前言
上一文中,我们从官方的图示了解到Nacos的服务数据结构。但我关心的是,Nacos2.x不是重构了吗?怎么还是这种数据结构?我推测,必然是为了对Nacos1.x的兼容,实际存储应该不是这样的。于是,沿着这个问题出发我们一起来翻一下源码。
从NamingService的使用开始
在扎入源码之前,我们需要回忆一下,我们是怎么使用Nacos的?
- 构建NamingService
NamingService serviceRegistry = NacosFactory.createNamingService(properties);
实际上,这个动作的背后,意味着我们连接了Nacos服务端。 - 注册服务
serviceRegistry.registerInstance(serviceName, groupName, instance); - 查询服务
serviceRegistry.getAllInstances(serviceName, groupName, List.of(clusterName));
因此,我们就沿着这几个操作,摸一摸源码。
!!!高能警告!!!
没有耐心看源码的同学,可以直接翻到总结,直接看结论。
构建NamingService
客户端
// com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.NacosNamingService
/**
* 初始化方法
* <p>由NacosNamingService构造器调用,用于初始NamingService</p>
*/
private void init(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
final NacosClientProperties nacosClientProperties = NacosClientProperties.PROTOTYPE.derive(properties);
// 省略...
// 创建客户端
this.clientProxy = new NamingClientProxyDelegate(this.namespace, serviceInfoHolder, nacosClientProperties, changeNotifier);
}
// com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.remote.NamingClientProxyDelegate
/**
* NamingClientProxyDelegate构造器
*/
public NamingClientProxyDelegate(String namespace, ServiceInfoHolder serviceInfoHolder, NacosClientProperties properties,
InstancesChangeNotifier changeNotifier) throws NacosException {
// 省略...
// 初始化了两个客户端,一个是Http,另一个是Grpc。不过,在注册实例时,如果该实例为临时实例,则使用Grpc,因此我们重点关注Grpc
this.httpClientProxy = new NamingHttpClientProxy(namespace, securityProxy, serverListManager, properties);
this.grpcClientProxy = new NamingGrpcClientProxy(namespace, securityProxy, serverListManager, properties,
serviceInfoHolder);
}
// com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.remote.gprc.NamingGrpcClientProxy
/**
* NamingGrpcClientProxy构造器
*/
public NamingGrpcClientProxy(String namespaceId, SecurityProxy securityProxy, ServerListFactory serverListFactory,
NacosClientProperties properties, ServiceInfoHolder serviceInfoHolder) throws NacosException {
// 省略...
// 创建RPC客户端
this.rpcClient = RpcClientFactory.createClient(uuid, ConnectionType.GRPC, labels);
this.redoService = new NamingGrpcRedoService(this);
// 启动客户端
start(serverListFactory, serviceInfoHolder);
}
// com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.remote.gprc.NamingGrpcClientProxy
private void start(ServerListFactory serverListFactory, ServiceInfoHolder serviceInfoHolder) throws NacosException {
rpcClient.serverListFactory(serverListFactory);
rpcClient.registerConnectionListener(redoService);
rpcClient.registerServerRequestHandler(new NamingPushRequestHandler(serviceInfoHolder));
// 启动客户端
rpcClient.start();
NotifyCenter.registerSubscriber(this);
}
// com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.RpcClient#start
/**
* 启动客户端
*/
public final void start() throws NacosException {
// 控制只启动一次
boolean success = rpcClientStatus.compareAndSet(RpcClientStatus.INITIALIZED, RpcClientStatus.STARTING);
if (!success) {
return;
}
// 创建一个只有2个线程的定时任务线程池
clientEventExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2, r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.remote.worker");
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
});
// 提交-处理连接事件的Task
clientEventExecutor.submit(() -> {
while (!clientEventExecutor.isTerminated() && !clientEventExecutor.isShutdown()) {
ConnectionEvent take;
take = eventLinkedBlockingQueue.take();
if (take.isConnected()) {
notifyConnected();
} else if (take.isDisConnected()) {
notifyDisConnected();
}
}
});
// 提交-心跳任务
clientEventExecutor.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
// 由于这里有一大堆逻辑,省略。
// 1. 超过时间间隔,发起心跳请求
// 1.1 心跳请求失败,记录当前状态为不健康,并记录上下文。
// 1.2 检查当前配置的推荐的Nacos服务器是否在服务器列表中。在,则尝试重新连接推荐的服务器。
});
// connect to server, try to connect to server sync retryTimes times, async starting if failed.
// 连接服务端,尝试retryTimes次,同步地连接服务端,如果依然失败,则改为异步连接。
Connection connectToServer = null;
rpcClientStatus.set(RpcClientStatus.STARTING);
int startUpRetryTimes = rpcClientConfig.retryTimes();
while (startUpRetryTimes > 0 && connectToServer == null) {
try {
startUpRetryTimes--;
ServerInfo serverInfo = nextRpcServer();
// 连接服务器
connectToServer = connectToServer(serverInfo);
} catch (Throwable e) {
LoggerUtils.printIfWarnEnabled(LOGGER,
"[{}] Fail to connect to server on start up, error message = {}, start up retry times left: {}",
rpcClientConfig.name(), e.getMessage(), startUpRetryTimes, e);
}
}
if (connectToServer != null) {
this.currentConnection = connectToServer;
rpcClientStatus.set(RpcClientStatus.RUNNING);
eventLinkedBlockingQueue.offer(new ConnectionEvent(ConnectionEvent.CONNECTED));
} else {
switchServerAsync();
}
registerServerRequestHandler(new ConnectResetRequestHandler());
// register client detection request.
// 注册客户端检测请求处理器,用于响应服务端的探测
registerServerRequestHandler(request -> {
if (request instanceof ClientDetectionRequest) {
return new ClientDetectionResponse();
}
return null;
});
}
服务端-处理连接请求
服务端的源码首先我们得找到GrpcServer
@Override
public void startServer() throws Exception {
// 1. 创建请求处理器注册器
final MutableHandlerRegistry handlerRegistry = new MutableHandlerRegistry();
// 2. 注册请求处理器,并封装拦截器器。封装后,有点类似于SpringMVC的HandlerAdapter
addServices(handlerRegistry, new GrpcConnectionInterceptor());
NettyServerBuilder builder = NettyServerBuilder.forPort(getServicePort()).executor(getRpcExecutor());
// 省略
server = builder.maxInboundMessageSize(getMaxInboundMessageSize()).fallbackHandlerRegistry(handlerRegistry)
.compressorRegistry(CompressorRegistry.getDefaultInstance())
.decompressorRegistry(DecompressorRegistry.getDefaultInstance())
.addTransportFilter(new AddressTransportFilter(connectionManager))
.keepAliveTime(getKeepAliveTime(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.keepAliveTimeout(getKeepAliveTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.permitKeepAliveTime(getPermitKeepAliveTime(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.build();
// 启动服务
server.start();
}
private void addServices(MutableHandlerRegistry handlerRegistry, ServerInterceptor... serverInterceptor) {
// unary common call register.
// 通用调用注册
final MethodDescriptor<Payload, Payload> unaryPayloadMethod = MethodDescriptor.<Payload, Payload>newBuilder()
.setType(MethodDescriptor.MethodType.UNARY)
.setFullMethodName(MethodDescriptor.generateFullMethodName(GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_SERVICE_NAME,
GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_METHOD_NAME))
.setRequestMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance()))
.setResponseMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance())).build();
// 定义服务器调用处理器。核心处理逻辑可就在这lambda表达式定义的匿名内部类里了。也只有一个方法:
// grpcCommonRequestAcceptor.request(request, responseObserver)
final ServerCallHandler<Payload, Payload> payloadHandler = ServerCalls
.asyncUnaryCall((request, responseObserver) -> grpcCommonRequestAcceptor.request(request, responseObserver));
final ServerServiceDefinition serviceDefOfUnaryPayload = ServerServiceDefinition.builder(
GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_SERVICE_NAME)
.addMethod(unaryPayloadMethod, payloadHandler).build();
handlerRegistry.addService(ServerInterceptors.intercept(serviceDefOfUnaryPayload, serverInterceptor));
// bi stream register.
// bi流式调用服务,主要是连接请求、连接断开
// 核心处理逻辑:
// grpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor.requestBiStream(responseObserver)
final ServerCallHandler<Payload, Payload> biStreamHandler = ServerCalls.asyncBidiStreamingCall(
(responseObserver) -> grpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor.requestBiStream(responseObserver));
final MethodDescriptor<Payload, Payload> biStreamMethod = MethodDescriptor.<Payload, Payload>newBuilder()
.setType(MethodDescriptor.MethodType.BIDI_STREAMING).setFullMethodName(MethodDescriptor
.generateFullMethodName(GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_BI_STREAM_SERVICE_NAME,
GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_BI_STREAM_METHOD_NAME))
.setRequestMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.newBuilder().build()))
.setResponseMarshaller(ProtoUtils.marshaller(Payload.getDefaultInstance())).build();
final ServerServiceDefinition serviceDefOfBiStream = ServerServiceDefinition
.builder(GrpcServerConstants.REQUEST_BI_STREAM_SERVICE_NAME).addMethod(biStreamMethod, biStreamHandler).build();
handlerRegistry.addService(ServerInterceptors.intercept(serviceDefOfBiStream, serverInterceptor));
}
处理连接请求:
// com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.grpc.GrpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor
@Override
public StreamObserver<Payload> requestBiStream(StreamObserver<Payload> responseObserver) {
StreamObserver<Payload> streamObserver = new StreamObserver<Payload>() {
final String connectionId = GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get();
final Integer localPort = GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_LOCAL_PORT.get();
final int remotePort = GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_PORT.get();
String remoteIp = GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_IP.get();
String clientIp = "";
@Override
public void onNext(Payload payload) {
// 处理连接请求
clientIp = payload.getMetadata().getClientIp();
traceDetailIfNecessary(payload);
Object parseObj;
// 省略...
// 检查
if (parseObj instanceof ConnectionSetupRequest) {
ConnectionSetupRequest setUpRequest = (ConnectionSetupRequest) parseObj;
// 设置label,省略
// 构建Connection
ConnectionMeta metaInfo = new ConnectionMeta(connectionId, payload.getMetadata().getClientIp(),
remoteIp, remotePort, localPort, ConnectionType.GRPC.getType(),
setUpRequest.getClientVersion(), appName, setUpRequest.getLabels());
metaInfo.setTenant(setUpRequest.getTenant());
// 第三个参数Channel,是发生网路数据的关键
Connection connection = new GrpcConnection(metaInfo, responseObserver, GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CHANNEL.get());
connection.setAbilities(setUpRequest.getAbilities());
boolean rejectSdkOnStarting = metaInfo.isSdkSource() && !ApplicationUtils.isStarted();
// 注册连接, 重点在 “或” 条件上
// connectionManager.register
if (rejectSdkOnStarting || !connectionManager.register(connectionId, connection)) {
//Not register to the connection manager if current server is over limit or server is starting.
// 如果当前服务器已超限制,或者服务器还在启动过程中,则注册失败。
connection.request(new ConnectResetRequest(), 3000L);
connection.close();
}
}
// 省略。。。
}
// 省略。。。
};
return streamObserver;
}
这里出现了我们接触到的第一个概念:Connection-连接,他有个属性ConnectionMeta,记录连接相关的信息。当需要发起请求时,他会将这些信息设置到Request中,然后通过GrpcUtils转换成Payload发出请求
继续看com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.ConnectionManager#register
public synchronized boolean register(String connectionId, Connection connection) {
if (connection.isConnected()) {
String clientIp = connection.getMetaInfo().clientIp;
// 省略入参检查
// 注册客户端
connections.put(connectionId, connection);
// 登记客户端IP
if (!connectionForClientIp.containsKey(clientIp)) {
connectionForClientIp.put(clientIp, new AtomicInteger(0));
}
connectionForClientIp.get(clientIp).getAndIncrement();
// 通知客户端连接Listener
clientConnectionEventListenerRegistry.notifyClientConnected(connection);
return true;
}
return false;
}
此处出现第一个Manager:ConnectionManager。用来管理所有客户端的连接。登记连接后,调用了所有的Listener的clientConnected方法。其中,有个ConnectionBasedClientManager,看名字就知道,可能是负责管理客户端的。
// > ConnectionBasedClientManager#clientConnected(com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.Connection)
// > ConnectionBasedClientManager#clientConnected(java.lang.String, com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.client.ClientAttributes)
// ConnectionBasedClientManager
@Override
public boolean clientConnected(String clientId, ClientAttributes attributes) {
String type = attributes.getClientAttribute(ClientConstants.CONNECTION_TYPE);
ClientFactory clientFactory = ClientFactoryHolder.getInstance().findClientFactory(type);
// 通过ClientFactory创建客户端
// 从以上的两行代码,我们通过ClientConstants.CONNECTION_TYPE就知道工厂是ConnectionBasedClientFactory,对应的客户端自然是ConnectionBasedClient
return clientConnected(clientFactory.newClient(clientId, attributes));
}
@Override
public boolean clientConnected(final Client client) {
// 登记客户端
clients.computeIfAbsent(client.getClientId(), s -> {
return (ConnectionBasedClient) client;
});
return true;
}
至此,我们又发现一个新概念:Client-客户端。由Grpc连接的客户端,都由ConnectionBasedClientManager进行管理。
小结
| 概念 | 类 | 管理者 |
|---|---|---|
| 连接 | com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.Connection | ConnectionManager |
| 客户端 | com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.client.Client | ClientManager |
注册实例
客户端
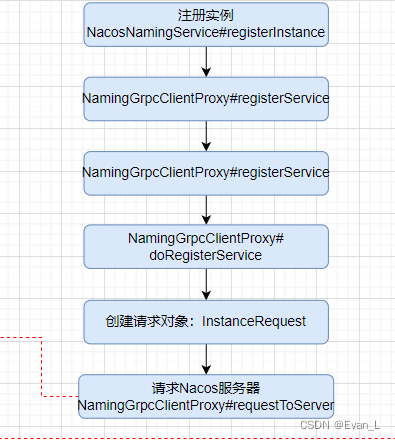
我们重点看看
public void doRegisterService(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
// 创建请求。每个Request在Nacos服务端都由对应的Handler
InstanceRequest request = new InstanceRequest(namespaceId, serviceName, groupName,
NamingRemoteConstants.REGISTER_INSTANCE, instance);
requestToServer(request, Response.class);
redoService.instanceRegistered(serviceName, groupName);
}
服务端
我们前面说服务端启动时,说这个是负责处理通用请求的:
final ServerCallHandler<Payload, Payload> payloadHandler = ServerCalls.asyncUnaryCall((request, responseObserver) -> grpcCommonRequestAcceptor.request(request, responseObserver));
我们就顺着往下看
// com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.grpc.GrpcRequestAcceptor#request
@Override
public void request(Payload grpcRequest, StreamObserver<Payload> responseObserver) {
String type = grpcRequest.getMetadata().getType();
// 省略如下内容:
// 检查服务是否已启动
// 如果是客户端对服务端的健康检查,则直接响应
// ----------------------------
// 从对应的请求处理器
RequestHandler requestHandler = requestHandlerRegistry.getByRequestType(type);
// 省略:no handler found. 的异常处理
// ----------------------------
String connectionId = GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get();
// 省略:检查连接是否正常.
Object parseObj = null;
parseObj = GrpcUtils.parse(grpcRequest);
// 省略:转换异常、无效请求异常
Request request = (Request) parseObj;
// 从ConnectionManager获取到对应的Connection
Connection connection = connectionManager.getConnection(GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get());
// 组装RequestMeta
RequestMeta requestMeta = new RequestMeta();
requestMeta.setClientIp(connection.getMetaInfo().getClientIp());
requestMeta.setConnectionId(GrpcServerConstants.CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get());
requestMeta.setClientVersion(connection.getMetaInfo().getVersion());
requestMeta.setLabels(connection.getMetaInfo().getLabels());
connectionManager.refreshActiveTime(requestMeta.getConnectionId());
// 调用requestHandler处理请求
Response response = requestHandler.handleRequest(request, requestMeta);
Payload payloadResponse = GrpcUtils.convert(response);
traceIfNecessary(payloadResponse, false);
responseObserver.onNext(payloadResponse);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
这些便是通用请求处理的核心逻辑。现在我们便来看InstanceRequest的处理com.alibaba.nacos.naming.remote.rpc.handler.InstanceRequestHandler
@Override
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public InstanceResponse handle(InstanceRequest request, RequestMeta meta) throws NacosException {
Service service = Service
.newService(request.getNamespace(), request.getGroupName(), request.getServiceName(), true);
switch (request.getType()) {
case NamingRemoteConstants.REGISTER_INSTANCE:
return registerInstance(service, request, meta);
case NamingRemoteConstants.DE_REGISTER_INSTANCE:
return deregisterInstance(service, request, meta);
default:
throw new NacosException
}
}
private InstanceResponse registerInstance(Service service, InstanceRequest request, RequestMeta meta)
throws NacosException {
// 1. 注册实例
clientOperationService.registerInstance(service, request.getInstance(), meta.getConnectionId());
// 2. 发布事件:RegisterInstanceTraceEvent
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new RegisterInstanceTraceEvent(System.currentTimeMillis(),
meta.getClientIp(), true, service.getNamespace(), service.getGroup(), service.getName(),
request.getInstance().getIp(), request.getInstance().getPort()));
return new InstanceResponse(NamingRemoteConstants.REGISTER_INSTANCE);
}
// 注册实例:
// com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.service.impl.EphemeralClientOperationServiceImpl#registerInstance
@Override
public void registerInstance(Service service, Instance instance, String clientId) throws NacosException {
NamingUtils.checkInstanceIsLegal(instance);
// 从ServiceManager获取已注册服务。而我们当前是要注册实例,所以,这个方法肯定还内含玄机
Service singleton = ServiceManager.getInstance().getSingleton(service);
// 省略:如果获取到的是持久化实例,意味着当前注册临时实例冲突了,返回异常。
Client client = clientManager.getClient(clientId);
InstancePublishInfo instanceInfo = getPublishInfo(instance);
// 记录当前客户端发布的实例
client.addServiceInstance(singleton, instanceInfo);
client.setLastUpdatedTime();
client.recalculateRevision();
// 发布服务注册事件
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new ClientOperationEvent.ClientRegisterServiceEvent(singleton, clientId));
NotifyCenter
.publishEvent(new MetadataEvent.InstanceMetadataEvent(singleton, instanceInfo.getMetadataId(), false));
}
// com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.ServiceManager
/**
* Get singleton service. Put to manager if no singleton.
* 获取单例服务(单例意味着整个应用只有一个对象),如果不存在,则注册到Manager
*/
public Service getSingleton(Service service) {
// 如果不存在就注册
singletonRepository.computeIfAbsent(service, key -> {
// 发布服务元信息数据事件。不过该事件对于持久实例才有用处。
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new MetadataEvent.ServiceMetadataEvent(service, false));
return service;
});
Service result = singletonRepository.get(service);
// 将服务登记到namespace
namespaceSingletonMaps.computeIfAbsent(result.getNamespace(), namespace -> new ConcurrentHashSet<>());
namespaceSingletonMaps.get(result.getNamespace()).add(result);
return result;
}
// 再看看ClientOperationEvent.ClientRegisterServiceEvent
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ClientServiceIndexesManager#onEvent
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ClientServiceIndexesManager#handleClientOperation
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ClientServiceIndexesManager#addPublisherIndexes
// 登记发布服务的客户端
private void addPublisherIndexes(Service service, String clientId) {
publisherIndexes.computeIfAbsent(service, key -> new ConcurrentHashSet<>());
publisherIndexes.get(service).add(clientId);
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new ServiceEvent.ServiceChangedEvent(service, true));
}
小结
我们总结一下,以上涉及到的概念。
| 概念 | 类 | 管理者 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 服务 | com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.pojo.Service | ServiceManager |
除了这个概念,实际上我们还看到Client的内部结构:
AbstractClient:
- 记录客户端发布的服务:ConcurrentHashMap<Service, InstancePublishInfo> publishers
- 记录客户端订阅的服务:ConcurrentHashMap<Service, Subscriber> subscribers
这个点其实要到订阅服务请求才会分析到,但为了信息不会太分散,所以就放到一起了。
ClientServiceIndexesManager
- 客户端索引管理者。这里的索引指的是,通过Service快速找到客户端,只是客户端有ClientManager,如果这里再存一份也不合适,不利于数据维护。因此这里存的是clientId。估计也是如此,他才叫客户端索引管理者。
查询和订阅实例
> com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.NacosNamingService#getAllInstances(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.util.List<java.lang.String>)
> com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.NacosNamingService#getAllInstances(java.lang.String, java.lang.String, java.util.List<java.lang.String>, boolean)
> com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.NacosNamingService#getAllInstances(String serviceName, String groupName, List<String> clusters, boolean subscribe)
> com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.remote.gprc.NamingGrpcClientProxy#subscribe
> com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.remote.gprc.NamingGrpcClientProxy#doSubscribe
public ServiceInfo doSubscribe(String serviceName, String groupName, String clusters) throws NacosException {
// 重点SubscribeServiceRequest,看服务端代码需要知道是什么请求
SubscribeServiceRequest request = new SubscribeServiceRequest(namespaceId, groupName, serviceName, clusters, true);
SubscribeServiceResponse response = requestToServer(request, SubscribeServiceResponse.class);
redoService.subscriberRegistered(serviceName, groupName, clusters);
return response.getServiceInfo();
}
服务端
// com.alibaba.nacos.naming.remote.rpc.handler.SubscribeServiceRequestHandler
@Override
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.READ)
public SubscribeServiceResponse handle(SubscribeServiceRequest request, RequestMeta meta) throws NacosException {
String namespaceId = request.getNamespace();
String serviceName = request.getServiceName();
String groupName = request.getGroupName();
String app = request.getHeader("app", "unknown");
String groupedServiceName = NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName);
Service service = Service.newService(namespaceId, groupName, serviceName, true);
// 订阅者
Subscriber subscriber = new Subscriber(meta.getClientIp(), meta.getClientVersion(), app, meta.getClientIp(),
namespaceId, groupedServiceName, 0, request.getClusters());
// 服务信息,这里有几个参数是需要通过方法来获取的
// 重点是:serviceStorage.getData(service)
// 而这个方法也是个重要的方法,过滤cluster、健康实例,并执行自动保护机制,都是他实现的
ServiceInfo serviceInfo = ServiceUtil.selectInstancesWithHealthyProtection(serviceStorage.getData(service),
metadataManager.getServiceMetadata(service).orElse(null), subscriber.getCluster(), false,
true, subscriber.getIp());
if (request.isSubscribe()) {
// 订阅服务
clientOperationService.subscribeService(service, subscriber, meta.getConnectionId());
// 发布订阅事件
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new SubscribeServiceTraceEvent(System.currentTimeMillis(),
meta.getClientIp(), service.getNamespace(), service.getGroup(), service.getName()));
} else {
// 取消订阅
clientOperationService.unsubscribeService(service, subscriber, meta.getConnectionId());
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new UnsubscribeServiceTraceEvent(System.currentTimeMillis(),
meta.getClientIp(), service.getNamespace(), service.getGroup(), service.getName()));
}
return new SubscribeServiceResponse(ResponseCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), "success", serviceInfo);
}
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ServiceStorage#getData
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ServiceStorage#getPushData
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ServiceStorage#getAllInstancesFromIndex
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.utils.ServiceUtil#selectInstancesWithHealthyProtection(com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.pojo.ServiceInfo, com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.metadata.ServiceMetadata, java.lang.String, boolean, boolean, java.lang.String)
// > com.alibaba.nacos.naming.utils.ServiceUtil#doSelectInstances
// 上面是调用路径,这里把生产数据的方法重点捞出来
// ServiceStorage的数据生产
public ServiceInfo getPushData(Service service) {
ServiceInfo result = emptyServiceInfo(service);
if (!ServiceManager.getInstance().containSingleton(service)) {
return result;
}
Service singleton = ServiceManager.getInstance().getSingleton(service);
result.setHosts(getAllInstancesFromIndex(singleton));
// 从ServiceManager拿到服务的实例信息,并登记到ServiceStorage#serviceDataIndexes中
serviceDataIndexes.put(singleton, result);
return result;
}
private List<Instance> getAllInstancesFromIndex(Service service) {
Set<Instance> result = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> clusters = new HashSet<>();
for (String each : serviceIndexesManager.getAllClientsRegisteredService(service)) {
// 获取实例信息
Optional<InstancePublishInfo> instancePublishInfo = getInstanceInfo(each, service);
if (instancePublishInfo.isPresent()) {
InstancePublishInfo publishInfo = instancePublishInfo.get();
//If it is a BatchInstancePublishInfo type, it will be processed manually and added to the instance list
if (publishInfo instanceof BatchInstancePublishInfo) {
BatchInstancePublishInfo batchInstancePublishInfo = (BatchInstancePublishInfo) publishInfo;
List<Instance> batchInstance = parseBatchInstance(service, batchInstancePublishInfo, clusters);
result.addAll(batchInstance);
} else {
Instance instance = parseInstance(service, instancePublishInfo.get());
result.add(instance);
clusters.add(instance.getClusterName());
}
}
}
// cache clusters of this service
// 缓存集群信息
serviceClusterIndex.put(service, clusters);
return new LinkedList<>(result);
}
private Optional<InstancePublishInfo> getInstanceInfo(String clientId, Service service) {
// 通过客户端ID,获取到Client,进而从其获取客户端发布的服务。
Client client = clientManager.getClient(clientId);
if (null == client) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.ofNullable(client.getInstancePublishInfo(service));
}
从查询实例这里,我们看到有个数据存储:ServiceStorage。重要的是,这个虽然叫存储,但是实际上里面的数据却是从别处获取来的。来源于:ServiceManager、ServiceIndexesManager、ClientManager。从这个角度说,更像是个缓存。
总结
上面的整了一堆源代码,容易看烦了。感兴趣的,可以根据上面的源码深入看看。为了方便大家,我画了图给大家:

为了让大家重点看到数据生产过程:
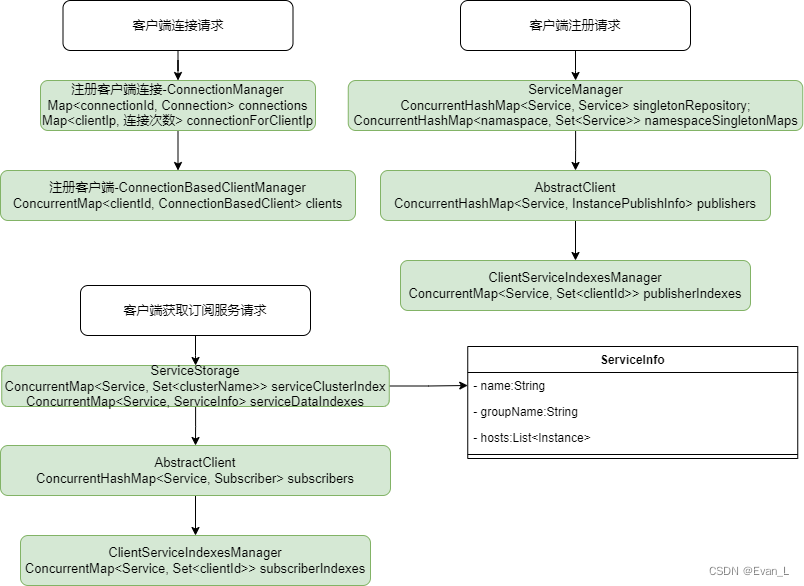
从图中,我们可以看到,nacos2.x的数据结构并不像官方的Service->Group->Instance。而是按照Connection、Client、Service分别通过对应的管理器进行管理。此外,为了避免数据多处存储,还有ClientServiceIndexesManager作为Client和Service的桥梁。
除此之外,还有ServiceStorage,作为数据缓存。不过,当我们深入了解ServiceStorage时,会发现他的数据一致性/数据的更新,是在给订阅服务的客户端定时推送时通过调用com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.index.ServiceStorage#getPushData来实现的。个人认为这是有可以优化空间的,他们完全可以通过各种事件来监听实例的生死来更新数据。
总而言之,如果不算ServiceStorage这个缓存,那么数据主要存在于一下的Manager中:
ConnectionManager、ClientManager、ServiceManager、ClientServiceIndexesManager。
到这里,可能有同学就有疑问了。那么Group、Cluster这些概念去哪了呢?
这些概念都成为了属性/字段了。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.v2.pojo.Service#group
com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.pojo.Instance#clusterName
即使在ServiceStorage封装ServiceInfo时,他们也是作为属性来存储的。通过ServiceUtil来过滤目标实例。
最后,提醒大家一下,我们这里只是分析了临时实例。是最常用的场景。当然,如果我们用Nacos的持久实例,SpringCloud也就自然支持了持久实例。不过,咱们不深究了,感兴趣的同学,可以顺着往下挖一挖持久实例。
后记
这种深度刨析源码、深挖一个技术细节的实现,太费时间、也太费篇幅了。我自己都感觉差点把整个nacos的源码都搬上来了。莫见怪。。。
关于nacos的一致性协议,就不在这里聊了,这个东西得单独倒腾,还要与其他分布式中间件相互对比,还有理论。。
下次,咱们先往后聊OpenFeign。
推荐
Nacos的实现原理在官网有一电子书《Nacos架构&原理》,想要了解顶层设计原理的同学,建议看看。