一 问题描述
有 N 家旅馆,每家旅馆都有位置和价格,有 M 个客人希望找到一家价格可接受的最近旅馆。
二 输入和输出
1 输入
每个测试用例的第 1 行都包含两个整数 N(N ≤200000)和 M(M ≤20000),分别表示旅馆数量和客人数量。接下来的 N 行,每行都包含3个整数 x、y 和 c(1≤x , y,c ≤N),其中 x、y 是旅馆的坐标,c 是其价格,保证 N 个旅馆都有不同的 x、y 和 c 。接下来的 M 行,每行都描述一个客人的查询,其中 x 、y 是客人的坐标,c 是客人可接受的最高价格。
2 输出
对每个客人的查询,都单行输出价格可接受的最近旅馆。若有多个旅馆的价格可以接受且距离最小,则输出第 1 个。
三 输入和输出样例
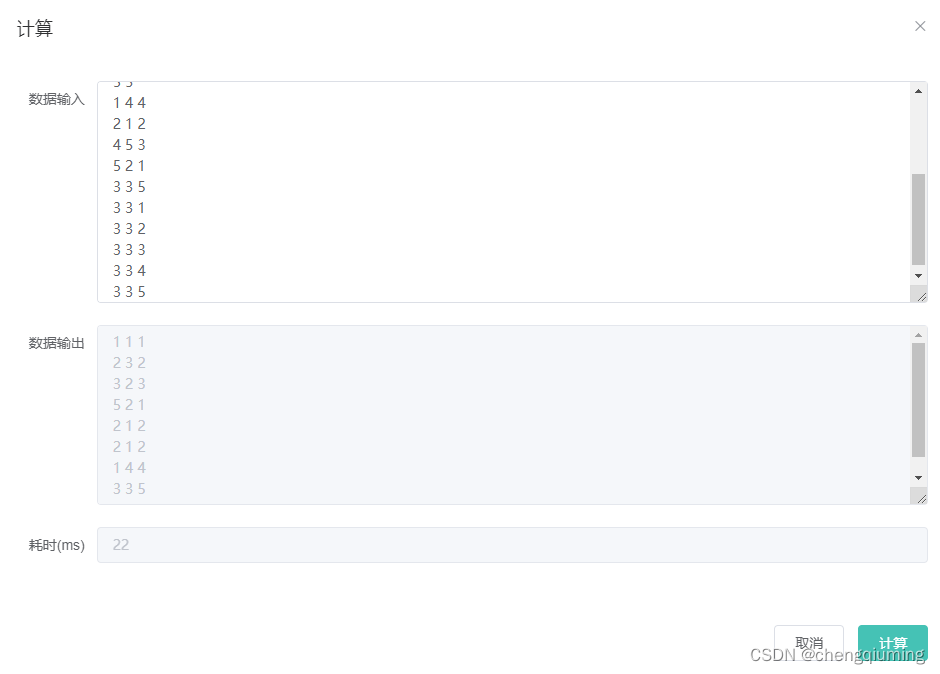
1 输入样例
2
3 3
1 1 1
3 2 3
2 3 2
2 2 1
2 2 2
2 2 3
5 5
1 4 4
2 1 2
4 5 3
5 2 1
3 3 5
3 3 1
3 3 2
3 3 3
3 3 4
3 3 5
2 输出样例
1 1 1
2 3 2
3 2 3
5 2 1
2 1 2
2 1 2
1 4 4
3 3 5
四 分析和设计
1 分析
本问题为三维数据,包括二维坐标和价格,可采用 KD 树解决。
2 算法设计
(1)根据输入数据的二维坐标创建 KD 树。
(2)在 KD 树中查询距离 p 最近且价格不超过 c 的旅馆。
3 算法实现
查询距离给定点 p 最近且价格不超过c 的点,算法步骤如下。
(1)创建一个序对,第 1 个元素记录当前节点到 p 的距离,第 2 个元素记录当前节点;然后定义一个变量 res,存储离 p 最近且价格不超过 c 的序对。
(2)查询时从树根开始,首先计算树根与 p 的距离,用 cur 记录距离、节点序对。
(3)若 p.x [dim]<kd[rt].x[dim],则首先在左子树 lc 中查询,否则在右子树 rc 中查询。若 p.x [dim]≥kd[rt].x [dim],则交换 lc 和 rc,这样就可以统一为首先在 lc 中查询。
(4)若 lc 不空,则在 lc 中递归查询 query(lc, m , dep+1, p)。
(5)若还没有答案,且当前节点的价格小于 p 的价格,则更新答案为当前节点 res=cur,flag=1,还需要在右子树中查询;若当前节点的价格小于 p 的价格且当前节点到 p 的距离小于 res 到 p 的距离,或者
两者相等但 cur 的序号在前,则更新 res=cur;若以 p 为球心且以 p 到 res 的距离为半径的圆与树根的另一区域相交,则 flag=1,还需要在右子树中查询。
(6)若 rc 不空且 flag=1,则在 rc 中递归查询 query(rc,m,dep+1, p)。
五 代码
package com.platform.modules.alg.alglib.hdu5992;
import javafx.util.Pair;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Hdu5992 {
private int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
private int maxn = 200000 + 10;
int idx;
public String output = "";
int sz[] = new int[maxn << 2];
Node a[] = new Node[maxn];
Node kd[] = new Node[maxn << 2];
Pair<Long, Node> res;
public Hdu5992() {
res = new Pair<>(-1L, new Node());
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = new Node();
}
for (int i = 0; i < kd.length; i++) {
kd[i] = new Node();
}
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r, int dep) {
if (l > r) return;
sz[rt] = 1;
sz[rt << 1] = sz[rt << 1 | 1] = 0;
idx = dep % 2;// 注意只按二维建树
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
Arrays.sort(a, l, r + 1);
kd[rt] = a[mid];
build(rt << 1, l, mid - 1, dep + 1);
build(rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, dep + 1);
}
Long dis(int rt, Node p) { // 求距离二维
return Long.valueOf((p.x[0] - kd[rt].x[0]) * (p.x[0] - kd[rt].x[0]) +
(p.x[1] - kd[rt].x[1]) * (p.x[1] - kd[rt].x[1]));
}
void query(int rt, Node p, int dep) {
if (sz[rt] == 0) return;
Pair<Long, Node> cur = new Pair(dis(rt, p), kd[rt]);
int lc = rt << 1, rc = rt << 1 | 1, dim = dep % 2, flag = 0;
if (p.x[dim] >= kd[rt].x[dim]) {
int temp = lc;
lc = rc;
rc = temp;
}
if (sz[lc] > 0)
query(lc, p, dep + 1);
if (res.getKey() == -1) {//第一个
if (cur.getValue().x[2] <= p.x[2])
res = cur;
flag = 1;
} else {
if (cur.getValue().x[2] <= p.x[2] && (cur.getKey() < res.getKey()
|| (cur.getKey() == res.getKey() && cur.getValue().id < res.getValue().id)))
res = cur;
if ((kd[rt].x[dim] - p.x[dim]) * (kd[rt].x[dim] - p.x[dim]) <= res.getKey())
flag = 1;
}
if (sz[rc] > 0 && flag == 1)
query(rc, p, dep + 1);
}
public String cal(String input) {
int t, n, m;
String[] line = input.split("\n");
t = Integer.parseInt(line[0]);
int count = 1;
while (t-- > 0) {
String[] num = line[count++].split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(num[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(num[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
String[] postion = line[count++].split(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; ++j) {
a[i].x[j] = Integer.parseInt(postion[j]);
}
a[i].id = i;
}
build(1, 0, n - 1, 0);
while (m-- > 0) {
Node p = new Node();
Node ans;
String[] query = line[count++].split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
p.x[i] = Integer.parseInt(query[i]);
}
res = new Pair<>(-1L, new Node());
query(1, p, 0);
ans = res.getValue();
output += ans.x[0] + " " + ans.x[1] + " " + ans.x[2] + "\n";
}
}
return output;
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int x[] = new int[3];
int id; // 输入序号
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return x[idx] > o.x[idx] ? 1 : -1; // 升序
}
}
}六 测试