一、修改启动进程数
worker_processes 1;
#允许的启动工作进程数数量,和你真实的cpu数量有关 1worker_processes auto;
#如果设置为auto 就是你真实的cpu数量ps axo pid,cmd,psr,ni|grep nginx
#可以看到 nginx的 worker数量




二、日制分割
[root@yuji ~]# vim /opt/rzfg.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Filename: rzfg.sh
# nginx日志分割,按时间分割
#显示前一天的时间
day=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d")
#旧日志文件目录
logs_path="/var/log/nginx"
#nginx进程的PID
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
#如果旧日志目录不存在,则创建日志文件目录
[ -d $logs_path ] || mkdir -p $logs_path
#将日志移动到旧日志目录,并重命名日志文件
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${logs_path}/tt.com-access.log-$day
#重建新日志文件
kill -USR1 $(cat $pid_path)
#删除30天之前的日志文件
find $logs_path -mtime +30 -exec rm -rf {} ;
2. #赋予执行权限,执行脚本。查看日志文件目录。
[root@yuji ~]# chmod +x /usr/local/nginx/nginx_log.sh
[root@yuji ~]# /opt/fenge.sh
[root@yuji ~]# ls /var/log/nginx/
tt.com-access.log-20220516
//旧日志文件已被移动到设置好的目录
[root@yuji ~]# ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/ //已重建新日志文件
access.log error.log nginx.pid 3. #编写计划任务,每天定点执行
[root@localhost nginx]#crontab -e
0 1 * * * /opt/rzfg.sh


三、nginx进程的优先级(work进程的优先级)
nice的优先级是 -20 到 19
worker_priority 0;
#工作进程优先级,-20~20(19)



四、http设置
4.1http 协议配置说明
http {
include mime.types; #导入支持的文件类型,是相对于/apps/nginx/conf的目录
default_type application/octet-stream; #除mime.types中文件类型外,设置其它文件默认类型,访问其它类型时会提示下载不匹配的类型文件
#日志配置部分
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#自定义优化参数
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on; #在开启了sendfile的情况下,合并请求后统一发送给客户端。
#tcp_nodelay off; #在开启了keepalived模式下的连接是否启用TCP_NODELAY选项,当为off时,延迟0.2s发送,默认On时,不延迟发送,立即发送用户响应报文。
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65 65; #设置会话保持时间,第二个值为响应首部:keepAlived:timeout=65,可以和第一个值不同
#gzip on; #开启文件压缩
server {
listen 80; #设置监听地址和端口
server_name localhost; #设置server name,可以以空格隔开写多个并支持正则表达式,如:*.kgc.com www.kgc.* ~^www\d+\.kgc\.com$ default_server
#charset koi8-r; #设置编码格式,默认是俄语格式,建议改为utf-8
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #定义错误页面
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ { #以http的方式转发php请求到指定web服务器
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ { #以fastcgi的方式转发php请求到php处理
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht { #拒绝web形式访问指定文件,如很多的网站都是通过.htaccess文件
来改变自己的重定向等功能。
# deny all;
#}
location ~ /passwd.html {
deny all;
}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server { #自定义虚拟server
3.3.1 MIME
范例: 识别php文件为text/html
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm; #指定默认网页文件,此指令由
ngx_http_index_module模块提供
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server { #https服务器配置
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
4.2mime
此项为支持的 文件格式,如果不支持的格式 会自动帮你下载,如果支持 就会显示在网页上
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/nginx/mime.types
types {
text/html html htm shtml;
.....................................................................
image/png png;
image/svg+xml svg svgz;
image/tiff tif tiff;
image/vnd.wap.wbmp wbmp;
image/webp webp;
image/x-icon ico;
image/x-jng jng;
image/x-ms-bmp bmp;
4.3 server块构建虚拟主机




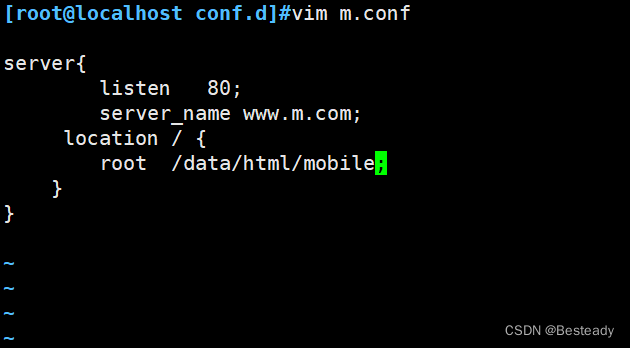



去第二台机器修改/etc/hosts 文件


4.4 location
在一个server中location配置段可存在多个,用于实现从uri到文件系统的路径映射;ngnix会根据用户请求的URI来检查定义的所有location,按一定的优化级找出一个最佳匹配,而后应用其配置在没有使用正则表达式的时候,nginx会先在server中的多个location选取匹配度最高的一个uri,uri是用户请求的字符串,即域名后面的web文件路径,然后使用该location模块中的正则url和字符串,如果匹配成功就结束搜索,并使用此location处理此请求。
#语法规则:
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }= #用于标准uri前,需要请求字串与uri精确匹配,大小敏感,如果匹配成功就停止向下匹配并立即处理请求
^~ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式,并且匹配以指定的正则表达式开头,对URI的最左边部分做匹配检查,不区分字符大小写
~ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式,并且区分大小写
~* #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式,并且不区分大写
不带符号 #匹配起始于此uri的所有的uri
\ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且转义字符。可以将 . * ?等转义为普通符号#匹配优先级从高到低:
=, ^~, ~/~*, 不带符号


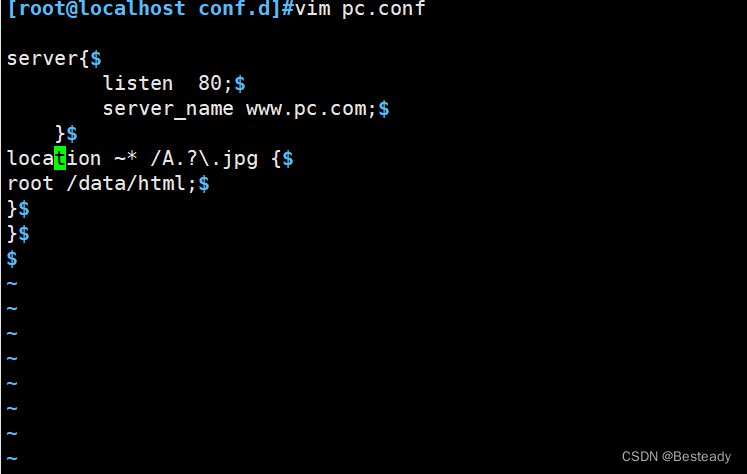
不区分大小写-案例
#正则表达式匹配:
location ~* /A.?\.jpg {
#匹配 已A后面一个或没有字符,已.jpg结尾的图片
root /opt/nginx/html/image;
}
只要是图片就去 images中找
server{
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|bmp|png|tiff|tif|ico|wmf|js|css)$ {
root /data/nginx/images/;
}
}#####匹配优先级#########
此处的优先级有小问题
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.pc.com;
location = / {
root /data/nginx/pc;
}
location / {
root /mnt/nginx/news;
}
}
生产案例
#直接匹配网站根会加速Nginx访问处理
location = /index.html {
......;
}
location / {
......;
}
#静态资源配置方法1
location ^~ /static/ {
......;
}
#静态资源配置方法2,应用较多
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
......;
}
#多应用配置
location ~* /app1 {
......;
}
location ~* /app2 {
......;








![HTML总结2 [转]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3d8a28eb78b04b62bbddd62cc1b8b2ed.png)