前言
查看此文章前强烈建议先看这篇文章:Java江湖路 | 专栏目录
该文章纪录的是SpringBoot使用RestTemplate发送http请求,每一步都有记录,争取每一位看该文章的小伙伴都能操作成功。达到自己想要的效果~
文章目录
- 前言
- 1、SpringBoot调用外部接口的三种方式
- 2、什么是RestTemplate
- 3、SpringBoot中使用RestTmplate
- 3.1、前置准备
- 3.2、Get请求方式
- 3.3、Post请求
- 3.4、解决中文乱码
- 3.5、封装工具类
- 总结
1、SpringBoot调用外部接口的三种方式
- 原始httpClient
- RestTemplate
- Feign
本文着重介绍RestTemplate方式
2、什么是RestTemplate
RestTemplate是Spring 框架提供的 ,可用于在应用中调用 rest 服务,它简化了与 http 服务的通信方式,统一了 RESTful 的标准,封装了 http 链接, 我们只需要传入url及返回值类型即可。相较于之前常用的 HttpClient,RestTemplate 是一种更优雅的调用 RESTful 服务的方式。
3、SpringBoot中使用RestTmplate
3.1、前置准备
1、创建一个普通的SpringBoot项目
2、创建一个配置类,
package com.eric.springbootresttemplate.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
/**
* @author Eric
* @date 2023-08-03 9:37
*/
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
3、准备一个实体类
package com.eric.springbootresttemplate.entity;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author Eric
* @date 2023-08-03 9:33
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
}
4、创建两个被请求的接口(模拟其他服务接口)
@GetMapping("/getUserInfo")
public User getUserList(Long id, String name) {
User user = User.builder().id(id).name(name).build();
return user;
}
@PostMapping("/postUserInfo")
public User postUserInfo(@RequestBody JSONObject jsonObject) {
Long id = jsonObject.getLong("id");
String name = jsonObject.getString("name");
User user = User.builder().id(id).name(name).build();
return user;
}
3.2、Get请求方式
get有两种请求方式,一种正常的在url拼接参数,一种是使用占位符的方式
方式一:参数拼接
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
/**
* Get请求方式一:参数拼接
* @param id
* @param name
*/
@GetMapping("/getUserInfoRest")
public void getUserInfoRest(Long id, String name) {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/rest/getUserInfo?id=" + id + "&name=" + name;
ResponseEntity<String> result = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class);
System.out.println(result.getStatusCode());
System.out.println(result.getBody());
System.out.println(result.getHeaders());
}
方式二:占位符方式
直接在方法中指定参数:
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
/**
* Get请求方式二:占位符方式
* @param id
* @param name
*/
@GetMapping("/getUserInfoRest2")
public void getUserInfoRest2(Long id, String name) {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/rest/getUserInfo?id={id}&name={name}";
ResponseEntity<String> result = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class,id,name);
System.out.println(result.getStatusCode());
System.out.println(result.getBody());
System.out.println(result.getHeaders());
}
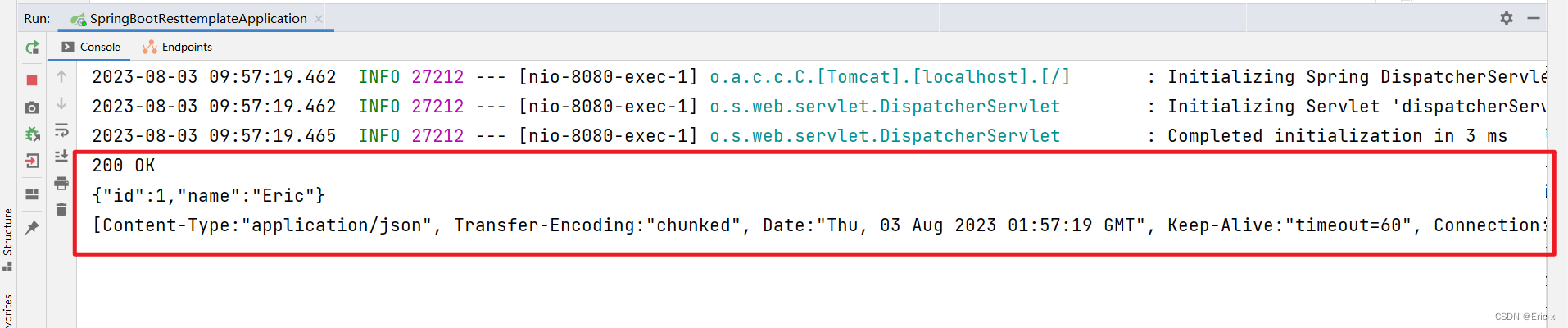
两种方式的执行结果如下:
3.3、Post请求
/**
* Post请求方式:带@RequestBody
*/
@PostMapping("/postUserInfoRest")
public void postUserInfoRest() {
Map<String, Object> requestBody = new HashMap<>();
requestBody.put("id", 1L);
requestBody.put("name", "Eric");
HttpHeaders requestHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
requestHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> r = new HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>>(requestBody, requestHeaders);
String url = "http://localhost:8080/rest/postUserInfo";
String result = restTemplate.postForObject(url, r, String.class);
System.out.println(result);
}
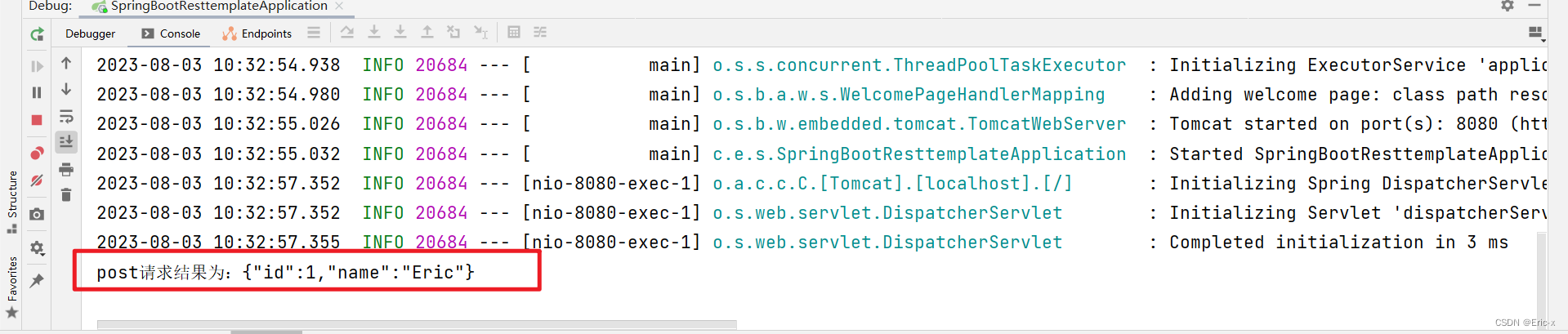
结果如下:
3.4、解决中文乱码
上述请求可能会存在中文乱码,只需要额外设置下即可
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().set(1, new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
3.5、封装工具类
在日常中,我们可以直接将get和post简单的封装为一个工具类, 方便我们直接调用(这里我只是简单的封装了下,大家如果可以根据自己的使用场景再次封装~)
package com.wzhy.smart.common.common.utils;
package com.eric.springbootresttemplate.utils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* RestTemplate请求工具类
*
* @author Eric
* @date 2023-08-03 10:36
*/
@Slf4j
public class RestTemplateUtil {
/**
* post请求
*
* @param url 请求路径
* @param parameter 请求参数
* @return 返回值
*/
public static String post(String url, Map<String, Object> parameter) {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().set(1, new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
HttpHeaders requestHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
requestHeaders.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> r = new HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>>(parameter, requestHeaders);
String body = restTemplate.postForObject(url, r, String.class);
// log.info("远程调用结果,body为:{}", body);
return body;
}
/**
* get请求
*
* @param url 请求路径
* @param parameter 请求参数
* @return 返回值
*/
public static String get(String url, Map<String, Object> parameter) {
if (!parameter.isEmpty()) {
url = url + "?";
for (String key : parameter.keySet()) {
url = url + key + "=" + parameter.get(key) + "&";
}
url = url.substring(0, url.length() - 1);
}
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().set(1, new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String body = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class, parameter).getBody();
// log.info("远程调用结果,body为:{}", body);
return body;
}
}
总结
怎么样,是不是特别的方便和简单~