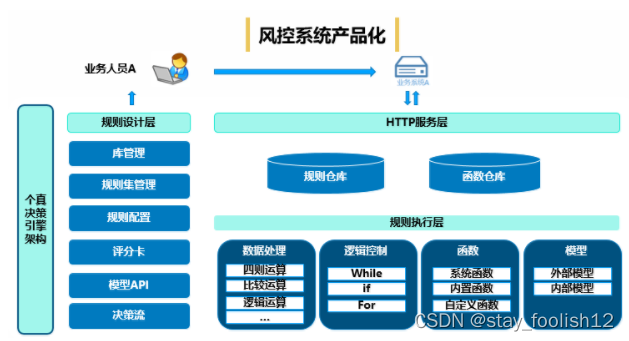
三大特点: 封装 继承 多态



面试题:java如何实现多继承(除了使用接口之外)
实现多继承有三个方法:
- 多层继承
- 内部类
- 接口
参考 java实现多继承的三种方式
多层继承
如果要直接继承类,子类是不可以直接多继承的,但是可以通过多层继承来实现多继承,但多层继承一般不建议超过三次。
A 有一个成员变量 num
class A {
private int num = 10;
A() {
}
public int getNum() {
return this.num;
}
public void fun() {
System.out.println(this.getNum());
}
}
B有一个成员变量 name
class B extends A {
private String name = "张三";
B() {
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void fun() {
System.out.println(this.getNum());
}
}C 从B继承(继承了name和num):覆盖name
class C extends B {
private String name = "刘能";
C() {
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void fun() {
System.out.println(this.getName());
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}测试类:
public class Test {
public Test() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.fun();
print(new B());
print(new C());
}
public static void print(A a) {
a.fun();
}
}输出:
10
10
刘能
刘能
内部类: 和组合类型,相当于C包含A 和 B的两个实例对象
class C1 {
//C类
private String name = "刘能";
class OneA extends A {//C中内部类继承A类
public void printA() {
System.out.println(this.getNum());
fun();
}
}
class OneB extends B {//C类内部类继承B类
public void printB() {
System.out.println(this.getName());
fun();
}
}
public void print() {
//在C类中生成普通方法print()
new OneA().printA();
// 匿名实例化OneA类对象并调用printA方法
new OneB().printB();
}
}接口:默认支持多个implements
//接口实现多继承
interface IA {
//父接口A(接口为更纯粹的抽象类,结构组成只含全局常量和抽象方法)
void funA();
}
interface IB {
//父接口B(接口前添加I用以区分接口)
void funB();
}
interface CImpl extends IA, IB {
//接口可继承多个父接口,用,分隔开即可,子接口的命名可选择较为重要的父接口进行命名或自行命名,一般子接口后添加Impl用以区分
void funC();
}
class Impl implements CImpl {
//定义类实现接口(也可直接实现父接口(多个))
public void funC() {
//抽象方法的实现
System.out.println("你昨天真好看!");
}
public void funA() {
System.out.println("你今天真好看!");
}
public void funB() {
System.out.println("你明天真好看!");
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Impl im = new Impl();
// 实例化对象
im.funA();
im.funB();
im.funC();
}
}
知识来源:
【基础】面向对象_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
【2023年面试】Java面向对象有哪些特征_哔哩哔哩_bilibili