目录
- 概述
- 1.Gradle Kotlin-DSL配置
- 1.1 在根目录下建立一个buildSrc目录,
- 1.2.新建build.gradle.kts文件并添加Kotlin dsl相关配置
- 2.Gradle Kotlin DSL 的编写
- 2.1 定义项目的版本号信息
- 2.2.定义Dependencies管理项目中需要使用的库依赖
- 2.3 定义APK的打包脚本
- 构建APK的类
- 构建Module的类
- 3.使用Gradle Kotlin DSL
- 3.1 新建应用模块,产物是APK
- 3.2 构建库Module
概述
Gradle的出现可以说是为Android的项目构建插上了翅膀,让Android的apk打包构建更简单高效。开发者可以自己去定义打包的过程,比如在打包的过程中进行字节码插桩,多渠道打包,在老版本的Android中还可以依赖Gradle实现APP的插件化开发。但是Gradle是使用Groovy语言开发的,虽然说是和JAVA语言差不多,语法啥的差异也不大,但是终究他们两个还是不同的语言,开发者要想做Android打包的配置,还需要去了解Groovy语言,这无疑增加了开发者的负担。
但是由于Oracle公司将Google公司给告了,导致google不得不将Android的官方语言改成Kotlin,这一改,很多开发者之前可就不开心了,包括我也一样。但是后面真香定律生效了,Kotlin是真的香。更爽的是Google推出了ComposeUI,让使用XML写布局的时代渐行渐远了。这让我特别开心,因为我只需要学习Kotlin,一种语言,我就可以进行Android开发了,不需要再去记忆xml中的那些语法了。然后我意识到,构建工具还是其他语言呀,要是能都用Kotlin就爽了。然后Google仿佛听到了我的心声,推出了基于Kotlin dsl的gradle,也就是说,我们也可以使用Kotlin来编写Gradle脚本了。真的是爽翻天了呀,然后我就去尝试了下,真的很爽,依赖管理啥的特别清晰。而且只需要一次定义,然后在很多地方都可以使用,本文就是记录如何使用Kotlin dsl语言来编写Android项目的构建插件
1.Gradle Kotlin-DSL配置
Android的构建产物一般有两种,一种是APK的形式,直接可以安装运行,另外一种是AAR的形式,作为SDK库提供给其他应用使用。本文会分别介绍这两种方式的配置和编写。步骤如下:
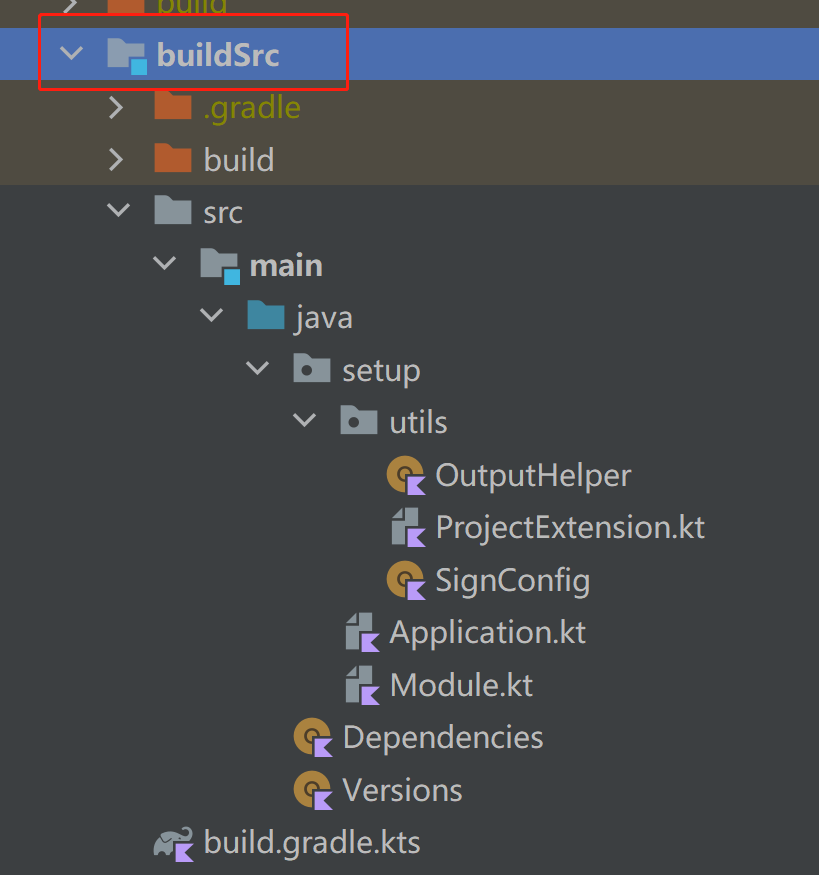
1.1 在根目录下建立一个buildSrc目录,
这里需要注意的是名字必须是buildSrc,这个目录是gradle插件的一种方式,也就是这个目录会被自动参与构建,在目录下面创建出下图中的包结构和类,准备开始编写我们的项目构建脚本
1.2.新建build.gradle.kts文件并添加Kotlin dsl相关配置
要想使用 KotlinDsl,需要我们引入kotlin 的插件,我们在上一步创建的buildSrc目录下新建build.gradle.kts并引入kotlin相关的配置,代码如下:
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation("com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.2.2")
implementation(kotlin("gradle-plugin","1.7.10"))
}
这样就将Kotlin dsl引入到项目中了,下面我们需要使用Kotlin编写我们构建Android项目时的配置了。
2.Gradle Kotlin DSL 的编写
在新建完buildSrc目录和build.gradle.kts文件引入了kotlin dsl的插件后,我们就可以使用Kotlin dsl插件配置构建Android项目了,步骤如下:
2.1 定义项目的版本号信息
在构建Android项目时,我们需要定义项目的最小支持Android SDK和最大支持的Android SDK,以及编译使用的SDK等信息,这些信息我们可以在buildSrc目录下新建一个Version类保存,代码如下所示:
object Versions {
const val applicationId = "com.xxx.xxxx" // apk的包名
const val compileSdkVersion = 33
const val minSdkVersion = 24
const val targetSdkVersion = 33
const val versionCode = 1
const val versionName = "1.0.0"
}
2.2.定义Dependencies管理项目中需要使用的库依赖
在之前使用groovy语言定义的依赖中,我们在需要第三方库或者官方库的时候,都会去使用 implementation("xxx.xxx.xxx.A库") 这种方式引入依赖,假设在项目的另一个Module中也需要使用这个库,因为是implementation的,所以另一个模块需要再去引用这个库,这些都还好,主要是涉及库的版本更新时不好管理,假设两个模块使用的库版本不一致,而恰好这两个版本的库中的功能做了修改,那么就会导致一个模块能工作另一个模块不能工作了,所以将依赖集中到一个地方管理很有必要,下面我们可以使用一个Dependencies类管理我们项目中的所有依赖,代码如下:
object Dependencies {
private object DependencieVersions {
const val kotlin = "1.5.31"
const val kotlin_coroutines = "1.6.4"
const val arouter = "1.5.2"
const val retrofit = "2.9.0"
const val exoplayer = "2.18.1"
const val compose_ui_version = "1.3.0"
const val moshi = "1.13.0"
const val room = "2.4.3"
}
fun getComposeUiVersion(): String {
return DependencieVersions.compose_ui_version
}
object Apache {
const val commons_net = "commons-net:commons-net:3.7.2"
}
object Alibaba {
const val arouter_api = "com.alibaba:arouter-api:${DependencieVersions.arouter}"
const val arouter_compiler = "com.alibaba:arouter-compiler:${DependencieVersions.arouter}"
}
object AndroidX {
const val junit_ext = "androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.1"
const val espresso = "androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0"
const val core = "androidx.core:core-ktx:1.8.0"
const val activity_ktx = "androidx.activity:activity-ktx:1.5.1"
const val appcompat = "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.5.0"
const val lifecycle_runtime_ktx = "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.3.1"
const val room_ktx = "androidx.room:room-ktx:${DependencieVersions.room}"
const val room = "androidx.room:room-runtime:${DependencieVersions.room}"
const val room_compiler = "androidx.room:room-compiler:${DependencieVersions.room}"
const val androidx_recyclerview = "androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.3.0"
const val constraintlayout = "androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.1.4"
const val swiperefreshlayout = "androidx.swiperefreshlayout:swiperefreshlayout:1.1.0"
const val androidx_collection_ktx = "androidx.collection:collection-ktx:1.2.0"
const val paging = "androidx.paging:paging-runtime-ktx:3.1.1"
}
object ComposeUI {
const val activity_compose = "androidx.activity:activity-compose:1.3.1"
const val compose_ui = "androidx.compose.ui:ui:${DependencieVersions.compose_ui_version}"
const val compose_ui_tooling_preview =
"androidx.compose.ui:ui-tooling-preview:${DependencieVersions.compose_ui_version}"
const val compose_material = "androidx.compose.material:material:1.2.0"
const val compose_ui_test_manifest =
"androidx.compose.ui:ui-test-manifest:${DependencieVersions.compose_ui_version}"
}
object Junit {
const val junit = "junit:junit:4.12"
}
object Kotlin {
const val lib = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${DependencieVersions.kotlin}"
const val stdlib_jdk7 =
"org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:${DependencieVersions.kotlin}"
const val coroutines_core =
"org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:${DependencieVersions.kotlin_coroutines}"
const val coroutines_android =
"org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:${DependencieVersions.kotlin_coroutines}"
}
object Square {
const val leakcanary = "com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.9.1"
const val retrofit = "com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:${DependencieVersions.retrofit}"
const val retrofit_moshi =
"com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-moshi:${DependencieVersions.retrofit}"
const val moshi = "com.squareup.moshi:moshi:${DependencieVersions.moshi}"
const val moshi_codegen =
"com.squareup.moshi:moshi-kotlin-codegen:${DependencieVersions.moshi}"
}
object GitHub {
//switch keyboard panel
const val keyboard_panel = "com.github.albfernandez:juniversalchardet:2.4.0"
const val banner = "io.github.youth5201314:banner:2.2.2"
const val glide = "com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.13.2"
//ftp
const val nano_http = "org.nanohttpd:nanohttpd:2.3.1"
//smb
const val smbj = "com.hierynomus:smbj:0.10.0"
const val dcerpc = "com.rapid7.client:dcerpc:0.10.0"
const val jsoup = "org.jsoup:jsoup:1.11.2"
}
object Google {
const val material = "com.google.android.material:material:1.8.0-alpha01"
const val exoplayer =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:exoplayer:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
const val exoplayer_core =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:exoplayer-core:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
const val exoplayer_dash =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:exoplayer-dash:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
const val exoplayer_hls =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:exoplayer-hls:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
const val exoplayer_smoothstraming =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:exoplayer-smoothstreaming:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
const val exoplayer_rtmp =
"com.google.android.exoplayer:extension-rtmp:${DependencieVersions.exoplayer}"
}
object Tencent {
const val mmkv = "com.tencent:mmkv-static:1.2.14"
const val bugly = "com.tencent.bugly:crashreport:4.1.9"
}
object VLC {
const val vlc = "org.videolan.android:libvlc-all:3.5.1"
}
}
如上面的类所示,我们将所有依赖都分类管理,当需要使用的时候,直接找对应的依赖就行了
2.3 定义APK的打包脚本
在此之前,我们可以先准备好相关的辅助工具类,如下所示:
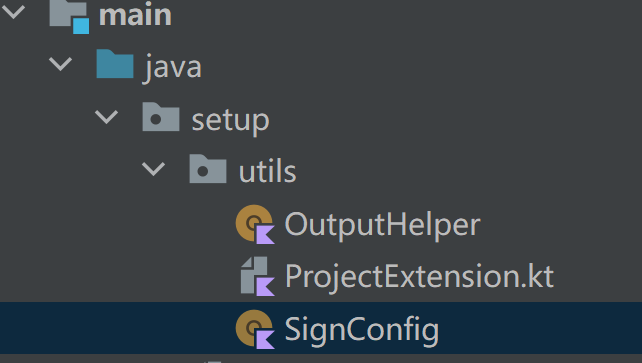 首先是OutputHelper,主要时定义输出的产物名称之类的配置,代码如下所示:
首先是OutputHelper,主要时定义输出的产物名称之类的配置,代码如下所示:
object OutputHelper {
private val format = SimpleDateFormat("MMddHHmm", Locale.CHINA)
fun outputFileName(variant: BaseVariantOutput):String{
val time = format.format(Date())
return"otterPlayer_v
${Versions.versionName}_${variant.name}_$time.apk"
}
}
然后是ProjectExtension.kt,这个类主要做的是一些Project的扩展,使用kotlin的扩展函数定义,主要用于做一些默认的配置,签名的配置等,由于项目中的很多配置可能都是相同的,所以为了不重复定义,可以在这里添加上默认的这些配置,代码如下:
fun BaseExtension.setupKotlinOptions() {
val extensions = (this as ExtensionAware).extensions
val kotlinOptions = extensions.getByName<KotlinJvmOptions>
("kotlinOptions")
kotlinOptions.apply {
jvmTarget = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8.toString()
}
}
fun BaseExtension.setUpComposeFeature() {
val extensions = (this as ExtensionAware).extensions
val kotlinOptions = extensions
.getByName<KotlinJvmOptions>("kotlinOptions")
}
fun Project.setupDefaultdDependencies() {
dependencies.apply {
add(
"implementation",
fileTree("include" to listOf("*.jar"), "dir" to "libs")
)
add("testImplementation", Dependencies.Junit.junit)
add("androidTestImplementation", Dependencies.AndroidX.junit_ext)
add("androidTestImplementation", Dependencies.AndroidX.espresso)
}
}
fun AppExtension.setUpSignConfigs(project: Project) =
apply {
signingConfigs {
named("debug") {
SignConfig.debug(project, this)
}
create("release") {
SignConfig.release(project, this)
}
}
buildTypes {
getByName("debug") {
signingConfig = signingConfigs.findByName(this.name)
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile(
"proguard-android-optimize.txt"),"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
getByName("release") {
signingConfig = signingConfigs.findByName(this.name)
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile(
"proguard-android-optimize.txt"),"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
create("beta") {
initWith(getByName("release"))
}
}
}
fun AppExtension.setupOutputApk() = apply {
applicationVariants.all {
outputs.forEach {
if (it is ApkVariantOutput) {
it.outputFileName = OutputHelper.outputFileName(it)
}
}
}
}
最后是签名配置,我们可以把签名的信息放到gradle文件夹下,如下:
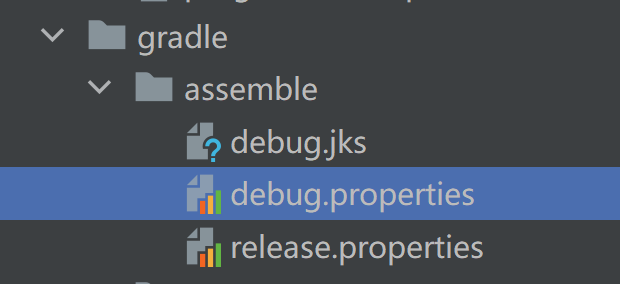
注意:不要把项目上线时使用的签名信息放到这里,不安全
然后我们使用一个配置类去读取这个配置,代码如下所示:
object SignConfig {
fun debug(project: Project, config: SigningConfig) {
val properties = loadProperties(project) ?: return
config.apply {
storeFile(project.getAssembleFile(properties["KEY_LOCATION"]
.toString()))
storePassword(properties["KEYSTORE_PASS"].toString())
keyAlias(properties["ALIAS_NAME"].toString())
keyPassword(properties["ALIAS_PASS"].toString())
enableV1Signing = true
}
}
fun release(project: Project, config: SigningConfig) {
val keystoreFile = project.getAssembleFile("dandanplay.jks")
config.apply {
storeFile = keystoreFile
storePassword(System.getenv("KEYSTORE_PASS"))
keyAlias(System.getenv("ALIAS_NAME"))
keyPassword(System.getenv("ALIAS_PASS"))
}
}
private fun loadProperties(project: Project): Properties? {
var propertiesFile = project.getAssembleFile("keystore.properties")
if (propertiesFile.exists().not()) {
propertiesFile = project.getAssembleFile("debug.properties")
}
if (propertiesFile.exists()) {
val properties = Properties()
properties.load(FileInputStream(propertiesFile))
return properties
}
return null
}
private fun Project.getAssembleFile(fileName: String): File {
return File(rootDir, "gradle/assemble/$fileName")
}
}
定义完辅助的工具类后,我们就可以开始编写我们的项目构建脚本了,我们都知道Android可以有两种构建方式,一种是构建应用,输出的是一个APK的文件,可以放到Android手机上安装运行,另一种是库文件,包括AAR和JAR。所以我们需要对这两种构建方式分别配置,使用的时候选择对应的配置使用就行了。首先是构建APK
构建APK的类
un Project.applicationSetup(isComposeUi: Boolean) {
extensions.getByName<AppExtension>("android").apply {
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
buildFeatures.apply {
dataBinding.isEnabled = true
}
setupKotlinOptions()
setUpSignConfigs(this@applicationSetup)
setupOutputApk()
if (isComposeUi) {
buildFeatures.apply {
compose = true
}
composeOptions.apply {
kotlinCompilerExtensionVersion =
Dependencies.getComposeUiVersion()
}
}
}
setupDefaultdDependencies()
}
构建Module的类
fun Project.moduleSetup() {
extensions.getByName<LibraryExtension>("android").apply {
compileSdk = Versions.compileSdkVersion
defaultConfig {
minSdk = Versions.minSdkVersion
targetSdk = Versions.targetSdkVersion
}
buildTypes {
getByName("release") {
isMinifyEnabled = false
proguardFiles(
getDefaultProguardFile(
"proguard-android-optimize.txt"),
"proguard-rules.pro"
)
}
getByName("debug") {
initWith(buildTypes.getByName("debug"))
}
create("beta") {
initWith(buildTypes.getByName("beta"))
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
buildFeatures {
dataBinding = true
}
setupKotlinOptions()
}
setupDefaultdDependencies()
}
}
代码很好懂,就不一行行的解释了,构建脚本嘛能用就行了,主要原理就是Kotlin的扩展函数和使用提供的kotlin dsl gradle插件来编写Android 项目的构建脚本
3.使用Gradle Kotlin DSL
当我们的构建脚本编写完后就可以使用了,使用起来很简单,我们新建完Module或者应用模块后,只需要将对应的build.gradle文件改造一下就好了,如下所示:
3.1 新建应用模块,产物是APK
如果新建的是一个应用模块,我们需要使用的是applicationSetup这个扩展函数,应用模块下的build.gradle.kts代码如下所示:
import setup.applicationSetup // 引入我们之前编写的kotlin dsl构建脚本
plugins {
id("com.android.application") // 表示包产物是应用
kotlin("android")
kotlin("kapt")
}
applicationSetup(true) // 调用构建APK的扩展函数
// remove warning message because of @Incubating
@Suppress("UnstableApiUsage")
android {
compileSdk = Versions.compileSdkVersion
defaultConfig {
namespace = Versions.applicationId
applicationId = Versions.applicationId
minSdk = Versions.minSdkVersion
targetSdk = Versions.targetSdkVersion
targetSdk = Versions.targetSdkVersion
versionCode = Versions.versionCode
versionName = Versions.versionName
multiDexEnabled = true
testInstrumentationRunner
= "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
}
dependencies {
// 引入依赖
implementation(Dependencies.Junit.junit)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.lifecycle_runtime_ktx)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.espresso)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.core)
implementation(Dependencies.ComposeUI.compose_ui)
implementation(Dependencies.ComposeUI.activity_compose)
implementation(Dependencies.ComposeUI.compose_material)
implementation(Dependencies.ComposeUI.compose_ui_test_manifest)
implementation(Dependencies.ComposeUI.compose_ui_tooling_preview)
}
3.2 构建库Module
若新建的是一个module,即产物是AAR或者JAR,我们可以使用moduleSetup() 构建,代码如下:
import setup.moduleSetup
plugins {
id("com.android.library")
kotlin("android")
kotlin("kapt")
id("kotlin-parcelize")
}
moduleSetup() // 使用构建module的方式构建模块
// remove warning message because of @Incubating
@Suppress("UnstableApiUsage")
android {
namespace = "com.otter.core.player"
sourceSets {
getByName("main") {
jniLibs.srcDir("libs")
}
}
}
kapt {
arguments {
arg("AROUTER_MODULE_NAME", name)
}
}
dependencies {
implementation(Dependencies.VLC.vlc)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.appcompat)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.activity_ktx)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.core)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.room)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.junit_ext)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.androidx_recyclerview)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.constraintlayout)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.swiperefreshlayout)
implementation(Dependencies.AndroidX.androidx_collection_ktx)
}
构建库和构建应用的步骤差不多,建议读者可以去多实践下,体验一下kotlin gradle dsl带来的便利。若有高见,欢迎评论区留言哦