关于作者:CSDN内容合伙人、技术专家, 从零开始做日活千万级APP。
专注于分享各领域原创系列文章 ,擅长java后端、移动开发、商业变现、人工智能等,希望大家多多支持。
目录
- 一、概览
- 二、setContentView()
- 三、inflate
- 四、view的绘制展示
- 4.1 Activity.onResume
- 4.2 WindowManager addView
- 4.3 ViewRootImpl
- 4.4 addWindow & makeVisible
- 五、 推荐阅读

接 - > 上 篇,Activity创建后,还只是调用了onCreate方法,页面并没有展示出来,还需要调用setContentView方法,加载页面布局,并进行渲染,最后展示。
一、概览
本源码基于Android 12
看代码前,我们先上一张Activity,Window, DecorView三者之间的关系图
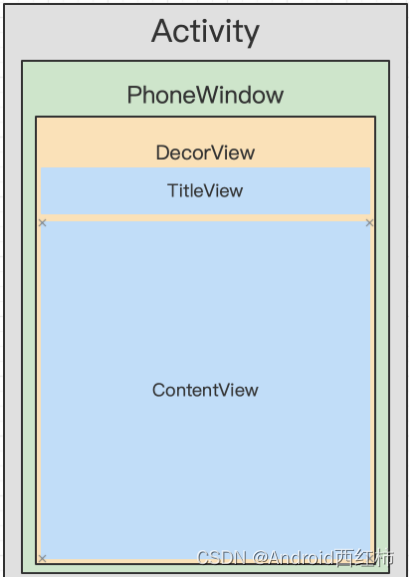
DecorView是整个ViewTree的最顶层View,它是一个FrameLayout布局,代表了整个应用的界面。
在该布局下面,有标题view和内容view两个子元素。
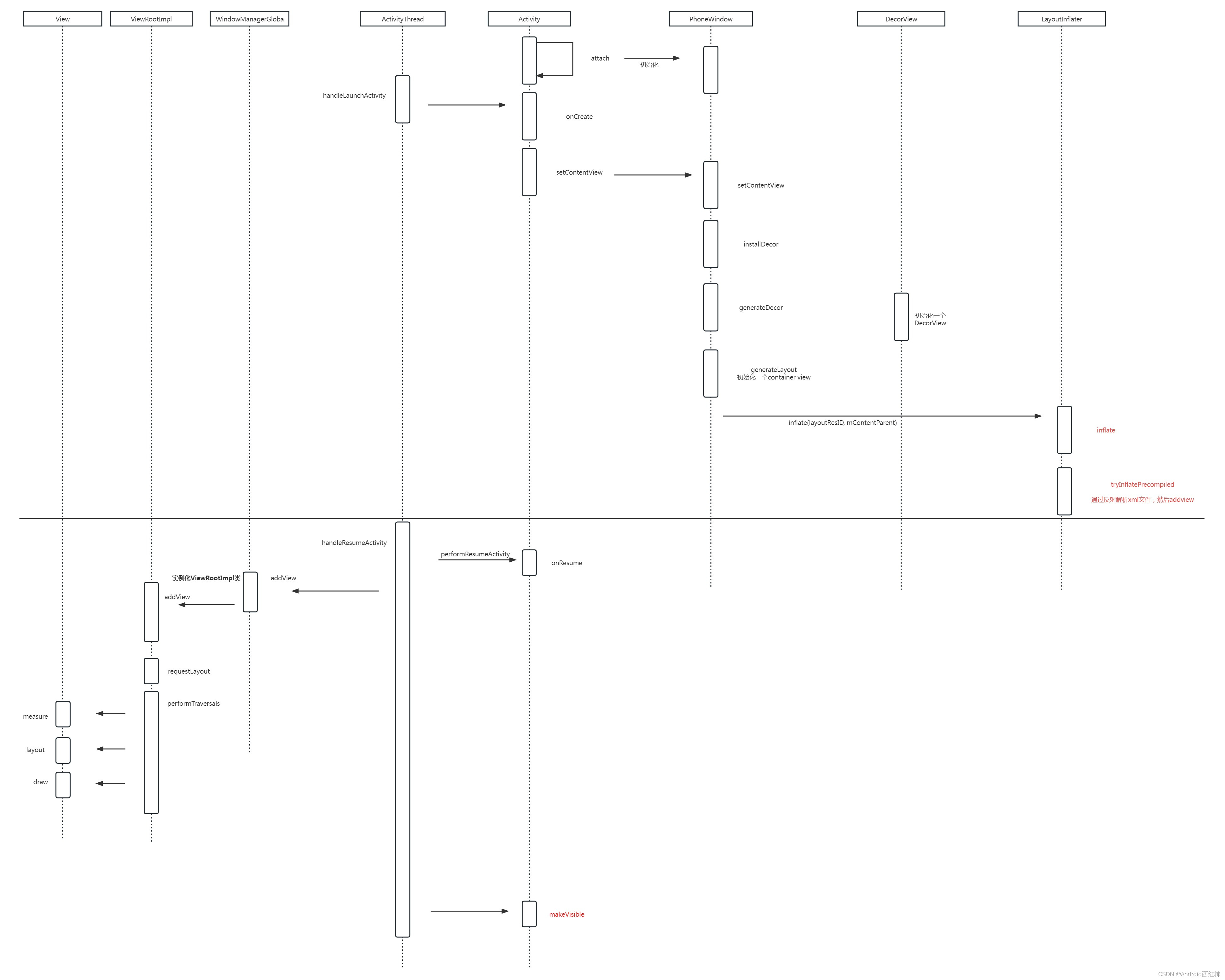
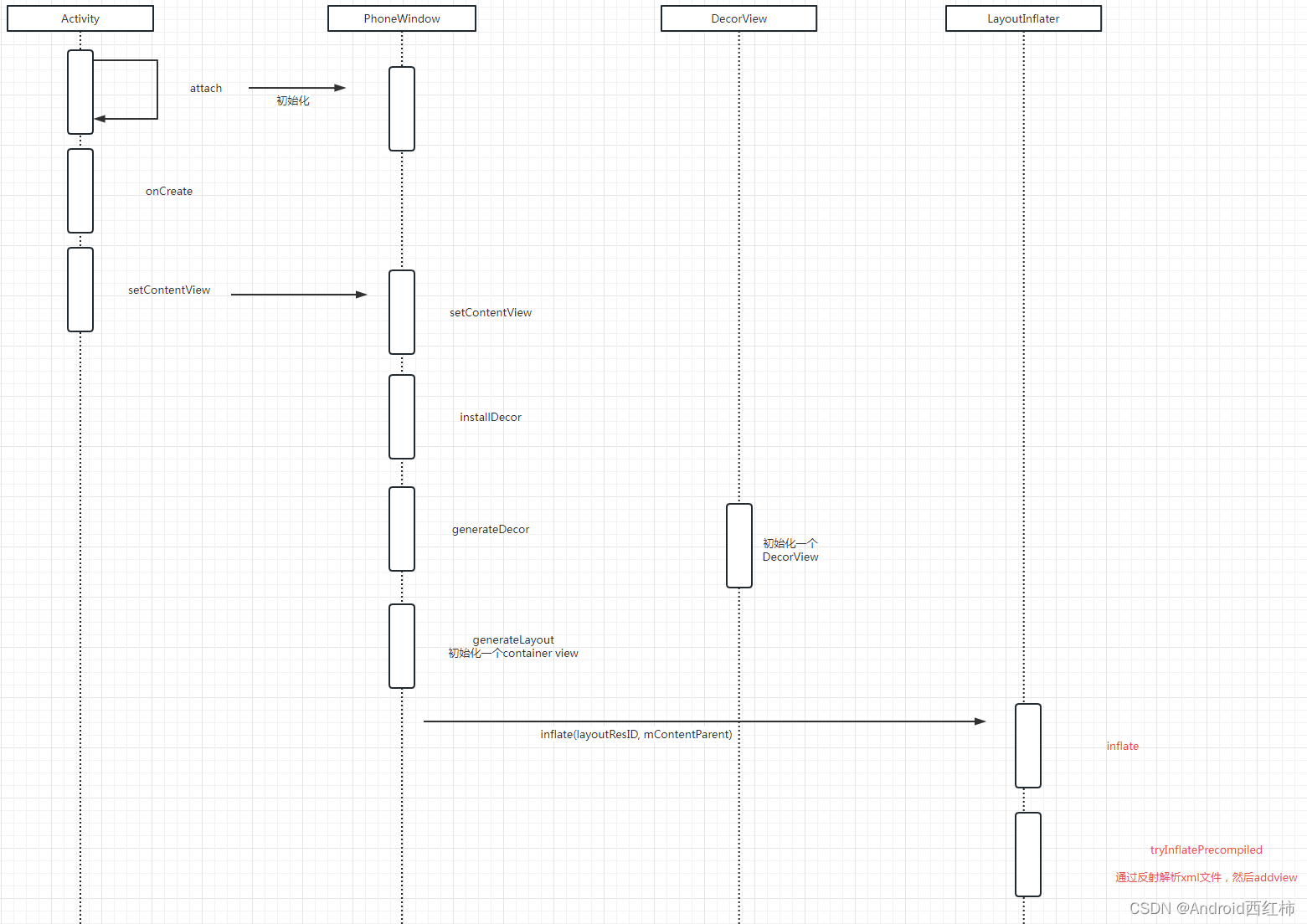
Activity setContentView 核心就是PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,其主要干了两件事:
1.完成DecorView的创建与加载,这个DecorView会在后面onresume后添加到window中
2.将MainActivity的布局加载到DecorView内的一个ViewGroup中
创建DecorView,即installDecor方法,其内部用到了两个核心的方法:
1.generateDecor方法创建出DecorView对象
2.generateLayout方法完成这个DecorView对象的布局加载,并完成了MainActivity的父容器的赋值(即contentParent变量)
先上一张流程图
二、setContentView()
我们跟踪一下源码,看看这个方法是怎么做的
public void setContentView(View view) {
getWindow().setContentView(view);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
这里window即为 PhoneWindow,
window的初始化是在 Acticity 创建的时候初始化, 在Acticity对象创建后,会调用attach方法
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread, ...) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(mWindowControllerCallback);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
}
PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
根view 为空,则初始 mDecor view
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
// 将布局文件添加到 mContentParent
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
调用installDecor()进行DecorView的初始化
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
// 创建出一个DecorView并返回
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
//对mContentParent进行赋值,作为Activity布局的父容器,
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
}
}
首先判断了mContentParent是否为null,如果为空则执行installDecor()方法,同时初始化一个mContentParent,这个就是Activity布局的父容器
三、inflate
LayoutInflater.java
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
final Resources res = getContext().getResources();
View view = tryInflatePrecompiled(resource, res, root, attachToRoot);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
XmlResourceParser parser = res.getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
}
}
private @Nullable
View tryInflatePrecompiled(@LayoutRes int resource, Resources res, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("" + pkg + ".CompiledView", false, mPrecompiledClassLoader);
Method inflater = clazz.getMethod(layout, Context.class, int.class);
View view = (View) inflater.invoke(null, mContext, resource);
if (view != null && root != null) {
XmlResourceParser parser = res.getLayout(resource);
try {
AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
advanceToRootNode(parser);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (attachToRoot) {
root.addView(view, params);
} else {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
}
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
return view;
} catch (Throwable e) {
} finally {
}
return null;
}
布局就是这么添加进mContentParent中的。
但是,view还是没有显示出来的,此时代码所做的事情仅仅只是加载了布局,并没有开始view的测量、布局、绘制工作。
对应方法是onMeasure, onLayout, onDraw,这些操作在后面
四、view的绘制展示
每一个Activity组件都有一个关联的Window对象,用来描述一个应用程序窗口。每一个应用程序窗口内部又包含一个View对象,用来描述应用程序窗口的视图。
我们再看下图:

Activity#onResume()之后才是布局由不可见变为可见的,我们看源码
4.1 Activity.onResume
ActivityThread.java
下面这个方法是在Activity onCreate创建后调用的,handleResumeActivity,不清楚的可以看前面app启动文章.
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finalStateRequest,
boolean isForward, String reason) {
// 这个方法会调用 activity的 onResume 方法
if (!performResumeActivity(r, finalStateRequest, reason)) {
return;
}
final Activity a = r.activity;
// window 未被添加进 windowmanager
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
// window
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
// decorView
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
} else if (!willBeVisible){
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
if (!a.mWindowAdded) {
// DecorView 添加到 window
wm.addView(decor, l);
} else {
a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible && r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
使布局可见
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
r.nextIdle = mNewActivities;
}
在上面的代码中,会先调用Activity的onResume, 然后再是view的绘制,最后将DecorView 设置 可见;
4.2 WindowManager addView
WindowManagerImpl.java
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
...
@Override
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
这里也是一个空壳代码,调用WindowManagerGlobal
WindowManagerGlobal.java
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) {
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
// 加锁
synchronized (mLock) {
//实例化ViewRootImpl类
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
// //调用ViewRootImpl.setView方法,把DecorView作为参数传递进去
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
在方法内部,会通过跨进程方式向WMS(WindowManagerService)发起一个调用,从而将DecorView最终加到Window上,在这个过程中,ViewRootImpl、DecorView和WMS会彼此关联。
最后,WMS调用ViewRootImpl.performTraversals 方法开始View的测量、布局、绘制。
4.3 ViewRootImpl
一个 Window 对应着一个 ViewRootImpl 和 一个 VIew。这个 View 就是被 ViewRootImpl 操作的.
从上面代码,我们可以看到,ViewRootImpl的初始化是在WindowManagerGlobal的addView中
ViewRootImpl.java
/**
* We have one child
*/
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView, int userId) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
mAdded = true;
int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
// 刷新布局的操作,触发view的measure -> layout -> draw 操作
requestLayout();
try {
//将 View 添加到 WMS 中
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes, ...);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
} finally {
}
// Set up the input pipeline. 设置了一系列的输入通道
CharSequence counterSuffix = attrs.getTitle();
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
}
}
}
首先会调用requestLayout方法来刷新布局,然后将 View 添加到 WMS 中,最后是view事件的处理;
view事件的处理,最后还是会回到了 PhoneWindow 中的 DecorView 来处理,剩下的就是从 DecorView 开始将事件层层传递给内部的子 View 中了
这里就不展开
ViewGroup.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
}
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
performTraversals();
}
}
requestLayout()最终会调用到performTraversals,在这个方法中会调用 View 的 measure() ,layout() ,draw() 方法。
我们看下面源码
private void performTraversals() {
final View host = mView;
if (mFirst || windowShouldResize || viewVisibilityChanged || params != null
|| mForceNextWindowRelayout) {
try {
if (!mPendingMergedConfiguration.equals(mLastReportedMergedConfiguration)) {
performConfigurationChange(new MergedConfiguration(mPendingMergedConfiguration),
!mFirst, INVALID_DISPLAY /* same display */);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
if (!mStopped || wasReportNextDraw) {
//View 的测量
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (measureAgain) {
//View 的测量
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
layoutRequested = true;
}
}
} else {
}
if (didLayout) {
// View 的布局
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
}
if (!cancelDraw) {
// View 的绘制
performDraw();
} else {
}
mIsInTraversal = false;
}
4.4 addWindow & makeVisible
com.android.server.wm.Session.java
@Override
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, InsetsVisibilities requestedVisibilities,
InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) {
return mService.addWindow(this, window, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
UserHandle.getUserId(mUid), requestedVisibilities, outInputChannel, outInsetsState,
outActiveControls);
}
Activity.java
把DecorView的状态设置为可见,那么布局也就可见了
void makeVisible() {
if (!mWindowAdded) {
ViewManager wm = getWindowManager();
wm.addView(mDecor, getWindow().getAttributes());
mWindowAdded = true;
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
五、 推荐阅读
Java 专栏
SQL 专栏
数据结构与算法
Android学习专栏