- 阶乘
这个比较简单就不说了。
int factorial(int n) {
if (n <= 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
- fibonacci
如此简单的算法,复试的时候竟然写错了!😳囧!
int fibonacci(unsigned int n) {
if (n == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (n == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else {
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
}
- ackerman
这个函数究竟是干嘛的不太清楚。但是感觉跟fabnacci没啥本质区别。
int ackerman(unsigned int m, unsigned int n) {
if (m == 0)
{
printf("%d\r\n",n+1);
return n + 1;
}
else if (n == 0)
{
int res = ackerman(m - 1, 1);
printf("%d\r\n", res);
return res;
}
else {
int res= ackerman(m - 1, ackerman(m, n - 1));
printf("%d\r\n", res);
return res;
}
}
- hanoi
提供2个函数,都差不多,当然,其中有一个是我写的。
hannoi的时间复杂度是 2 n − 1 2^n -1 2n−1
/*
算法思路:1将 n-1个盘子先放到B座位上
2.将A座上地剩下的一个盘移动到C盘上
3、将n-1个盘从B座移动到C座上
*/
void move(unsigned int x, unsigned int y, unsigned long* count)
{
printf("%d--->%d\r\n", x, y);
(*count)++;
}
void hannuo(int n, char one, char two, char three, unsigned long* count)
{
if (n == 1)
move(one, three, count); //递归截止条件
else
{
hannuo(n - 1, one, three, two, count);//将 n-1个盘子先放到B座位上
move(one, three, count);//将A座上地剩下的一个盘移动到C盘上
hannuo(n - 1, two, one, three, count);//将n-1个盘从B座移动到C座上
}
}
void hanoi(unsigned int a, unsigned int c, unsigned int b, int level, unsigned long* count) {
if (level == 1)
{
move(a, c, count);
}
else {
hanoi(a, b, c, level - 1, count);
move(a, c, count);
hanoi(b, c, a, level - 1, count);
}
}
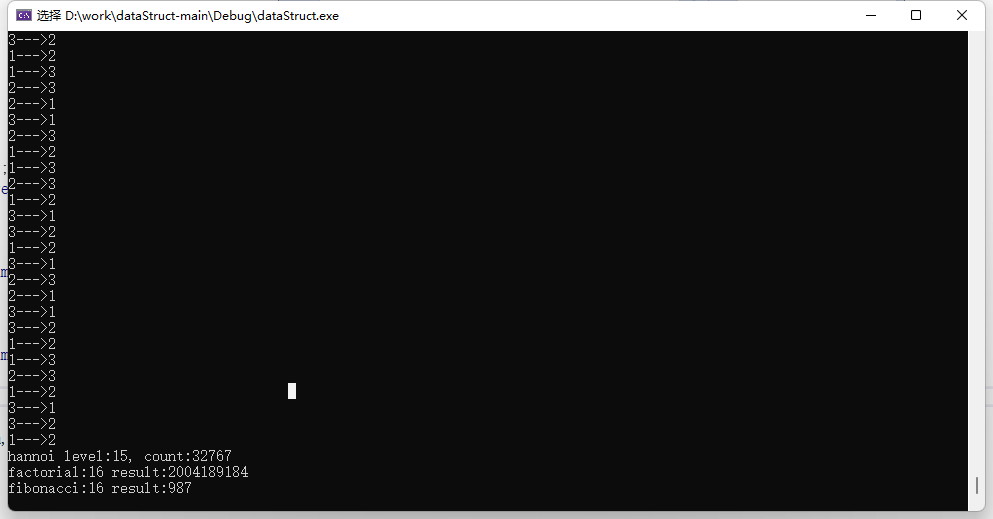
测试结果:
工程地址:https://github.com/satadriver/dataStruct