目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 Theta*算法局限性
- 2 Lazy Theta*算法原理
- 3 Theta* VS. Lazy Theta*
- 4 仿真实现
- 4.1 ROS C++实现
- 4.2 Python实现
- 4.3 Matlab实现
0 专栏介绍
🔥附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码🔥课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
🚀详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 Theta*算法局限性
Theta*的运行瓶颈在于,每次扩展节点 v v v的邻节点 w w w时,都需要对 p a r e n t ( v ) \mathrm{parent}(v) parent(v)和 w w w进行一次Bresenham视线检测。然而,大部分邻节点最终不会被扩展,大量应用在视线检测上的计算资源被浪费。

Theta*的变种算法Lazy Theta*算法通过延迟评估技术提升Theta*的路径搜索速度。实验证明,在26邻域三维地图上,Lazy Theta*的视线检查数量比Theta*减少了一个数量级,且路径长度没有增加。
2 Lazy Theta*算法原理
Lazy Theta*在扩展节点
v
v
v的邻节点
w
w
w时,默认
p
a
r
e
n
t
(
v
)
\mathrm{parent}(v)
parent(v)和
w
w
w间存在视线,而无需对
p
a
r
e
n
t
(
v
)
\mathrm{parent}(v)
parent(v)和
w
w
w进行碰撞检测。当以节点
w
w
w为基础开始扩展时,才正式对它与父节点
p
a
r
e
n
t
(
v
)
\mathrm{parent}(v)
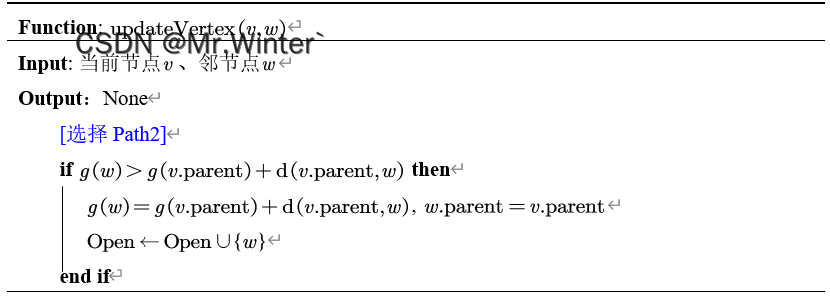
parent(v)计算视线。若视线存在,则无需更新信息(path2);若视线不存在,则在邻域重新选择父节点(path1)。
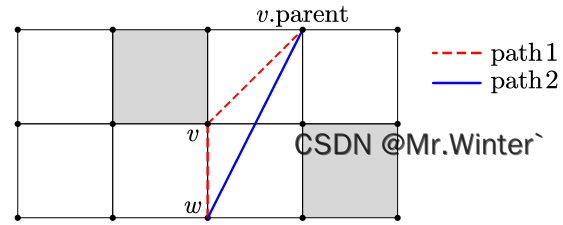
Lazy Theta*的算法流程如下所示。

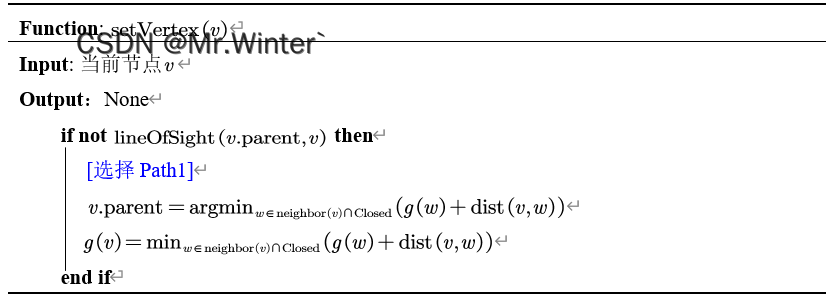
3 Theta* VS. Lazy Theta*
Lazy Theta*牺牲了一定的路径优度,因为节点 v v v与其父节点间可能存在障碍,使节点 v v v的 g g g值往往小于真实值,导致从Open表中取出的优先节点可能并非最优的,所以Lazy Theta*的规划路径可能会更长。同时,当判定节点 与其父节点间存在障碍后, v v v的父节点只能从邻域中更新,可能产生锯齿。Theta*与Lazy Theta*的对比实例如下
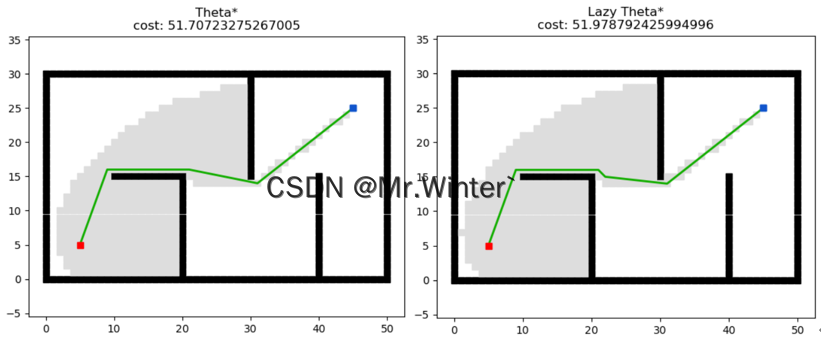
4 仿真实现
4.1 ROS C++实现
核心代码如下
bool LazyThetaStar::plan(const unsigned char* global_costmap, const Node& start, const Node& goal,
std::vector<Node>& path, std::vector<Node>& expand)
{
// initialize
costs_ = global_costmap;
closed_list_.clear();
path.clear();
expand.clear();
motion_ = getMotion();
// push the start node into open list
std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, compare_cost> open_list;
open_list.push(start);
// main process
while (!open_list.empty())
{
// pop current node from open list
Node current = open_list.top();
open_list.pop();
_setVertex(current);
if (current.g_ >= INFINITE_COST)
continue;
// current node does not exist in closed list
if (closed_list_.find(current) != closed_list_.end())
continue;
closed_list_.insert(current);
expand.push_back(current);
// goal found
if (current == goal)
{
path = _convertClosedListToPath(closed_list_, start, goal);
return true;
}
// explore neighbor of current node
for (const auto& m : motion_)
{
// explore a new node
// path 1
Node node_new = current + m; // add the x_, y_, g_
node_new.h_ = dist(node_new, goal);
node_new.id_ = grid2Index(node_new.x_, node_new.y_);
node_new.pid_ = current.id_;
// current node do not exist in closed list
if (closed_list_.find(node_new) != closed_list_.end())
continue;
// next node hit the boundary or obstacle
if ((node_new.id_ < 0) || (node_new.id_ >= ns_) || (costs_[node_new.id_] >= lethal_cost_ * factor_))
continue;
// get parent node
Node parent;
parent.id_ = current.pid_;
index2Grid(parent.id_, parent.x_, parent.y_);
auto find_parent = closed_list_.find(parent);
if (find_parent != closed_list_.end())
{
parent = *find_parent;
// path 2
_updateVertex(parent, node_new);
}
open_list.push(node_new);
}
}
return false;
}

4.2 Python实现
核心代码如下
def plan(self):
# OPEN set with priority and CLOSED set
OPEN = []
heapq.heappush(OPEN, self.start)
CLOSED = []
while OPEN:
node = heapq.heappop(OPEN)
# set vertex: path 1
try:
...
except:
pass
# exists in CLOSED set
if node in CLOSED:
continue
# goal found
if node == self.goal:
CLOSED.append(node)
return self.extractPath(CLOSED), CLOSED
for node_n in self.getNeighbor(node):
# exists in CLOSED set
if node_n in CLOSED:
continue
# path1
node_n.parent = node.current
node_n.h = self.h(node_n, self.goal)
try:
p_index = CLOSED.index(Node(node.parent))
node_p = CLOSED[p_index]
except:
node_p = None
if node_p:
# path2
self.updateVertex(node_p, node_n)
# goal found
if node_n == self.goal:
heapq.heappush(OPEN, node_n)
break
# update OPEN set
heapq.heappush(OPEN, node_n)
CLOSED.append(node)
return ([], []), []
4.3 Matlab实现
核心代码如下
while ~isempty(OPEN)
% pop
f = OPEN(:, 3) + OPEN(:, 4);
[~, index] = min(f);
cur_node = OPEN(index, :);
OPEN(index, :) = [];
% set vertex: path 1
p_index = loc_list(cur_node(5: 6), CLOSED, [1, 2]);
...
% exists in CLOSED set
if loc_list(cur_node, CLOSED, [1, 2])
continue
end
% update expand zone
if ~loc_list(cur_node, EXPAND, [1, 2])
EXPAND = [EXPAND; cur_node(1:2)];
end
% goal found
if cur_node(1) == goal(1) && cur_node(2) == goal(2)
CLOSED = [cur_node; CLOSED];
goal_reached = true;
cost = cur_node(3);
break
end
if (cur_node(1) ==17) &&(cur_node(2) == 26)
cur_node(1);
end
% explore neighbors
for i = 1:motion_num
% path 1
node_n = [
cur_node(1) + motion(i, 1), ...
cur_node(2) + motion(i, 2), ...
cur_node(3) + motion(i, 3), ...
0, ...
cur_node(1), cur_node(2)];
node_n(4) = h(node_n(1:2), goal);
% exists in CLOSED set
if loc_list(node_n, CLOSED, [1, 2])
continue
end
% obstacle
if map(node_n(1), node_n(2)) == 2
continue
end
p_index = loc_list(cur_node(5: 6), CLOSED, [1, 2]);
if p_index
node_p = CLOSED(p_index, :);
else
node_p = 0;
end
if node_p ~= 0
node_n = update_vertex(node_p, node_n);
end
% update OPEN set
OPEN = [OPEN; node_n];
end
CLOSED = [cur_node; CLOSED];
end

完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
🔥 更多精彩专栏:
- 《ROS从入门到精通》
- 《Pytorch深度学习实战》
- 《机器学习强基计划》
- 《运动规划实战精讲》
- …