哈喽,大家好,我是小林。今天给大家分享一下对二叉树的一些常规操作。
愿我们都能保持一颗向上的心。
目录
- 一、前序遍历
- 二、中序遍历
- 三、后序遍历
- 四、 统计节点个数
- 五、统计叶子节点个数
- 六、第K层的节点个数
- 七、二叉树的深度
- 八、查找值为x的节点
- 九、层序遍历
- 十、判断是否是完全二叉树
一、前序遍历
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
//如果根为NULL,直接返回
if (root == NULL)
{
//printf("NULL "); //可打印可不打印
return;
}
//前序遍历,先打印根
printf("%c ", root->val);
//遍历左孩子
PreOrder(root->left);
//遍历右孩子
PreOrder(root->right);
}
二、中序遍历
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* BT)
{
if (BT == NULL)
{
//printf("NULL "); //可打印可不打印
return;
}
//先遍历左孩子
InOrder(BT->left);
//打印根
printf("%c ", BT->val);
//遍历右孩子
InOrder(BT->right);
}
三、后序遍历
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* BT)
{
if (BT == NULL)
{
//printf("NULL "); //可打印可不打印
return;
}
//先遍历左孩子
PostOrder(BT->left);
//再遍历右孩子
PostOrder(BT->right);
//打印根
printf("%c ", BT->val);
}
四、 统计节点个数
//统计个数
size_t BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* BT)
{
//如果BT是NULL,则说明不是节点,所以返回0,节点就+1
return BT == NULL ? 0 : 1 + BinaryTreeSize(BT->left) + BinaryTreeSize(BT->right);
}
五、统计叶子节点个数
//统计叶子个数
size_t BinaryLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//左孩子和右孩子都为空,是叶子节点,返回1
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
//递归遍历
return BinaryLeafSize(root->left) +
BinaryLeafSize(root->right);
}
六、第K层的节点个数
//第K层的节点个数
size_t BinaryLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//如果k等于1,说明在第k层,返回1
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return BinaryLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) +
BinaryLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
七、二叉树的深度
//二叉树的深度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//接收左孩子的深度
int leftRet = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);
//接收右孩子深度
int rightRet = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);
//返回左右孩子较大的那一个
return leftRet < rightRet ? rightRet + 1 : leftRet + 1;
}
八、查找值为x的节点
//查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
//根为空,返回NULL
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
//root的值等于val,返回root
if (root->val == x)
return root;
//遍历左孩子找x
BTNode* left = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
//如果值等于x,返回当前节点
if (left->val == x)
return left;
//遍历右孩子找x
BTNode* right = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
//如果值等于x,返回当前节点
if (right->val == x)
return right;
//左右孩子都没找到,返回null
return NULL;
}
九、层序遍历
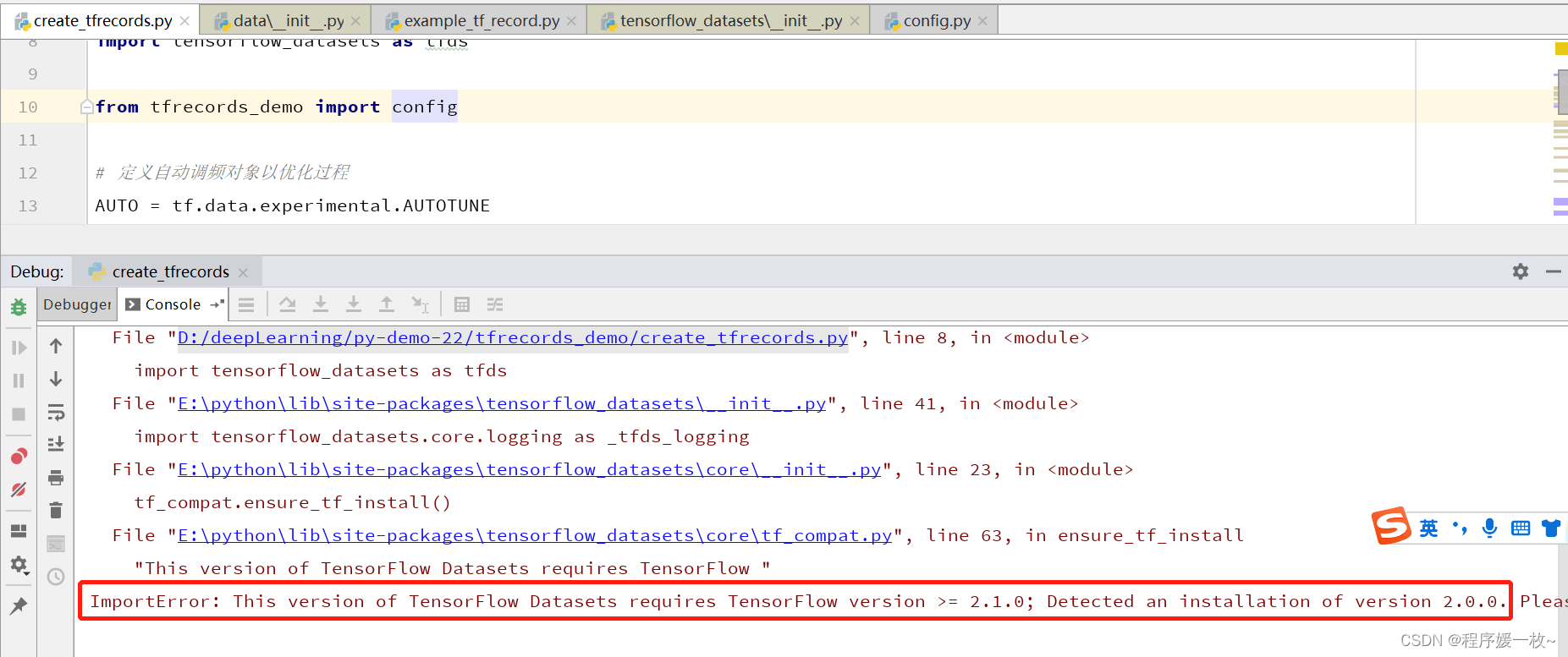
层序遍历需要用到队列,如果不知道队列的朋友可以看看我分享的这篇文章队列的实现,队列的实现链接git链接。只需要把.h和.c文件拿过来用并修改一下队列存放的数据类型即可使用。
//层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
//如果root为空,返回
if (root == NULL)
return;
//创建一个队列
Queue q;
//初始化队列
QueueInto(&q);
//根节点入队
QueuePush(&q, root);
//循环入队出队
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
//保存队头节点
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
//队头节点,也就是根节点出队
QueuePop(&q);
//俩个孩子入队,但确保该节点不能为空
if (Front != NULL)
{
//打印
printf("%c ", Front->val);
//俩孩子入队
QueuePush(&q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&q, Front->right);
}
else
printf("NULL "); //可要可不要
}
printf("\n");
}
十、判断是否是完全二叉树
先给大家看看完全二叉树和非完全二叉树的区别。
非完全二叉树
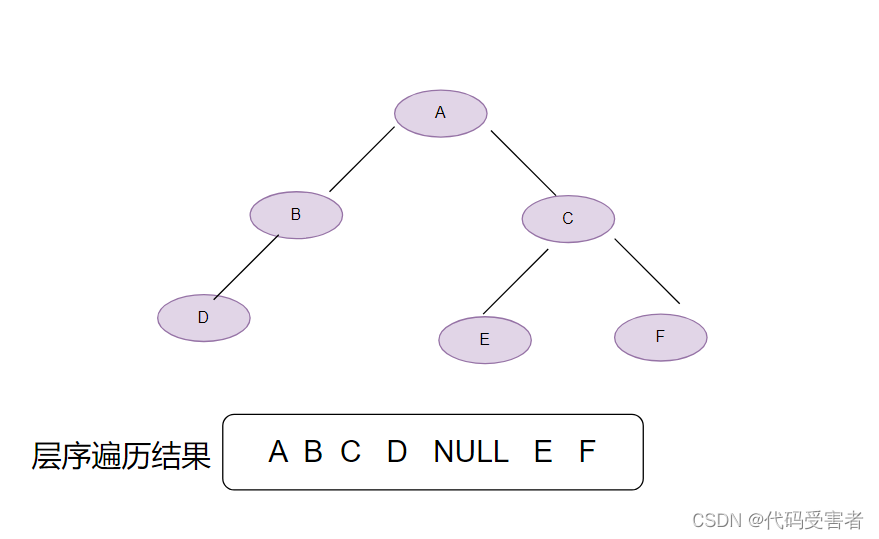
层序遍历结果是: A B C D NULL E F
完全二叉树
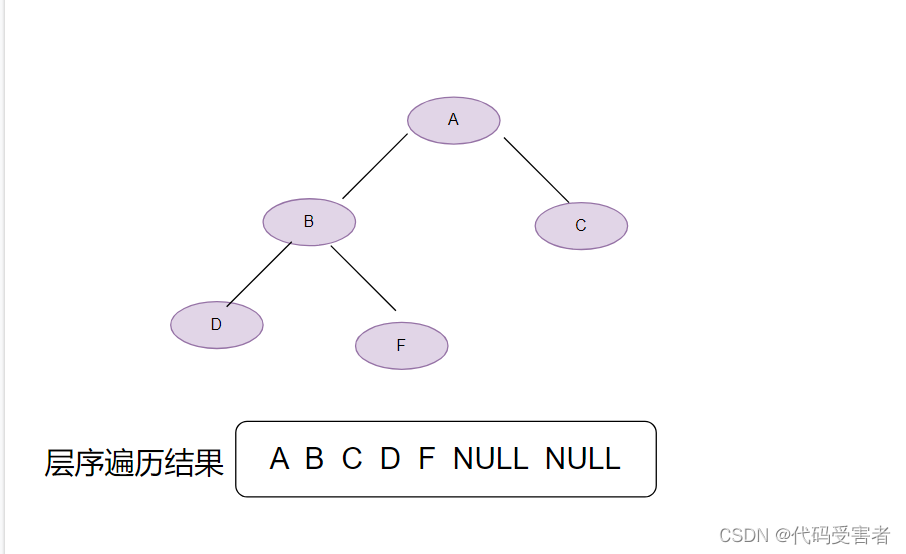
层序遍历结果 : A B C D F NULL NULL
结论: 完全二叉树层序遍历在遇到NULL后,后面将会是连续的NULL,如果在出现NULL之后还遇到非NULL的值,那么说明这不是一个完全二叉树。
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
//创建一个队列
Queue q;
//初始化队列
QueueInto(&q);
//根入队
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//如果队头是NULL,那么说明到了最后的后一个节点
if (Front == NULL)
break;
//Front不为空,2个孩子入队
QueuePush(&q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&q, Front->right);
}
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
//继续以上操作,不过接下来的Front必须全为空,否则就不是完全二叉树
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
//循环结束说明后面都是NULL,所以是完全二叉树
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
全部代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Queue.h"
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType val;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* Node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if(Node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
}
Node->val = x;
Node->left = Node->right = NULL;
return Node;
}
BTNode* BinaryCreate()
{
BTNode* BTNodeA = BuyNode('A');
BTNode* BTNodeB = BuyNode('B');
BTNode* BTNodeC = BuyNode('C');
BTNode* BTNodeD = BuyNode('D');
BTNode* BTNodeE = BuyNode('E');
BTNode* BTNodeF = BuyNode('F');
//BTNode* BTNodeG = BuyNode('G');
BTNodeA->left = BTNodeB;
BTNodeA->right = BTNodeC;
BTNodeB->left = BTNodeD;
//链上G那么就是完全二叉树了,不链上则不是
//BTNodeB->right = BTNodeG;
BTNodeC->left = BTNodeE;
BTNodeC->right = BTNodeF;
return BTNodeA;
}
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
//如果根为NULL,直接返回
if (root == NULL)
return;
//前序遍历,先打印根
printf("%c ", root->val);
//遍历左孩子
PreOrder(root->left);
//遍历右孩子
PreOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
//统计节点个数
size_t BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : 1 + BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right);
}
//统计叶子个数
size_t BinaryLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//左孩子和右孩子都为空,是叶子节点,返回1
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
//递归遍历
return BinaryLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryLeafSize(root->right);
}
//第K层的节点个数
size_t BinaryLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//如果k等于1,说明在第k层,返回1
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return BinaryLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
//二叉树的深度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
//根为空,返回0
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//接收左孩子的深度
int leftRet = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);
//接收右孩子深度
int rightRet = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);
//返回左右孩子较大的那一个
return leftRet < rightRet ? rightRet + 1 : leftRet + 1;
}
//查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
//根为空,返回NULL
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
//root的值等于val,返回root
if (root->val == x)
return root;
//遍历左孩子找x
BTNode* left = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
//如果值等于x,返回当前节点
if (left->val == x)
return left;
//遍历右孩子找x
BTNode* right = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
//如果值等于x,返回当前节点
if (right->val == x)
return right;
//左右孩子都没找到,返回null
return NULL;
}
//层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
//如果root为空,返回
if (root == NULL)
return;
//创建一个队列
Queue q;
//初始化队列
QueueInto(&q);
//根节点入队
QueuePush(&q, root);
//循环入队出队
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
//保存队头节点
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
//队头节点,也就是根节点出队
QueuePop(&q);
//俩个孩子入队,但确保该节点不能为空
if (Front != NULL)
{
//打印
printf("%c ", Front->val);
//俩孩子入队
QueuePush(&q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&q, Front->right);
}
else
printf("NULL "); //可要可不要
}
printf("\n");
}
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
//创建一个队列
Queue q;
//初始化队列
QueueInto(&q);
//根入队
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//如果队头是NULL,那么说明到了最后的后一个节点
if (Front == NULL)
break;
//Front不为空,2个孩子入队
QueuePush(&q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&q, Front->right);
}
while (!QueueIsEmpty(&q))
{
//继续以上操作,不过接下来的Front必须全为空,否则就不是完全二叉树
BTNode* Front = QueueGetFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
//循环结束说明后面都是NULL,所以是完全二叉树
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = BinaryCreate();
printf("前序遍历:");
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("中序遍历:");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("后序遍历:");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("树的总节点个数:");
printf("%d",BinaryTreeSize(root));
printf("\n");
printf("树的叶子节点个数");
printf("%d", BinaryLeafSize(root));
printf("\n");
printf("找到的节点值为:");
BTNode* BT = BinaryTreeFind(root,'B');
printf("%c ",BT->val);
printf("\n");
printf("树的深度是:");
printf("%d ", BinaryTreeDepth(root));
printf("\n");
int i = 3;
printf("树的第%d层的节点数:",i);
printf("%d ", BinaryLevelKSize(root,i));
printf("\n");
printf("层序遍历:");
LevelOrder(root);
bool a = BinaryTreeComplete(root);
if (a)
printf("是完全二叉树\n");
else
printf("不是完全二叉树\n");
}
队列的代码 Queue.c
#include "Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInto(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
}
//创建节点
QueueNode* CreateNode(QDataType x)
{
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc faile\n");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->val = x;
return newNode;
}
//数据入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{
//断言
assert(q);
//创建节点
QueueNode* newNode = CreateNode(x);
//如果head NULL
if (q->head == NULL)
{
q->head = newNode;
q->tail = newNode;
}
else
{
//尾节点指向新节点
q->tail->next = newNode;
//尾节点移动位置
q->tail = newNode;
}
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueIsEmpty(Queue* q)
{
return q->head == NULL;
}
//数据出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
//要保证队列里有数据可以删除
assert(!QueueIsEmpty(q));
//头删
QueueNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
//获取队头
QDataType QueueGetFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
//要保证队列里有数据
assert(!QueueIsEmpty(q));
return q->head->val;
}
//获取队尾
QDataType QueueGetBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
//要保证队列里有数据
assert(!QueueIsEmpty(q));
return q->tail->val;
}
//获取队列长度
size_t QueueGetSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
//要保证队列里有数据
assert(!QueueIsEmpty(q));
int len = 1;
QueueNode* head = q->head;
QueueNode* tail = q -> tail;
while (head != tail)
{
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
QueueNode* cru = q->head;
while (cru != NULL)
{
//存储下一个位置地址
QueueNode* next = cru->next;
free(cru);
cru = next;
}
}
Queue.h的代码
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
struct BinaryTreeNode;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
//队列的节点
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
//队列
typedef struct Queue
{
//一个指针指向头
QueueNode* head;
//一个指针指向尾
QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
//队列初始化
void QueueInto(Queue* q);
//数据入队
void QueuePush(Queue* q,QDataType x);
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueIsEmpty(Queue* q);
//数据出队
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
//获取队头
QDataType QueueGetFront(Queue* q);
//获取队尾
QDataType QueueGetBack(Queue* q);
//获取队列长度
size_t QueueGetSize(Queue* q);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
感谢大家支持,如果不嫌弃,给个关注呗。谢谢大佬们了。