本项目主要是基于Opencv完成的人脸识别的考勤系统
人脸检测器的5种实现方法
方法一:haar方法进行实现(以下是基于notebook进行编码)
# 步骤
# 1、读取包含人脸的图片
# 2.使用haar模型识别人脸
# 3.将识别结果用矩形框画出来
# 导入相关包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 200
# 读取图片
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces1.jpg')
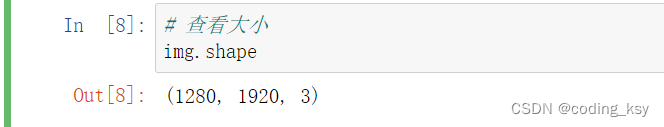
# 查看大小
img.shape
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))

# 构造haar检测器
face_detector = cv2.CascadeClassifier('./cascades/haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
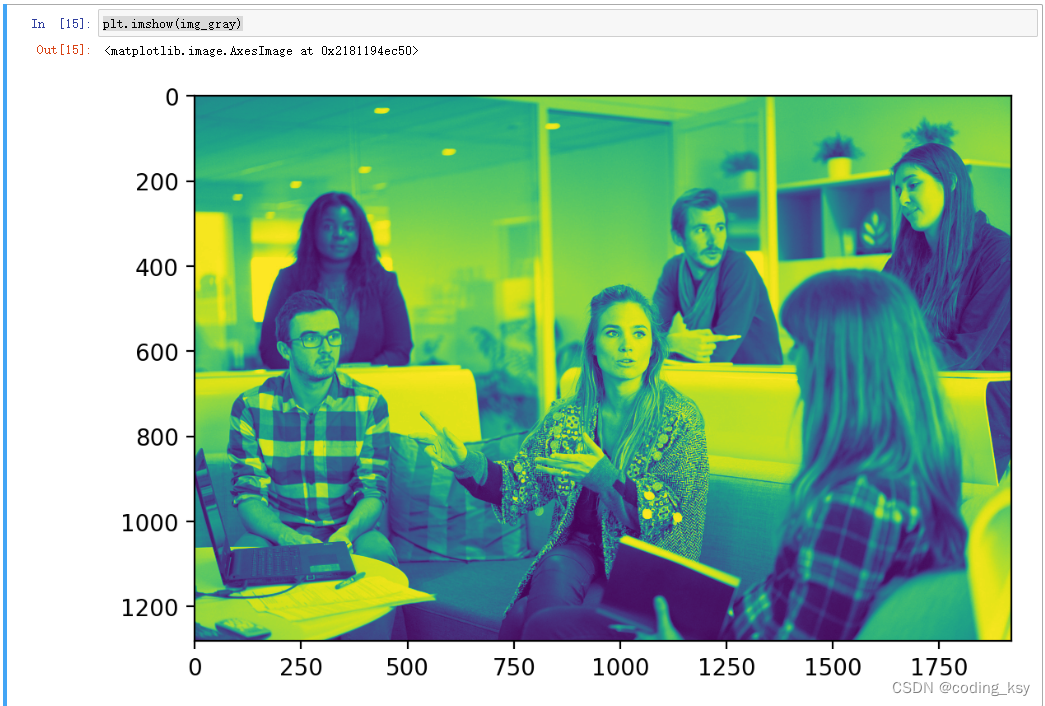
# 转为灰度图
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.imshow(img_gray)
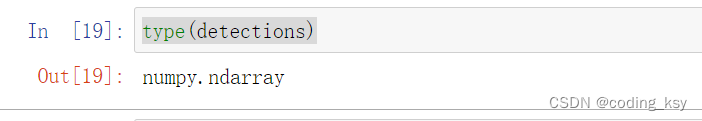
# 检测结果
detections = face_detector.detectMultiScale(img_gray)
type(detections)
# 打印
detections

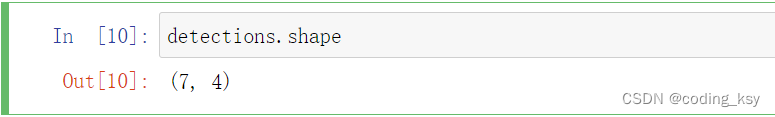
#查看detections的数据结构
detections.shape
#解析结果
for (x,y,w,h) in detections:
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),5)
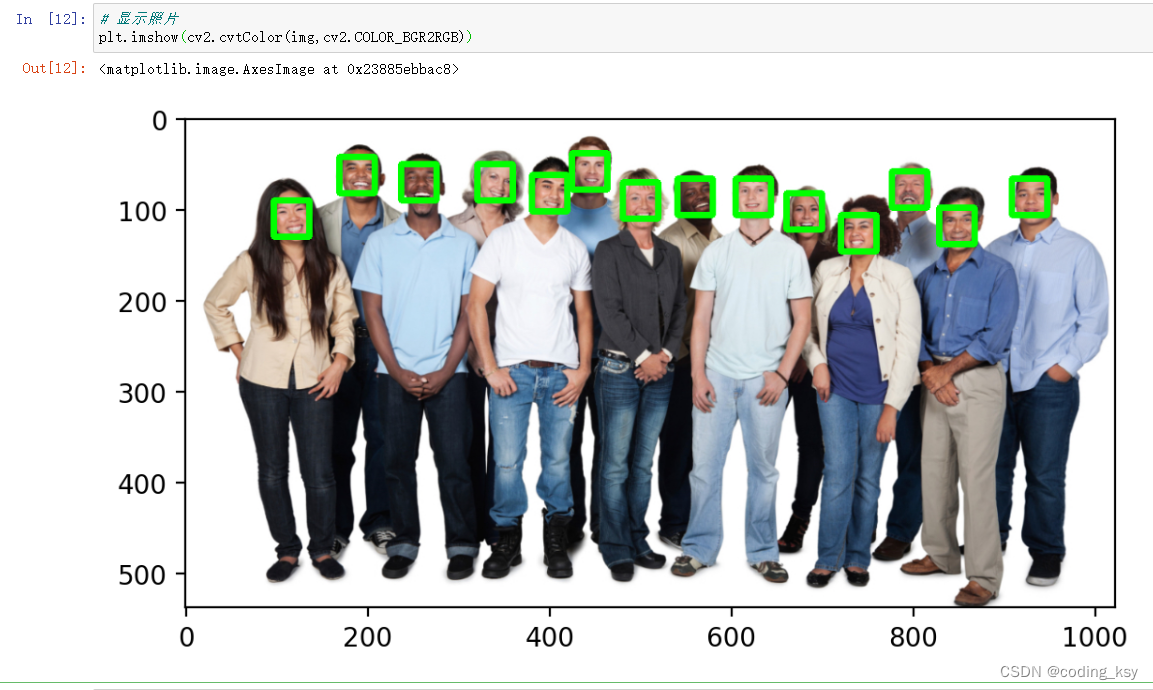
# 显示绘制结果
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
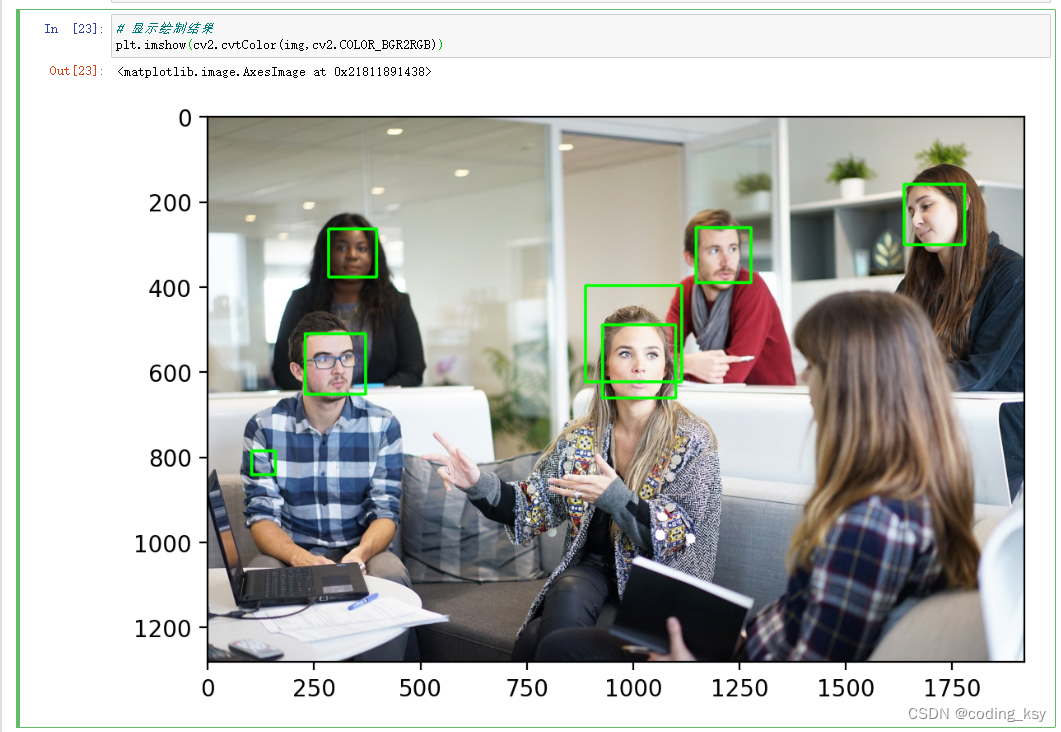
# 调节参数
# scaleFactor:调整图片尺寸
# minNeighbors:候选人脸数量
# minSize:最小人脸尺寸
# maxSize:最大人脸尺寸
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
detections = face_detector.detectMultiScale(img_gray,scaleFactor=1.2,minNeighbors=7,minSize=(10,10),maxSize=(100,100))
# 解析检测结果
for (x,y,w,h) in detections:
print(w,h)
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),5)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
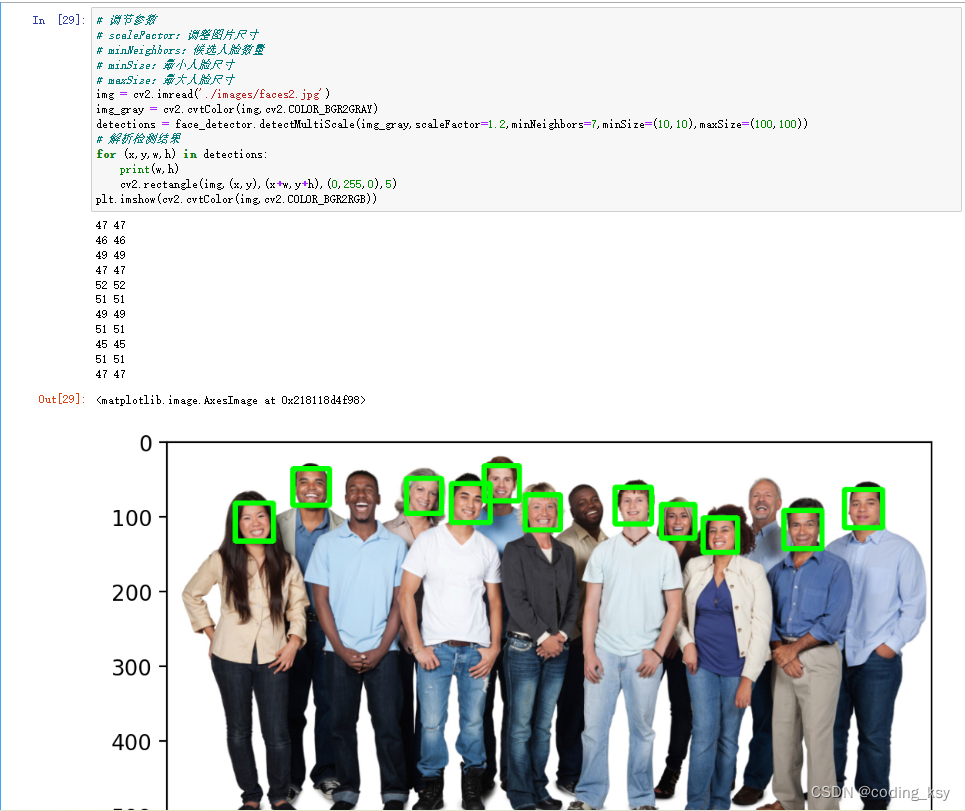
方法二:hog方法进行实现(以下是基于notebook进行编码)
# 导入相关包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 200
# 读取照片
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
# 显示照片
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 安装DLIB
import dlib
# 构造HOG人脸检测器
hog_face_detetor = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 检测人脸
# scale 类似haar的scaleFactor
detections = hog_face_detetor(img,1)
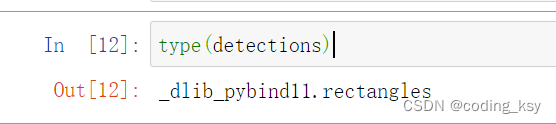
#查看一下detections的类型
type(detections)
# 打印一下
detections

len(detections)
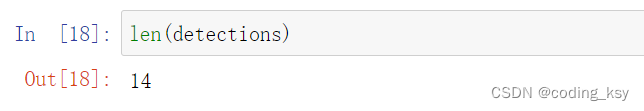
# 解析矩形结果
for face in detections:
x = face.left()
y = face.top()
r = face.right()
b = face.bottom()
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(r,b),(0,255,0),5)
# 显示照片
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
方法三:CNN方法进行实现(以下是基于notebook进行编码)
# 导入相关包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 200
# 读取照片
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
# 显示照片
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 安装DLIB
import dlib
# 构造CNN人脸检测器
cnn_face_detector = dlib.cnn_face_detection_model_v1('./weights/mmod_human_face_detector.dat')
# 检测人脸
detections = cnn_face_detector(img,1)
#查看detections的类型
type(detections)

# 解析矩形结果
for face in detections:
x = face.rect.left()
y = face.rect.top()
r = face.rect.right()
b = face.rect.bottom()
#置信度
c = face.confidence
print(c)
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(r,b),(0,255,0),5)
# 显示照片
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
方法四:SSD方法进行实现(以下是基于notebook进行编码)
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi']=200
# 读取照片
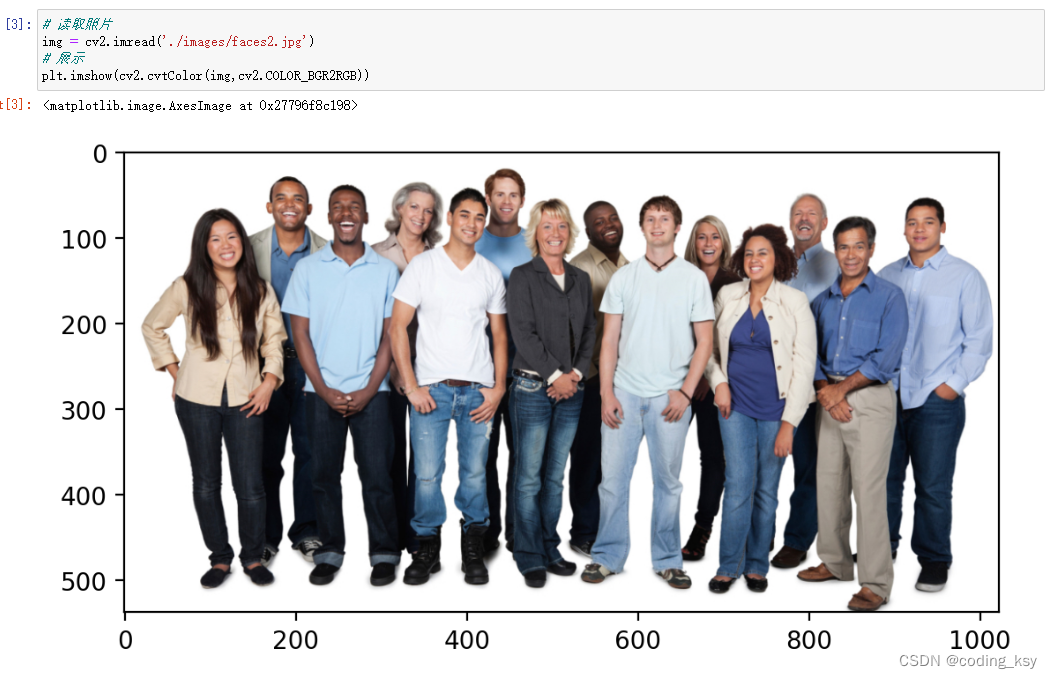
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
# 展示
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# deploy.prototxt.txt:https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/master/samples/dnn/face_detector
# res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel:https://github.com/Shiva486/facial_recognition/blob/master/res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel
# 加载模型
face_detector = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe('./weights/deploy.prototxt.txt','./weights/res10_300x300_ssd_iter_140000.caffemodel')
# 原图尺寸
img_height = img.shape[0]
img_width = img.shape[1]
# 缩放至模型输入尺寸
img_resize = cv2.resize(img,(500,300))
# 图像转为blob(二进制)
img_blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img_resize,1.0,(500,300),(104.0, 177.0, 123.0))
# 输入
face_detector.setInput(img_blob)
# 推理
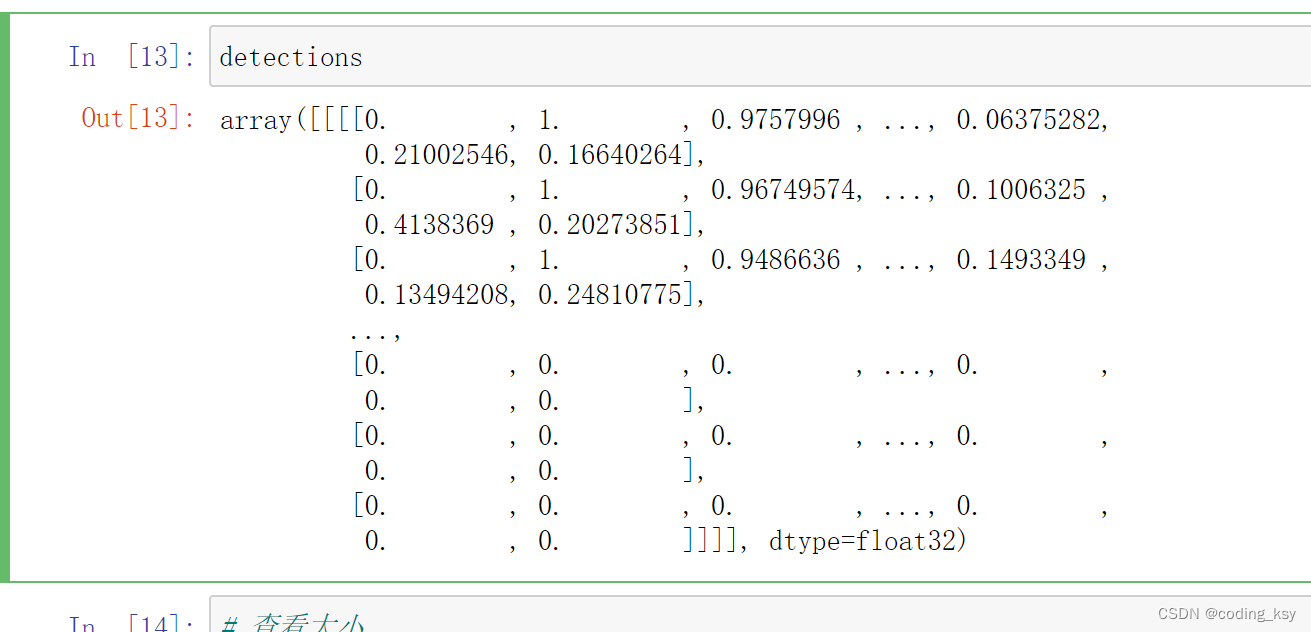
detections = face_detector.forward()
detections
# 查看大小
detections.shape
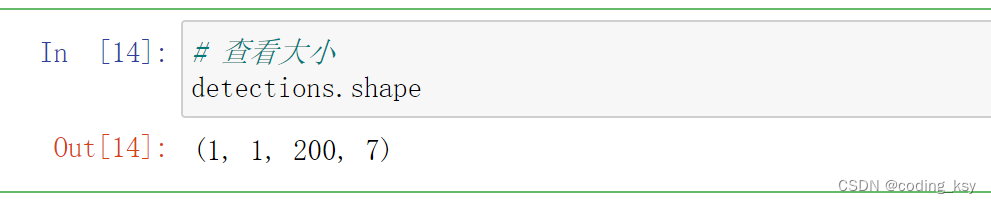
# 查看检测人脸数量
num_of_detections = detections.shape[2]
print(num_of_detections)
# 原图复制,一会绘制用
img_copy = img.copy()
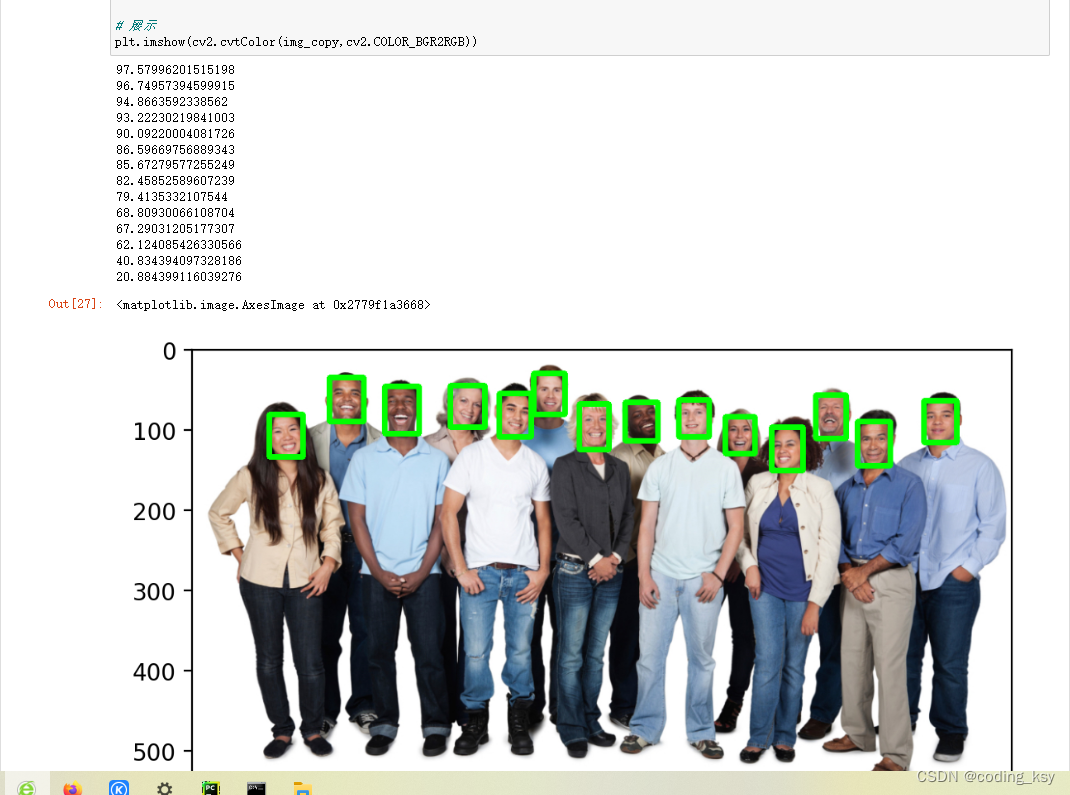
for index in range(num_of_detections):
# 置信度
detection_confidence = detections[0,0,index,2]
# 挑选置信度
if detection_confidence>0.15:
# 位置
locations = detections[0,0,index,3:7] * np.array([img_width,img_height,img_width,img_height])
# 打印
print(detection_confidence * 100)
lx,ly,rx,ry = locations.astype('int')
# 绘制
cv2.rectangle(img_copy,(lx,ly),(rx,ry),(0,255,0),5)
# 展示
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_copy,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
方法五:MTCNN方法进行实现(以下是基于notebook进行编码)
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi']=200
# 读取照片
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
# MTCNN需要RGB通道顺序
img_cvt = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 展示
plt.imshow(img_cvt)
# 导入MTCNN
from mtcnn.mtcnn import MTCNN
# 加载模型
face_detetor = MTCNN()
# 检测人脸
detections = face_detetor.detect_faces(img_cvt)
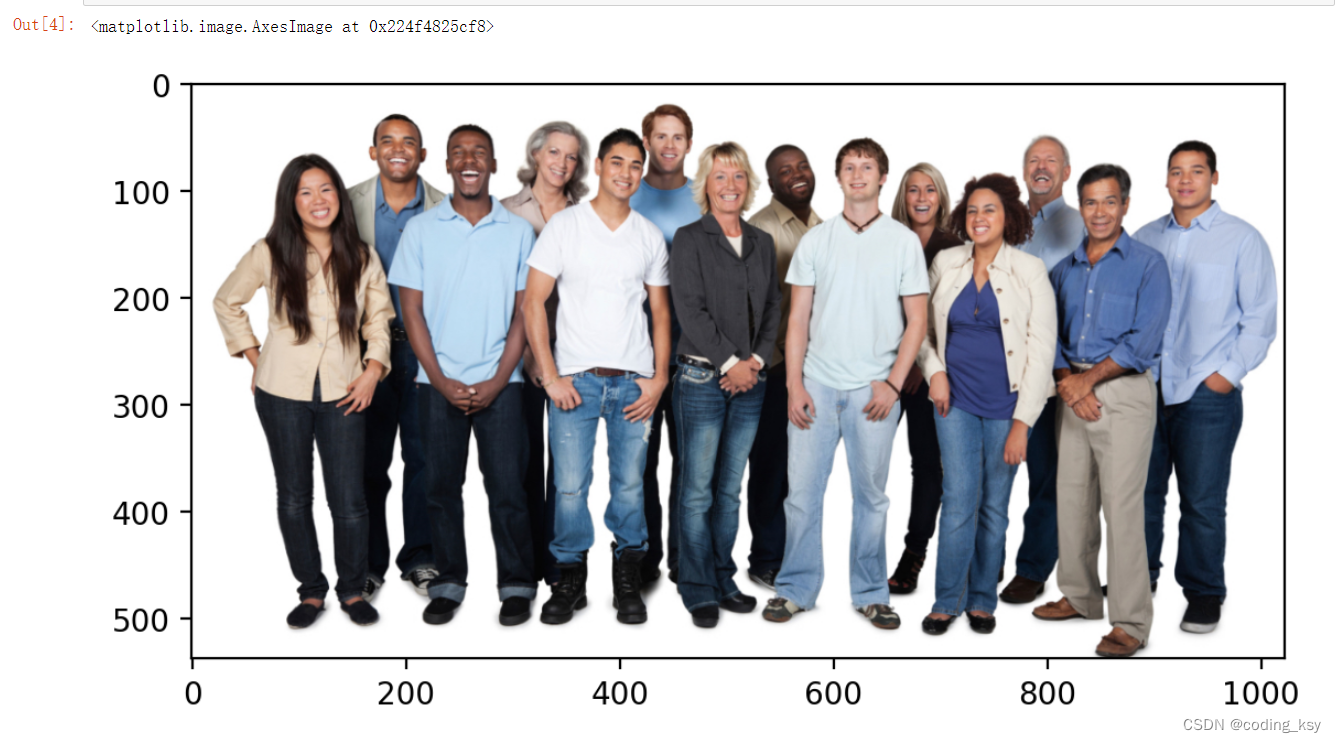
for face in detections:
(x, y, w, h) = face['box']
cv2.rectangle(img_cvt, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0,255,0), 5)
plt.imshow(img_cvt)
# 读取照片
img = cv2.imread('./images/test.jpg')
img_cvt = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 展示
plt.imshow(img_cvt)
# 检测人脸
detections = face_detetor.detect_faces(img_cvt)
for face in detections:
(x, y, w, h) = face['box']
cv2.rectangle(img_cvt, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0,255,0), 5)
plt.imshow(img_cvt)

人脸识别器的2种实现方法
方法一:Eigen_fisher_LBPH(基于notebook进行实现)
# 步骤
# 1、图片数据预处理
# 2、加载模型
# 3、训练模型
# 4、预测图片
# 5、评估测试数据集
# 6、保存模型
# 7、调用加载模型
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import dlib
%matplotlib inline
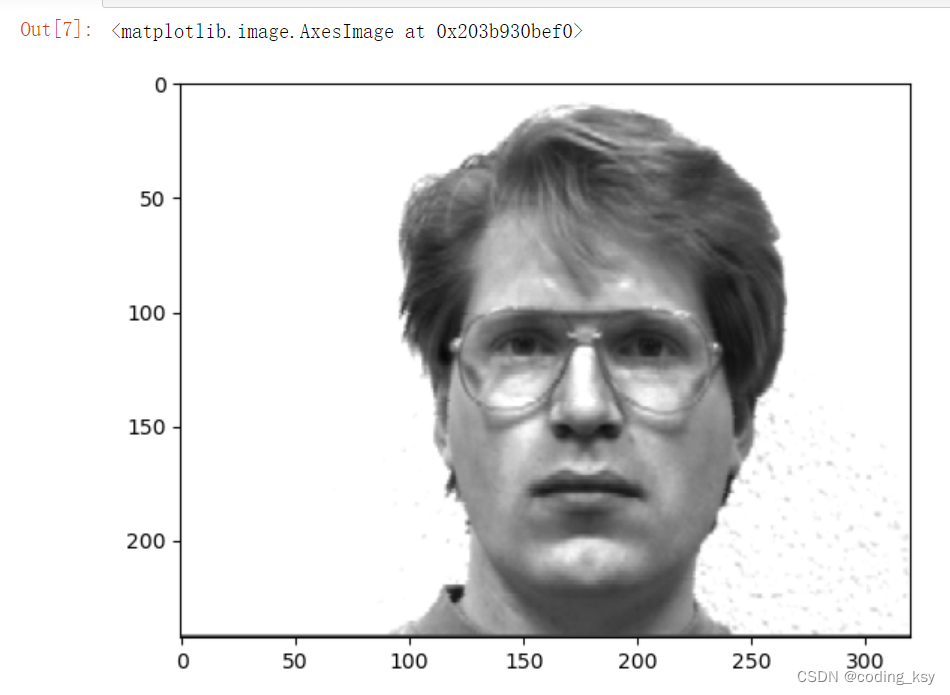
# 随机选一张图片
img_path = './yalefaces/train/subject01.glasses.gif'
# 读取GIF格式图片
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(img_path)
ret,img = cap.read()
img.shape

plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 图片预处理
# img_list:numpy格式图片
# label_list:numpy格式的label
# cls.train(img_list,np.array(label_list))
# 为了减少运算,提高速度,将人脸区域用人脸检测器提取出来
# 构造hog人脸检测器
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
def getFaceImgLabel(fileName):
# 读取图片
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(fileName)
ret,img = cap.read()
# 转为灰度图
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(img,1)
# 判断是否有人脸
if len(detections) > 0:
# 获取人脸区域坐标
x = detections[0].left()
y = detections[0].top()
r = detections[0].right()
b = detections[0].bottom()
# 截取人脸
img_crop = img[y:b,x:r]
# 缩放解决冲突
img_crop = cv2.resize(img_crop,(120,120))
# 获取人脸labelid
label_id = int(fileName.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0].split('subject')[-1])
# 返回值
return img_crop,label_id
else:
return None,-1
img_path = './yalefaces/train/subject01.glasses.gif'
# 测试一张图片
img,label = getFaceImgLabel(img_path)

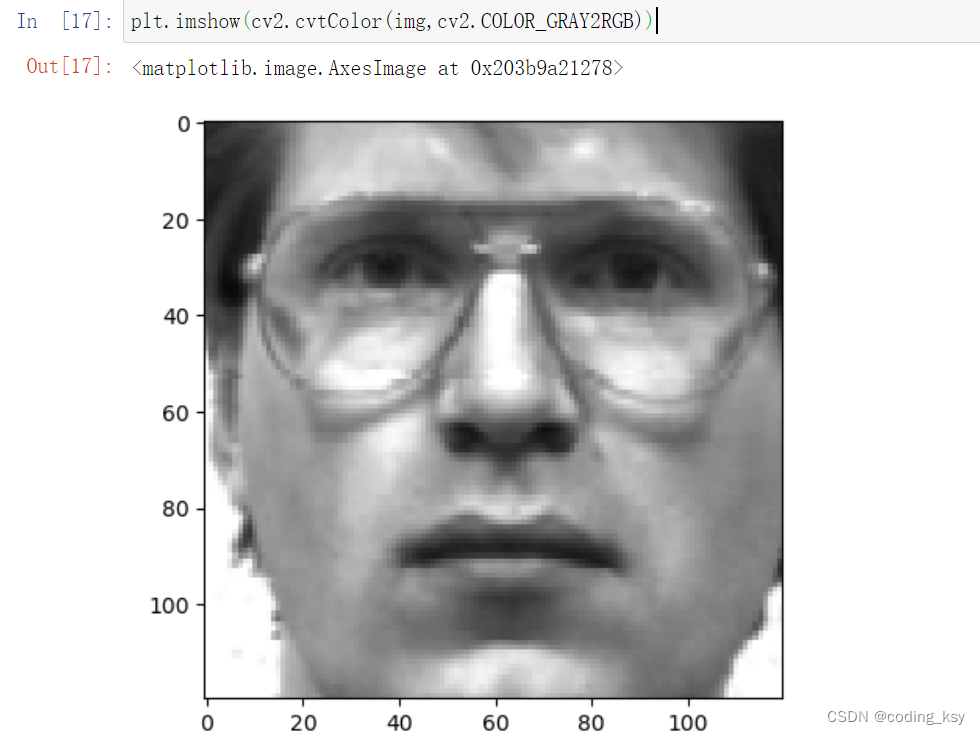
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB))
# 遍历train文件夹,对所有图片同样处理
# 拼接成大的list
import glob
file_list =glob.glob('./yalefaces/train/*')
# 构造两个空列表
img_list = []
label_list = []
for train_file in file_list:
# 获取每一张图片的对应信息
img,label = getFaceImgLabel(train_file)
#过滤数据
if label != -1:
img_list.append(img)
label_list.append(label)
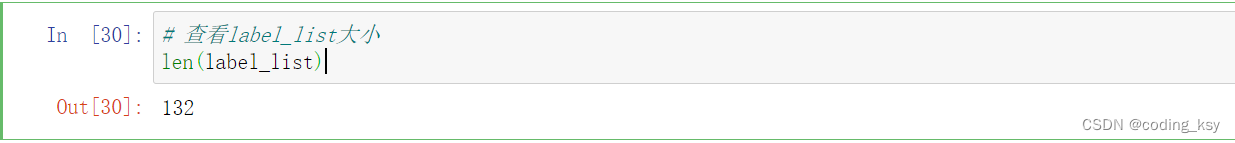
# 查看label_list大小
len(label_list)
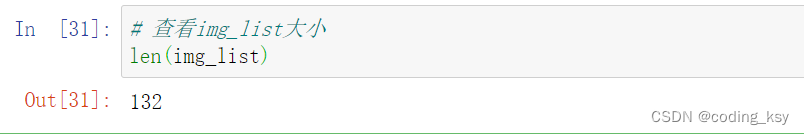
# 查看img_list大小
len(img_list)
# 构造分类器
face_cls = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
# cv2.face.EigenFaceRecognizer_create()
# cv2.face.FisherFaceRecognizer_create()
# 训练
face_cls.train(img_list,np.array(label_list))
# 预测一张图片
test_file = './yalefaces/test/subject03.glasses.gif'
img,label = getFaceImgLabel(test_file)
#过滤数据
if label != -1:
predict_id,distance = face_cls.predict(img)
print(predict_id)
# 评估模型
file_list =glob.glob('./yalefaces/test/*')
true_list = []
predict_list = []
for test_file in file_list:
# 获取每一张图片的对应信息
img,label = getFaceImgLabel(test_file)
#过滤数据
if label != -1:
predict_id,distance = face_cls.predict(img)
predict_list.append(predict_id)
true_list.append(label)
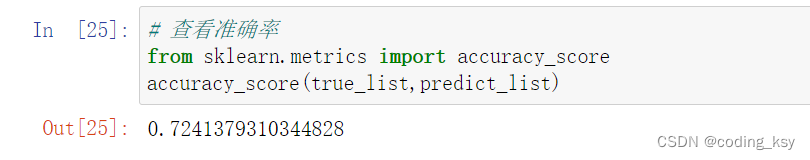
# 查看准确率
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_score(true_list,predict_list)
# 获取融合矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(true_list,predict_list)
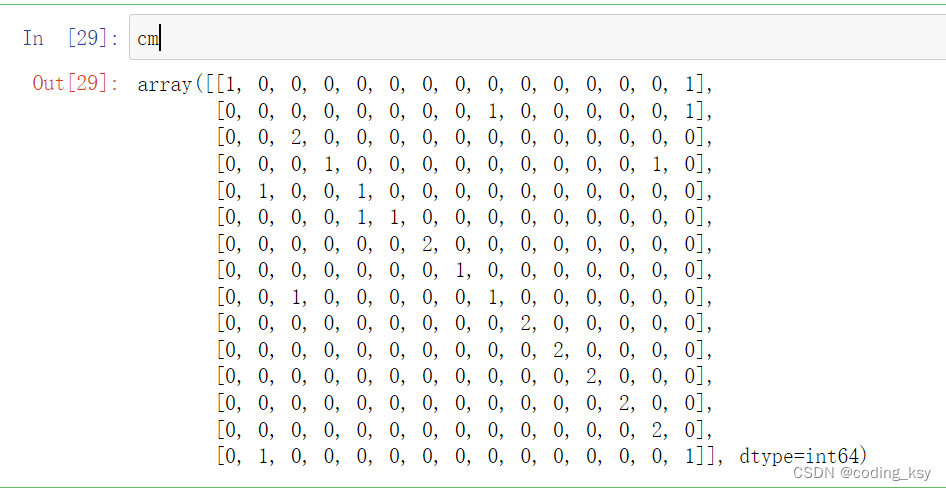
# 可视化
import seaborn
seaborn.heatmap(cm,annot=True)
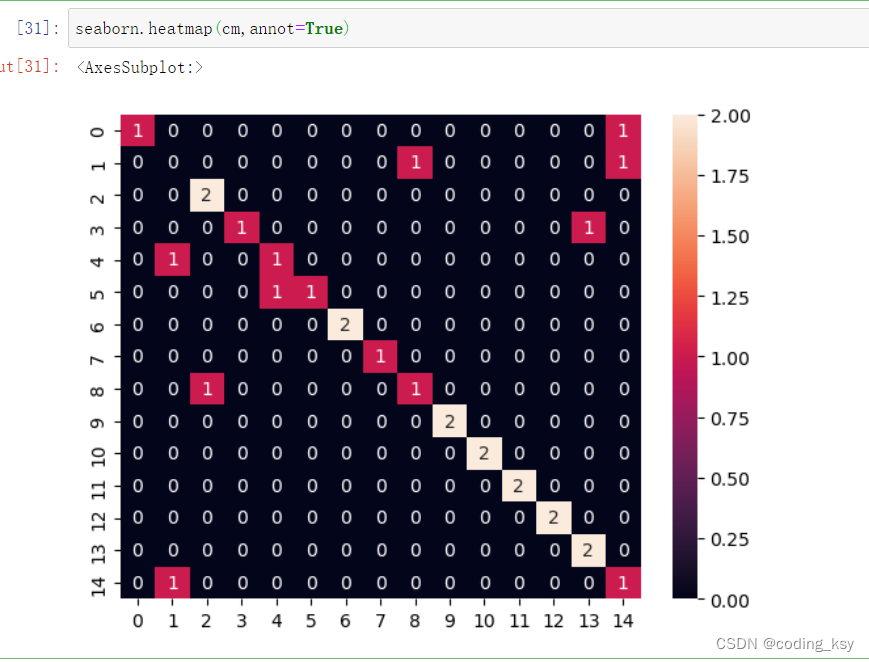
# 保存模型
face_cls.save('./weights/LBPH.yml')
# 调用模型
new_cls = cv2.face.LBPHFaceRecognizer_create()
new_cls.read('./weights/LBPH.yml')
# 预测一张图片
test_file = './yalefaces/test/subject03.glasses.gif'
img,label = getFaceImgLabel(test_file)
#过滤数据
if label != -1:
predict_id,distance = new_cls.predict(img)
print(predict_id)
方法二:resnet(基于notebook进行实现)
# 步骤
# 1、图片数据预处理
# 2、加载模型
# 3、提取图片的特征描述符
# 4、预测图片:找到欧氏距离最近的特征描述符
# 5、评估测试数据集
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import dlib
# %matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 200
# 获取人脸的68个关键点
# 人脸检测模型
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点 检测模型
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 读取一张测试图片
img = cv2.imread('./images/faces2.jpg')
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(img,1)
for face in detections:
# 人脸框坐标
l,t,r,b = face.left(),face.top(),face.right(),face.bottom()
# 获取68个关键点
points = shape_detector(img,face)
# 绘制关键点
for point in points.parts():
cv2.circle(img,(point.x,point.y),2,(0,255,0),1)
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img,(l,t),(r,b),(0,255,0),2)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
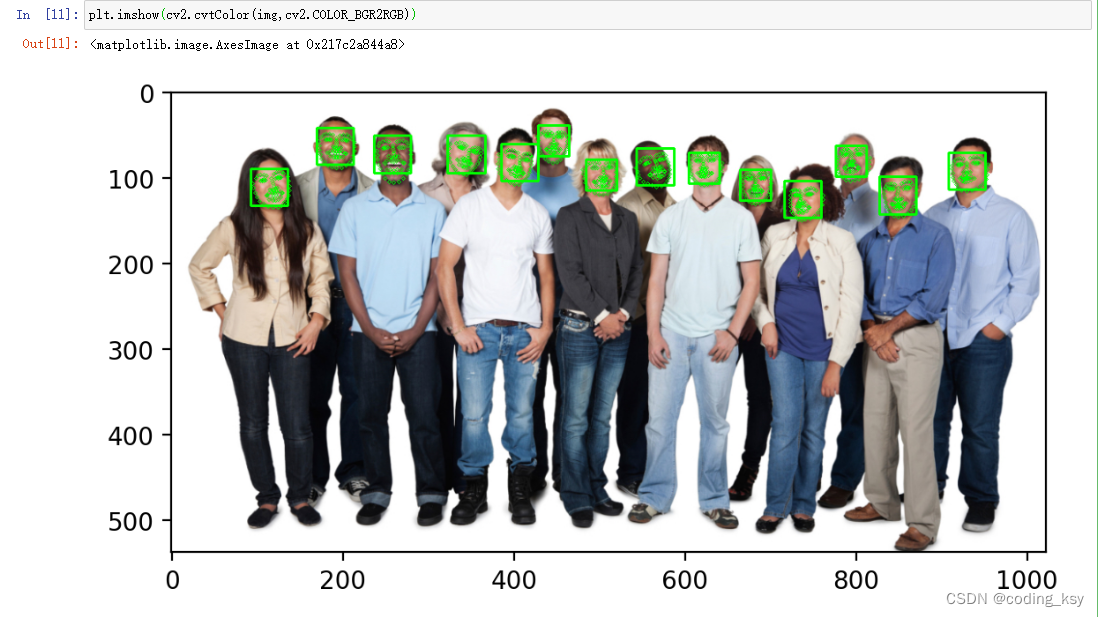
# 面部特征描述符
# 人脸检测模型
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点 检测模型
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# resnet模型
face_descriptor_extractor = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('./weights/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat')
# 提取单张图片的特征描述符,label
def getFaceFeatLabel(fileName):
# 获取人脸labelid
label_id = int(fileName.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0].split('subject')[-1])
# 读取图片
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(fileName)
ret,img = cap.read()
# 转为RGB
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#人脸检测
detections = hog_face_detector(img,1)
face_descriptor = None
for face in detections:
# 获取关键点
points = shape_detector(img,face)
# 获取特征描述符
face_descriptor = face_descriptor_extractor.compute_face_descriptor(img,points)
# 转为numpy 格式的数组
face_descriptor = [f for f in face_descriptor]
face_descriptor = np.asarray(face_descriptor,dtype=np.float64)
face_descriptor = np.reshape(face_descriptor,(1,-1))
return label_id,face_descriptor
# 测试一张图片
id1,fd1 = getFaceFeatLabel('./yalefaces/train/subject01.leftlight.gif')
fd1.shape
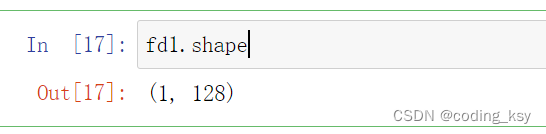
# 对train文件夹进行处理
import glob
file_list =glob.glob('./yalefaces/train/*')
# 构造两个空列表
label_list = []
feature_list = None
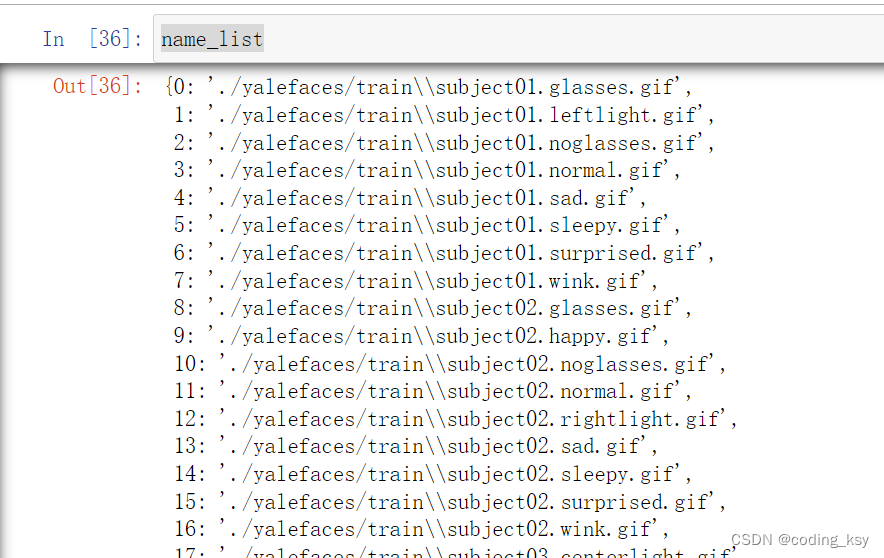
name_list = {}
index= 0
for train_file in file_list:
# 获取每一张图片的对应信息
label,feat = getFaceFeatLabel(train_file)
#过滤数据
if feat is not None:
#文件名列表
name_list[index] = train_file
#label列表
label_list.append(label)
if feature_list is None:
feature_list = feat
else:
# 特征列表
feature_list = np.concatenate((feature_list,feat),axis=0)
index +=1
len(label_list)
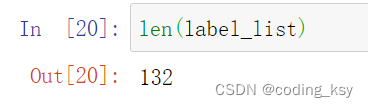
feature_list.shape
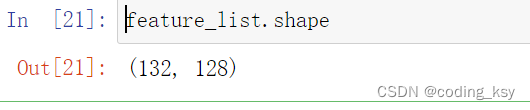
len(name_list)
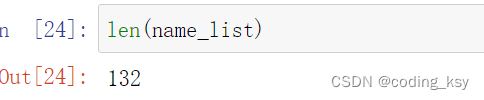
name_list
feature_list[100]
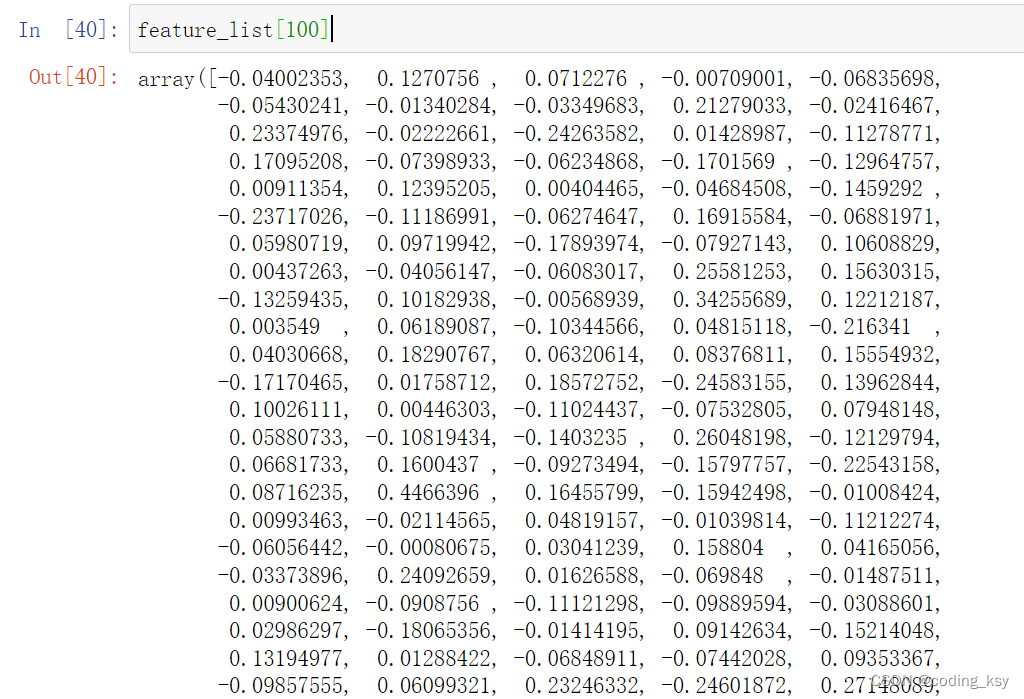
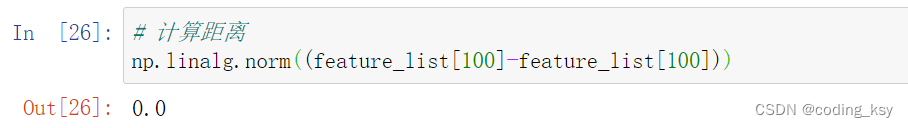
# 计算距离
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[100]-feature_list[100]))
# 计算距离
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[100]-feature_list[101]))
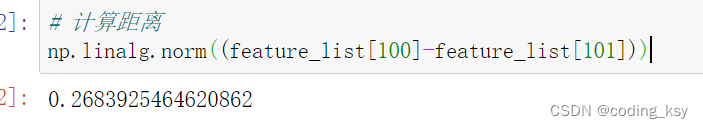
# 计算距离
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[100]-feature_list[112]))
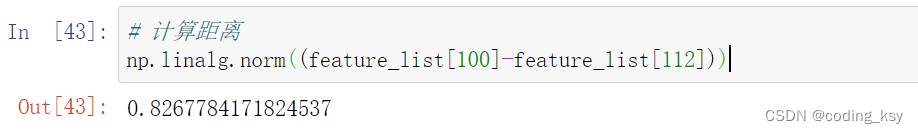
# 计算距离
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[100]-feature_list[96]))
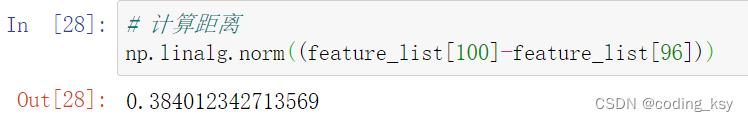
# 计算一个特征描述符与所有特征的距离
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[0]-feature_list),axis=1)
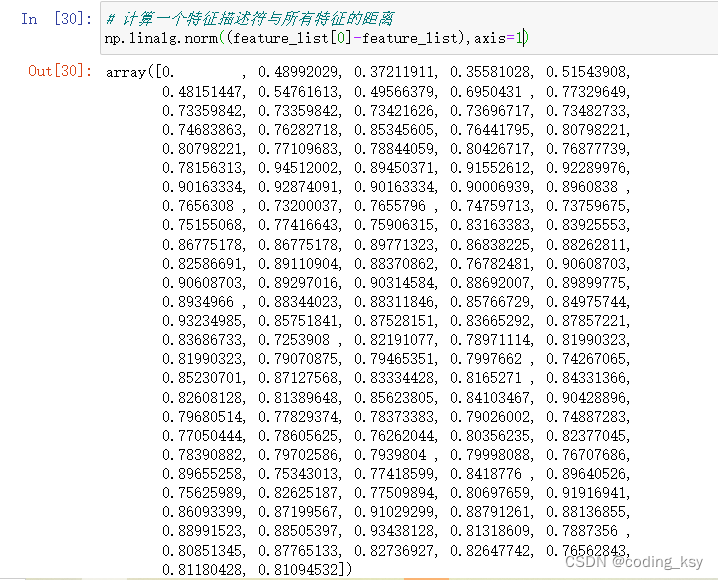
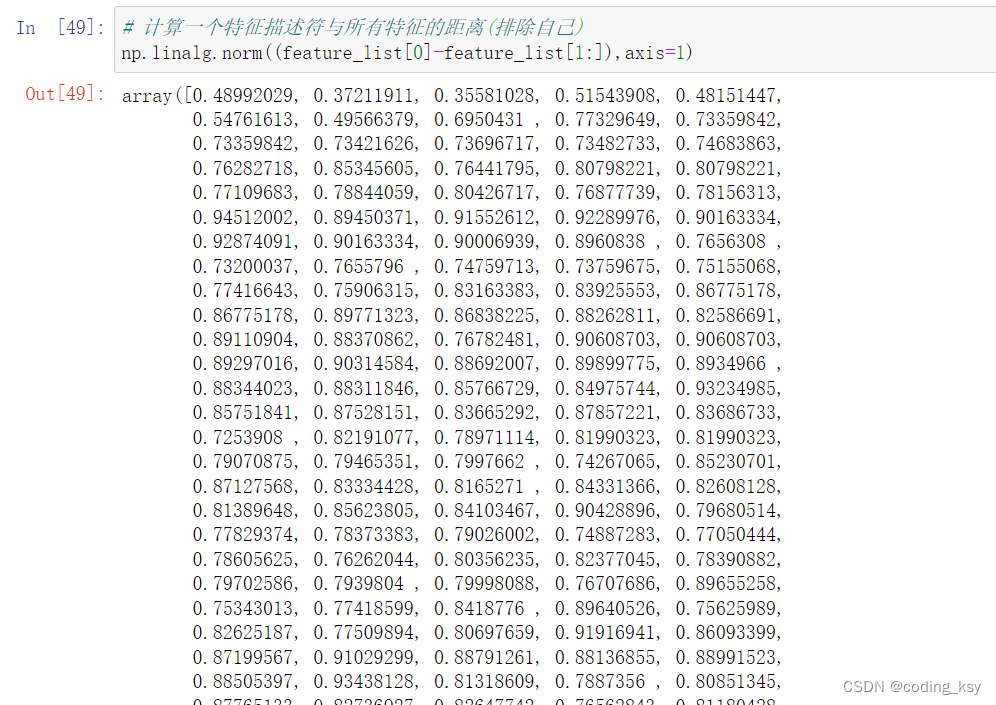
# 计算一个特征描述符与所有特征的距离(排除自己)
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[0]-feature_list[1:]),axis=1)
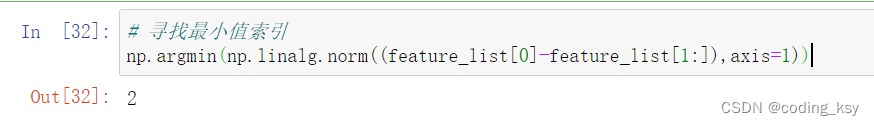
# 寻找最小值索引
np.argmin(np.linalg.norm((feature_list[0]-feature_list[1:]),axis=1))
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[0]-feature_list[1:]),axis=1)[2]
name_list[1+2]
np.linalg.norm((feature_list[0]-feature_list[3]))
# 评估测试数据集
file_list =glob.glob('./yalefaces/test/*')
# 构造两个空列表
predict_list = []
label_list= []
# 距离阈值
threshold = 0.5
for test_file in file_list:
# 获取每一张图片的对应信息
label,feat = getFaceFeatLabel(test_file)
# 读取图片
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(test_file)
ret,img = cap.read()
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#过滤数据
if feat is not None:
# 计算距离
distances = np.linalg.norm((feat-feature_list),axis=1)
min_index = np.argmin(distances)
min_distance = distances[min_index]
if min_distance < threshold:
# 同一人
predict_id = int(name_list[min_index].split('/')[-1].split('.')[0].split('subject')[-1])
else:
predict_id = -1
predict_list.append(predict_id)
label_list.append(label)
cv2.putText(img,'True:'+str(label),(10,30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,1,(0,255,0))
cv2.putText(img,'Pred:'+str(predict_id),(10,50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,1,(0,255,0))
cv2.putText(img,'Dist:'+str(min_distance),(10,70),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,1,(0,255,0))
# 显示
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img)

# 公式评估
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy_score(label_list,predict_list)

人脸考勤机的整体项目(pycharm上运行)
项目整体架构
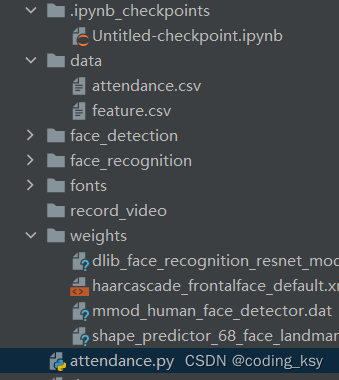
导入包
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import dlib
import time
import csv
人脸注册方法
# 人脸注册方法
def faceRegister(label_id=1, name='enpei', count=3, interval=3):
"""
label_id:人脸ID
Name:人脸姓名
count:采集数量
interval:采集间隔时间
"""
# 检测人脸
# 获取68个关键点
# 获取特征描述符
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 获取长宽
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 构造人脸检测器
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点检测器
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 特征描述符
face_descriptor_extractor = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('./weights/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat')
# 开始时间
start_time = time.time()
# 执行次数
collect_count = 0
# CSV Writer
f = open('./data/feature.csv', 'a', newline="")
csv_writer = csv.writer(f)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# 缩放
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (width // 2, height // 2))
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1)
# 转为灰度图
frame_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(frame, 1)
# 遍历人脸
for face in detections:
# 人脸框坐标
l, t, r, b = face.left(), face.top(), face.right(), face.bottom()
# 获取人脸关键点
points = shape_detector(frame, face)
for point in points.parts():
cv2.circle(frame, (point.x, point.y), 2, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 矩形人脸框
cv2.rectangle(frame, (l, t), (r, b), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 采集:
if collect_count < count:
# 获取当前时间
now = time.time()
# 时间间隔
if now - start_time > interval:
# 获取特征描述符
face_descriptor = face_descriptor_extractor.compute_face_descriptor(frame, points)
# 转为列表
face_descriptor = [f for f in face_descriptor]
# 写入CSV 文件
line = [label_id, name, face_descriptor]
csv_writer.writerow(line)
collect_count += 1
start_time = now
print("采集次数:{collect_count}".format(collect_count=collect_count))
else:
pass
else:
# 采集完毕
print('采集完毕')
return
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('Face attendance', frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
f.close()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
获取csv中的特征
# 获取并组装CSV文件中特征
def getFeatureList():
# 构造列表
label_list = []
name_list = []
feature_list = None
with open('./data/feature.csv', 'r') as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for line in csv_reader:
label_id = line[0]
name = line[1]
label_list.append(label_id)
name_list.append(name)
# string 转为list
face_descriptor = eval(line[2])
#
face_descriptor = np.asarray(face_descriptor, dtype=np.float64)
face_descriptor = np.reshape(face_descriptor, (1, -1))
if feature_list is None:
feature_list = face_descriptor
else:
feature_list = np.concatenate((feature_list, face_descriptor), axis=0)
return label_list, name_list, feature_list
# 人脸识别
# 1、实时获取视频流中人脸的特征描述符
# 2、将它与库里特征做距离判断
# 3、找到预测的ID、NAME
# 4、考勤记录存进CSV文件:第一次识别到存入或者隔一段时间存
def faceRecognizer(threshold=0.5):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 获取长宽
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 构造人脸检测器
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点检测器
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 特征描述符
face_descriptor_extractor = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('./weights/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat')
# 读取特征
label_list, name_list, feature_list = getFeatureList()
# 字典记录人脸识别记录
recog_record = {}
# CSV写入
f = open('./data/attendance.csv', 'a', newline="")
csv_writer = csv.writer(f)
# 帧率信息
fps_time = time.time()
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# 缩放
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (width // 2, height // 2))
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1)
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(frame, 1)
# 遍历人脸
for face in detections:
# 人脸框坐标
l, t, r, b = face.left(), face.top(), face.right(), face.bottom()
# 获取人脸关键点
points = shape_detector(frame, face)
# 矩形人脸框
cv2.rectangle(frame, (l, t), (r, b), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 获取特征描述符
face_descriptor = face_descriptor_extractor.compute_face_descriptor(frame, points)
# 转为列表
face_descriptor = [f for f in face_descriptor]
# 计算与库的距离
face_descriptor = np.asarray(face_descriptor, dtype=np.float64)
distances = np.linalg.norm((face_descriptor - feature_list), axis=1)
# 最短距离索引
min_index = np.argmin(distances)
# 最短距离
min_distance = distances[min_index]
if min_distance < threshold:
predict_id = label_list[min_index]
predict_name = name_list[min_index]
cv2.putText(frame, predict_name + str(round(min_distance, 2)), (l, b + 40),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
now = time.time()
need_insert = False
# 判断是否识别过
if predict_name in recog_record:
# 存过
# 隔一段时间再存
if now - recog_record[predict_name] > 3:
# 超过阈值时间,再存一次
need_insert = True
recog_record[predict_name] = now
else:
# 还没到时间
pass
need_insert = False
else:
# 没有存过
recog_record[predict_name] = now
# 存入CSV文件
need_insert = True
if need_insert:
time_local = time.localtime(recog_record[predict_name])
# 转换格式
time_str = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time_local)
line = [predict_id, predict_name, min_distance, time_str]
csv_writer.writerow(line)
print('{time}: 写入成功:{name}'.format(name=predict_name, time=time_str))
else:
print('未识别')
# 计算帧率
now = time.time()
fps = 1 / (now - fps_time)
fps_time = now
cv2.putText(frame, "FPS: " + str(round(fps, 2)), (20, 40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 2, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('Face attendance', frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
f.close()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
项目整体代码(attendance.py)
"""
人脸考勤
人脸注册:将人脸特征存进feature.csv
人脸识别:将检测的人脸特征与CSV中人脸特征作比较,如果比中的把考勤记录写入 attendance.csv
"""
# 导入包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import dlib
import time
import csv
# 人脸注册方法
def faceRegister(label_id=1,name='enpei',count=3,interval=3):
"""
label_id:人脸ID
Name:人脸姓名
count:采集数量
interval:采集间隔时间
"""
# 检测人脸
# 获取68个关键点
# 获取特征描述符
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 获取长宽
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 构造人脸检测器
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点检测器
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 特征描述符
face_descriptor_extractor = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('./weights/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat')
# 开始时间
start_time = time.time()
# 执行次数
collect_count = 0
# CSV Writer
f = open('./data/feature.csv','a',newline="")
csv_writer = csv.writer(f)
while True:
ret,frame = cap.read()
# 缩放
frame = cv2.resize(frame,(width//2,height//2))
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
# 转为灰度图
frame_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(frame,1)
# 遍历人脸
for face in detections:
# 人脸框坐标
l,t,r,b = face.left(),face.top(),face.right(),face.bottom()
# 获取人脸关键点
points = shape_detector(frame,face)
for point in points.parts():
cv2.circle(frame,(point.x,point.y),2,(0,255,0),-1)
# 矩形人脸框
cv2.rectangle(frame,(l,t),(r,b),(0,255,0),2)
# 采集:
if collect_count < count:
# 获取当前时间
now = time.time()
# 时间间隔
if now -start_time > interval:
# 获取特征描述符
face_descriptor = face_descriptor_extractor.compute_face_descriptor(frame,points)
# 转为列表
face_descriptor = [f for f in face_descriptor]
# 写入CSV 文件
line = [label_id,name,face_descriptor]
csv_writer.writerow(line)
collect_count +=1
start_time = now
print("采集次数:{collect_count}".format(collect_count= collect_count))
else:
pass
else:
# 采集完毕
print('采集完毕')
return
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('Face attendance',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
f.close()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 获取并组装CSV文件中特征
def getFeatureList():
# 构造列表
label_list = []
name_list = []
feature_list = None
with open('./data/feature.csv','r') as f:
csv_reader = csv.reader(f)
for line in csv_reader:
label_id = line[0]
name = line[1]
label_list.append(label_id)
name_list.append(name)
# string 转为list
face_descriptor = eval(line[2])
#
face_descriptor = np.asarray(face_descriptor,dtype=np.float64)
face_descriptor = np.reshape(face_descriptor,(1,-1))
if feature_list is None:
feature_list = face_descriptor
else:
feature_list = np.concatenate((feature_list,face_descriptor),axis=0)
return label_list,name_list,feature_list
# 人脸识别
# 1、实时获取视频流中人脸的特征描述符
# 2、将它与库里特征做距离判断
# 3、找到预测的ID、NAME
# 4、考勤记录存进CSV文件:第一次识别到存入或者隔一段时间存
def faceRecognizer(threshold = 0.5):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 获取长宽
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# 构造人脸检测器
hog_face_detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 关键点检测器
shape_detector = dlib.shape_predictor('./weights/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# 特征描述符
face_descriptor_extractor = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1('./weights/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat')
# 读取特征
label_list,name_list,feature_list = getFeatureList()
# 字典记录人脸识别记录
recog_record = {}
# CSV写入
f = open('./data/attendance.csv','a',newline="")
csv_writer = csv.writer(f)
# 帧率信息
fps_time = time.time()
while True:
ret,frame = cap.read()
# 缩放
frame = cv2.resize(frame,(width//2,height//2))
# 镜像
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1)
# 检测人脸
detections = hog_face_detector(frame,1)
# 遍历人脸
for face in detections:
# 人脸框坐标
l,t,r,b = face.left(),face.top(),face.right(),face.bottom()
# 获取人脸关键点
points = shape_detector(frame,face)
# 矩形人脸框
cv2.rectangle(frame,(l,t),(r,b),(0,255,0),2)
# 获取特征描述符
face_descriptor = face_descriptor_extractor.compute_face_descriptor(frame,points)
# 转为列表
face_descriptor = [f for f in face_descriptor]
# 计算与库的距离
face_descriptor = np.asarray(face_descriptor,dtype=np.float64)
distances = np.linalg.norm((face_descriptor-feature_list),axis=1)
# 最短距离索引
min_index = np.argmin(distances)
# 最短距离
min_distance = distances[min_index]
if min_distance < threshold:
predict_id = label_list[min_index]
predict_name = name_list[min_index]
cv2.putText(frame,predict_name + str(round(min_distance,2)),(l,b+40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,1,(0,255,0),1)
now = time.time()
need_insert = False
# 判断是否识别过
if predict_name in recog_record:
# 存过
# 隔一段时间再存
if now - recog_record[predict_name] > 3:
# 超过阈值时间,再存一次
need_insert =True
recog_record[predict_name] = now
else:
# 还没到时间
pass
need_insert =False
else:
# 没有存过
recog_record[predict_name] = now
# 存入CSV文件
need_insert =True
if need_insert :
time_local = time.localtime(recog_record[predict_name])
# 转换格式
time_str = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time_local)
line = [predict_id,predict_name,min_distance,time_str]
csv_writer.writerow(line)
print('{time}: 写入成功:{name}'.format(name =predict_name,time = time_str ))
else:
print('未识别')
# 计算帧率
now = time.time()
fps = 1/(now - fps_time)
fps_time = now
cv2.putText(frame,"FPS: "+str(round(fps,2)),(20,40),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL,2,(0,255,0),1)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('Face attendance',frame)
# 退出条件
if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
f.close()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# faceRegister(label_id=1,name='enpei',count=3,interval=3)
# faceRecognizer(threshold = 0.5)