文章目录
- 一、背景
- 二、@Value 取值为 null 原因分析
- 2.1. @Value 取值为 null 常见原因分析
- 常见现象一:类没有交给 Spring 管理,比如类没有加上 @Component 等注解
- 常见现象二:手动 new 对象实例,没有从 Spring 容器中获取
- 常见现象三:使用 static 或 final 修饰成员变量
- 2.2 案例原因分析
- 三、解决方案
一、背景
近期应用中因业务迭代需要接入 user 客户端,接入后总是启动失败,报注册 user bean 依赖的配置属性为 null(如 appName,group 等都为空),示例代码如下:
@Configuration
public class ConsumerBeanConfig {
@Value("${project.name}")
private String appName;
@Value("${spring.hsf.group}")
private String group;
@Value("${spring.hsf.version}")
private String version;
@Bean
public UserCommonContext userCommonContext() {
UserCommonContext commonContext = new UserCommonContext();
commonContext.setAppName(appName);
return commonContext;
}
@Bean
public HSFSpringConsumerBean userReadService() {
HSFSpringConsumerBean consumer = new HSFSpringConsumerBean();
consumer.setInterfaceClass(UserReadService.class);
consumer.setVersion(version);
consumer.setGroup(group);
return consumer;
}
//......
}
二、@Value 取值为 null 原因分析
2.1. @Value 取值为 null 常见原因分析
常见现象一:类没有交给 Spring 管理,比如类没有加上 @Component 等注解
- 错误案例
// 配置类
public class PeopleConfigValue {
@Value("${people.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${people.age}")
private String age;
public PeopleConfigValue() {
}
// getter and setter...
}
// 测试类(以下取值为空)
PeopleConfigValue peopleConfigValue = new PeopleConfigValue();
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-name value " + peopleConfigValue.getName());
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-age value " + peopleConfigValue.getAge());
- 正常案例
@Component
public class PeopleConfigValue {
@Value("${people.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${people.age}")
private String age;
public PeopleConfigValue() {
}
// getter and setter...
}
// 测试类(以下取值正常)
PeopleConfigValue peopleConfigValue = SpringContextUtil.getBean(PeopleConfigValue.class);
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-name value " + peopleConfigValue.getName());
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-age value " + peopleConfigValue.getAge());
常见现象二:手动 new 对象实例,没有从 Spring 容器中获取
- 错误案例
@Component
public class PeopleConfigValue {
@Value("${people.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${people.age}")
private String age;
public PeopleConfigValue() {
}
// getter and setter...
}
// 测试类(以下取值为空)
PeopleConfigValue peopleConfigValue = new PeopleConfigValue();
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-name value " + peopleConfigValue.getName());
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-age value " + peopleConfigValue.getAge());
- 正确案例,参考第一个现象。
常见现象三:使用 static 或 final 修饰成员变量
使用 static 或 final 修饰成员变量值不可改变,注解无法注入配置值。
- 错误案例
@Component
public class PeopleConfigValue {
@Value("${people.name}")
private static String name;
@Value("${people.age}")
private static String age;
public PeopleConfigValue() {
}
// getter
}
// 测试类(以下取值为空)
PeopleConfigValue peopleConfigValue = SpringContextUtil.getBean(PeopleConfigValue.class);
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-name value " + peopleConfigValue.getName());
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-age value " + peopleConfigValue.getAge());
-
正确案例
以下方式不推荐,作为 static 或 final 修饰成员变量值应该是不可变的,以下可通过 setter 方式修改值:
@Component
public class PeopleConfigValue {
private static String name;
private static String age;
public PeopleConfigValue() {
}
public static String getName() {
return name;
}
@Value("${people.name}")
public void setName(String nameValue) {
name = nameValue;
}
public static String getAge() {
return age;
}
@Value("${people.age}")
public void setAge(String ageValue) {
age = ageValue;
}
}
// 测试类,取值正常
PeopleConfigValue peopleConfigValue = SpringContextUtil.getBean(PeopleConfigValue.class);
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-name value " + peopleConfigValue.getName());
System.out.println("get peopleConfigValue-age value " + peopleConfigValue.getAge());
2.2 案例原因分析
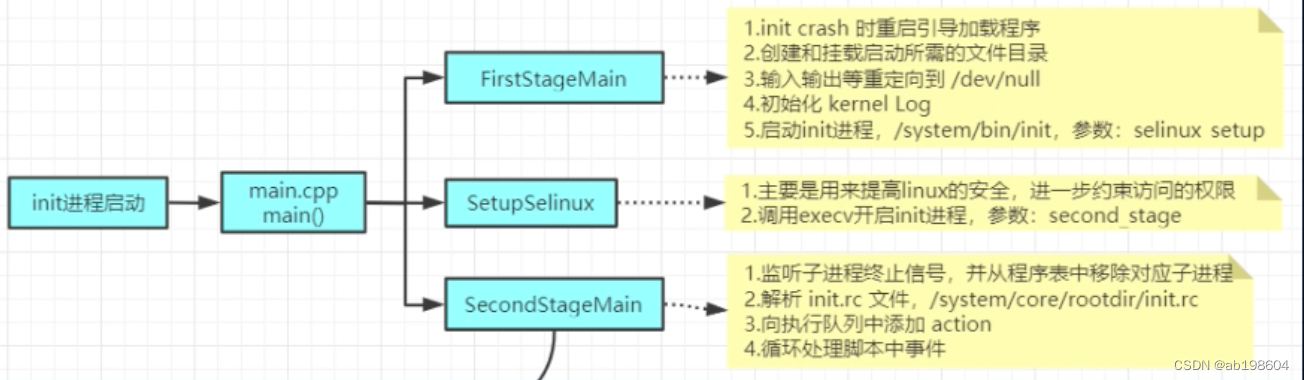
上述案例中 @Value 的使用方式是常规使用方式,不应该出现问题,开始怀疑是与 Spring 应用上下文 Bean 的初始化顺序有关,排查这个问题还是先摸清一下 Spring Boot 的启动原理及 @Value 解析机制,直接上图:

图片箭头指向即 SpringApplication 启动阶段,在这个过程中进行 Bean 的实例化,进一步细化 SpringApplication 启动流程如下:

众所周知,应用中配置的 bean 在 Spring 启动时会全部解析为 BeanDefinition(可视为 bean 的元信息,图中第 2 步),同时 Spring 提供了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口用于用户扩展(图中第 5 步,比如在这里可以修改 BeanDefinition 的元数据) ,最后在实例化 bean 过程时(SpringApplication 启动流程图中第 11.3 步)会读取相应的 BeanDefinition 进行初始化。
回到 @Value 注解占位符的解析机制,@Value 注解占位符靠 PropertyResourceConfigurer 来解析(PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 会调用 PropertyResourceConfigurer 解析能力来解析占位符,并存储到 propertySources 属性集合中),而 PropertyResourceConfigurer 正是实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,在 BeanFactory 后处理阶段进行了占位符替换,且 PropertyResourceConfigurer 的优化级最低(这里有个风险点:任何应用依赖的实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 bean 都会比 PropertyResourceConfigurer 先执行)。

理解了 Spring 的启动机制和 @Value 注解占位符的解析机制,再排查应用代码发现 UserCommonContext 也实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,也就是说,出现了下述情况:

由于 UserCommonContext 依赖了 UserBeanConfig,导致 UserBeanConfig 提前初始化,但此时 @Value 中的占位符还未替换,那么 UserBeanConfig 中所有标记 @Value 注解属性都为 null,导致启动失败。
三、解决方案
上述情况虽然会导致 UserBeanConfig 中所有标记 @Value 注解属性都为 null,其他 bean 的配置就不要依赖 UserBeanConfig 中标记 @Value 注解的属性即可(不依赖干扰 bean 生命周期):
@Bean
public HSFSpringConsumerBean userReadService(@Value("${spring.hsf.version}") String version, @Value("${spring.hsf.group}") String group) {
HSFSpringConsumerBean consumer = new HSFSpringConsumerBean();
consumer.setInterfaceClass(UserReadService.class);
consumer.setVersion(version);
consumer.setGroup(group);
return consumer;
}