文章链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
代码地址:GitHub - google-research/vision_transformer
Pytorch实现代码: https://github.com/WZMIAOMIAO/deep-learning-for-image-processing/tree/master/pytorch_classification/vision_transformer
Tensorflow2实现代码:https://github.com/WZMIAOMIAO/deep-learning-for-image-processing/tree/master/tensorflow_classification/vision_transformer
在bilibili上的视频讲解:11.1 Vision Transformer(vit)网络详解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
一.引言
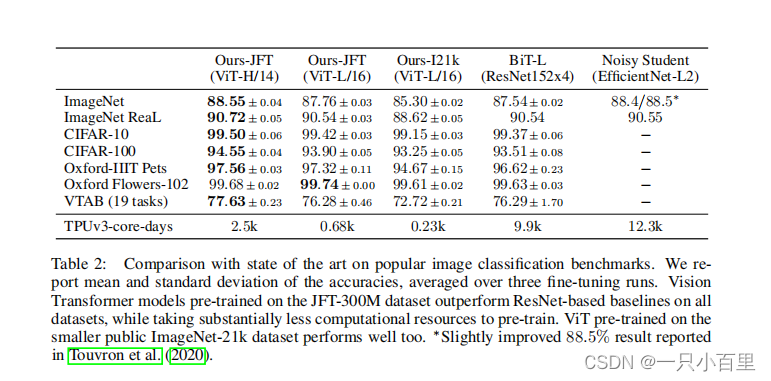
在 "An Image Is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers For Image Recognition At Scale" 论文的实验部分,与其他方法相比,该方法取得了以下突破性的成果:
-
在大规模图像分类任务上超越传统方法:论文中的方法在 ImageNet-1K 数据集上进行了实验,并与传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)进行了比较。结果显示,该方法在准确性方面超越了传统的CNN模型,取得了更好的图像分类性能。
-
大规模预训练模型的有效性:论文中的方法使用大规模的图像数据集进行了预训练,并通过自监督学习的方式学习图像的特征表示。这种预训练方法使得Transformer模型能够捕捉到广泛的视觉特征,并在具体任务的微调中展现出优势。
-
有效处理大尺寸图像的能力:传统的CNN模型在处理大尺寸图像时可能面临计算和内存限制的问题。然而,论文中的方法通过将图像分割成较小的块,并利用Transformer模型对这些块进行编码,展示了对大尺寸图像的高效处理能力。这使得该方法在处理高分辨率图像时具有优势,并能够在保持准确性的同时提高计算效率。
二.ViT模型架构
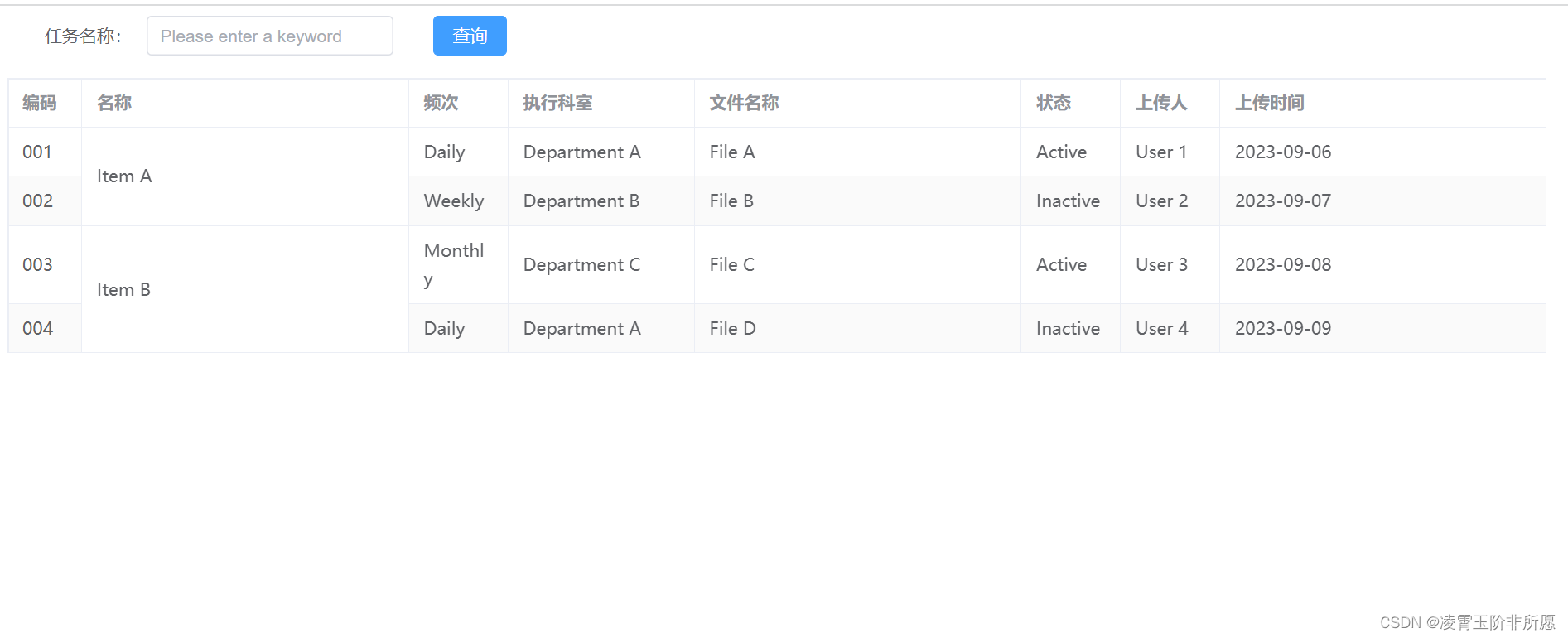
其原始架构图如下所示,可以看到首先输入图片分为很多 patch,论文中为 16。将 patch 输入一个 Linear Projection of Flattened Patches 这个 Embedding 层,就会得到一个个向量,通常就称作 token。紧接着在一系列 token 的前面加上加上一个新的 token(类别token,有点像输入给 Transformer Decoder 的 START,就是对应着 * 那个位置),此外还需要加上位置的信息,对应着 0~9。然后输入到 Transformer Encoder 中,对应着右边的图,将 block 重复堆叠 L 次。Transformer Encoder 有多少个输入就有多少个输出。最后只进行分类,所以将 class 位置对应的输出输入 MLP Head 进行预测分类输出。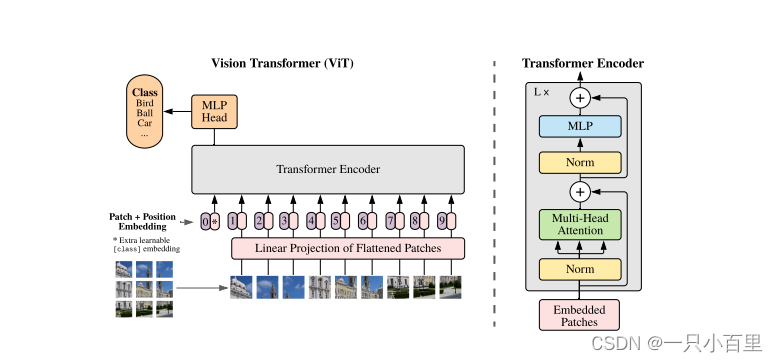
2.1embedding层
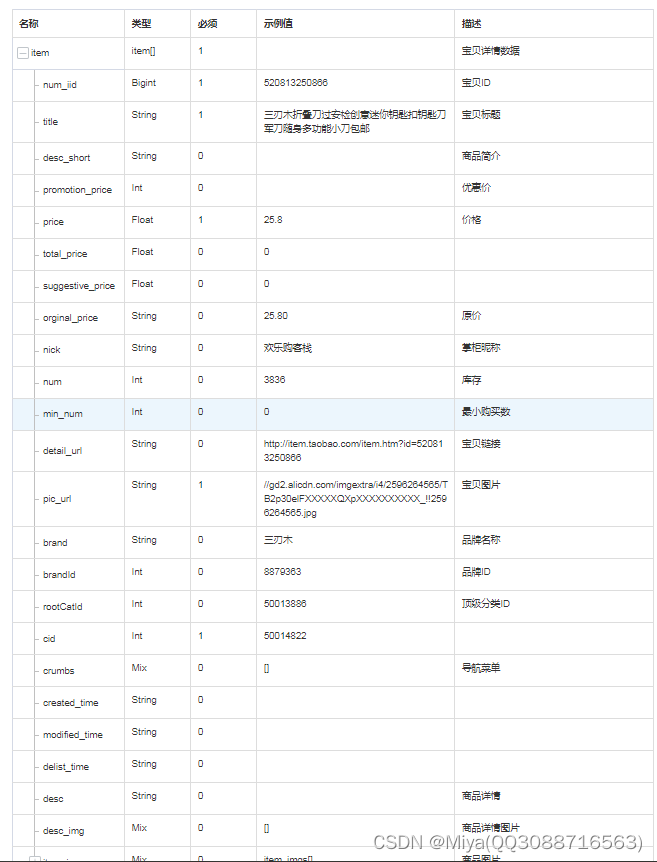
接下来对每个模块进行细讲,首先是 Embedding 层。对于标准的 Transformer 模块,要求的输入是 token 向量的序列,即二维矩阵 [num_token, token_dim]。在具体的代码实现过程中呢,我们实际是通过一个卷积层来实现以 ViT-B/16 为例,使用卷积核大小为 16 × 16 16 \times 1616×16, stride 为 16,卷积核个数为 768 来实现的,即 [224,224,3] --> [14,14,768] --> [196, 768]。即一共 196 个token,每个 token 向量长度为 768。此外我们还需要加上一个类别的 token,为此我们实际上是初始化了一个可训练的参数 [1, 768],将其与 token 序列进行拼接得到 Cat([1, 768], [196,768]) --> [197, 768]。然后再叠加上位置编码 Position Embedding: [197,768] --> [197, 768]。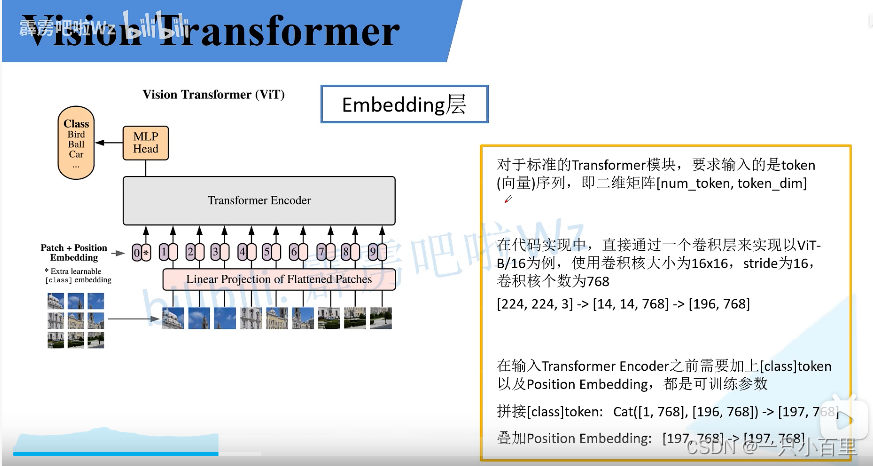
再详细考虑下 Position Embedding,如果不是用 Position Embedding 得到的结果是 0.61382,使用一维的位置编码得到的结果是 0.64206,明显比不使用位置编码高了三个百分点。使用 2D 以及相对位置编码其实和 1D 差不多啊。论文中也提到说 the difference in how to encoder spatial information is less important,即位置编码的差异其实不是特别重要。1D 的话,简单效果好参数少,所以默认使用 1D 的位置编码。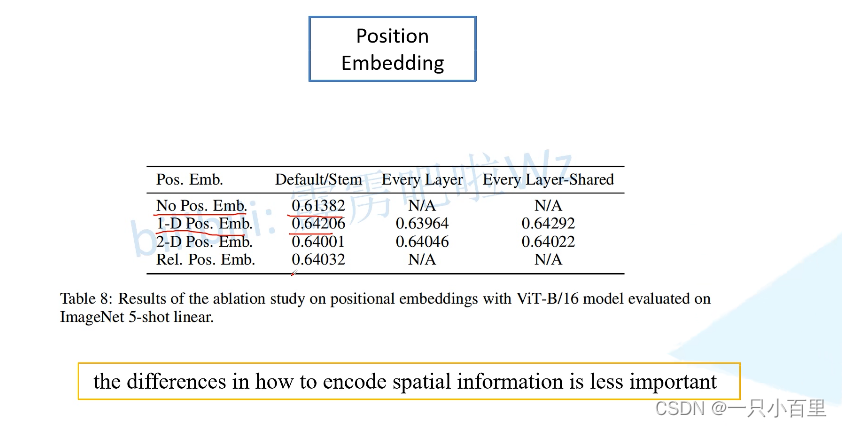
论文中有给这样一个图,我们训练得到的位置编码与其他位置编码之间的余弦相似度。这里的 patches 大小是 32 × 32 32 \times 3232×32 的,224 / 32 = 7 224/32=7224/32=7,所以这里的大小是 7 × 7 7 \times 77×7。这张图怎么理解呢?我们会在每个 token 上叠加一个位置编码,中间那个图的 49 个小图中,每个小图其实也是 7 × 7 7 \times 77×7 的。左上角第一行第一个 patch 的位置编码与自己的位置编码是一样的,所以余弦相似度是1,所以左上角是黄色。然后在与其他位置编码进行计算。就得到了左上角的小图。其他的也都是类似的规律。注意,这个是学出来的。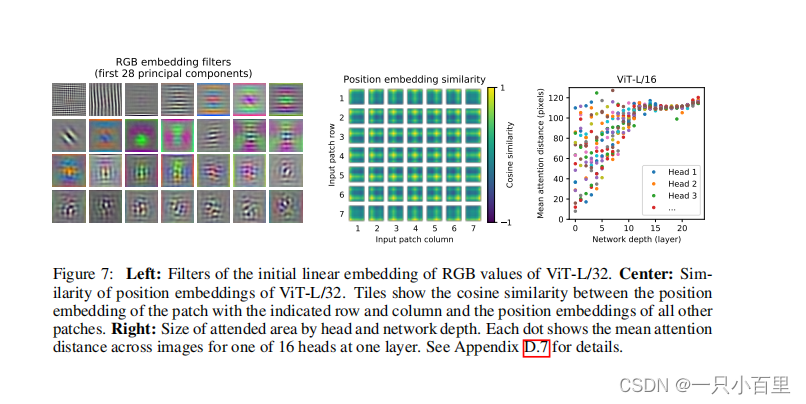
2.2 Transformer Encoder 层
Transformer Encoder 就是将 Encoder Block 重复堆叠 L 次。我们来看看单个 Encoder Block。首先输入一个 Norm 层,这里的 Norm 指的是 Layer Normalization 层(有论文比较了 BN 在 transformer 中为什么不好,不如 LN |这里先 Norm 再 Multihead Attention 也是有论文研究的,原始的 Transformer 先 Attention 再 Norm,此外这个先 Norm 再操作和 DenseNet 的先 BN 再 Conv 异曲同工)。经过 LN 后经过 Multi-Head Attention,然后源码经过 Dropout 层,有些复现大神使用的是 DropPath 方法,根据以往的经验可能使用后者会更好一点。然后残差之后经过 LN,MLP Block,Dropout/DropPath 之后残差即可。
MLP Block 其实也很简单,就是一个全连接,GELU 激活函数,Dropout,全连接,Dropout。需要注意第一个全连接层的节点个数是输入向量长度的 4 倍,第二个全连接层会还原会原来的大小。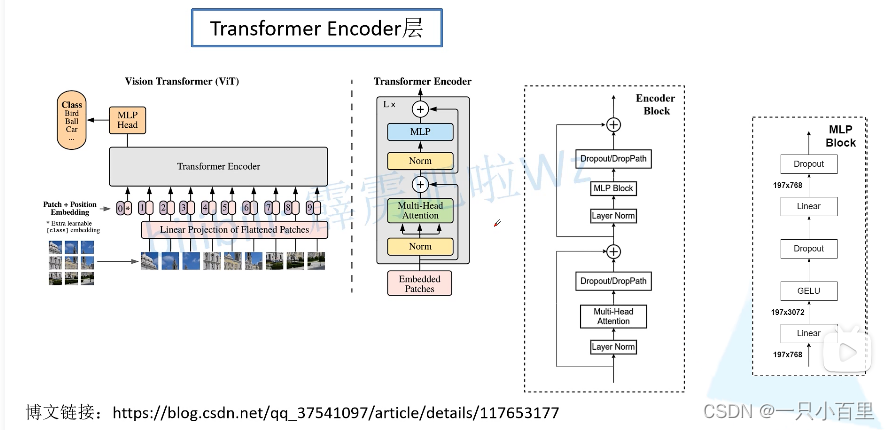
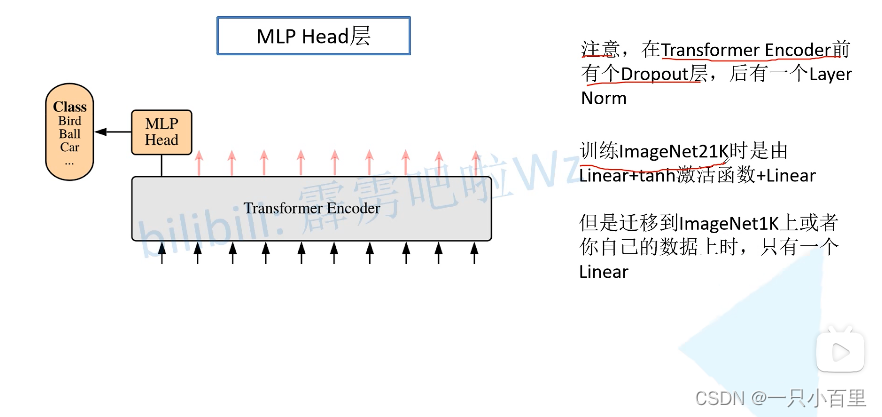
有一个地方要注意,在 Transformer Encoder 前有个 Dropout 层,在之后有一个 Layer Norm 层,这些在图中还没有画出来的。在 Transformer Encoder 前有个 Dropout 层,对此我的理解是在原图上随机加 Mask 遮挡,然后依然要进行分类。
2.3 MLP Head 层
在训练 ImageNet21K 时候是由 Linear + tanh 激活函数 + Linear 构成的。但是迁移到 ImageNet1k 之后或者做迁移学习时,其实只需要一个 Linear 就足够了。(获得类别概率需要一个 softmax)
2.4 ViT B/16
我们来从头梳理一次 ViT B/16 的结构,假设输入图为 224 × 224 × 3 224 \times 224 \times 3224×224×3,首先经过一个卷积层,然后进行高度和宽度方向的展平处理。紧接着 concat 一个 class token,再加上 Position Embedding 的相加操作,这里的 Position Embedding 也是可训练的参数。经过 Dropout 之后输入 12 个堆叠的 Encoder Block。Encoder 输出经过 LN 得到的输出为 197 × 768 197 \times 768197×768,即是不变的。然后我们提取第一个 class token 对应的输出,切片之后即变成了 1 × 768 1 \times 7681×768,将其输入 MLP Head 中。如果在 ImageNet21K 预训练的时候,Pre-Logits 就是一个全连接层,tanh 激活函数。如果是在 ImageNet1k 或者自己的数据集上的时候训练的时候,可以不要这个 Pre-Logits。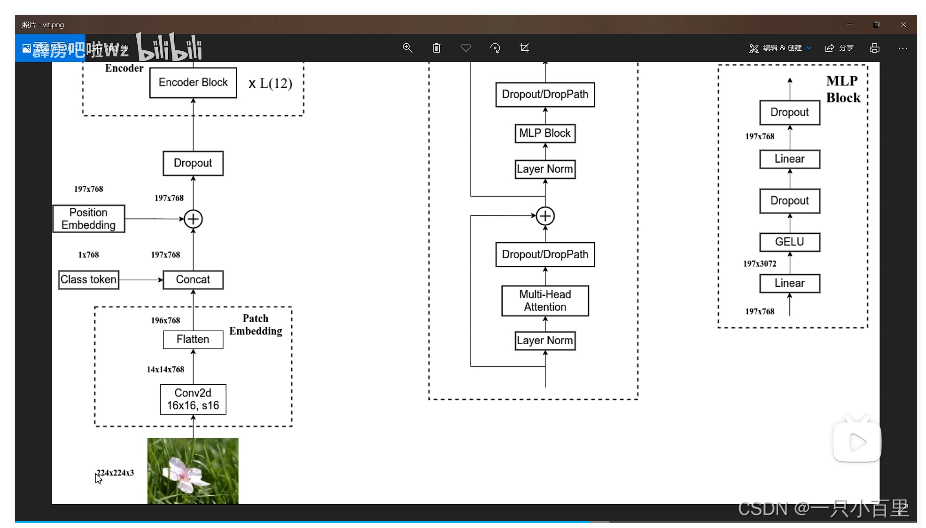
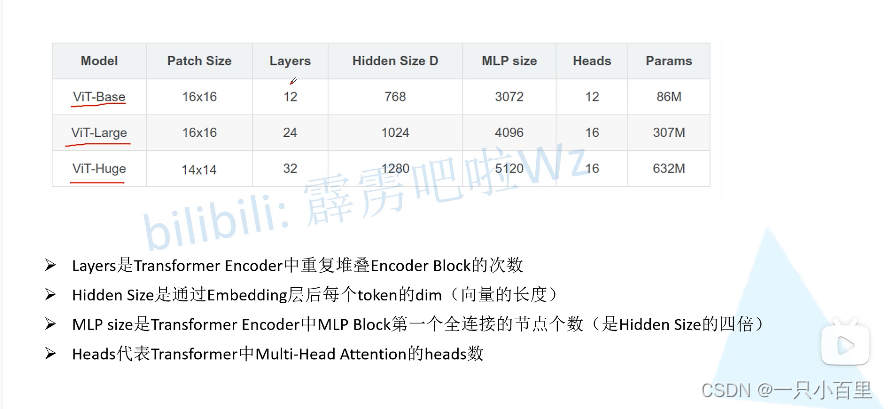
2.5 ViT 模型参数
我们来看看论文给出的 ViT 模型的参数。ViT B 对应的就是 ViT-Base,ViT L 对应的是 ViT-Large,ViT H 对应的是 ViT-Huge。patch size 是图片切片大小(源码中还有 32 × 32 32 \times 3232×32 的);layers 则是 encoder block 堆叠的次数;Hidden size 是 token 向量的长度;MLP size 是 Hidden size 的四倍,即 Encoder block 中 MLP block 第一个全连接层节点个数;Heads 则是 Multi-head Attention 中 heads 的个数。
三.hybrid混合模型
我们来看看 CNN 和 Transformer 的混合模型。首先用传统的神经网络 backbone 来提取特征,然后再通过 ViT 模型进一步得到最终的结果。这里的特征提取部分采用的是 ResNet50 网络,但是和原来的有所不同,第一点是采用 stdConv2d,第二点则是使用GN而非BN,第三点是将 stage4 中的 3 个 block 移动到 stage3 中。R50 backbone 的输出为 14 × 14 × 1024 14 \times 14 \times 102414×14×1024,然后通过 1 × 1 1 \times 11×1 卷积变为 14 × 14 × 768 14 \times 14 \times 76814×14×768,然后进行展平处理就得到 token 了。之后就是和 ViT 一摸一样的了。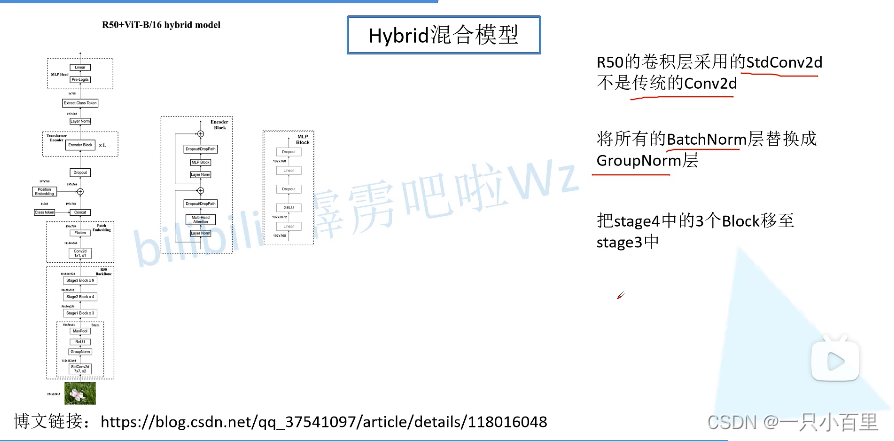
结果可见,混合模型比纯 transformer 模型的效果会好一些,这也是迁移学习之后的结果。在少量微调中混合模型占有,但是随着迭代次数的上升,纯 transformer 也能达到混合模型的效果,例如 14 个 epoches 时 ViT-L/16 和 Res50x1+ViT-L/16 就基本一样了。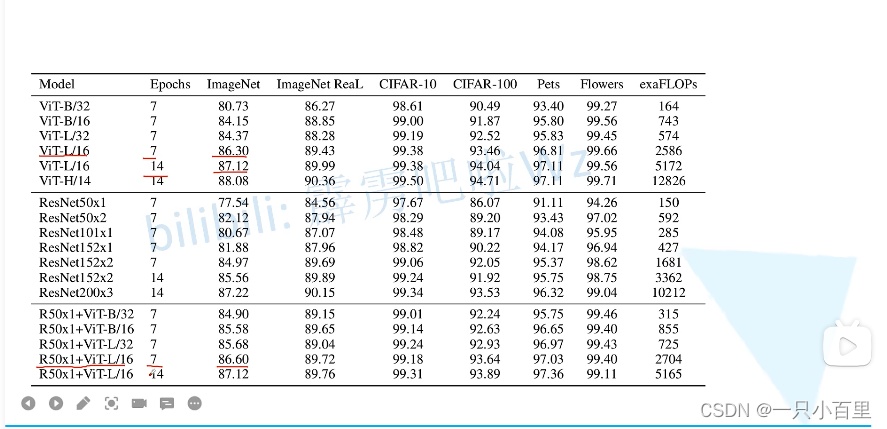
代码
"""
original code from rwightman:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
"""
from functools import partial
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1) # work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
random_tensor = keep_prob + torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
"""
2D Image to Patch Embedding
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=16, in_c=3, embed_dim=768, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = (img_size, img_size)
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.grid_size = (img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1])
self.num_patches = self.grid_size[0] * self.grid_size[1]
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_c, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
B, C, H, W = x.shape
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({H}*{W}) doesn't match model ({self.img_size[0]}*{self.img_size[1]})."
# flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW]
# transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C]
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim, # 输入token的dim
num_heads=8,
qkv_bias=False,
qk_scale=None,
attn_drop_ratio=0.,
proj_drop_ratio=0.):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop_ratio)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
# [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim]
B, N, C = x.shape
# qkv(): -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, num_patches + 1]
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, num_patches + 1]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class Mlp(nn.Module):
"""
MLP as used in Vision Transformer, MLP-Mixer and related networks
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim,
num_heads,
mlp_ratio=4.,
qkv_bias=False,
qk_scale=None,
drop_ratio=0.,
attn_drop_ratio=0.,
drop_path_ratio=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = Attention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, proj_drop_ratio=drop_ratio)
# NOTE: drop path for stochastic depth, we shall see if this is better than dropout here
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path_ratio) if drop_path_ratio > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=16, in_c=3, num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=768, depth=12, num_heads=12, mlp_ratio=4.0, qkv_bias=True,
qk_scale=None, representation_size=None, distilled=False, drop_ratio=0.,
attn_drop_ratio=0., drop_path_ratio=0., embed_layer=PatchEmbed, norm_layer=None,
act_layer=None):
"""
Args:
img_size (int, tuple): input image size
patch_size (int, tuple): patch size
in_c (int): number of input channels
num_classes (int): number of classes for classification head
embed_dim (int): embedding dimension
depth (int): depth of transformer
num_heads (int): number of attention heads
mlp_ratio (int): ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim
qkv_bias (bool): enable bias for qkv if True
qk_scale (float): override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
representation_size (Optional[int]): enable and set representation layer (pre-logits) to this value if set
distilled (bool): model includes a distillation token and head as in DeiT models
drop_ratio (float): dropout rate
attn_drop_ratio (float): attention dropout rate
drop_path_ratio (float): stochastic depth rate
embed_layer (nn.Module): patch embedding layer
norm_layer: (nn.Module): normalization layer
"""
super(VisionTransformer, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_features = self.embed_dim = embed_dim # num_features for consistency with other models
self.num_tokens = 2 if distilled else 1
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6)
act_layer = act_layer or nn.GELU
self.patch_embed = embed_layer(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_c=in_c, embed_dim=embed_dim)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.dist_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim)) if distilled else None
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + self.num_tokens, embed_dim))
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_ratio)
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_ratio, depth)] # stochastic depth decay rule
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[
Block(dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop_ratio=drop_ratio, attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, drop_path_ratio=dpr[i],
norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
# Representation layer
if representation_size and not distilled:
self.has_logits = True
self.num_features = representation_size
self.pre_logits = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("fc", nn.Linear(embed_dim, representation_size)),
("act", nn.Tanh())
]))
else:
self.has_logits = False
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
# Classifier head(s)
self.head = nn.Linear(self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.head_dist = None
if distilled:
self.head_dist = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
# Weight init
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
if self.dist_token is not None:
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.dist_token, std=0.02)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
self.apply(_init_vit_weights)
def forward_features(self, x):
# [B, C, H, W] -> [B, num_patches, embed_dim]
x = self.patch_embed(x) # [B, 196, 768]
# [1, 1, 768] -> [B, 1, 768]
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
if self.dist_token is None:
x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1) # [B, 197, 768]
else:
x = torch.cat((cls_token, self.dist_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1), x), dim=1)
x = self.pos_drop(x + self.pos_embed)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.norm(x)
if self.dist_token is None:
return self.pre_logits(x[:, 0])
else:
return x[:, 0], x[:, 1]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
if self.head_dist is not None:
x, x_dist = self.head(x[0]), self.head_dist(x[1])
if self.training and not torch.jit.is_scripting():
# during inference, return the average of both classifier predictions
return x, x_dist
else:
return (x + x_dist) / 2
else:
x = self.head(x)
return x
def _init_vit_weights(m):
"""
ViT weight initialization
:param m: module
"""
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.01)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out")
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
def vit_base_patch16_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Base model (ViT-B/16) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_base_patch16_224_in21k-e5005f0a.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
representation_size=768 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_base_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Base model (ViT-B/32) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_base_patch32_224_in21k-8db57226.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=32,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
representation_size=768 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_large_patch16_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Large model (ViT-L/16) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_large_patch16_224_in21k-606da67d.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=1024,
depth=24,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1024 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_large_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Large model (ViT-L/32) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_large_patch32_224_in21k-9046d2e7.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=32,
embed_dim=1024,
depth=24,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1024 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_huge_patch14_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Huge model (ViT-H/14) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
NOTE: converted weights not currently available, too large for github release hosting.
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=14,
embed_dim=1280,
depth=32,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1280 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
参考博文:深度学习之图像分类(十八)-- Vision Transformer(ViT)网络详解_vit网络_木卯_THU的博客-CSDN博客