一、引言
作者目前在做的平台使用到了H2,这里介绍下使用场景、使用方式,出于以下两个原因会使用H2:
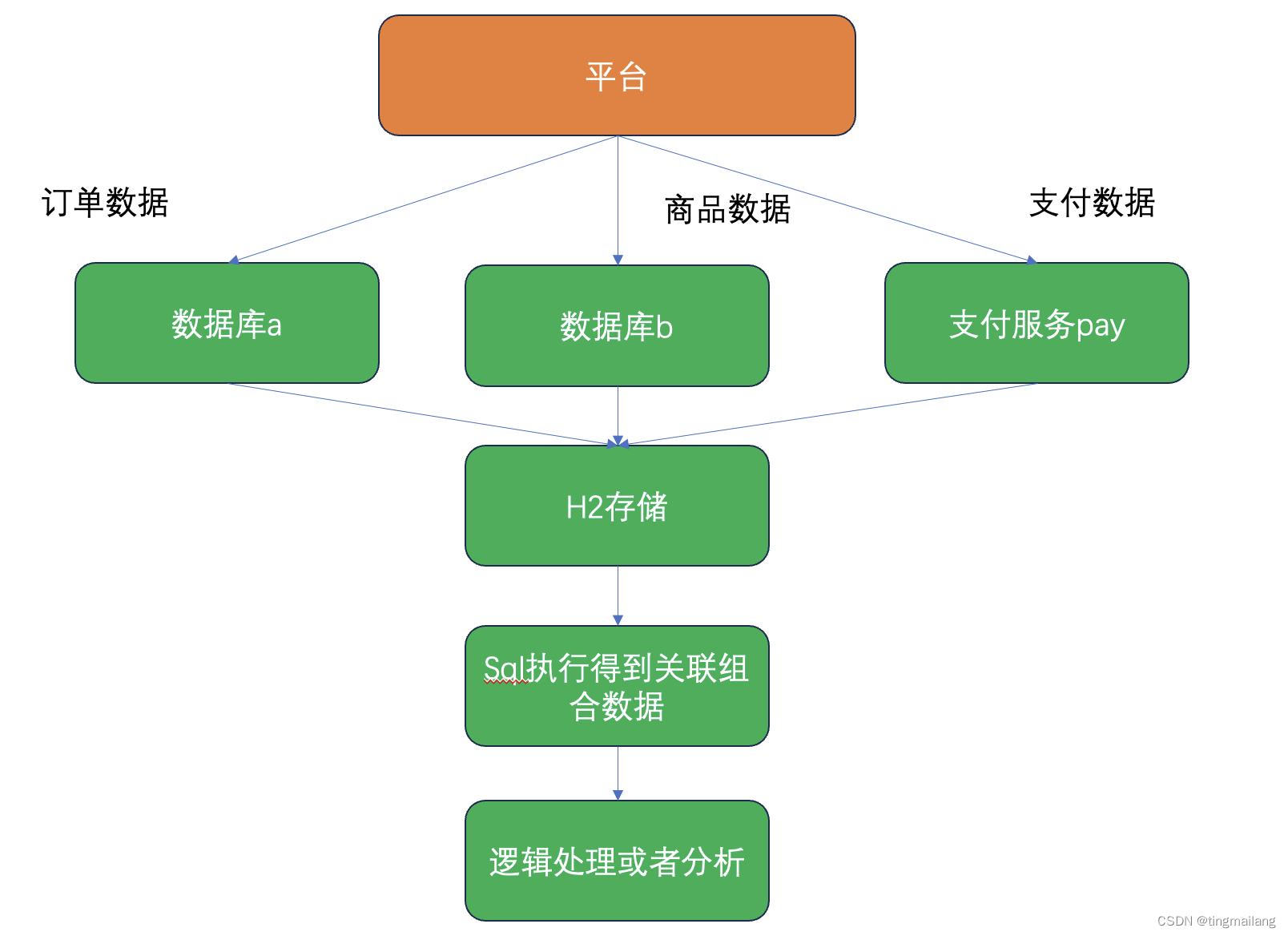
1、平台化的项目一般是用户使用脚本或者sql进行通用的执行,这样可以实现低代码平台,不需要管理类之间的引入、依赖、编译,页面上点点点和输入就可以了,所以很多时候需要把数据放入H2进行sql解析实现跨库、跨实例、跨服务的数据分析
2、在数据集合写起来非常复杂的时候,举个例子:集合a、b,ab的对象有字段c是一一对应的,然后集合a的其他字段和b元素下面挂着的集合又是对应的,这个组合写起来就很麻烦,但是如果存入H2用sql进行关联组合,形成一张大宽表,那么接下来的逻辑和分析验证就会好做。
二、H2介绍
H2是一个用Java编写的开源关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS)。它被设计为一个嵌入式数据库,可以作为应用程序的一部分直接嵌入到Java应用程序中使用,也可以作为独立的数据库服务器运行。
H2数据库具有以下特点:
1. 嵌入式数据库:H2数据库可以作为一个库文件嵌入到Java应用程序中,这样应用程序可以直接访问和管理数据库,而无需额外的数据库服务器。
2. 支持多种模式:H2数据库支持多种模式,包括内存模式、磁盘模式和混合模式。内存模式可以用于临时数据存储,磁盘模式可以持久化数据到磁盘,混合模式可以将数据存储在内存和磁盘上,提供更高的性能和可靠性。
3. 支持多种数据库引擎:H2数据库支持多种数据库引擎,包括嵌入式模式、服务器模式和集群模式。嵌入式模式适用于单个应用程序,服务器模式适用于多个应用程序共享数据库,集群模式适用于高可用性和负载均衡的场景。
4. 支持标准SQL语法:H2数据库支持标准的SQL语法,包括DDL(数据定义语言)、DML(数据操作语言)和DQL(数据查询语言)。它还支持事务、索引、触发器、存储过程和用户定义函数等高级特性。
5. 轻量级和高性能:H2数据库是一个轻量级的数据库管理系统,具有快速的启动时间和低内存消耗。它采用了高效的数据存储和索引算法,提供了优秀的读写性能。
6. 跨平台支持:H2数据库可以在多个平台上运行,包括Windows、Linux和Mac OS等。
三、使用
1、Pom
要引入H2的依赖,还有链接池有已经封装好的,毕竟不能用一下h2就开一个链接,这个消耗的句柄和socket就可怕了。链接复用是必须的。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>2.2.220</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
<version>4.0.3</version>
</dependency>2、链接
这里只要引入H2的依赖包就会自动在运行时创建
url = "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb";
username = "sa";
password = "";
的内存数据库,所以要是不用很多包是不能随便引入的,你不知道这些包都自己做了什么事。
public class H2ConnectionPool {
private static final String url = "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb";
private static final String username = "sa";
private static final String password = "";
private static final HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
private static final HikariDataSource dataSource;
static {
config.setJdbcUrl(url);
config.setUsername(username);
config.setPassword(password);
// 设置连接池大小,默认为10
config.setMaximumPoolSize(10);
dataSource = new HikariDataSource(config);
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();
}
public static void close() {
dataSource.close();
}
}3、建表
实时动态的建表就需要知道表名称,字段名称和类型,有两种情况,一种是从数据库查出来的ResultSet,经过转化之后会变成List<HashMap<String,Object>>,hashmap是表的字段名和值,每行数据形成了一个map,做过底层通用转化的应该都知道,不清楚的同学也没关系,可以私聊作者。
这种情况就可以根据map生成建表语句。
public static boolean createTable(String tableName, HashMap map) throws SQLException {
if (StringUtilsExt.isBlank(tableName)) {
return false;
}
if (map == null) {
return false;
}
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 连接到H2数据库
conn = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
// 创建Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 创建表的SQL语句
String sql = getCreateSql(tableName, map);
// 执行SQL语句
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}
return true;
}
private static String getCreateSql(String tableName, HashMap map) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE " + tableName + " (");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
builder.append(key);
builder.append(" ");
if (value instanceof Long) {
builder.append("bigint");
} else if (value instanceof Integer) {
builder.append("int");
} else if (value instanceof String) {
builder.append("varchar");
} else if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
builder.append("decimal");
} else if (value instanceof Boolean) {
builder.append("int");
} else if (value instanceof Timestamp) {
builder.append("datetime");
}
builder.append(",");
});
builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
// 创建表的SQL语句
return builder + ")";
}第二种情况是调用接口或者查其他一些数据的时候,得到的是List<T>,那就要根据反射获取T的字段名称和值了。
public boolean createTableByT(String tableName, T t) throws SQLException {
if (StringUtilsExt.isBlank(tableName)) {
return false;
}
if (t == null) {
return false;
}
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 连接到H2数据库
conn = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
// 创建Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 创建表的SQL语句
String sql = getCreateSqlByT(tableName, t);
// 执行SQL语句
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}
return true;
}
private String getCreateSqlByT(String tableName, T t) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE " + tableName + " (");
Class<?> clazz = t.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String fieldName = field.getName();
Object fieldValue = null;
try {
fieldValue = field.get(t);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
builder.append(fieldName);
builder.append(" ");
if (fieldValue instanceof Long) {
builder.append("bigint");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof Integer) {
builder.append("int");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof String) {
builder.append("varchar");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof BigDecimal) {
builder.append("decimal");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof Boolean) {
builder.append("int");
} else if (fieldValue instanceof Timestamp) {
builder.append("datetime");
}
}
builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
// 创建表的SQL语句
return builder + ")";
}4、插数据
第一种是根据数据库转化的map插入
public static boolean insertByHashMap(String tableName, List<HashMap> listMap) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 连接到H2数据库
connection = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap = new HashMap<>(listMap.get(0).size());
String sql = getInsertSql(tableName, listMap.get(0), indexMap);
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
setValue(listMap, indexMap, statement);
// 执行批处理
int[] rowsInserted = statement.executeBatch();
if (rowsInserted.length != listMap.size()) {
return false;
}
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
}
return true;
}
private static void setValue(List<HashMap> listMap, HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap,
PreparedStatement statement) throws SQLException {
// 批量插入数据
for (HashMap m : listMap) {
m.forEach((key, value) -> {
if (value instanceof Long) {
try {
statement.setLong(indexMap.get(key), (Long)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Integer) {
try {
statement.setInt(indexMap.get(key), (Integer)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof String) {
try {
statement.setString(indexMap.get(key), (String)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
try {
statement.setBigDecimal(indexMap.get(key), (BigDecimal)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Boolean) {
int flag = (Boolean) value ? 1 : 0;
try {
statement.setInt(indexMap.get(key), flag);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Byte) {
try {
statement.setByte(indexMap.get(key), (Byte) value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
statement.addBatch();
}
}
private static String getInsertSql(String tableName, HashMap map, HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("INSERT INTO " + tableName + " (");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder(" VALUES (");
AtomicInteger index = new AtomicInteger(1);
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
builder.append(key);
builder.append(" ");
builder.append(",");
builder2.append("?");
builder2.append(" ");
builder2.append(",");
indexMap.put((String)key, index.get());
index.getAndIncrement();
});
builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
builder2.deleteCharAt(builder2.length() - 1);
// 插入表的SQL语句
return builder + ")" + builder2 + ")";
}第二种就是根据list插入数据
public boolean insertByList(String tableName, List<T> list) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 连接到H2数据库
connection = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap = new HashMap<>();
String sql = getInsertSqlByList(tableName, list.get(0), indexMap);
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
setValueByList(list, indexMap, statement);
// 执行批处理
int[] rowsInserted = statement.executeBatch();
if (rowsInserted.length != list.size()) {
return false;
}
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
}
return true;
}
private void setValueByList(List<T> list, HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap,
PreparedStatement statement) throws SQLException {
// 批量插入数据
for (T t : list) {
Class<?> clazz = t.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String key = field.getName();
Object value = null;
try {
value = field.get(t);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (value instanceof Long) {
try {
statement.setLong(indexMap.get(key), (Long)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Integer) {
try {
statement.setInt(indexMap.get(key), (Integer)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof String) {
try {
statement.setString(indexMap.get(key), (String)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof BigDecimal) {
try {
statement.setBigDecimal(indexMap.get(key), (BigDecimal)value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Boolean) {
int flag = (Boolean) value ? 1 : 0;
try {
statement.setInt(indexMap.get(key), flag);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else if (value instanceof Byte) {
try {
statement.setByte(indexMap.get(key), (Byte) value);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
statement.addBatch();
}
}
private String getInsertSqlByList(String tableName, T t, HashMap<String, Integer> indexMap) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("INSERT INTO " + tableName + " (");
StringBuilder builder2 = new StringBuilder(" VALUES (");
AtomicInteger index = new AtomicInteger(1);
Class<?> clazz = t.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
String fieldName = field.getName();
builder.append(fieldName);
builder.append(" ");
builder.append(",");
builder2.append("?");
builder2.append(" ");
builder2.append(",");
indexMap.put(fieldName, index.get());
index.getAndIncrement();
}
builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
builder2.deleteCharAt(builder2.length() - 1);
// 插入表的SQL语句
return builder + ")" + builder2 + ")";
}5、查询
查询没什么,执行sql就好,这里就能看到数据库查询出来的ResultSet被通用的转化
public static List<HashMap> query(String sql) throws SQLException {
// 创建List对象来存储查询结果
List<HashMap> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
connection = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
// 执行查询
stmt = connection.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// 获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
// 处理查询结果
while (rs.next()) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(columnCount);
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
map.put(metaData.getColumnName(i), rs.getObject(i));
}
resultList.add(map);
}
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
}
return resultList;
}6、删表
public static boolean dropTable(String tableName) throws SQLException {
if (StringUtilsExt.isBlank(tableName)) {
return false;
}
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 连接到H2数据库
conn = H2ConnectionPool.getConnection();
// 创建Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "DROP TABLE " + tableName;
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}
return true;
}四、总结
平台化的建设要考虑低代码和通用,不然源码处处改就很完蛋,这里作者介绍了H2做通用化跨库、跨实例、跨服务数据分析和逻辑,有兴趣的同学欢迎讨论!