说明
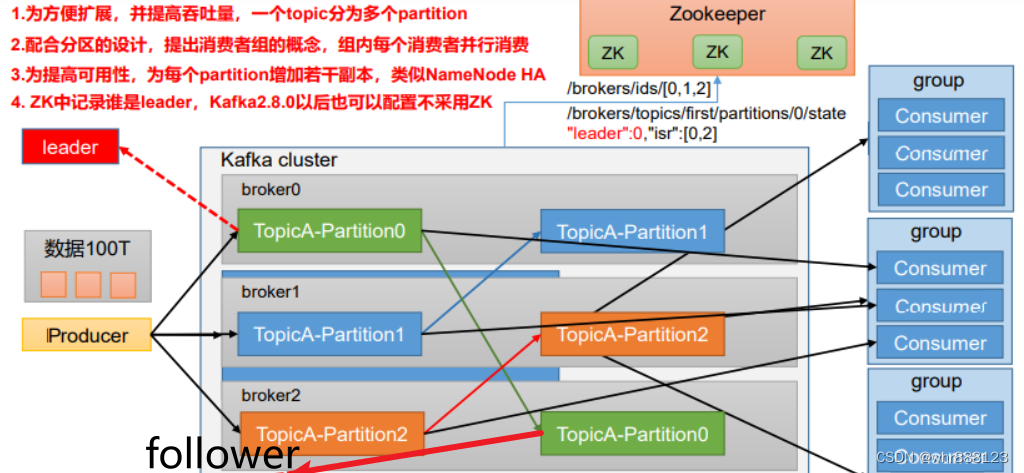
【跟月影学可视化】学习笔记。
如何用 Canvas2D 绘制带宽度的曲线?
Canvas2D 提供了相应的 API,能够绘制出不同宽度、具有特定连线方式(lineJoin)和线帽形状(lineCap)的曲线,绘制曲线非常简单。
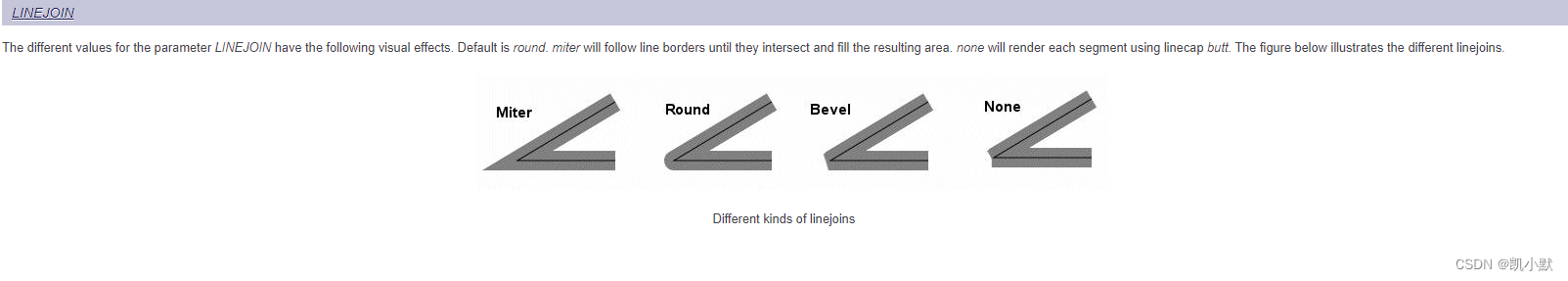
什么是连线方式(lineJoin)?
线宽超过一个像素,两个线段中间转折的部分处就会有缺口,不同的填充方式,就对应了不同的 lineJoin。
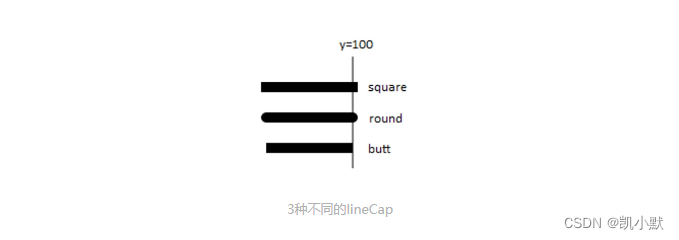
线帽形状(lineCap)?
lineCap 就是指曲线头尾部的形状。
- 第一种:
square,方形线帽,它会在线段的头尾端延长线宽的一半。 - 第二种:
round,圆弧线帽,它会在头尾端延长一个半圆。 - 第三种:
butt,不添加线帽。
绘制曲线例子
注意:Canvas2D 的 lineJoin 只支持 miter、bevel 和 round,不支持 none。lineCap 支持 butt、square 和 round。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何用 Canvas2D 绘制带宽度的曲线</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed #fa8072;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="800" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
// 设置 lineWidth、lingJoin、lineCap,然后根据 points 数据的内容设置绘图指令执行绘制。
function drawPolyline(context, points, {lineWidth = 1, lineJoin = 'miter', lineCap = 'butt', miterLimit = 10} = {}) {
context.lineWidth = lineWidth;
context.lineJoin = lineJoin;
context.lineCap = lineCap;
// The CanvasRenderingContext2D.miterLimit 是 Canvas 2D API 设置斜接面限制比例的属性。
// 当获取属性值时,会返回当前的值(默认值是10.0 )。
// 当给属性赋值时,0、负数、 Infinity 和 NaN 都会被忽略;除此之外都会被赋予一个新值。
context.miterLimit = miterLimit;
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(...points[0]);
for(let i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
context.lineTo(...points[i]);
}
context.stroke();
}
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// 第一组
const points = [
[100, 100],
[100, 200],
[200, 150],
[300, 200],
[300, 100],
];
ctx.strokeStyle = 'salmon';
drawPolyline(ctx, points, { lineWidth: 10 });
ctx.strokeStyle = 'slateblue';
drawPolyline(ctx, points);
// 第二组
const point2s = [
[100, 300],
[100, 400],
[200, 350],
[300, 400],
[300, 300],
];
ctx.strokeStyle = 'seagreen';
drawPolyline(ctx, point2s, { lineWidth: 10, lineCap: 'round', lineJoin: 'bevel' });
ctx.strokeStyle = 'goldenrod';
drawPolyline(ctx, point2s);
// 第三组
const point3s = [
[400, 200],
[400, 300],
[500, 250],
[600, 300],
[600, 200],
];
ctx.strokeStyle = 'goldenrod';
drawPolyline(ctx, point3s, { lineWidth: 10, lineCap: 'round', lineJoin: 'miter', miterLimit: 1.5});
ctx.strokeStyle = 'slateblue';
drawPolyline(ctx, point3s);
</script>
</body>
</html>
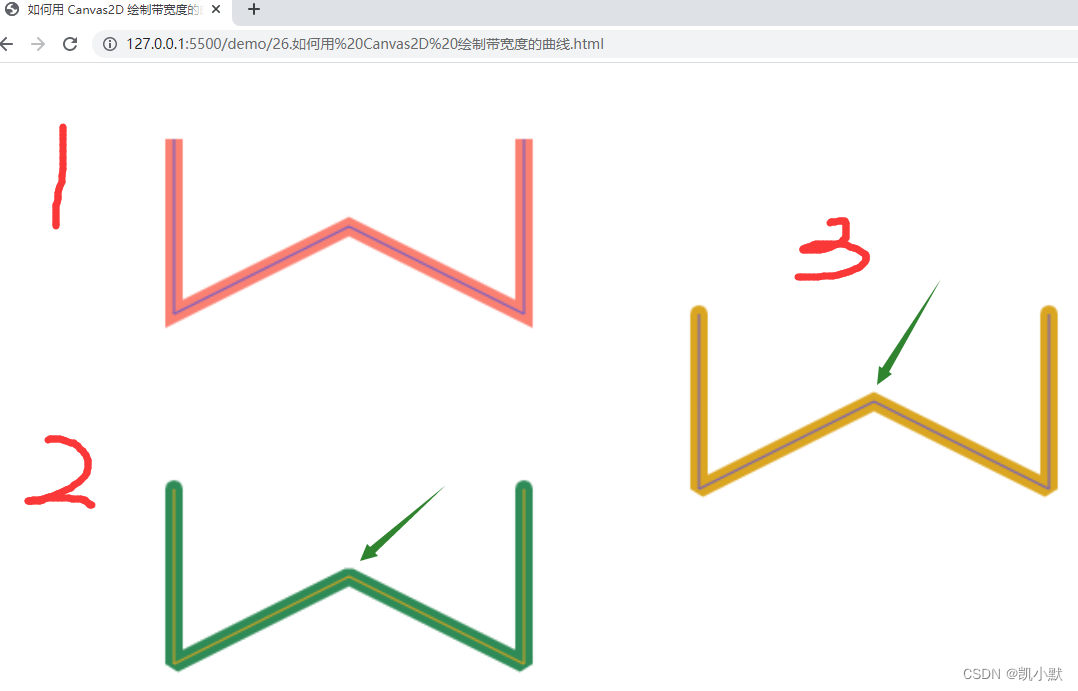
效果如下:图三中,两侧的转角由于超过了 miterLimit 限制,所以表现为斜角,而中间的转角因为没有超过 miterLimit 限制,所以是尖角。
如何用 WebGL 绘制带宽度的曲线
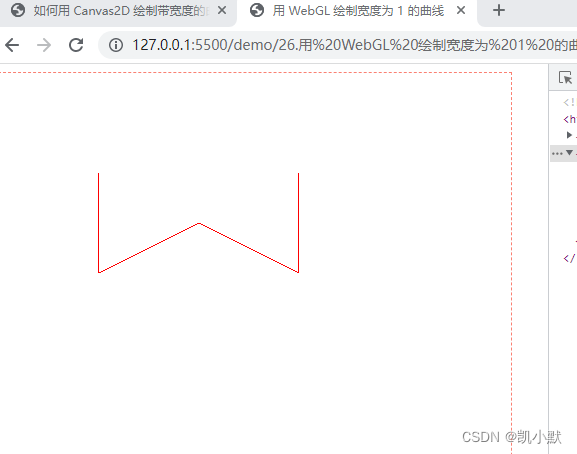
WebGL 支持线段类的图元,LINE_STRIP 是一种图元类型,表示以首尾连接的线段方式绘制。
用 WebGL 绘制宽度为 1 的曲线
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>用 WebGL 绘制宽度为 1 的曲线</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed #fa8072;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
import { Renderer, Program, Geometry, Transform, Mesh } from './common/lib/ogl/index.mjs';
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 position;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 10.0;
float scale = 1.0 / 256.0;
mat3 projectionMatrix = mat3(
scale, 0, 0,
0, -scale, 0,
-1, 1, 1
);
vec3 pos = projectionMatrix * vec3(position, 1);
gl_Position = vec4(pos.xy, 0, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
precision highp float;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1, 0, 0, 1);
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new Renderer({
canvas,
width: 512,
height: 512,
});
const gl = renderer.gl;
gl.clearColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
const program = new Program(gl, {
vertex,
fragment,
});
const geometry = new Geometry(gl, {
position: {size: 2,
data: new Float32Array(
[
100, 100,
100, 200,
200, 150,
300, 200,
300, 100,
],
)},
});
const scene = new Transform();
const polyline = new Mesh(gl, {geometry, program, mode: gl.LINE_STRIP});
polyline.setParent(scene);
renderer.render({scene});
</script>
</body>
</html>
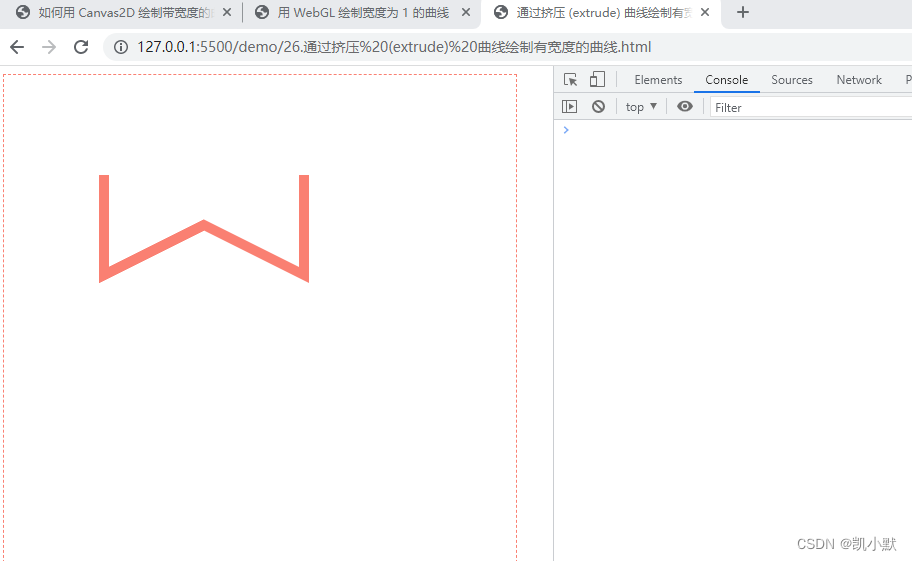
通过挤压 (extrude) 曲线绘制有宽度的曲线
挤压 (extrude) 曲线就是将曲线的顶点沿法线方向向两侧移出,让 1 个像素的曲线变宽。
大致步骤:
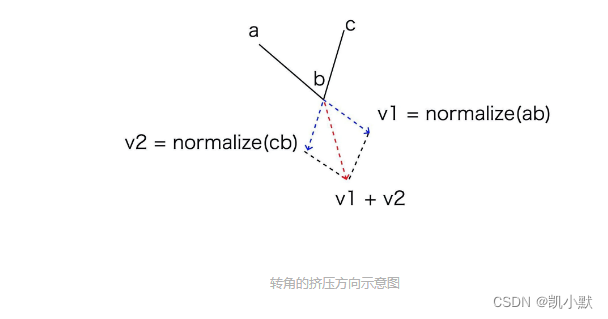
- 1、确定端点和转角的挤压方向,端点可以沿线段的法线挤压,转角则通过两条线段延长线的单位向量求和的方式获得。
- 2、确定端点和转角挤压的长度
- 端点两个方向的挤压长度是线宽 lineWidth 的一半。
- 求转角挤压长度的时候,要先计算方向向量和线段法线的余弦,然后将线宽 lineWidth 的一半除以我们计算出的余弦值。
- 3、由步骤 1、2 计算出顶点后,我们构建三角网格化的几何体顶点数据,然后将 Geometry 对象返回。
如下图所示:
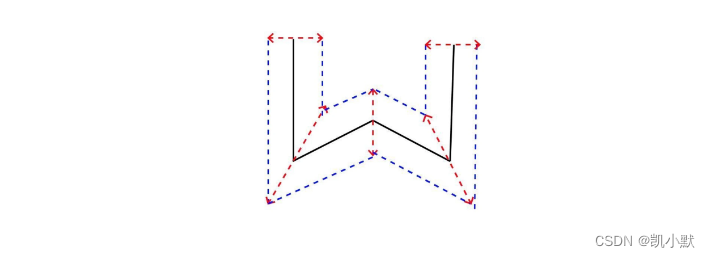
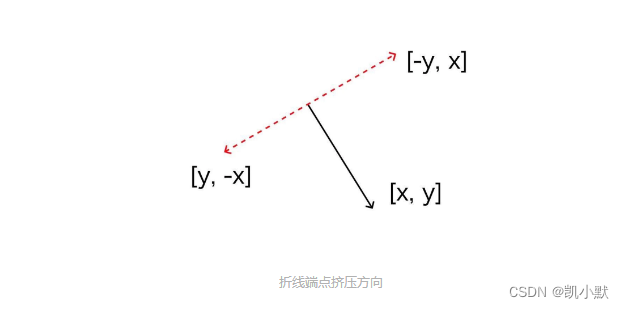
折线端点的挤压方向
顶点的两个移动方向为(-y, x)和(y, -x)。
转角的挤压方向
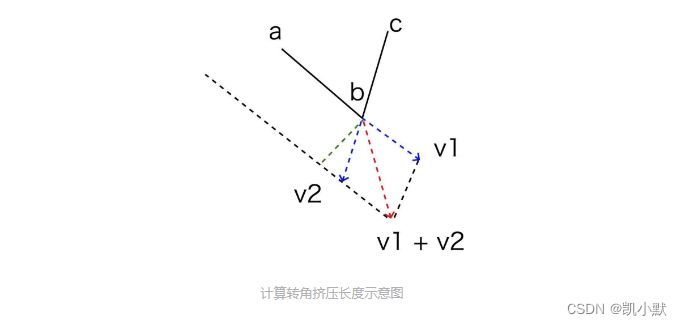
折线端点的挤压长度
折线端点的挤压长度等于 lineWidth 的一半。
转角的挤压长度
需要计算法线方向与挤压方向的余弦值,就能算出挤压长度
用 JavaScript 实现的代码如下所示:
function extrudePolyline(gl, points, {thickness = 10} = {}) {
const halfThick = 0.5 * thickness;
// 向内和向外挤压的点分别保存在 innerSide 和 outerSide 数组中。
const innerSide = [];
const outerSide = [];
// 构建挤压顶点
for(let i = 1; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
// v1、v2 是线段的延长线,v 是挤压方向
const v1 = (new Vec2()).sub(points[i], points[i - 1]).normalize();
const v2 = (new Vec2()).sub(points[i], points[i + 1]).normalize();
const v = (new Vec2()).add(v1, v2).normalize(); // 得到挤压方向
const norm = new Vec2(-v1.y, v1.x); // 法线方向
const cos = norm.dot(v);
const len = halfThick / cos;
if(i === 1) { // 起始点
const v0 = new Vec2(...norm).scale(halfThick);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[0], v0));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[0], v0));
}
v.scale(len);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[i], v));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[i], v));
if(i === points.length - 2) { // 结束点
const norm2 = new Vec2(v2.y, -v2.x);
const v0 = new Vec2(...norm2).scale(halfThick);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[points.length - 1], v0));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[points.length - 1], v0));
}
}
const count = innerSide.length * 4 - 4;
const position = new Float32Array(count * 2);
const index = new Uint16Array(6 * count / 4);
// 创建 geometry 对象
for(let i = 0; i < innerSide.length - 1; i++) {
const a = innerSide[i],
b = outerSide[i],
c = innerSide[i + 1],
d = outerSide[i + 1];
const offset = i * 4;
index.set([offset, offset + 1, offset + 2, offset + 2, offset + 1, offset + 3], i * 6);
position.set([...a, ...b, ...c, ...d], i * 8);
}
return new Geometry(gl, {
position: {size: 2, data: position},
index: {data: index},
});
}
根据 innerSide 和 outerSide 中的顶点来构建三角网格化的几何体顶点数据,最终返回 Geometry 对象来构建三角网格对象。
构建折线的顶点数据示意图:

下面实战一下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>通过挤压 (extrude) 曲线绘制有宽度的曲线</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed #fa8072;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script type="module">
import { Renderer, Program, Geometry, Transform, Mesh, Vec2 } from './common/lib/ogl/index.mjs';
function extrudePolyline(gl, points, {thickness = 10} = {}) {
const halfThick = 0.5 * thickness;
// 向内和向外挤压的点分别保存在 innerSide 和 outerSide 数组中。
const innerSide = [];
const outerSide = [];
// 构建挤压顶点
for(let i = 1; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
// v1、v2 是线段的延长线,v 是挤压方向
const v1 = (new Vec2()).sub(points[i], points[i - 1]).normalize();
const v2 = (new Vec2()).sub(points[i], points[i + 1]).normalize();
const v = (new Vec2()).add(v1, v2).normalize(); // 得到挤压方向
const norm = new Vec2(-v1.y, v1.x); // 法线方向
const cos = norm.dot(v);
const len = halfThick / cos;
if(i === 1) { // 起始点
const v0 = new Vec2(...norm).scale(halfThick);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[0], v0));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[0], v0));
}
v.scale(len);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[i], v));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[i], v));
if(i === points.length - 2) { // 结束点
const norm2 = new Vec2(v2.y, -v2.x);
const v0 = new Vec2(...norm2).scale(halfThick);
outerSide.push((new Vec2()).add(points[points.length - 1], v0));
innerSide.push((new Vec2()).sub(points[points.length - 1], v0));
}
}
const count = innerSide.length * 4 - 4;
const position = new Float32Array(count * 2);
const index = new Uint16Array(6 * count / 4);
// 创建 geometry 对象
for(let i = 0; i < innerSide.length - 1; i++) {
const a = innerSide[i],
b = outerSide[i],
c = innerSide[i + 1],
d = outerSide[i + 1];
const offset = i * 4;
index.set([offset, offset + 1, offset + 2, offset + 2, offset + 1, offset + 3], i * 6);
position.set([...a, ...b, ...c, ...d], i * 8);
}
return new Geometry(gl, {
position: {size: 2, data: position},
index: {data: index},
});
}
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 position;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 10.0;
float scale = 1.0 / 256.0;
mat3 projectionMatrix = mat3(
scale, 0, 0,
0, -scale, 0,
-1, 1, 1
);
vec3 pos = projectionMatrix * vec3(position, 1);
gl_Position = vec4(pos.xy, 0, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
precision highp float;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(0.9803921568627451, 0.5019607843137255, 0.4470588235294118, 1);
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new Renderer({
canvas,
width: 512,
height: 512,
antialias: true,
});
const gl = renderer.gl;
gl.clearColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
const program = new Program(gl, {
vertex,
fragment,
});
const points = [
new Vec2(100, 100),
new Vec2(100, 200),
new Vec2(200, 150),
new Vec2(300, 200),
new Vec2(300, 100),
];
const geometry = extrudePolyline(gl, points, {lineWidth: 10});
const scene = new Transform();
const polyline = new Mesh(gl, {geometry, program});
polyline.setParent(scene);
renderer.render({scene});
</script>
</body>
</html>
参考资料
- Cartographical Symbol Construction with MapServer