1. go hello world
创建文件夹gotest,在其中创建test1.go文件,并写入
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("hello world")
}运行命令
go run test1.go
可以看到输出hello world

2. cli 命令行的使用
代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/urfave/cli/v2"
)
func main() {
app := &cli.App{
Name: "hello",
Usage: "hello world example",
Action: func(c *cli.Context) error {
fmt.Println("hello world")
return nil
},
}
err := app.Run(os.Args)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// fmt.Println("hello world")
}运行:go build -o test1
可能会运行错误,找不到包。此时可以通过生成go.mod文件来管理包
生成go.mod文件
go mod init gotest //其中gotest是go文件所在文件夹的名称

注意:
在上面中,我们通过 go mod init xxx命令生成了go.mod文件之后,这只是一个空的文件, 其中依赖的各种包还没有生成。
可以使用以下2种命令获取:
<1> go get 包名 例如:go get github.com/urfave/cli/v2
如果依赖包比较多,那么 go get 就比较麻烦了。可以使用另外一个命令:
<2> go mod tidy 这个命令将会扫描所有我们写的.go文件中import到的库包,并生成对应的记录到go.mod文件里。
2.1 cli.Context
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/urfave/cli/v2"
)
func main() {
app := &cli.App{
Name: "hello",
Usage: "hello world example",
Action: func(c *cli.Context) error {
// fmt.Println("hello world")
fmt.Printf("Hello %s", c.Args().Get(0))
return nil
},
}
err := app.Run(os.Args)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// fmt.Println("hello world")
}运行结果:
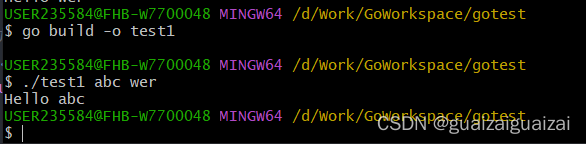
c.Args() //可以获取运行命令后的参数列表,是一个切片,cCtx.Args().Get(0)是获取第一个位置的参数,第二个第三个依次类推
fmt包输出函数
func Print(a ...interface{}) (n int, err error)
func Printf(format string, a ...interface{}) (n int err error)
func Printfln(a ...interface{}) (n int, err error)
参考:
https://juejin.cn/post/7098296317394288671


![[PyTorch][chapter 53][Auto Encoder 实战]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1f4a5174a09a4374a2a8935c457ec996.png)

![RK3588平台驱动调试篇 [ GPIO篇 ] - RK3588-对GPIO的操作控制](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/aa13f0fcd9814ca3adcc2c47a985780f.png)