param queue
*/
void priorityQueueFinalize(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION {
if (queue == NULL) {
throw Error(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION, "优先队列不能为空");
}
for (; !priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue);) {
priorityQueueDeQueue(queue);
}
free(queue->front);
free(queue);
}
/**
* 优先队列是否为空
* @param queue
* @return
*/
bool priorityQueueIsEmpty(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION {
if (queue == NULL) {
throw Error(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION, "优先队列不能为空");
}
if (queue->front == queue->rear) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 入队
* @param queue
* @param element
*/
void priorityQueueEnQueue(PriorityQueue queue, void *element) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION {
if (queue == NULL) {
throw Error(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION, "优先队列不能为空");
}
PriorityQueueNode *node = malloc(sizeof(PriorityQueueNode));
node->data = element;
//如果新加入元素优先级比队尾元素优先级小则直接插入队尾,否则就遍历优先队列找到合适的插入位置
if (priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue) || queue->compare(queue->rear->data, node->data) > 0) {
node->next = NULL;
node->prior = queue->rear;
queue->rear->next = node;
queue->rear = node;
} else {
for (PriorityQueueNode *temp = queue->front->next; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next) {
if (queue->compare(temp->data, node->data) <= 0) {
node->next = temp;
node->prior = temp->prior;
temp->prior->next = node;
temp->prior = node;
break;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 出队
* @param queue
* @return
*/
void *priorityQueueDeQueue(PriorityQueue queue) throws NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION {
if (queue == NULL) {
throw Error(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION, "优先队列不能为空");
}
if (!priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
PriorityQueueNode *node = queue->front->next;
void *data = node->data;
if (queue->rear == node) {
queue->rear = queue->front;
queue->front->next = NULL;
} else {
queue->front->next = node->next;
node->next->prior = queue->front;
}
free(node);
return data;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
基本类型的包装类型
为了方便基本类型指针的获取,我定义了基本类型的包装类型:
//PackagingType.h
#ifndef DSA_PACKAGINGTYPE_H
#define DSA_PACKAGINGTYPE_H
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef union PackagingType PackagingType, **PackagingTypeList;
int getIntValue(void *element);
float getFloatValue(void *element);
double getDoubleValue(void *element);
char getCharValue(void *element);
bool getBoolValue(void *element);
PackagingType *intValueOf(int value);
PackagingTypeList intBatchValueOf(int size, ...);
PackagingType *floatValueOf(float value);
PackagingTypeList floatBatchValueOf(int size, ...);
PackagingType *doubleValueOf(double value);
PackagingTypeList doubleBatchValueOf(int size, ...);
PackagingType *charValueOf(char value);
PackagingTypeList charBatchValueOf(int size, ...);
PackagingType *boolValueOf(bool value);
PackagingTypeList boolBatchValueOf(int size, ...);
#endif //DSA_PACKAGINGTYPE_H
//PackagingType.c
union PackagingType {
int intValue;
float floatValue;
double doubleValue;
char charValue;
bool boolValue;
};
int getIntValue(void *element) {
return ((PackagingType *) element)->intValue;
}
float getFloatValue(void *element) {
return ((PackagingType *) element)->floatValue;
}
double getDoubleValue(void *element) {
return ((PackagingType *) element)->doubleValue;
}
char getCharValue(void *element) {
return ((PackagingType *) element)->charValue;
}
bool getBoolValue(void *element) {
return ((PackagingType *) element)->boolValue;
}
PackagingType *intValueOf(int value) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = value;
return pack;
}
PackagingTypeList intBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, int);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
PackagingType *floatValueOf(float value) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->floatValue = value;
return pack;
}
PackagingTypeList floatBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, double);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
PackagingType *doubleValueOf(double value) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->doubleValue = value;
return pack;
}
PackagingTypeList doubleBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, double);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
PackagingType *charValueOf(char value) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->charValue = value;
return pack;
}
PackagingTypeList charBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, int);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
PackagingType *boolValueOf(bool value) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->boolValue = value;
return pack;
}
PackagingTypeList boolBatchValueOf(int size, ...) {
PackagingTypeList list = calloc(size, sizeof(PackagingType *));
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
union PackagingType *pack = malloc(sizeof(PackagingType));
pack->intValue = va_arg(argList, int);
*(list + i) = pack;
}
va_end(argList);
return list;
}
比较函数
通过创建多个数据结构发现,在数据结构内部用到的往往是比较函数,因此,我把常用的比较函数都定义了一下:
//Comparable.h
#ifndef DSA_COMPARABLE_H
#define DSA_COMPARABLE_H
#include "../packaging-type/PackagingType.h"
extern int (*intCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*intPackCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*floatCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*floatPackCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*doubleCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*doublePackCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*charCompare)(void *, void *);
extern int (*charPackCompare)(void *, void *);
#endif //DSA_COMPARABLE_H
//Comparable.c
#include "Comparable.h"
int intComp(void *a, void *b) {
return *((int *) a) - *((int *) b) > 0;
}
int intPackComp(void *a, void *b) {
return getIntValue(a) - getIntValue(b) > 0;
}
int floatComp(void *a, void *b) {
return *((float *) a) - *((float *) b) > 0;
}
int floatPackComp(void *a, void *b) {
return getFloatValue(a) - getFloatValue(b) > 0;
}
int doubleComp(void *a, void *b) {
return *((double *) a) - *((double *) b) > 0;
}
int doublePackComp(void *a, void *b) {
return getDoubleValue(a) - getDoubleValue(b) > 0;
}
int charComp(void *a, void *b) {
return *((char *) a) - *((char *) b) > 0;
}
int charPackComp(void *a, void *b) {
return getCharValue(a) - getCharValue(b) > 0;
}
int (*intCompare)(void *, void *) =intComp;
int (*intPackCompare)(void *, void *) =intPackComp;
int (*floatCompare)(void *, void *) =floatComp;
int (*floatPackCompare)(void *, void *) =floatPackComp;
int (*doubleCompare)(void *, void *) =doubleComp;
int (*doublePackCompare)(void *, void *) =doublePackComp;
int (*charCompare)(void *, void *) =charComp;
int (*charPackCompare)(void *, void *) =charPackComp;
演示
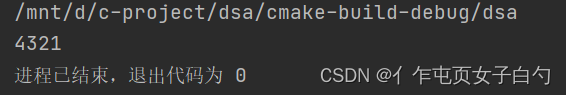
首先看一个基本类型的例子:
#include "util/Util.h"
#include "linear-structure/queue/priority-queue/PriorityQueue.h"
int main() {
PackagingTypeList list = intBatchValueOf(4, 1, 2, 3, 4);
PriorityQueue queue = priorityQueueConstructor(intPackCompare);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, *(list + i));
}
while (!priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
printf("%d", getIntValue(priorityQueueDeQueue(queue)));
}
return 0;
}
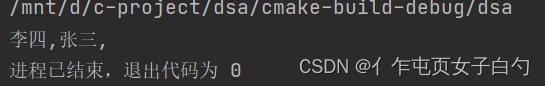
再看一个结构类型的例子:
#include "util/Util.h"
#include "linear-structure/queue/priority-queue/PriorityQueue.h"
struct Student {
int age;
char *name;
};
int studentCompare(void *a, void *b) {
return ((struct Student *) a)->age - ((struct Student *) b)->age > 0;
}
int main() {
struct Student a = {.age=18, .name="张三"}, b = {.age=28, .name="李四"};
PriorityQueue queue = priorityQueueConstructor(studentCompare);
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, &a);
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, &b);
while (!priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
printf("%s,", ((struct Student *) priorityQueueDeQueue(queue))->name);
}
return 0;
}
最后看一个抛异常的例子:
#include "util/Util.h"
#include "linear-structure/queue/priority-queue/PriorityQueue.h"
struct Student {
int age;
char *name;
};
int studentCompare(void *a, void *b) {
return ((struct Student *) a)->age - ((struct Student *) b)->age > 0;
}
int main() {
struct Student a = {.age=18, .name="张三"}, b = {.age=28, .name="李四"};
PriorityQueue queue = priorityQueueConstructor(studentCompare);
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, &a);
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, &b);
try {
while (!priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
printf("%s,", ((struct Student *) priorityQueueDeQueue(NULL))->name);//change to NULL
}
} catch(NULL_POINTER_EXCEPTION) {
stdErr();
}
return 0;
}

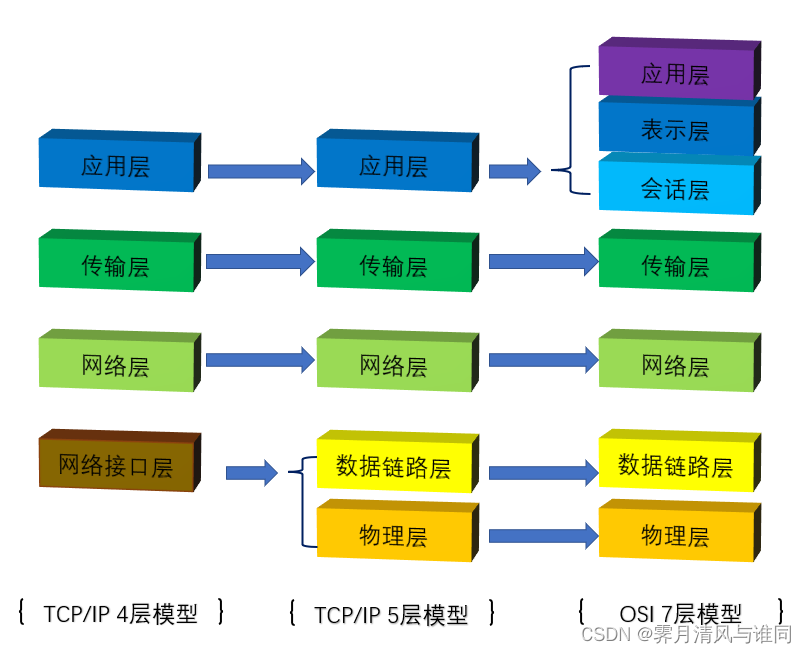
总结
- 第一种方法类似于C++的方式
- 第二种方法类似于Java的方式








![[acwing周赛复盘] 第 120 场周赛20230909](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c0a7734816574bd9bf11ece5ab4772bc.png)