迪杰斯特拉算法
- 图的最短路径的解法
单源最短路径
- 从一个点开始,可以找到其中任意一个点的最短路径。
多源最短路径
- 从任何一个点开始,可以找到其中任何一个点的最短路径。
解题过程
给定一个带权有向图G=(G, V), 另外,还给定 V 中的一个顶点,称为源。现在我们要计算从
源到所有其他各顶点的最短路径长度。这里的长度是指路上各边权之和。这个问题通常称为单
源最短路径问题。
Dijkstra算法的解决方案
即先求出长度最短的一条最短路径,再参照它求出长度次短的一条最短路径,依次类推,直到
1.选出一个顶点v作为源点,并将从源点v出发的所有边到各顶点的最短路径
创建一个数组dist,记录从这个点到其他点之间的距离
没有直接相连,就把两点之间的距离设置为无穷大
创建vistited状态数组,记录节点是否被访问
int index = startIndex;// 当前节点到自身的距离为0
this.dist[index] = 0;// 源点已被访问
visited[index] = true;// 3.从源到各个节点的最短距离LinkedList<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list = this.adj[index];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> entry = list.get(i); this.dist[entry.getKey()] = entry.getValue();
}
2.设置源点到自身的距离为0,并设置与源点直接相连点的距离
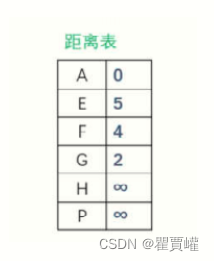
3.遍历距离表,循环的次数等于层数
在距离表中,从未被访问的节点中找一个距离最小的节点
将该节点设置为已访问,并将于该节点邻接的节点的值分别进行求和与其邻接的距离表中的值进行比较,如果小于距离表中的值,则进行替换
for (int i = 0; i < this.dist.length; i++) { // 循环的次数=层数
// 4.在距离表中,从未被访问的节点中找一个距离最小的节点
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minDistanceIndex = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < this.dist.length; j++) {
if (!this.visited[j] && this.dist[j] < minDistance) {
minDistance = this.dist[j];
minDistanceIndex = j;
}
/*if (!this.visited[j] && this.dist[j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, this.dist[j]);
minDistanceIndex = j;
}*/
}
// 特殊处理:源与任何节点都不连接
if (minDistance == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
break;
}
// 调整dist中各项点到源点的路径
// 先设置minDistanceIndex 已经被访问过
this.visited[minDistanceIndex] = true;
// 获取minDistanceIndex的邻接表
LinkedList<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list2 = this.adj[minDistanceIndex];
// 使用 minDistance+curNode的权值 与 距离表中的原来的值进行比较,如果小的话就更新
for (int k = 0; k < list2.size(); k++) {
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> entry2 = list2.get(k);
int key = entry2.getKey();
int value = entry2.getValue();
if(this.visited[key]){
continue;
}
if (minDistance + value < this.dist[key]) {
this.dist[key] = minDistance + value;
}
}
}
4.重复步骤3,直到任何节点都被访问
所有代码
package graph;
import java.util.AbstractMap;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法
*/
public class Graph03 {
// 邻接表,存储的是每一个节点的邻接节点与邻接节点的“关系”(key是索引,value是权值)
private LinkedList<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>>[] adj; // 邻接表
private Vertex[] vertexes; // 节点集合
// 1.创建一个距离表dist,存放从源到其他节点的最短距离
private int[] dist;
// 创建状态数组,记录节点是否被访问
private boolean[] visited;
// 图的构造
public Graph03(int size, String[] arr) {
this.vertexes = new Vertex[size];
// 初始化邻接表,创建每个节点list
this.adj = new LinkedList[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
this.vertexes[i] = new Vertex(arr[i], i);
// 每个节点对应的list不能为空,将每一个节点的list实体化
this.adj[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
// 2.对距离表进行初始化
dist = new int[size];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
visited = new boolean[size];
}
/**
* @param startIndex 代表源节点的索引
*/
public int[] dijkstra(int startIndex) {
int index = startIndex;
// 当前节点到自身的距离为0
this.dist[index] = 0;
// 源点已被访问
visited[index] = true;
// 3.从源到各个节点的最短距离
LinkedList<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list = this.adj[index];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> entry = list.get(i);
this.dist[entry.getKey()] = entry.getValue();
}
for (int i = 0; i < this.dist.length; i++) { // 循环的次数=层数
// 4.在距离表中,从未被访问的节点中找一个距离最小的节点
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minDistanceIndex = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < this.dist.length; j++) {
if (!this.visited[j] && this.dist[j] < minDistance) {
minDistance = this.dist[j];
minDistanceIndex = j;
}
/*if (!this.visited[j] && this.dist[j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, this.dist[j]);
minDistanceIndex = j;
}*/
}
// 特殊处理:源与任何节点都不连接
if (minDistance == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
break;
}
// 调整dist中各项点到源点的路径
// 先设置minDistanceIndex 已经被访问过
this.visited[minDistanceIndex] = true;
// 获取minDistanceIndex的邻接表
LinkedList<AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer>> list2 = this.adj[minDistanceIndex];
// 使用 minDistance+curNode的权值 与 距离表中的原来的值进行比较,如果小的话就更新
for (int k = 0; k < list2.size(); k++) {
AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<Integer, Integer> entry2 = list2.get(k);
int key = entry2.getKey();
int value = entry2.getValue();
if(this.visited[key]){
continue;
}
if (minDistance + value < this.dist[key]) {
this.dist[key] = minDistance + value;
}
}
}
return this.dist;
}
// 节点的类
class Vertex {
private String value; // 结点内容
private int index; // 结点在数组中的索引
private int weight; // 权
Vertex(String value, int index, int weight) {
this.value = value;
this.index = index;
this.weight = weight;
}
Vertex(String value, int index) {
this(value, index, 1);
}
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("---邻接表---");
for (int i = 0; i < this.adj.length; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < this.adj[i].size(); j++) {
System.out.print(this.adj[i].get(j).getKey() + "----->");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
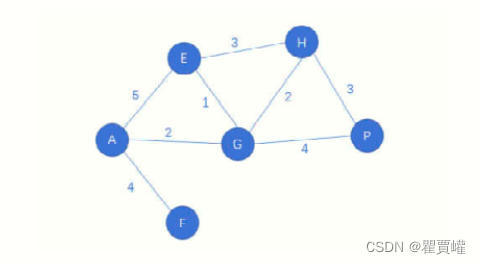
String[] arr = {"A", "E", "F", "G", "H", "P"};
int size = arr.length;
Graph03 graph02 = new Graph03(size, arr);
graph02.adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 5));
graph02.adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(2, 4));
graph02.adj[0].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 2));
graph02.adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 5));
graph02.adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 1));
graph02.adj[1].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));
graph02.adj[2].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 4));
graph02.adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(0, 2));
graph02.adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 1));
graph02.adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 2));
graph02.adj[3].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 4));
graph02.adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(1, 3));
graph02.adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 2));
graph02.adj[4].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(5, 3));
graph02.adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(3, 4));
graph02.adj[5].add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<>(4, 3));
graph02.print();
int[] dist = graph02.dijkstra(0);
for(Integer i:dist){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}











![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计儿童绘本租赁网站Django(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c4559878d7284cc79f4ada04dc4b5e08.png)