前言
零拷贝是老生常谈的话题了, 不管是Kafka还是Netty都用到了零拷贝的知识, 本篇着重讲解了什么是零拷贝, 同时在Java和Netty中分别是怎么实现零拷贝的
什么是零拷贝
零拷贝是指计算机在执行IO操作的时候, CPU不需要将数据从一个存储区复制到另一个存储区, 进而减少上下文切换以及 CPU 拷贝的时间, 这是一种IO操作优化技术
零拷贝不是没有拷贝数据, 而是减少用户态, 内核态的切换次数 和 CPU拷贝次数, 目前实现零拷贝的主要三种方式分别是:
- mmap + write
- sendfile
- 带有DMA收集拷贝功能的 sendfile
mmap
虚拟内存把内核空间和用户空间的虚拟地址映射到同一个物理地址, 从而减少数据拷贝次数, mmap技术就是利用了虚拟内存的这个特点, 它将内核中的读缓冲区与用户空间的缓冲区进行映射, 所有的IO操作都在内核中完成
sendfile
sendfile是Linux 2.1 版本之后内核引入的一个系统调用函数
sendfile表示在两个文件描述符之间传输数据, 他是在操作系统内核中完成的, 避免了数据从内核缓冲区和用户缓冲区之间的拷贝操作, 因此可以用其来实现零拷贝
在Linux 2.4版本之后, 对sendfile进行了升级, 引入了SG-DMA技术, 可以直接从缓冲区中将数据读取到网卡, 这样的话可以省去CPU拷贝
Java 实现的零拷贝
mmap
在Java NIO有一个ByteBuffer的子类MappedByteBuffer, 这个类采用direct buffer也就是内存映射的方式读写文件内容. 这种方式直接调用系统底层的缓存, 没有JVM和系统之间的复制操作, 主要用户操作大文件
sendfile
FileChannel的transferTo()方法或者transferFrom()方法,底层就是sendfile() 系统调用函数。 实现了数据直接从内核的读缓冲区传输到套接字缓冲区, 避免了用户态与内核态之间的数据拷贝
Kafka 就是使用到它
Netty 的零拷贝
Netty的哦零拷贝主要体现在以下几个方面
- slice
- duplicate
- CompositeByteBuf
- ....
我们主要讲一下slice, 其他的下次一定
log 工具类
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import static io.netty.buffer.ByteBufUtil.appendPrettyHexDump;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE;
public class ByteBufUtil {
// 打印
public static void log(ByteBuf buf){
final int length = buf.readableBytes();
int rows = length / 16 + (length % 15 == 0 ? 0 : 1) + 4;
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(rows * 80 * 2)
.append("read index:").append(buf.readerIndex())
.append(" write index: ").append(buf.writerIndex())
.append(" capacity:").append(buf.capacity())
.append(NEWLINE);
appendPrettyHexDump(str, buf);
System.out.println(str.toString());
}
}
复制代码slice
对原始的ByteBuf进行切片成多个ByteBuf, 切片后的ByteBuf并没有发生内存复制, 还是使用原始的ByteBuf内存, 但是切片后的ByteBuf各自有独立的read, write指针
注意:
slice不允许更改切片的容量, 切片时设置的长度是多少就是多少, 不允许扩容- 当我们释放原始
ByteBuf内存之后, 切片后的ByteBuf就不能再访问了
测试:
- 首先创建一个
ByteBuf, 然后对其进行切片 - 更改某一个切片查看原始
ByteBuf是否更改 - 原始数据跟着更改了说明内存地址没有发生改变
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 ByteBuf
ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10);
// 向 byteBuf 缓冲区写入数据
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
str.append("nx");
}
byteBuf.writeBytes(str.toString().getBytes());
// 打印当前 byteBug
ByteBufUtil.log(byteBuf);
// 切片的过程中并没有发生数据复制
final ByteBuf slice = byteBuf.slice(0, 5);
final ByteBuf slice1 = byteBuf.slice(5, 5);
// 打印第一个切片
ByteBufUtil.log(slice);
// 打印第二个切片
ByteBufUtil.log(byteBuf);
slice.setByte(0, 'a');
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
// 打印第一个切片
ByteBufUtil.log(slice);
// 打印原始数组
ByteBufUtil.log(byteBuf);
}
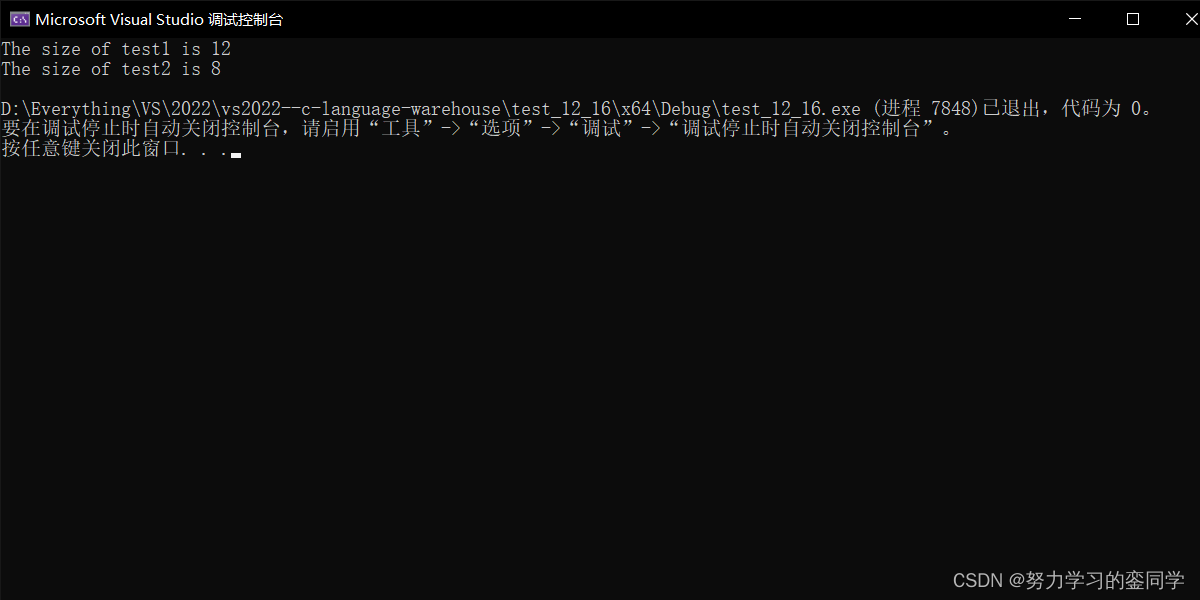
复制代码打印结果如下



![[深度学习基础]2.pycharm联合annaconda生成虚拟环境测试yoloV7](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/79bcb9c380634d1e8069cd357525c7db.png)