目录
字符串比较方法:
boolean equals(Object anObject):
int compareTo(String s):
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
字符串查找方法:
char charAt(int index):
int indexOf(int ch):
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
int indexOf(String str):
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
int lastIndexOf(int ch):
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
int lastIndexOf(String str):
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
字符串的转化
String.valueOf():
String toUpperCase();String toLowerCase():
char[] toCharArray();
String(char value[]):
字符串替换方法:
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):
String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
String[] split(String regex):
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex):
字符串比较方法:
boolean equals(Object anObject):
比较两个字符串是否相等,相等返回ture,否则返回false
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdf";
System.out.println(a.equals("aaa"));
System.out.println(a.equals("asdf"));
}
int compareTo(String s):
比较两个字符串是否相等,先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值;如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回两个字符串长度差值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdf";
System.out.println(a.compareTo("aaa"));
System.out.println(a.compareTo("asdf"));
System.out.println(a.compareTo("asd"));
}
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
忽略字符大小写进行比较,返回值规则为:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值;
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回两个字符串长度差值。
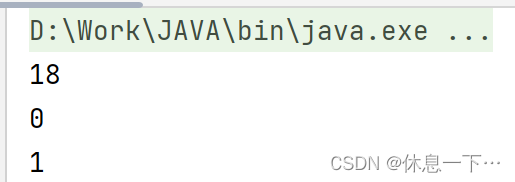
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdf";
System.out.println(a.compareToIgnoreCase("aaa"));
System.out.println(a.compareToIgnoreCase("ASDF"));
System.out.println(a.compareToIgnoreCase("asd"));
}
字符串查找方法:
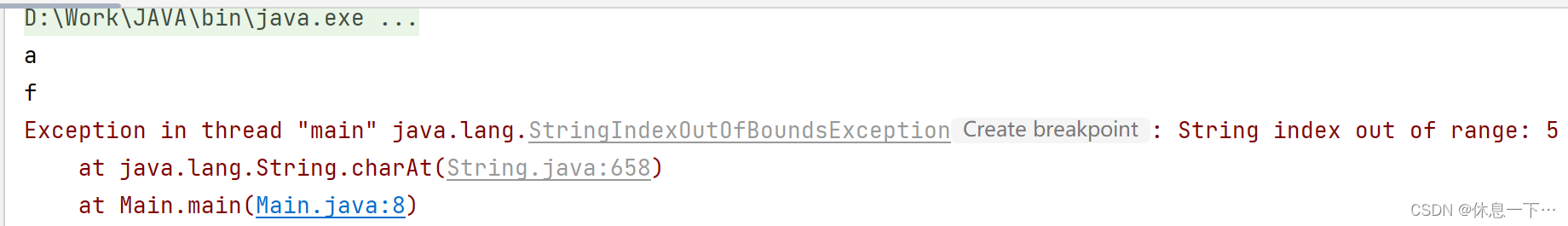
char charAt(int index):
返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdf";
System.out.println(a.charAt(0));
System.out.println(a.charAt(3));
System.out.println(a.charAt(5));
}
int indexOf(int ch):
返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有则返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.indexOf('d'));
System.out.println(a.indexOf('a'));
System.out.println(a.indexOf('h'));
}
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
从fromIndex位置开始找 ch 返回第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.indexOf('d', 3));
System.out.println(a.indexOf('a', 1));
System.out.println(a.indexOf('h',0));
}
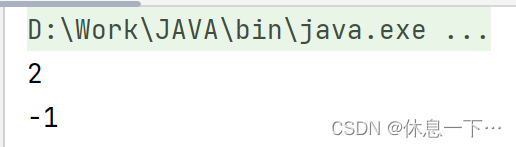
int indexOf(String str):
返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.indexOf("dd"));
System.out.println(a.indexOf("ss"));
}
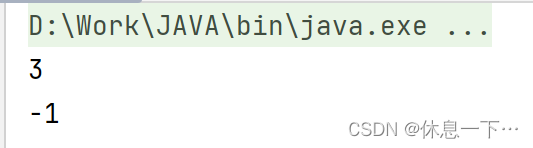
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.indexOf("dd", 3));
System.out.println(a.indexOf("ss", 0));
}
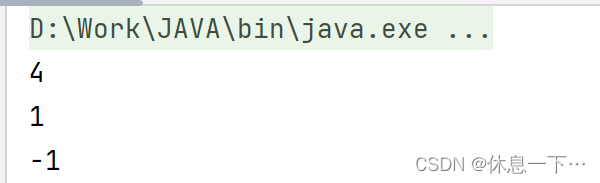
int lastIndexOf(int ch):
从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('d'));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('s'));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('v'));
}
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('d', 2));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('d', 3));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('d', 4));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf('g', 5));
} 
int lastIndexOf(String str):
从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("dd"));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("as"));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("bv"));
}
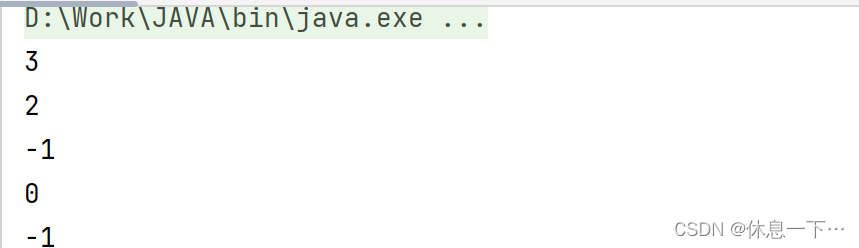
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,如果此位置的下标不大于fromIndex则返回,否则继续往前找。没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "asdddf";
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("dd", 3));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("dd", 2));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("dd", 1));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("as", 0));
System.out.println(a.lastIndexOf("bv", 0));
}
字符串的转化
String.valueOf():
将所有基本类型值转化为字符串类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf('a');
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
}
String toUpperCase();
String toLowerCase():
返回一个将原字符串转为大写的新串 。
返回一个将原字符串转为小写的新串 。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "heLLo";
String s2 = "HEllO";
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}
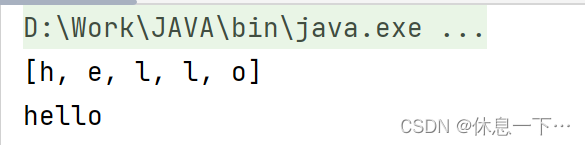
char[] toCharArray();
String(char value[]):
将字符串转为数组;原字符串不会受到影响
将数组转为字符串;原数组不会受到影响
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ch));
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}
字符串替换方法:
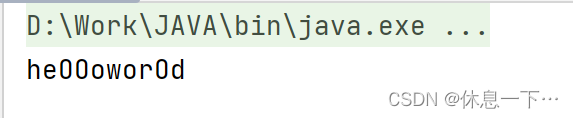
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement):
替换所有的指定内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "O"));
}
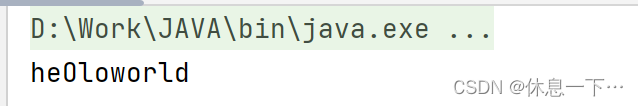
String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
替换首个内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "O"));
}
String[] split(String regex):
将字符串全部拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex):
截取 [ beginIndex ,endIndex ) 范围内的字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));
}