C++官网参考链接:https://cplusplus.com/reference/map/map/operator=/
公有成员函数
<map>
std::map::operator=
C++98
copy (1)
map& operator= (const map& x);
C++11
copy (1)
map& operator= (const map& x);
move (2)
map& operator= (map&& x);
initializer list (3)
map& operator= (initializer_list<value_type> il);
复制容器内容
将新内容分配给容器,替换其当前内容。
C++98
将x中的所有元素复制到容器中,并相应地更改其size。
容器保留其当前allocator(current allocator),该allocator用于在需要时分配额外的存储空间。
C++11
复制赋值操作(1)将x中的所有元素复制到容器中(x保留其内容)。
移动赋值(2)将x的元素移动到容器中(x保持未指定但有效的状态)。
初始化器列表赋值(3)将il的元素复制到容器中。
新的容器的size与调用前x(或il)的size相同。
容器保留其当前的allocator(current allocator),除非allocator traits指示x的allocator应该传播(propagate)。如果存储需求发生变化,则使用该allocator(通过其traits)进行allocate或deallocate,如果需要,则construct或destroy元素。
调用之前存储在容器中的元素要么被赋值,要么被销毁。
形参
x
一个相同类型的map对象(即具有相同的模板形参:key、T、Compare和Alloc)。
il
一个initializer_list对象。编译器将从初始化器列表声明器自动构造此类对象。
成员类型value_type是容器中元素的类型,在map中定义为pair<const key_type, mapped_type>的别名(参见map成员类型(map member types))。
返回值
*this。
用例
// assignment operator with maps
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
int main ()
{
std::map<char,int> first;
std::map<char,int> second;
first['x']=8;
first['y']=16;
first['z']=32;
second=first; // second now contains 3 ints
first=std::map<char,int>(); // and first is now empty
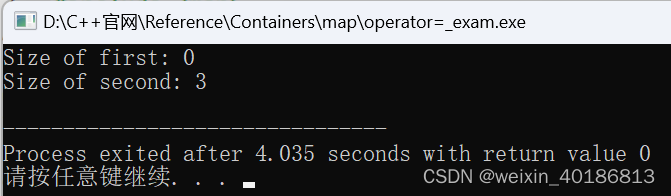
std::cout << "Size of first: " << first.size() << '\n';
std::cout << "Size of second: " << second.size() << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
复杂度
对于复制赋值(1):大小(销毁,复制)的线性。
对于移动赋值(2):当前容器的size(销毁)中的线性*。
对于初始化器列表赋值(3):最多达到大小(销毁,移动赋值)中的对数---如果il已经排序,则为线性。
*如果allocator不传播(propagate),则会增加赋值的复杂性。
iterator的有效性
与此容器相关的所有iterators、references和pointers都将失效。
在移动赋值操作中,指向x中的元素的iterators、pointers和references也会失效。
数据竞争
所有复制的元素都被访问。
移动赋值(2)修改x。
容器及其所有元素都被修改。
异常安全
基本保证:如果抛出异常,则容器处于有效状态。
如果元素结构的适当实参不支持allocator_traits::construct,或者value_type不能复制可赋值(copy assignable)(或对于(2)不能移动可赋值(move assignable)),则会导致未定义行为。