使用递归算法实现冒泡:
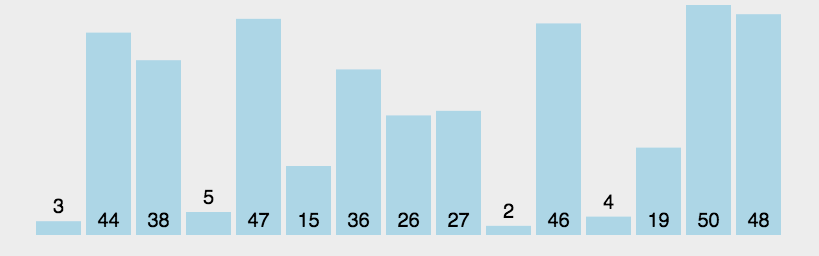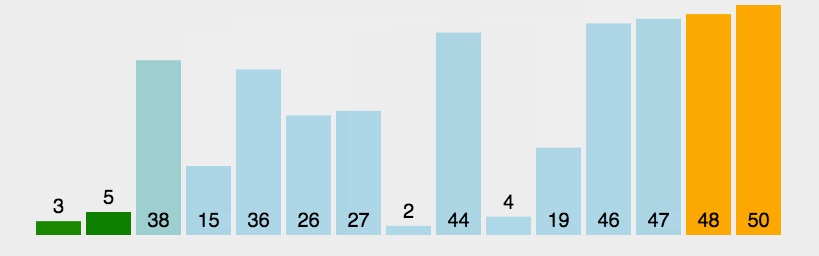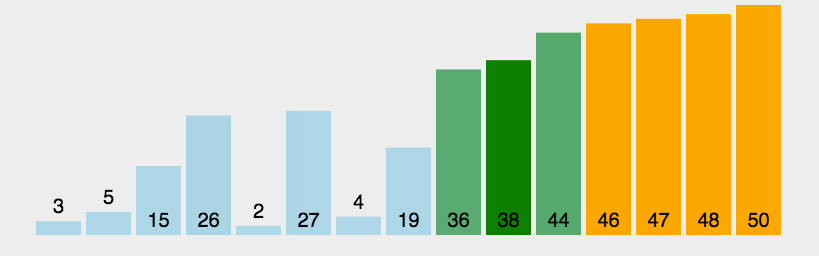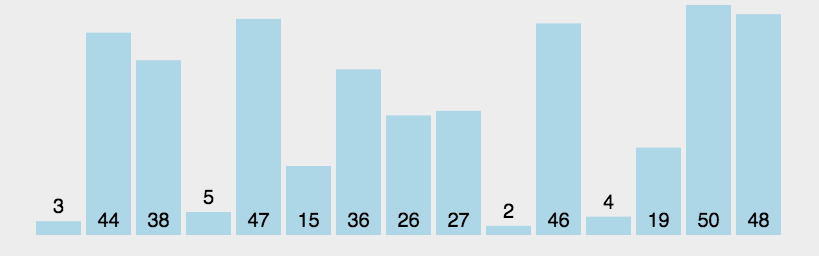
package com.nami.algorithm.study.day06;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* beyond u self and trust u self.
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2023-09-05 15:36
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class BubbleSort2 {
// public static void sort(int[] target, int num) {
// if (num == 0) {
// return;
// }
// bubble(target, num-1);
//
// sort(target, num-1);
// }
//
// private static void bubble(int[] target, int j) {
// for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
// if (target[i] > target[i + 1]) {
// int temp = target[i];
// target[i] = target[i+1];
// target[i+1] = temp;
// }
// }
// }
public static void sort(int[] target) {
bubble(target, target.length -1 );
}
private static void bubble(int[] target, int j) {
if (j == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (target[i] > target[i + 1]) {
int temp = target[i];
target[i] = target[i+1];
target[i+1] = temp;
}
}
bubble(target, j - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] test = new int[]{1, 54, 234, 675, 32432, 23, 78, 459, 354, 9, 344, 22, 46, 85, 236, 3278, 245, 83, 154, 2, 1, 34, 73, 23};
int[] test2= new int[] {2,4,7,3,2,1};
// sort(test, test.length);
sort(test2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test2));
}
}
优化数组稳定得情况, 减少无意义遍历,新增参数x, 标识是否发生了挪动,递归时使用x索引,非常巧妙。递归妙
package com.nami.algorithm.study.day06;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* beyond u self and trust u self.
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2023-09-05 15:36
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class BubbleSort {
public static void sort(int[] target) {
bubble(target, target.length -1 );
}
private static void bubble(int[] target, int j) {
if (j == 0) {
return;
}
// 变换标识 索引i
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (target[i] > target[i + 1]) {
int temp = target[i];
target[i] = target[i+1];
target[i+1] = temp;
x = i;
}
}
bubble(target, x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] test = new int[]{1, 54, 234, 675, 32432, 23, 78, 459, 354, 9, 344, 22, 46, 85, 236, 3278, 245, 83, 154, 2, 1, 34, 73, 23};
int[] test2= new int[] {2,4,7,3,2,1};
// sort(test, test.length);
sort(test2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test2));
}
}