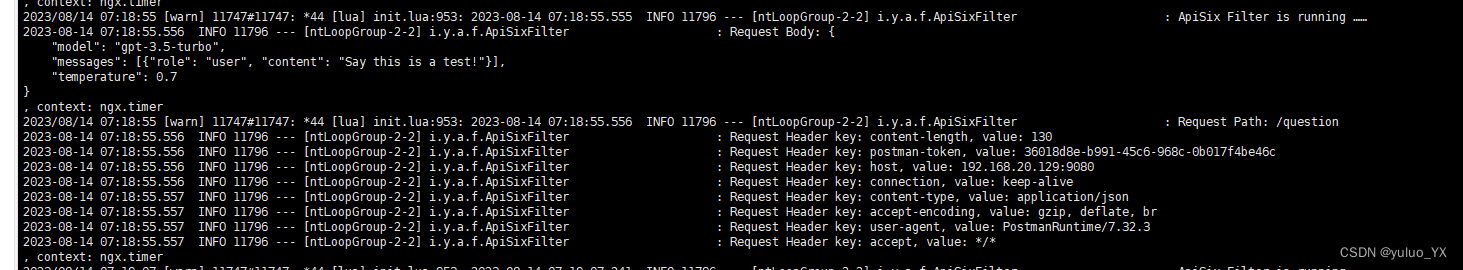
给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i
天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
示例 1:
输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
示例 2:
输入: temperatures = [30,40,50,60]
输出: [1,1,1,0]
示例 3:
输入: temperatures = [30,60,90]
输出: [1,1,0]
提示:
1 <= temperatures.length <= 10^5
30 <= temperatures[i] <= 100
解题思路:
1、本题需要栈来展缓储存数据,在遍历新数据时判断其是否比前面的数据大,方便进行后续操作
和 下一个更大元素 非常类似。
2、不同点是本题元素有重复!所以无法用map!
朴素代码:
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Deque<Integer> stacktmpts = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
Deque<Integer> stackindex = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
int len = temperatures.length;
int res[] = new int[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
while(!stacktmpts.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > stacktmpts.peekLast()) {
res[stackindex.peekLast()] = i - stackindex.pollLast();
stacktmpts.pollLast();
}
stacktmpts.add(temperatures[i]);
stackindex.add(i);
}
while(!stackindex.isEmpty()) res[stackindex.pollLast()] = 0;
return res;
}
}
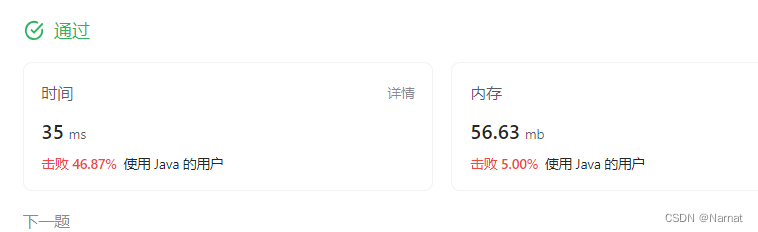
比较笨用两个栈分别存储下标和值
值得注意的是数组中下标和值是一对一的关系,所以理论上只存储下标即可
优化代码:
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
int len = temperatures.length;
int res[] = new int[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
while(!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peekLast()]) {
res[stack.peekLast()] = i - stack.pollLast();
}
stack.add(i);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()) res[stack.pollLast()] = 0;
return res;
}
}
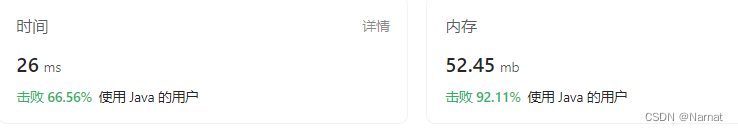
代码:
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int length = temperatures.length;
int[] ans = new int[length];
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
int prevIndex = stack.pop();
ans[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}




![[国产MCU]-BL602开发实例-LCD1602 I2C驱动](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3d016ce2df3747d3955b600e07890404.jpeg#pic_center)