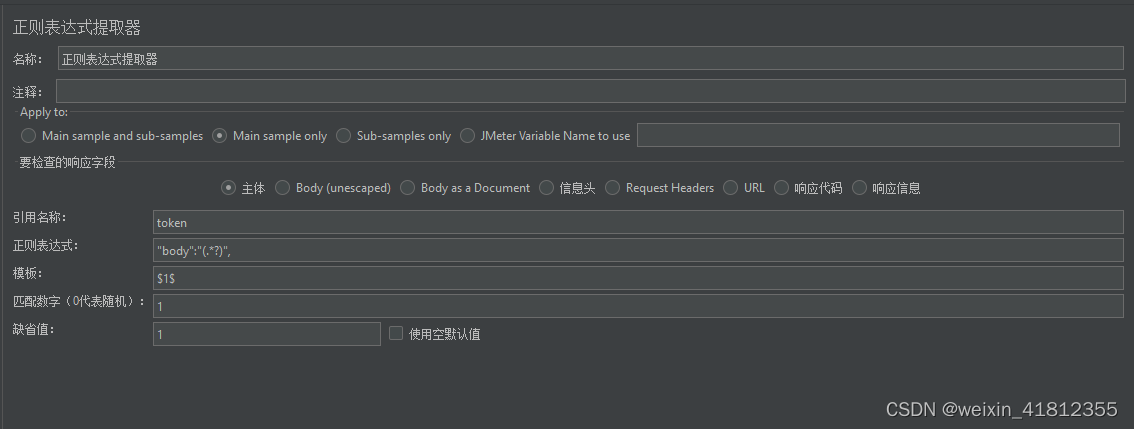
准备
| 机器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| server | 安装pxe相关软件,nfs-kernel-server,ip=192.168.1.2 |
| client1 | 带有硬盘,使用iso安装ubuntu系统,并安装日常工作需要用到的软件,做好相应配置,安装nfs客户端:nfs-common |
| client2 | 没有系统盘,其他硬件配置跟client1一致,测试用 ,ip=192.168.1.4 |
1、参考如下链接在server端部署pxe环境
https://blog.csdn.net/u010438035/article/details/128396790
2、参考如下链接在server端和client1端分别部署nfs服务端和客户端
https://blog.csdn.net/u010438035/article/details/128422999
在server端配置OS根目录
Create a directory to hold the OS files for the client
sudo mkdir /nfsroot
configure your /etc/exports to export your /nfsroot
/nfsroot 192.168.2.xxx(rw,no_root_squash,async,insecure)
NOTE: The ‘192.168.2.xxx’ should be replaced with either the client IP or hostname for single installations, or wildcards to match the set of servers you are using.
Note: In versions prior to Ubuntu 11.04 the option ‘,insecure’ is not required after async.
sync your exports
sudo exportfs -rv
在client1端克隆文件系统
mount -t nfs -onolock 192.168.1.2:/nfsroot /mnt
cp -ax /. /mnt/.
cp -ax /dev/. /mnt/dev/.
在client1端制作vmlinuz和initrd.img
Copy current kernel version to your home directory.
uname -r will print your kernel version, and ~ is shorthand for your home directory.
sudo cp /boot/vmlinuz-`uname -r` ~
Create an initrd.img file
Change the BOOT flag to nfs in /etc/initramfs-tools/initramfs.conf
#
# BOOT: [ local | nfs ]
#
# local - Boot off of local media (harddrive, USB stick).
#
# nfs - Boot using an NFS drive as the root of the drive.
#
BOOT=nfs
Change the MODULES flag to netboot in /etc/initramfs-tools/initramfs.conf
#
# MODULES: [ most | netboot | dep | list ]
#
# most - Add all framebuffer, acpi, filesystem, and harddrive drivers.
#
# dep - Try and guess which modules to load.
#
# netboot - Add the base modules, network modules, but skip block devices.
#
# list - Only include modules from the 'additional modules' list
#
MODULES=netboot
NOTE: if you have anything in /etc/initramfs-tools/conf.d/driver-policy, this line will be ignored.
Check which modules you will need for your network adapters and put their names into /etc/initramfs-tools/modules (for example forcedeth , r8169 or tulip)
Run mkinitramfs
mkinitramfs -o ~/initrd.img-`uname -r`在这里插入代码片
把在client1端生成的复制到server端的如下图所示的目录中:
scp ~/vmlinuz-uname -r 192.168.1.2:/var/ftpd/boot/live-server/vmlinuz
scp ~/initrd.img-uname -r 192.168.1.2:/var/ftpd/boot/live-server/initrd
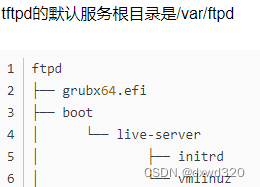
在server端修改grub.cfg
内容如下:
menuentry "Try or Install Ubuntu Server" {
set gfxpayload=keep
linux /boot/live-server/vmlinuz root=/dev/nfs ip=dhcp nfsroot=192.168.1.2:/nfsroot
initrd /boot/live-server/initrd
}
在server端修改网卡配置改为手动配置ip
编辑/nfsroot/etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
在server端修改fstab
/nfsroot/etc/fstab contains the information the client will use to mount file systems on boot, edit it to ensure it looks something like this ('note no swap')
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
#
# <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
/dev/nfs / nfs defaults 1 1
none /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0
none /var/run tmpfs defaults 0 0
none /var/lock tmpfs defaults 0 0
none /var/tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0
/dev/hdc /media/cdrom0 udf,iso9660 user,noauto 0 0
NOTE: if you have entries for other tmpfs that's fine to leave them in there
在server端修改/nfsroot/etc/kernel/postinst.d/zz-update-grub,禁用grub更新
cat /etc/kernel/postinst.d/zz-update-grub
#! /bin/sh
set -e
which update-grub >/dev/null 2>&1 || exit 0
if type systemd-detect-virt >/dev/null 2>&1 &&
systemd-detect-virt --quiet --container; then
exit 0
fi
set -- $DEB_MAINT_PARAMS
mode="${1#\'}"
mode="${mode%\'}"
case $0:$mode in
# Only run on postinst configure and postrm remove, to avoid wasting
# time by calling update-grub multiple times on upgrade and removal.
# Also run if we have no DEB_MAINT_PARAMS, in order to work with old
# kernel packages.
*/postinst.d/*:|*/postinst.d/*:configure|*/postrm.d/*:|*/postrm.d/*:remove)
if [ -e /boot/grub/grub.cfg ]; then
# exec update-grub
fi
;;
esac
exit 0
验证
设置client2从pxe启动,client2开机后会自动进入Ubuntu系统,系统和client1的一样。
参考
https://help.ubuntu.com/community/DisklessUbuntuHowto