文章目录
- 迭代器
- 模拟实现
本篇模拟实现简单的list和一些其他注意的点
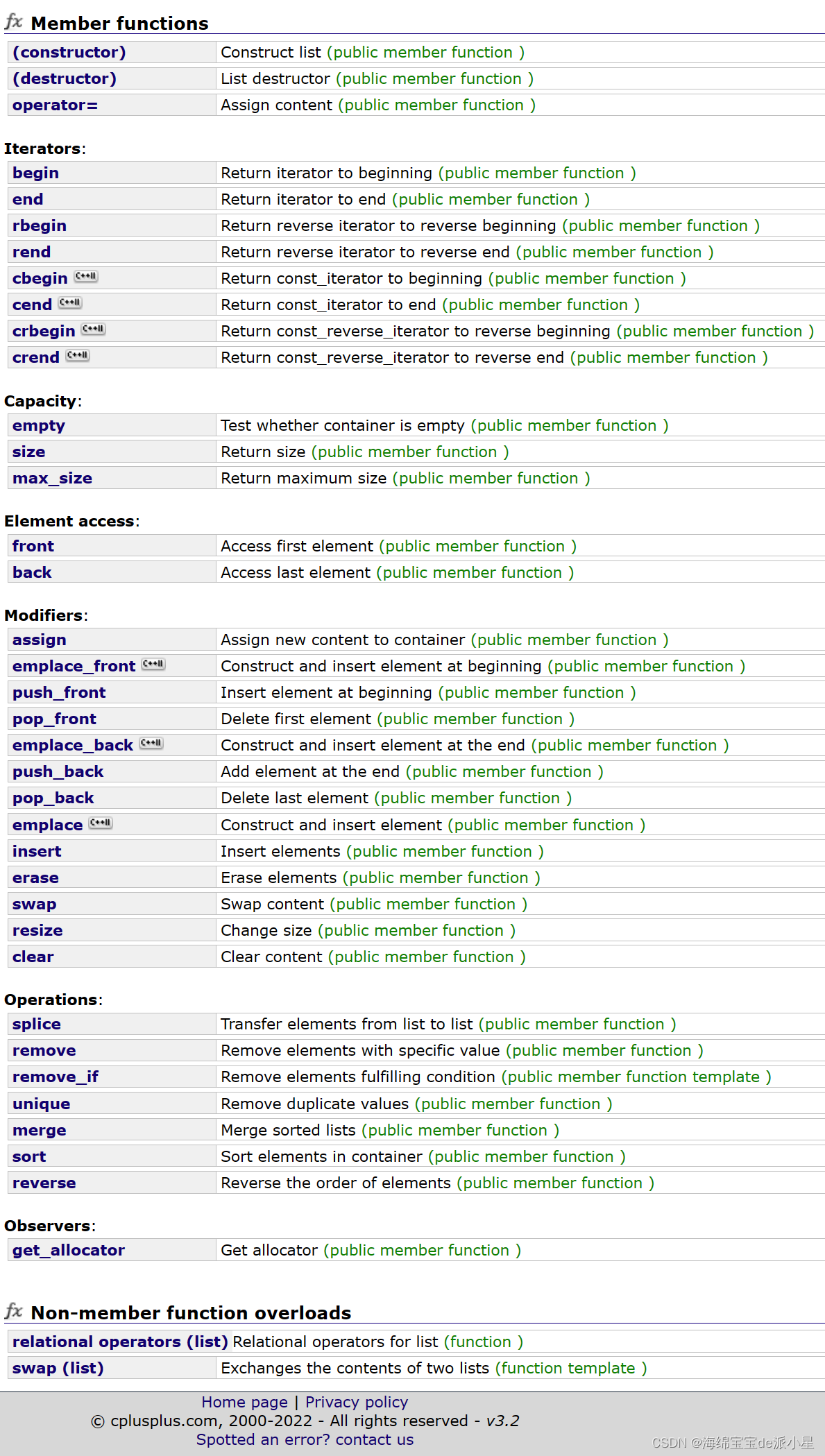
迭代器
如下所示是利用拷贝构造将一个链表中的数据挪动到另外一个链表中,构造两个相同的链表
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
emptyinit();
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
list<int> l2(lt);
}
lt作为形参,传引用可以提高传参的效率,同时应该加上const修饰来保证不会因为不小心修改了形参导致外部的实参也被修改,这样的结果是不应该的,因此就要加const把这个形参变成一个const对象
而问题又来了,const对象要使用的是const迭代器,而前面没有写const迭代器,因此这里就引入了const迭代器的实现
从vector的模拟实现中,看似似乎只需要在原来的迭代器的基础上加上一个const即可,但事实上:
const迭代器和普通迭代器是两种不同的迭代器,不能直接在普通的迭代器后面加const,原因?
要解决这个问题,先重新回顾一下vector中const迭代器的定义流程:
对比vector的迭代器,vector中的迭代器const版本和非const版本直接在非const版本后面加const使它变成const迭代器即可,这样在调用的时候就可以直接进行调用
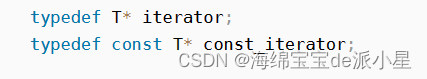
对iterator的定义,const版本就是在指针前面加上const,这样返回的就是const修饰的指针,因此就可以做到通过该迭代器只读,不可修改的作用
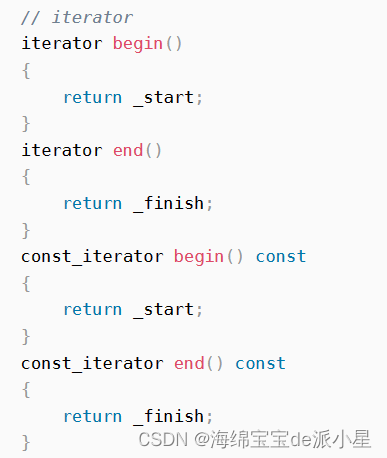
这里的迭代器本质上就是指针在底层进行访问,然后我们定义一个const指针,使得const指针就不能对指针指向的内容进行修改了
下面仿照vector修改的原理修改list
要修改的部分其实就是下面的代码:
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
在函数后加const很简单,但是核心是要把返回值也定义为const指针版本,这个过程要如何实现?
由于这里是把iterator封装成了一个类进行的实现,因此需要重新封装一个类进行实现
template <class T>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T> self;
// 成员
Node* _node;
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const self& pos)
{
return _node == pos._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& pos)
{
return !(*this == pos);
}
};
template <class T>
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_const_iterator<T> self;
// 成员
Node* _node;
__list_const_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
const T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const self& pos)
{
return _node == pos._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& pos)
{
return !(*this == pos);
}
};
但事实上,这两份代码只有很少的地方有区别,更多的内容都是相同的,这样是不满足较好的代码风格,因此在stl源码中,使用了模板对这两个类进行了封装
改进版本如下:
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr >
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
// 成员
Node* _node;
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const self& pos)
{
return _node == pos._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& pos)
{
return !(*this == pos);
}
};
template <class T>
class list
{
void emptyinit()
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
// 构造函数
list()
{
emptyinit();
}
// 拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
emptyinit();
auto it = lt.begin();
//*it = 30;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
// head tail->prev tail
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// newnode
// prev cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
// prev cur next
prev->_next = cur->_next;
next->_prev = cur->_prev;
return iterator(next);
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
这里引入了类模板的概念,简单来说,当需要调用const类型时就会模板实例化出一个const版本的迭代器,再进行相关的操作,这样的操作可以避免代码冗余,也是模板的强大之处
模拟实现
#pragma once
// 实现的是双向循环链表,链表中应该包含节点类和迭代器类,节点类用于从内存中申请节点,迭代器类用于获取节点指针
namespace mylist
{
// 把节点进行封装,可以动态获取一个节点
template <class T>
struct list_node
{
// 成员
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
T _data;
// 成员函数
list_node(const T& val = T())
:_data(val)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
};
// 对迭代器进行封装,使得外界看到的是迭代器
// 迭代器当中存储的是某个节点的指针
// 可以对迭代器进行各项操作
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr >
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
// 成员
Node* _node;
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const self& pos)
{
return _node == pos._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& pos)
{
return !(*this == pos);
}
};
// 适配器 -- 复用
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr >
struct __reverse_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __reverse_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
// 成员
Node* _node;
__reverse_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator==(const self& pos)
{
return _node == pos._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self& pos)
{
return !(*this == pos);
}
};
template <class T>
class list
{
void emptyinit()
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef __reverse_iterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef __reverse_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;
// 构造函数
list()
{
emptyinit();
}
// 拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
emptyinit();
auto it = lt.begin();
//*it = 30;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
// head tail->prev tail
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(_head);
}
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const
{
return const_reverse_iterator(_head->_prev);
}
const_reverse_iterator rend() const
{
return const_reverse_iterator(_head);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// newnode
// prev cur
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
// prev cur next
prev->_next = cur->_next;
next->_prev = cur->_prev;
return iterator(next);
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
cout << "正序" << endl;
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "逆序" << endl;
auto rit = lt.rbegin();
while (rit != lt.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
}






![[足式机器人]Part5 机械设计 Ch00/01 绪论+机器结构组成与连接 ——【课程笔记】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/74d59e1eaea643a8b8721b6172615477.png)