目录
引言:
获取ServiceManager
流程图
注册系统服务
获取系统服务
引言:
注册或使用服务之前,需要通过ServiceManager这个DNS来找到对应的服务。那怎么找到ServiceManager呢?
怎么注册系统服务?
怎么获取系统服务?
获取ServiceManager
framework/native/libs/binder/
- ProcessState.cpp
- BpBinder.cpp
- Binder.cpp
- IServiceManager.cpp
framework/native/include/binder/
- IServiceManager.h
- IInterface.h
通过defaultServiceManager方法来获取gDefaultServiceManager对象。如果对象存在则直接返回,对象不存在就创建该对象。
创建的过程:打开binder驱动,mmap映射内核地址空间,进入loop消息循环
流程图
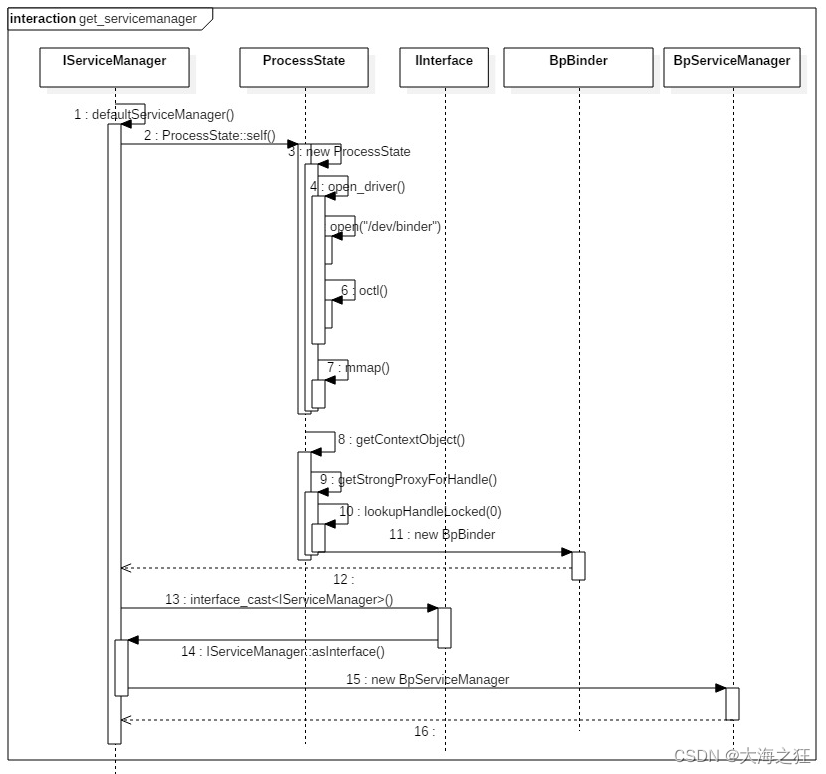
gDefaultServiceManager的创建过程,可分解为以下3个步骤:
1)ProcessState::self():用于获取ProcessState对象(也是单例模式),每个进程有且只有一个ProcessState对象,存在则直接返回,不存在则创建;
2)getContextObject(): 用于获取BpBinder对象,对于handle=0的BpBinder对象,存在则直接返回,不存在才创建;
3)interface_cast<IServiceManager>():用于获取BpServiceManager对象;
defaultServiceManager 等价于 new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0));
ProcessState::self()主要工作:
调用open(),打开/dev/binder驱动设备;
再利用mmap(),创建大小为1M-8K的内存地址空间;
设定当前进程最大的最大并发Binder线程个数为16。
BpServiceManager巧妙将通信层与业务层逻辑合为一体:
通过继承接口IServiceManager实现了接口中的业务逻辑函数;
通过成员变量mRemote= new BpBinder(0)进行Binder通信工作。
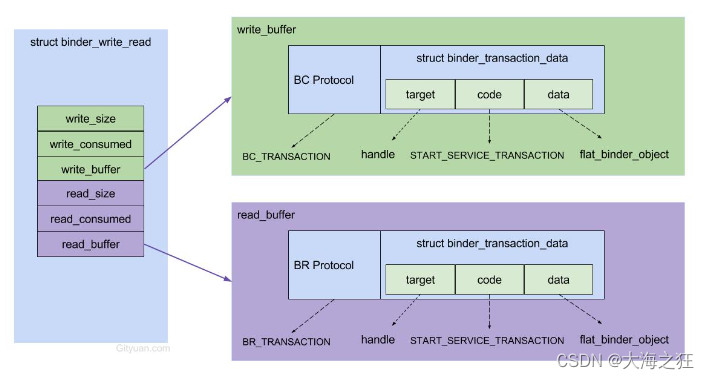
BpBinder通过handler来指向所对应BBinder, 在整个Binder系统中handle=0代表ServiceManager所对应的BBinder。
注册系统服务
framework/native/libs/binder/
- Binder.cpp
- BpBinder.cpp
- IPCThreadState.cpp
- ProcessState.cpp
- IServiceManager.cpp
- IInterface.cpp
- Parcel.cpp
frameworks/native/include/binder/
- IInterface.h (包括BnInterface, BpInterface)