What is VirtIO
VirtIO是virtual input & output的缩写,是在host device之上的一层抽象层,提供给虚拟机使用。VM虚机一般是通过virtio device来使用host devices设备的,所以一个VirtIO device的主要作用其实就是充当VM与host device hardware之间的数据传输媒介。
一个简化的例子:host主机上的一个VM虚机需要联网
VM并没有实际的NIC网卡连接网络,只有host主机有。VM通过virtio-net(VirtIO device)设备来借助于host主机的NIC网卡访问网络。如下图所示:

- VM: I want to go to google.com. Hey virtio-net, can you tell the host to retrieve this webpage for me?
- Virtio-net: Ok. Hey host, can you pull up this webpage for us?
- Host: Ok. I’m grabbing the webpage data now.
- Host: Here’s the requested webpage data.
- Virtio-net: Thanks. Hey VM, here’s that webpage you requested.
此外,VirtIO spec制定了一些标准,VirtIO device 和 VirtIO drivers开发必须满足这些标准(比如feature bits、statuses、configurations、general operations等等)。
Why VirtIO
上面访问网络的例子中,可以看到VM借助于host的NIC访问网络。那么是否可以直接在VM中emulate出一个网卡?
virtualization vs emulation
Emulation is preferred when you need to use a device or software that your host’s hardware doesn’t have or doesn’t support. However, emulation doesn’t come without costs as the software filling in for the missing hardware is extra code that the host’s CPU will have to process. Having dedicated hardware will always be faster!
In virtualization, software splits the host’s physical hardware for guest VMs to use. This splitting of the host’s hardware to each guest VM essentially “dedicates” that portion of hardware to that VM, making that VM think it has its own hardware (when really it’s just “borrowing” it from the host). The key idea for virtualization here is that each guest has dedicated direct access to that portion of the host’s hardware. Note that “dedicated” here does not mean that the host would be deprived of said device. It’s more like sharing rather than giving total ownership of specific hardware.
选择emulation的情况:
-
Run an OS meant for different hardware (e.g. MacOS on PC, console-based games on PC, etc.)
-
Run software meant for another OS (e.g. Microsoft Word on MacOS)
-
Run legacy devices on unsupported hardware
选择virtualization的情况:
-
Care about host and guest performance (dedicated hardware)
-
Don’t need support for legacy software or hardware
-
Need to run multiple guest instances with efficient utilization of the host’s resources
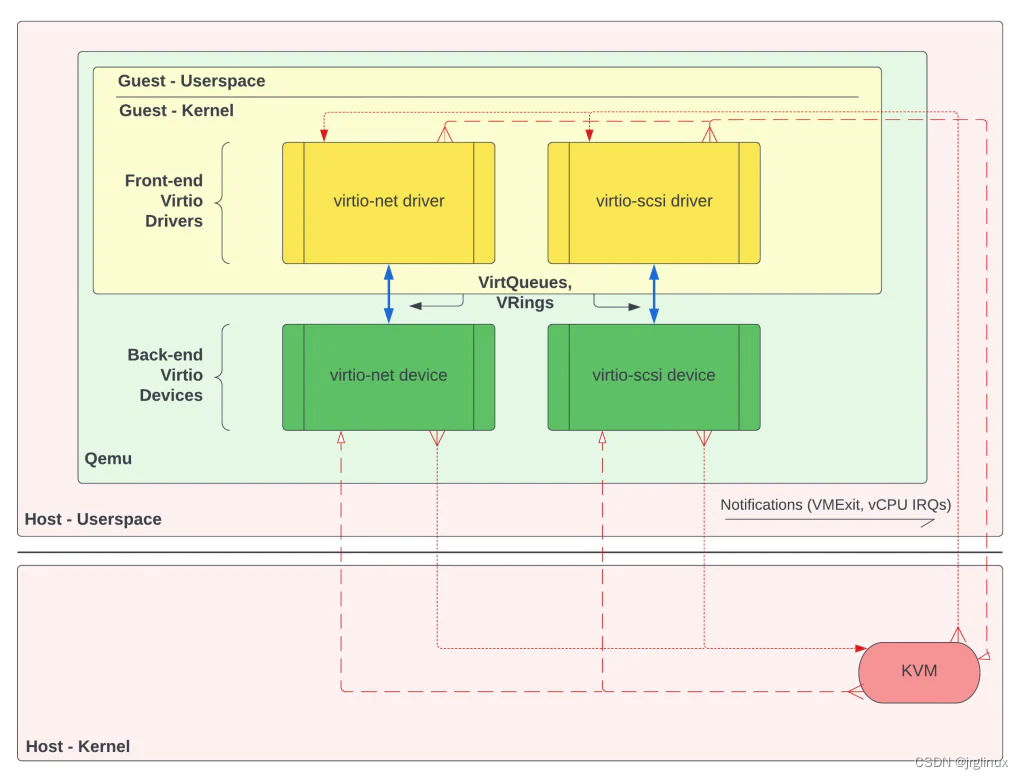
VirtIO Architecture
VirtIO主要包含三部分:
| front-end drivers | guest’s kernel |
| back-end devices | qemu |
| VirtQueues & VRings | data plane |
virtio drivers
In the guest’s OS, each VirtIO driver is considered a kernel module. A VirtIO driver’s core responsibilities are:
-
accept I/O requests from user processes
-
transfer those I/O requests to the corresponding back-end VirtIO device
-
retrieve completed requests from its VirtIO device counterpart
比如,用户需要读取文件,发起virtio-scsi的I/O请求。virtio-scsi driver接受该I/O请求,并将该请求转给后端的virtio-scsi device,然后virtio device完成了该请求,virtio driver便可以读取,virtio driver再将文件转呈给用户avaliable。
virtio devices
VirtIO devices exist in the hypervisor。如果使用Qemu,则Virtio device存在于qemu之中。它们的主要职责是:
-
accept I/O requests from the corresponding front-end VirtIO driver
-
handle the request by offloading the I/O operations to the host’s physical hardware
-
make the processed requested data available to the VirtIO driver
正如上面virtio driver中那个例子:当virtio driver发来了请求,virtio device去磁盘中检索需要获取的文件,之后,virtio device通过将数据存放于virtio device与virtio driver共享的virtqueues中,供virtio driver去获取。
virtqueues
The last key part to the VirtIO architecture is VirtQueues, which are data structures that essentially assist devices and drivers in performing various VRing operations. VirtQueues are shared in guest physical memory, meaning that each VirtIO driver & device pair access the same page in RAM. In other words, a driver and device’s VirtQueues are not two different regions that are synchronized.
virtio driver和virtio device是通过virtqueues来共享数据实现通信的。VirtQueues存在于guest physical memory中,也既是在guest客户机的RAM内存中。
描述virtqueues有很多种方式,有些教程中是和vrings(virtio rings)一起介绍的,这是因为vrings是virtqueues的主要特征功能。VRings是virtio device与virtio drivers之间共享数据的主要数据结构。
Qemu-5.1.0中VirtQueue和VRing的数据结构代码及其关系如下所示。在hw/virtio/virtio.c中定义
struct VirtQueue
{
VRing vring;
VirtQueueElement *used_elems;
/* Next head to pop */
uint16_t last_avail_idx;
bool last_avail_wrap_counter;
/* Last avail_idx read from VQ. */
uint16_t shadow_avail_idx;
bool shadow_avail_wrap_counter;
uint16_t used_idx;
bool used_wrap_counter;
/* Last used index value we have signalled on */
uint16_t signalled_used;
/* Last used index value we have signalled on */
bool signalled_used_valid;
/* Notification enabled? */
bool notification;
uint16_t queue_index;
unsigned int inuse;
uint16_t vector;
VirtIOHandleOutput handle_output;
VirtIOHandleAIOOutput handle_aio_output;
VirtIODevice *vdev;
EventNotifier guest_notifier;
EventNotifier host_notifier;
bool host_notifier_enabled;
QLIST_ENTRY(VirtQueue) node;
};
typedef struct VRing
{
unsigned int num;
unsigned int num_default;
unsigned int align;
hwaddr desc;
hwaddr avail;
hwaddr used;
VRingMemoryRegionCaches *caches;
} VRing;
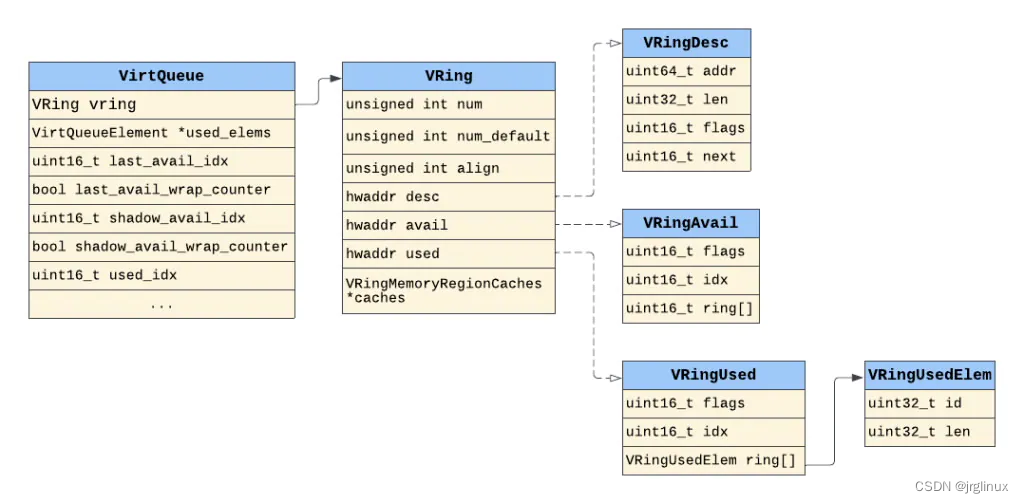
图中很明显的列出了qemu中virtqueue与vring的数据结构的区别,virtqueue包含vring,还要处理其他的一些flags、handlers等等。然后vring的操作是根据VirtIO标准来实现的(VRingDesc、VRingAvail、VringUsed等)。
而Linux-5.10内核中,在drivers/virtio/virtio_ring.c中定义vring_virtqueue结构
struct vring_virtqueue {
struct virtqueue vq;
/* Is this a packed ring? */
bool packed_ring;
/* Is DMA API used? */
bool use_dma_api;
/* Can we use weak barriers? */
bool weak_barriers;
/* Other side has made a mess, don't try any more. */
bool broken;
/* Host supports indirect buffers */
bool indirect;
/* Host publishes avail event idx */
bool event;
/* Head of free buffer list. */
unsigned int free_head;
/* Number we've added since last sync. */
unsigned int num_added;
/* Last used index we've seen. */
u16 last_used_idx;
union {
/* Available for split ring */
struct {
/* Actual memory layout for this queue. */
struct vring vring;
/* Last written value to avail->flags */
u16 avail_flags_shadow;
/*
* Last written value to avail->idx in
* guest byte order.
*/
u16 avail_idx_shadow;
/* Per-descriptor state. */
struct vring_desc_state_split *desc_state;
/* DMA address and size information */
dma_addr_t queue_dma_addr;
size_t queue_size_in_bytes;
} split;
/* Available for packed ring */
struct {
/* Actual memory layout for this queue. */
struct {
unsigned int num;
struct vring_packed_desc *desc;
struct vring_packed_desc_event *driver;
struct vring_packed_desc_event *device;
} vring;
/* Driver ring wrap counter. */
bool avail_wrap_counter;
/* Device ring wrap counter. */
bool used_wrap_counter;
/* Avail used flags. */
u16 avail_used_flags;
/* Index of the next avail descriptor. */
u16 next_avail_idx;
/*
* Last written value to driver->flags in
* guest byte order.
*/
u16 event_flags_shadow;
/* Per-descriptor state. */
struct vring_desc_state_packed *desc_state;
struct vring_desc_extra_packed *desc_extra;
/* DMA address and size information */
dma_addr_t ring_dma_addr;
dma_addr_t driver_event_dma_addr;
dma_addr_t device_event_dma_addr;
size_t ring_size_in_bytes;
size_t event_size_in_bytes;
} packed;
};
/* How to notify other side. FIXME: commonalize hcalls! */
bool (*notify)(struct virtqueue *vq);
/* DMA, allocation, and size information */
bool we_own_ring;
#ifdef DEBUG
/* They're supposed to lock for us. */
unsigned int in_use;
/* Figure out if their kicks are too delayed. */
bool last_add_time_valid;
ktime_t last_add_time;
#endif
};
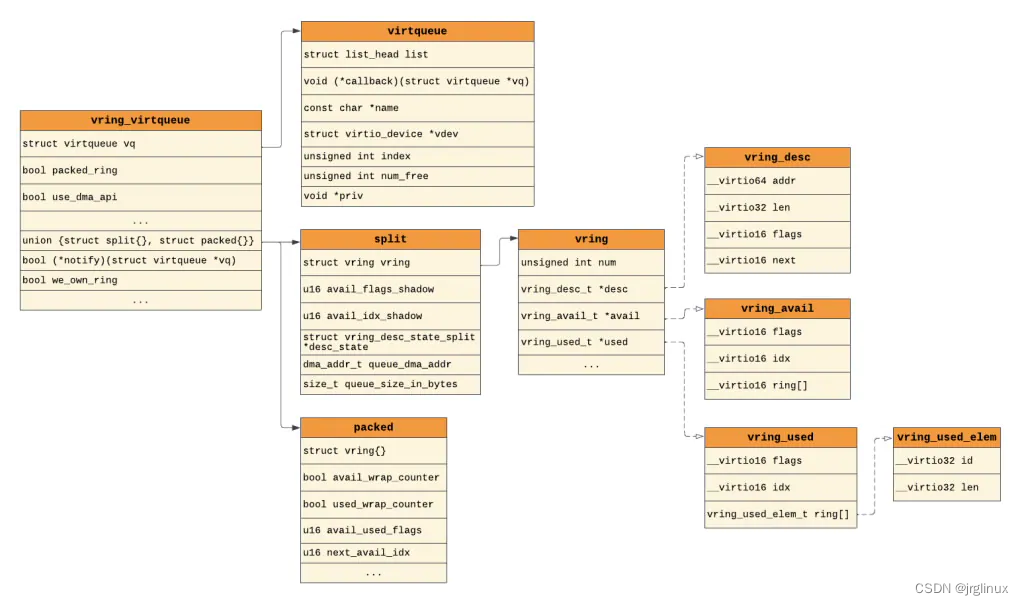
Linux内核中virtqueue与Qemu中的Virtqueue是明显有不同之处的,不过它们在最终的vring的操作上其实是相同的(desc、avail、used),这要归功于VirtIO spec标准。
vrings
As we just mentioned, VRings are the main feature of VirtQueues and are the core data structures that hold the actual data being transferred. The reason they’re referred to as “rings” is because it’s essentially an array that wraps back around to the beginning of itself once the last entry was written to. These VRings are now starting to be referred to as “areas”, but since Qemu still uses the VRing term in its source code we’ll stick with that name here.
Each VirtQueue can have up to, and usually does, three types of VRings (or areas):
-
Descriptor ring (descriptor area)
-
Available ring (driver area)
-
Used ring (device area)
descriptor ring
The descriptor ring (or descriptor table, descriptor area) is essentially a circular array of descriptors, where a descriptor is a data structure that describes a data buffer. A descriptor holds the following info about its data buffer:
-
addr: guest-physical address
-
len: length of the data buffer
-
flags: flags (NEXT, WRITE, INDIRECT)
-
next: index (in desc. ring) of next chained descriptor
descriptor ring包含四个元素:地址、长度、flags、next
flags值
| flags | ||
|---|---|---|
| N | Next | descriptor chain的后续buffer位置 |
| W | write-only | buffer只可写 |
| I | indiect | buffer包含indirect descriptor table |
next值
当flags包含Next时,表明buffer还有后续的buffer连接着(descriptor chains)。next域中的值则是Next flags的后续buffer在vring中的位置。descriptor chains中的buffer可以包含write-only和read-only两种属性的buffer。
only the driver can add (write) descriptors to the descriptor ring and a device can only write to a device-writable buffer if the descriptor’s flag says the buffer is writable. A buffer can either be write-only or read-only, but never both.
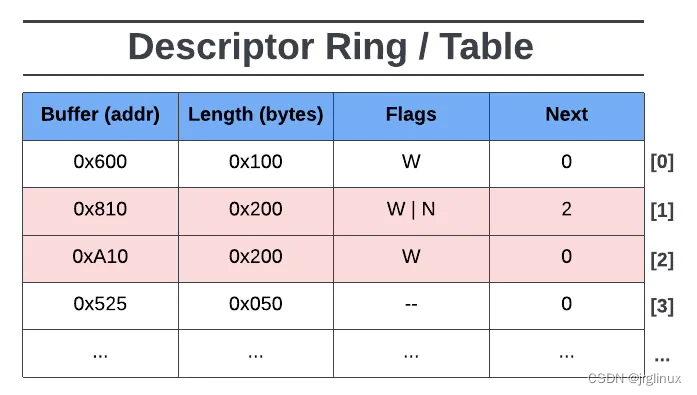
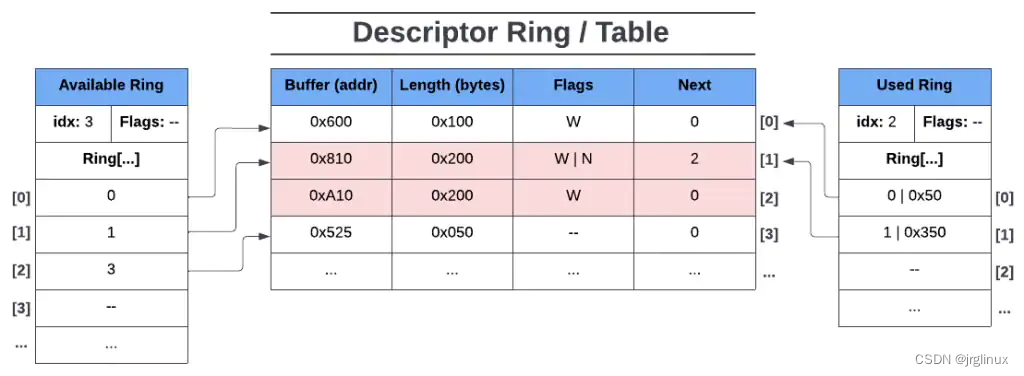
以上图为例,图中显示descriptor ring有4个descriptor entries,其中:
第一个入口index[0]的buffer地址为0x600(guest-physical address,GPA地址),长度为0x100,其flgas位是W,意味着该buffer device-writable,其Next位为0,则表示没有后续的buffer。
第二入口index[1]的buffer位置为0x810,长度为0x200,其flags位为W|N,意味着该buffer device-writable,并且该buffer还是某个descriptor chains的头,其Next buffer位置在index[2]位置。
第三入口index[2]是index[1]的后续,位置在0xA10,长度为0x200,其flgas是W,也是device-writable的,然后该descriptor chains到此就结束,因为index[2]的Next位是0。
第四入口是index[3],在GPA的位置是0x525,长度为0x050,其flags位是**–**,意味着该buffer device read-only,且Next位为0,表示没有descriptor chain。
available ring
available ring是一组指向descriptor ring中的描述符descriptor的循环数组,换句话说,每一个available ring中的entry入口都指向descriptor ring中的descriptor(或者descriptor chian的head)。
指向descriptor ring的可用buffer。
available ring包含三个位域值:
-
flags: configuration flags
-
idx: index of the next available avail ring entry
-
ring[]: the actual available ring array
The flags field represents the configuration of the available ring and some of its operations. The index field represents the next available entry in the available ring where the driver would put the next reference to a descriptor (or head of a descriptor chain). Lastly, the ring field represents the actual available ring array where descriptor ring references are stored by the driver.
只有driver可以配置、添加available ring的entry入口,而其对应的device只能read conly。
在driver添加第一个entry入口之前,available ring如下图所示:ring中没有entry,没有flags,idx为0(因为此时next available ring entry是ring[0])
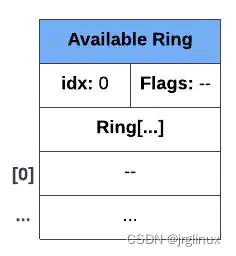
我们以descriptor ring中的图示例为例子,添加entry过程如下:
driver添加第一个entry
lets say the driver adds (or makes available) the first descriptor entry on the descriptor ring,那么如下图所示:
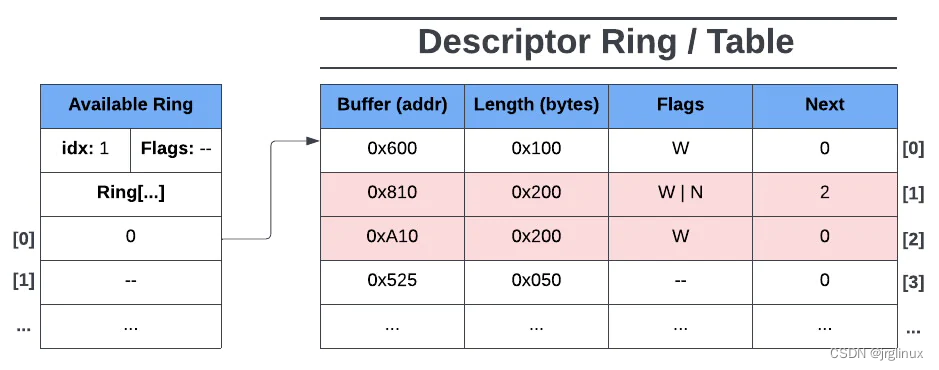
Here we can see that the driver made the first descriptor entry available to the device by adding the index of the descriptor table to the first available entry in the available ring (ring[0]). We can also see that idx is now 1 as ring[1] is now the next available entry on the ring. In this state, only the first entry of the descriptor ring is readable by the device and has no access to the other descriptors.
driver添加下一个entry
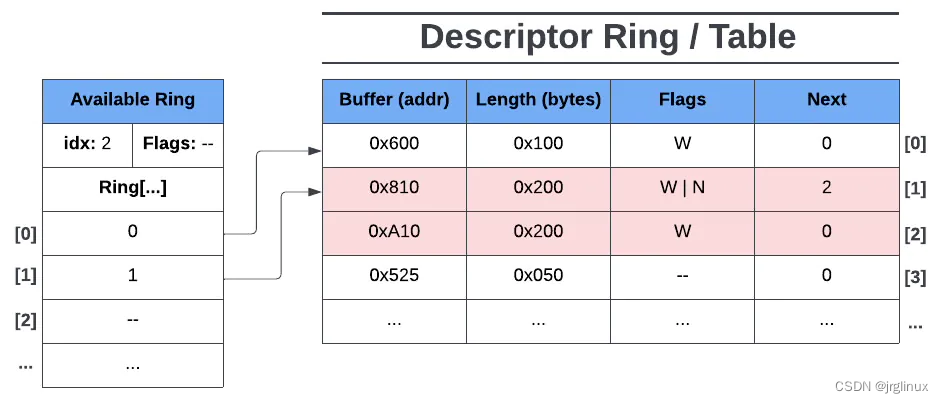
Here we see the driver made the second and third descriptor entries available (chained descriptors). Now ring[1] points to the head of a descriptor chain, giving the device access to all of its chained descriptors. idx is set to 2 since ring[2] is now the next available entry on the available ring.
最后,driver添加下一个entry
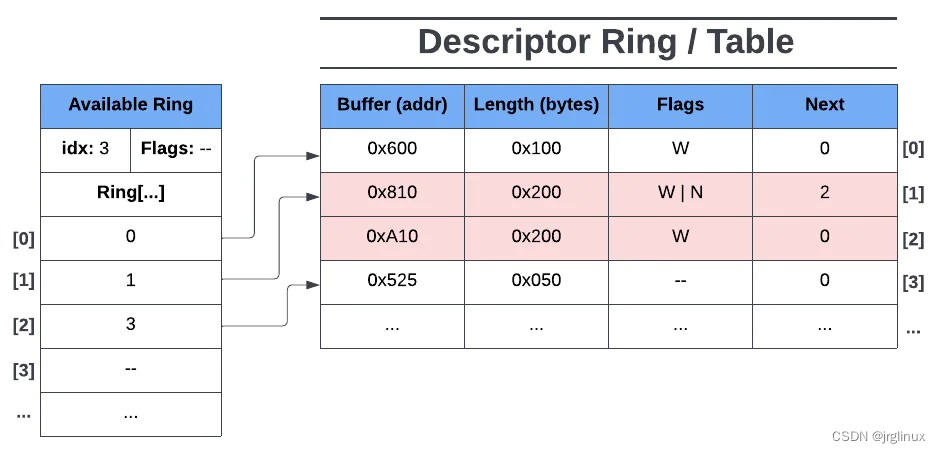
注意到这里ring[2]是ring index 3,已经指向descriptor ring的index 4也即descriptor ring[3],这是因为descriptor ring的index 2和index 3是chain。此时available ring的idx已经是3了,因为此时available ring的下一个entry是ring[3]了。
used ring
类似available ring,也是一组循环数组指向descriptor ring,不过used ring是指向descriptor ring中已经被used的buffer。
只有device可以配置、写,对应的driver只能read only。
used ring位域包含:
-
flags: configuration flags
-
idx: index of next available used ring entry
-
ring[]: the actual used ring array (of data pair structs)
- id: index of descriptor ring this element refers to
- len: length of data written to descriptor(s) buffer(s)
初始时,used ring如下图所示
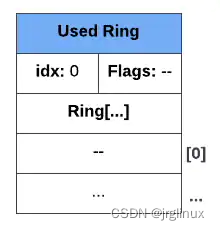
used ring与available ring不同之处还在于其ring[]是一组数据(包含id、len)。其中,id是指descriptor ring中used的buffer所处的index,len是指descriptor ring中写入的缓冲区总长度。
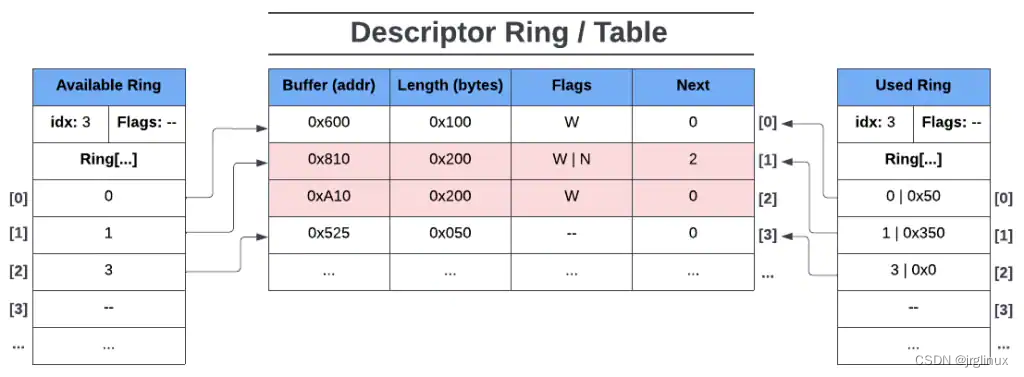
举例,假如device已经用完descriptor ring的第一个buffer,将其entry加入到used buffer中,假设只写了0x50长度的buffer; 接着,device在descriptor ring的第二个buffer写入0x200,第三个buffer写入0x150长度,则最终used ring如下图所示:其中,0 | 0x50 表示descriptor ring的ring[0]中写入长0x50的buffer,1 | 0x350表示descriptor ring中ring[1]写入0x200,ring[2]写入0x150长度的buffer。
接着,对于descriptor ring的第四个buffer,其flags是**–**,表示device只读,不可写。则used ring中就不会有已写入的len长度,记录如下:3 | 0x0表示descriptor ring的ring[3]中写入0长度的buffer(因为descriptor ring的ring[3]相对于device来说是read-only,没法写入数据)。
desc/avail/used ring对比
| ring | 说明 |
|---|---|
| descriptor ring | driver/device 可读可写,共享数据 |
| available ring | driver写,device只读 |
| used ring | device写,driver只读 |
综合来说,VirtIO driver通过available ring指向的descriptor ring来发起向VirtIO device的request请求,VirtIO device通过available ring来解析driver的request请求,然后VirtIO device通过used ring来给driver提供request请求处理好的结果。
VHost
这里简要介绍下VHost,因为这是VirtIO不可避开的知识点。
VirtIO devices & drivers 的data plane是在Qemu process中的。
VHost将data plane移到另外一个用户态进程(VHost-user)或者host kernel中(VHost内核模块)。这么做的目的是原来的纯VirtIO架构中,每当driver需要向host的物理设备发起处理请求,都会产生context
switch,这就是一笔开销,为了避开context switch带来的latency,将data plane移到vhost-user进程或者host kernel中,则可以bypass Qemu进程,减少了latency,提升了性能。不过这样也同样带来另一个问题:如果直接放到host kernel中,则有安全风险。
以VHost-SCSI为例:
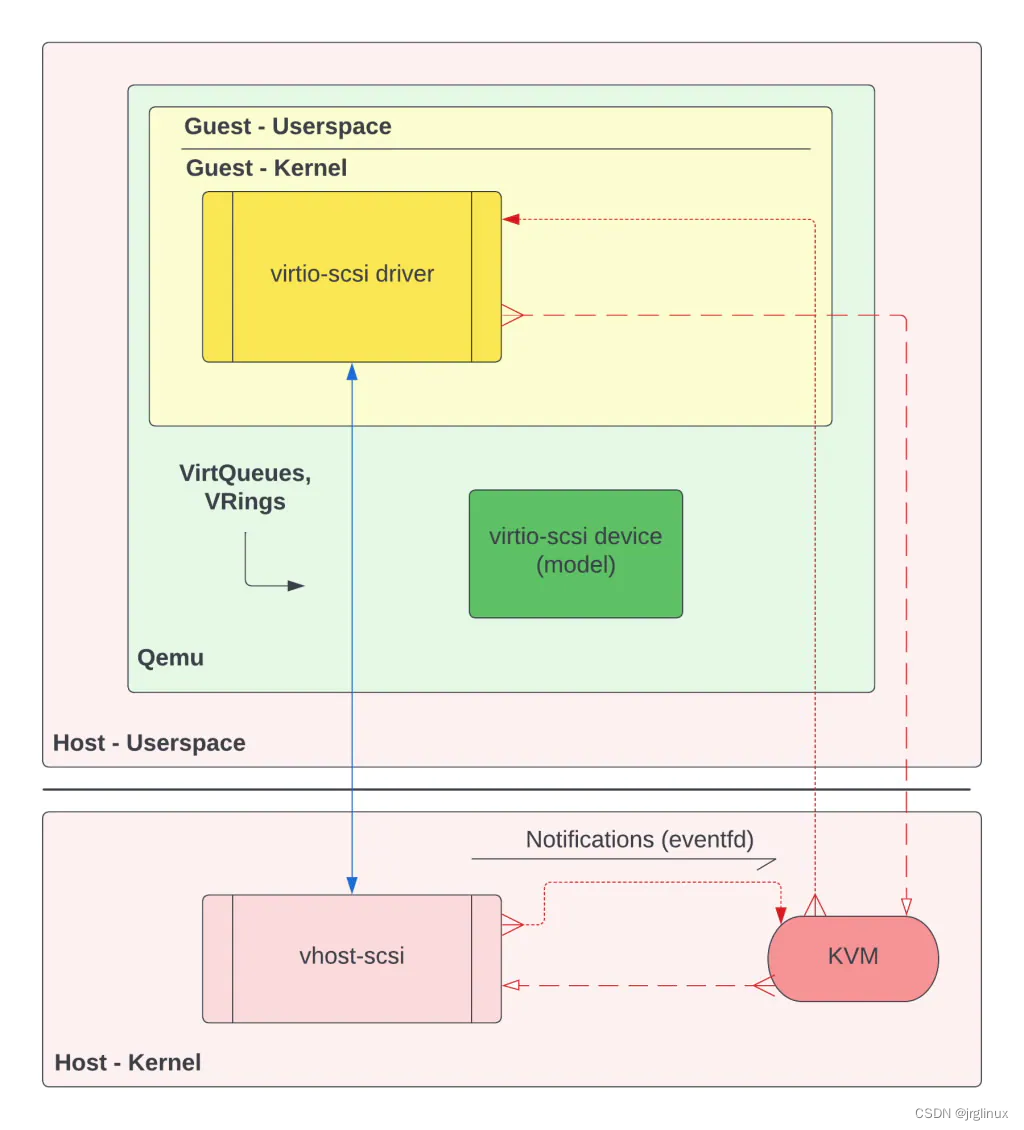
上图中显示的VHost与本文开头处的纯VirtIO架构图对比,可以看到:
-
data plane 从guest kernel移到了host kernel
-
VirtIO devices还存在,不过其主要职责是处理control plane
-
多了VHost-SCSI kernel module
VirtIO in Qemu
这里以VirtIO-SCSI为例,来说明Virtio device与VirtQueues/VRings的关系。
VirtIO-SCSI
VirtIO-SCSI是以SCSI协议为总线控制逻辑设备的virtual device。这里假设我们只用virtio-scsi来连接一块HDD磁盘,其qemu的命令参数如下:
-device virtio-scsi-pci
-device scsi-hd,drive=hd0,bootindex=0
-drive file=/home/qemu-imgs/test.img,if=none,id=hd0
Qemu中通过virtio_scsi_common_realize()函数来创建virtio-scsi device,通过virtio_scsi_common_unrealize()函数来销毁virtio-scsi device。
void virtio_scsi_common_realize(DeviceState *dev,
VirtIOHandleOutput ctrl,
VirtIOHandleOutput evt,
VirtIOHandleOutput cmd,
Error **errp)
{
VirtIOSCSICommon *s = VIRTIO_SCSI_COMMON(dev);
virtio_init(vdev, "virtio-scsi", VIRTIO_ID_SCSI,
sizeof(VirtIOSCSIConfig));
...
s->ctrl_vq = virtio_add_queue(vdev, s->conf.virtqueue_size, ctrl);
s->event_vq = virtio_add_queue(vdev, s->conf.virtqueue_size, evt);
for (i = 0; i < s->conf.num_queues; i++) {
s->cmd_vqs[i] = virtio_add_queue(vdev, s->conf.virtqueue_size, cmd);
}
}
大多数VirtIO devices都会拥有多个VirtQueues,每个VirtQueue都有其作用,这里以VirtIO-SCSI device为例:
| ctrl_vq | control virtqueue | 用于task management functions(TMFs),比如starting up/shutting down/ reseting virtio-SCSI device,也用于subscribing to and querying asynchronous notifications. |
| event_vq | event virtqueue | reporting information (events) from the host on logical units attached to virtio-SCSI,这些events包含transport events(比如device resets,rescans,hotplug)、asynchronous notifications and logical unit number parameters change. |
| cmd_vqs | command virtqueue | used for typical SCSI transport commands (e.g. reading and writing to and from files). |
the command virtqueue
这里主要关注下command virtqueue,cmd_vq用于传输SCSI transport command, 比如writing and reading to files。Virtio-SCSI可以有一个或者多个command Virtqueues。
Qemu中,VirtQueues会有一个handle output的回调函数,其指向handle_output:
/* hw/virtio/virtio.c中定义 */
VirtQueue *virtio_add_queue(VirtIODevice *vdev, int queue_size,
VirtIOHandleOutput handle_output)
{
...
vdev->vq[i].vring.num = queue_size;
vdev->vq[i].vring.num_default = queue_size;
vdev->vq[i].vring.align = VIRTIO_PCI_VRING_ALIGN;
vdev->vq[i].handle_output = handle_output;
vdev->vq[i].handle_aio_output = NULL;
vdev->vq[i].used_elems = g_malloc0(sizeof(VirtQueueElement) *
queue_size);
...
}
而在Virtio-SCSI device中,该handle_output是由virtio_scsi_handle_cmd()函数实现:
/* hw/virtio/virtio-scsi.c */
static void virtio_scsi_device_realize(DeviceState *dev, Error **errp)
{
VirtIODevice *vdev = VIRTIO_DEVICE(dev);
VirtIOSCSI *s = VIRTIO_SCSI(dev);
Error *err = NULL;
virtio_scsi_common_realize(dev,
virtio_scsi_handle_ctrl,
virtio_scsi_handle_event,
virtio_scsi_handle_cmd,
&err);
...
}
static void virtio_scsi_handle_cmd(VirtIODevice *vdev, VirtQueue *vq)
{
/* use non-QOM casts in the data path */
VirtIOSCSI *s = (VirtIOSCSI *)vdev;
if (s->ctx) {
virtio_device_start_ioeventfd(vdev);
if (!s->dataplane_fenced) {
return;
}
}
virtio_scsi_acquire(s);
virtio_scsi_handle_cmd_vq(s, vq);
virtio_scsi_release(s);
}
virtio_scsi_device_realize()函数中注册了cmd的回调函数virtio_scsi_handle_cmd()。
virtio-scsi driver通知qemu, qemu再去通知virtio-scsi device有命令需要处理, 通过available ring去获取命令.
而具体handle cmd是在virtio_scsi_handle_cmd_vq()中处理
/* hw/virtio/virtio-scsi.c */
bool virtio_scsi_handle_cmd_vq(VirtIOSCSI *s, VirtQueue *vq)
{
VirtIOSCSIReq *req, *next;
int ret = 0;
bool suppress_notifications = virtio_queue_get_notification(vq);
bool progress = false;
QTAILQ_HEAD(, VirtIOSCSIReq) reqs = QTAILQ_HEAD_INITIALIZER(reqs);
do {
if (suppress_notifications) {
virtio_queue_set_notification(vq, 0);
}
while ((req = virtio_scsi_pop_req(s, vq))) {
progress = true;
ret = virtio_scsi_handle_cmd_req_prepare(s, req);
if (!ret) {
QTAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&reqs, req, next);
} else if (ret == -EINVAL) {
/* The device is broken and shouldn't process any request */
while (!QTAILQ_EMPTY(&reqs)) {
req = QTAILQ_FIRST(&reqs);
QTAILQ_REMOVE(&reqs, req, next);
blk_io_unplug(req->sreq->dev->conf.blk);
scsi_req_unref(req->sreq);
virtqueue_detach_element(req->vq, &req->elem, 0);
virtio_scsi_free_req(req);
}
}
}
if (suppress_notifications) {
virtio_queue_set_notification(vq, 1);
}
} while (ret != -EINVAL && !virtio_queue_empty(vq));
QTAILQ_FOREACH_SAFE(req, &reqs, next, next) {
virtio_scsi_handle_cmd_req_submit(s, req);
}
return progress;
}
References
introduction to virtio