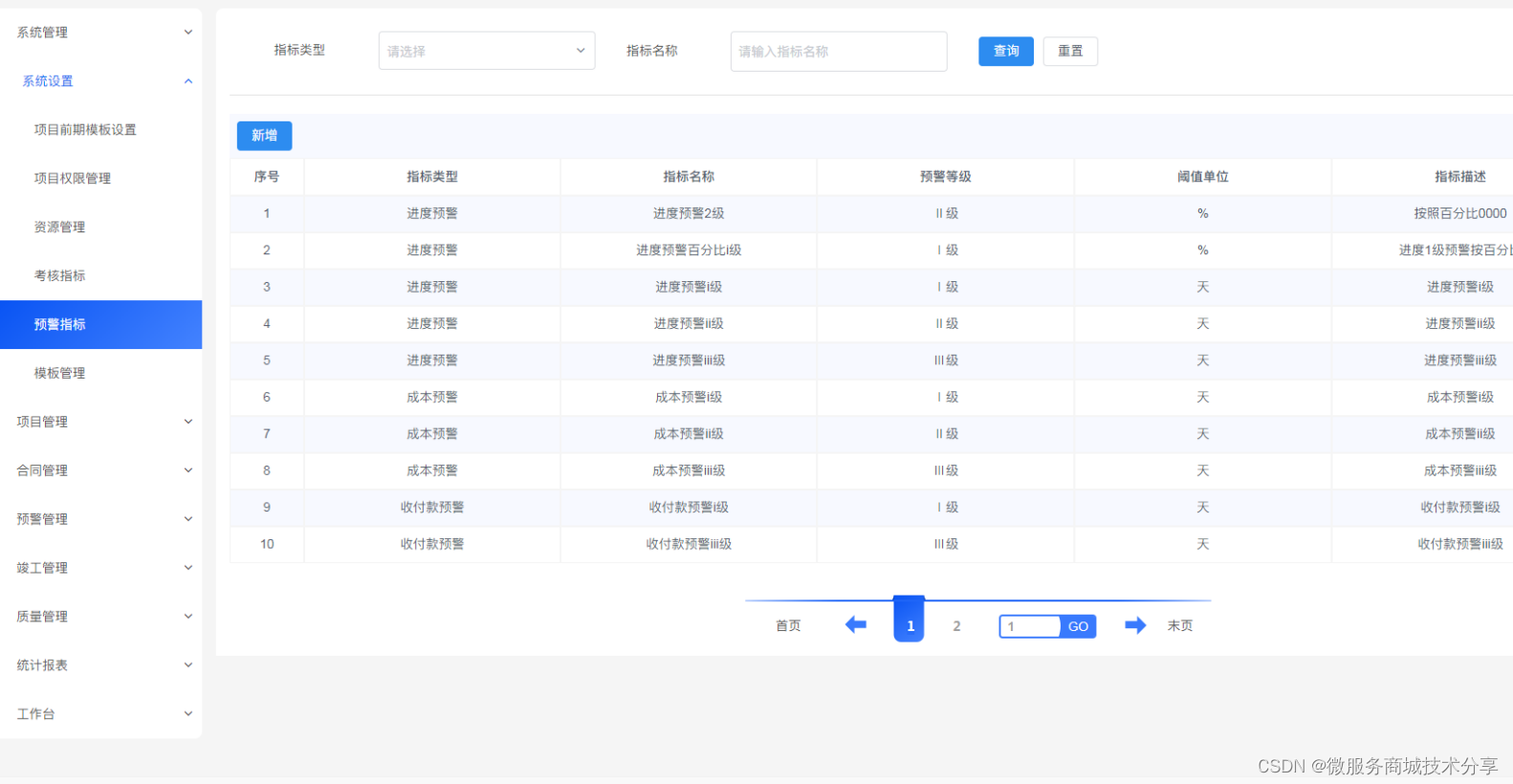
1.栈的概念
1.栈的定义
栈是仅限在表尾进行插入和删除的线性表,栈又被称为先进后出的线性表,简称“LIFO”
我们这次用数组作为我们栈的底层数据结构,代码会放到结尾供大家参考使用
2.栈顶的定义
栈是一个线性表,我们允许插入和删除的一端称为栈顶
3.栈底的定义
和栈顶相对的另一端称为栈底,实际上栈底的元素我们不需要关心
4.栈的创建
//数据容器
private T[] data;
//容积
private int capacity;
//实际存放的元素个数
private int size;2.入栈
1.入栈的定义
栈元素的插入操作叫做入栈,也可以称为进栈、压栈
2.动画演示
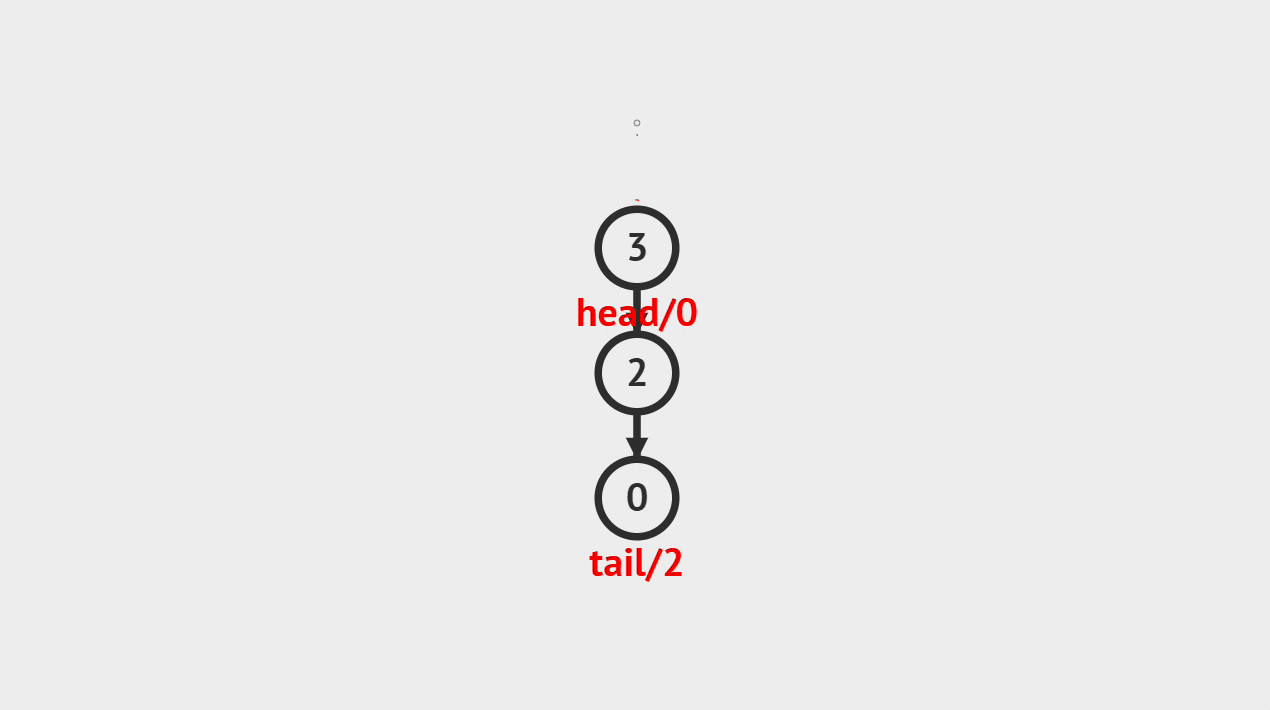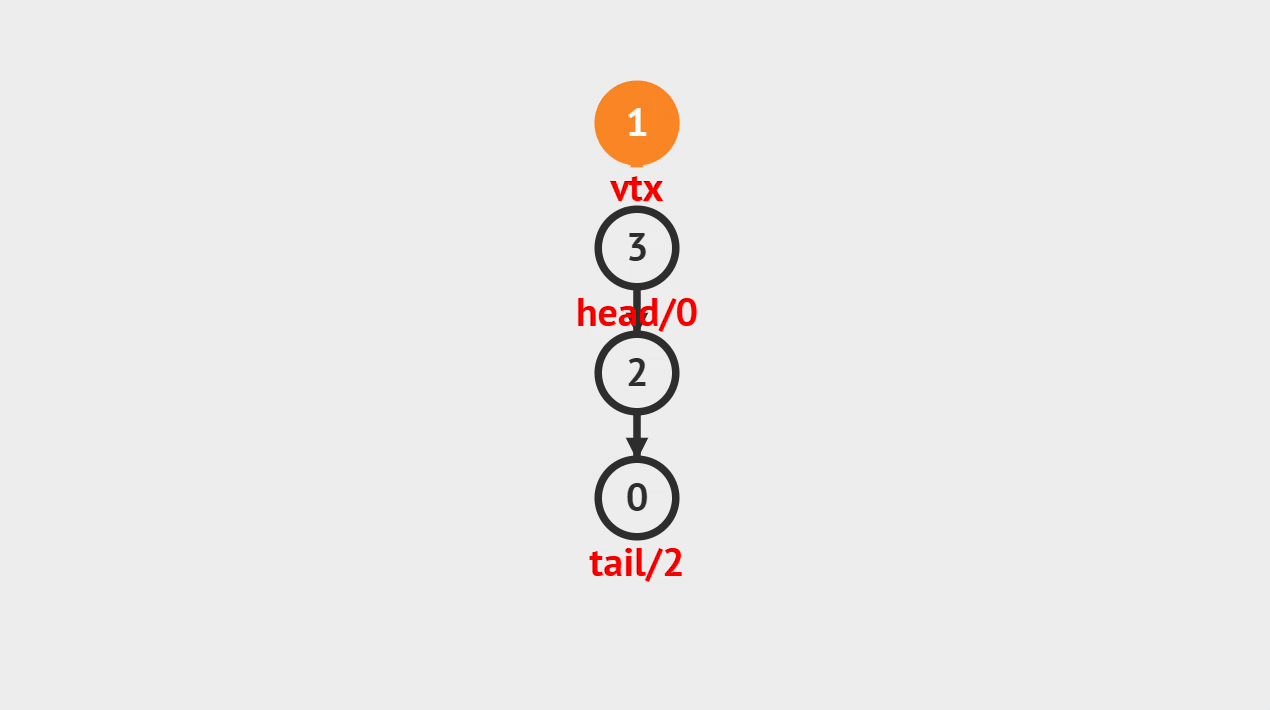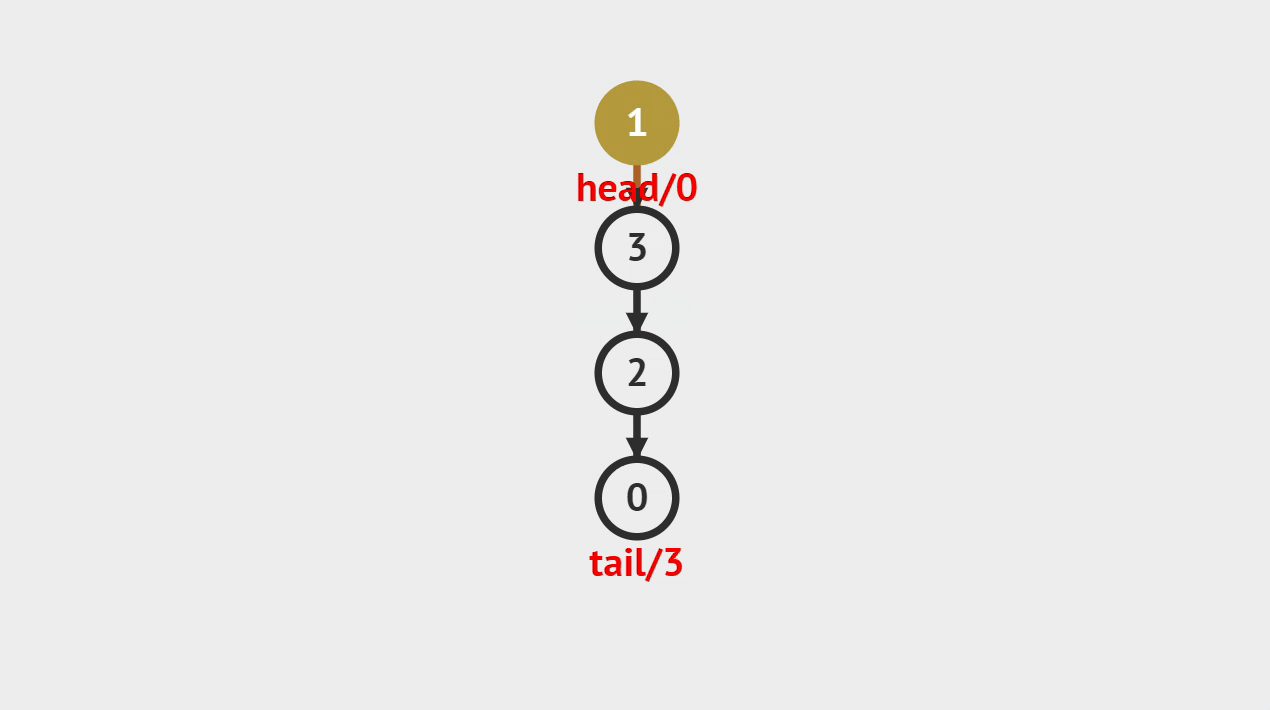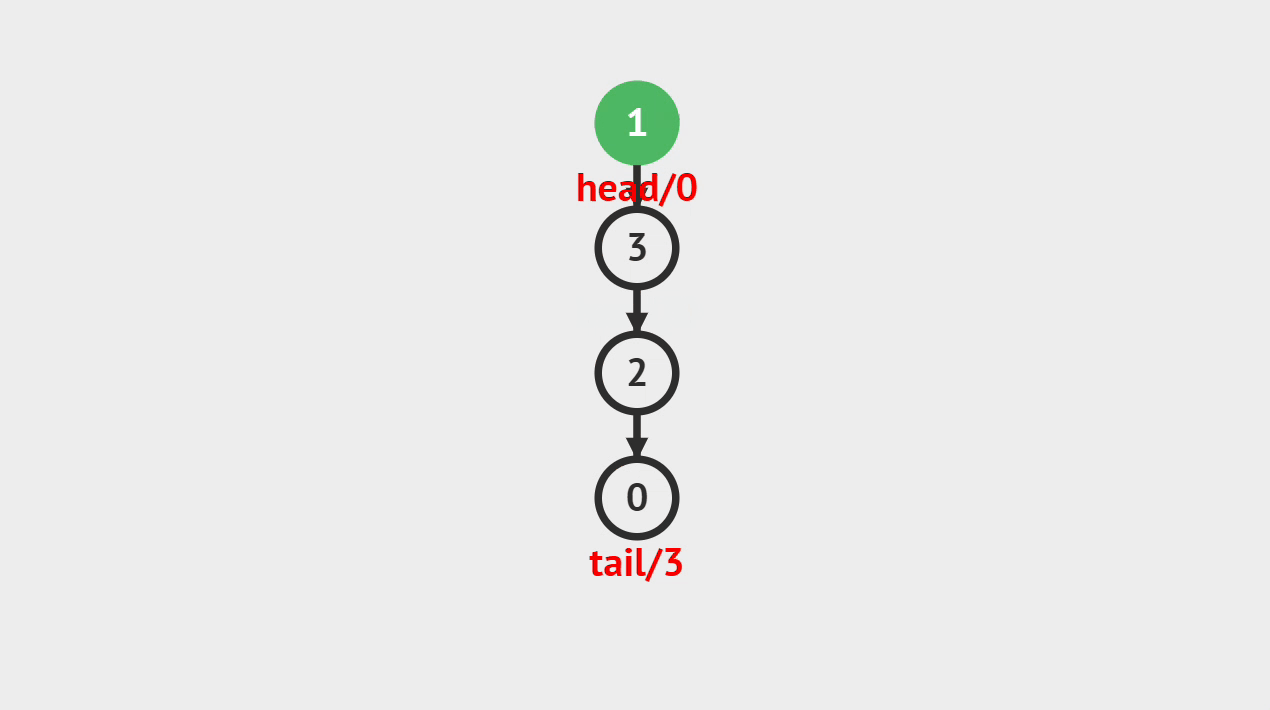
图中是以链表为底层数据结构的,大家看图了解个大概就可以了,具体可以看代码是怎么实现的
3.代码实现
//在末尾添加元素
public void addTail(T val) {
//this.data[size]=val;
this.add(this.size, val);
}
//在中间插入元素
public void add(int index, T val) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
//判断数组是否满
if(this.size==this.capacity){
//数组满的话扩容原来数组的两倍
int newCapacity=this.capacity*2;
T[] newDate=(T[]) new Object[newCapacity];//创建一个新的数组
//进行数组迁移
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newDate[i]=this.data[i];
}
this.capacity=newCapacity;
this.data=newDate;
}3.出栈
1.出栈的定义
栈元素的删除操作叫做出栈,也可称为弹栈
2.动画演示

3.代码演示
//移出末尾
public T removeTail() {
// T val=this.data[size-1];
// this.size-=1;
// return val;
return this.remove(this.size);
}
//中部移出
public T remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
T val = this.data[index];
for (int i = index; i < this.size; i++) {
this.data[i] = this.data[i+1];
}
this.size -= 1;
if(this.size<=this.capacity/4&&this.capacity/2>1){
int newCapacity=this.capacity/2;
T[] newDate=(T[])new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newDate[i]=this.data[i];
}
this.capacity=newCapacity;
this.data=newDate;
}4.查询栈顶
1.获取栈顶的定义
一般我们可以去查看栈顶的元素是什么
2.动画演示
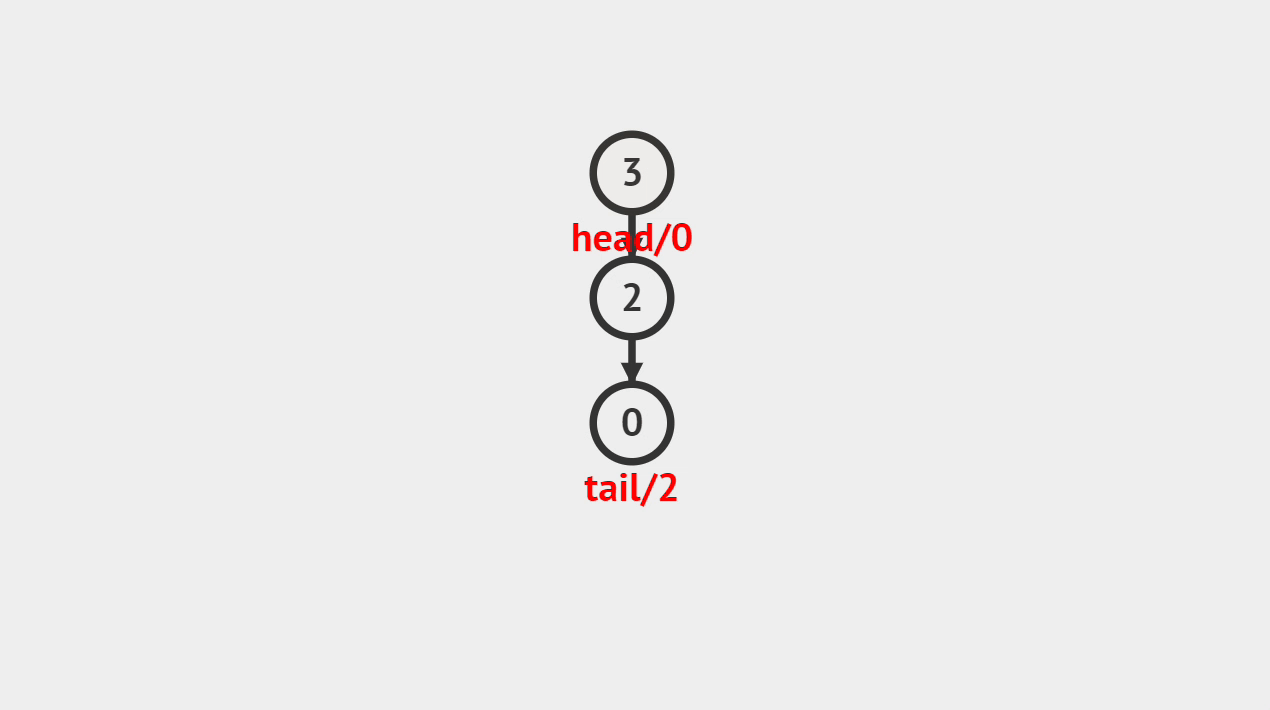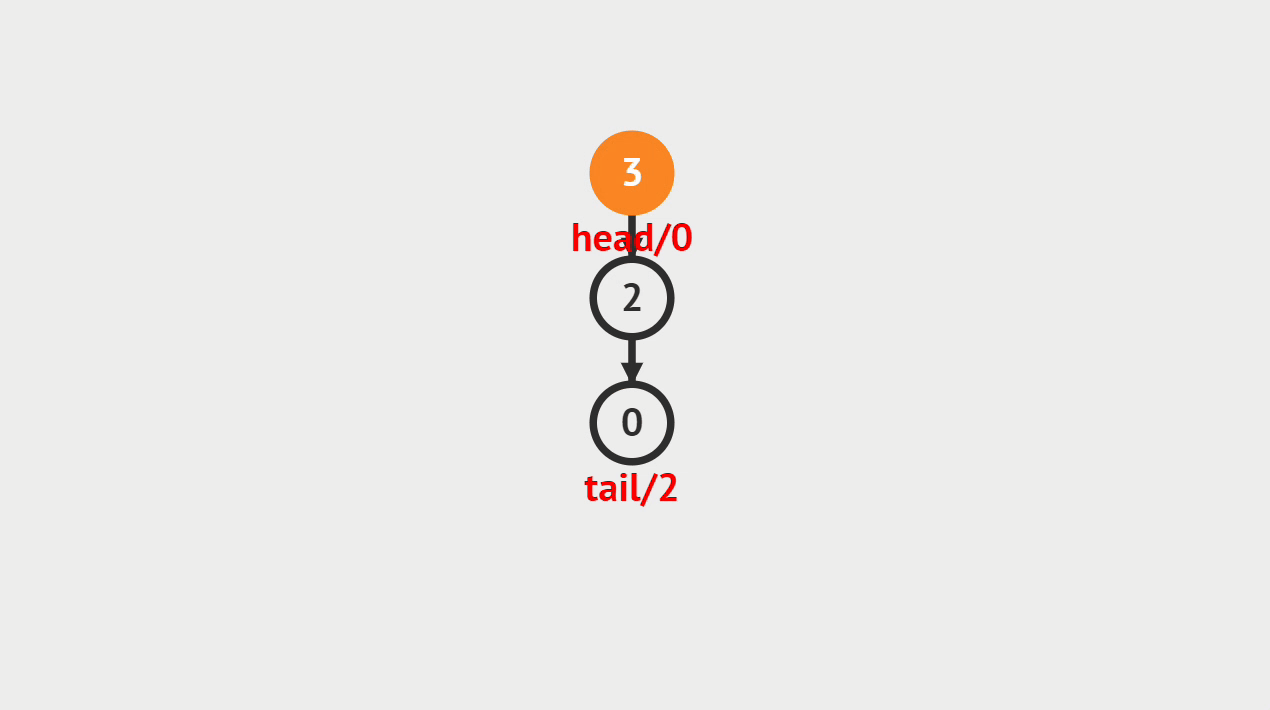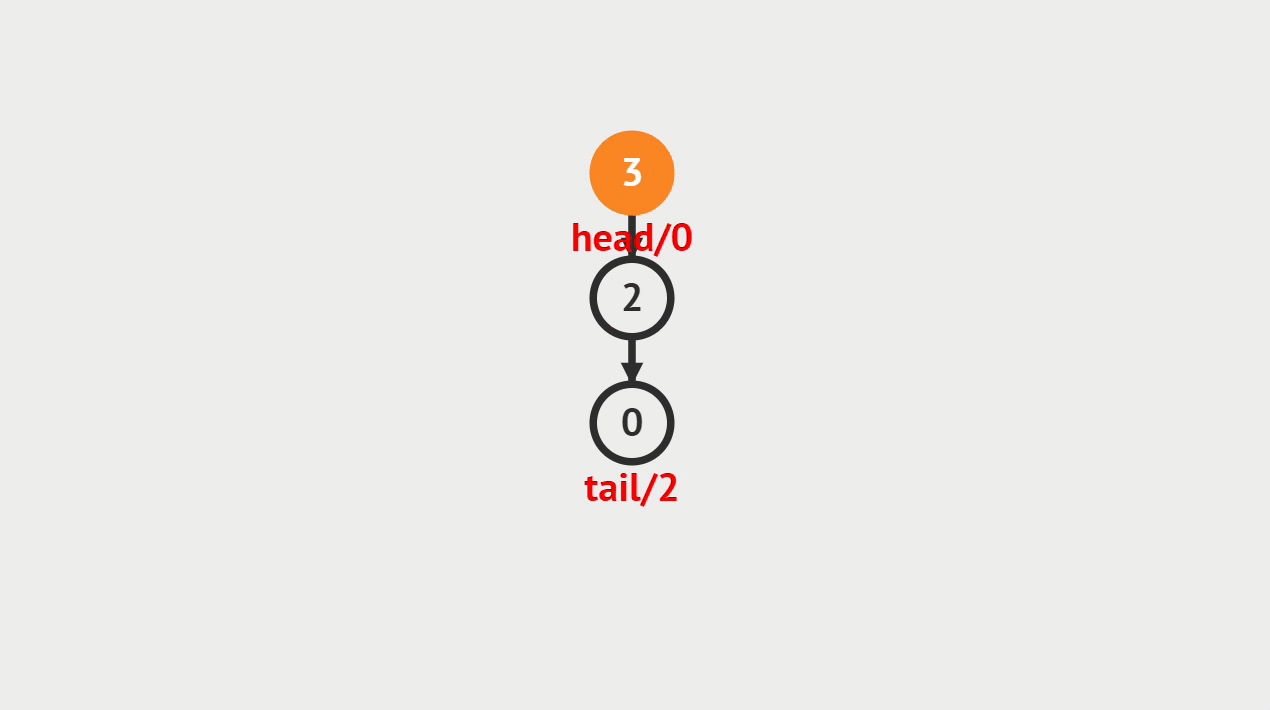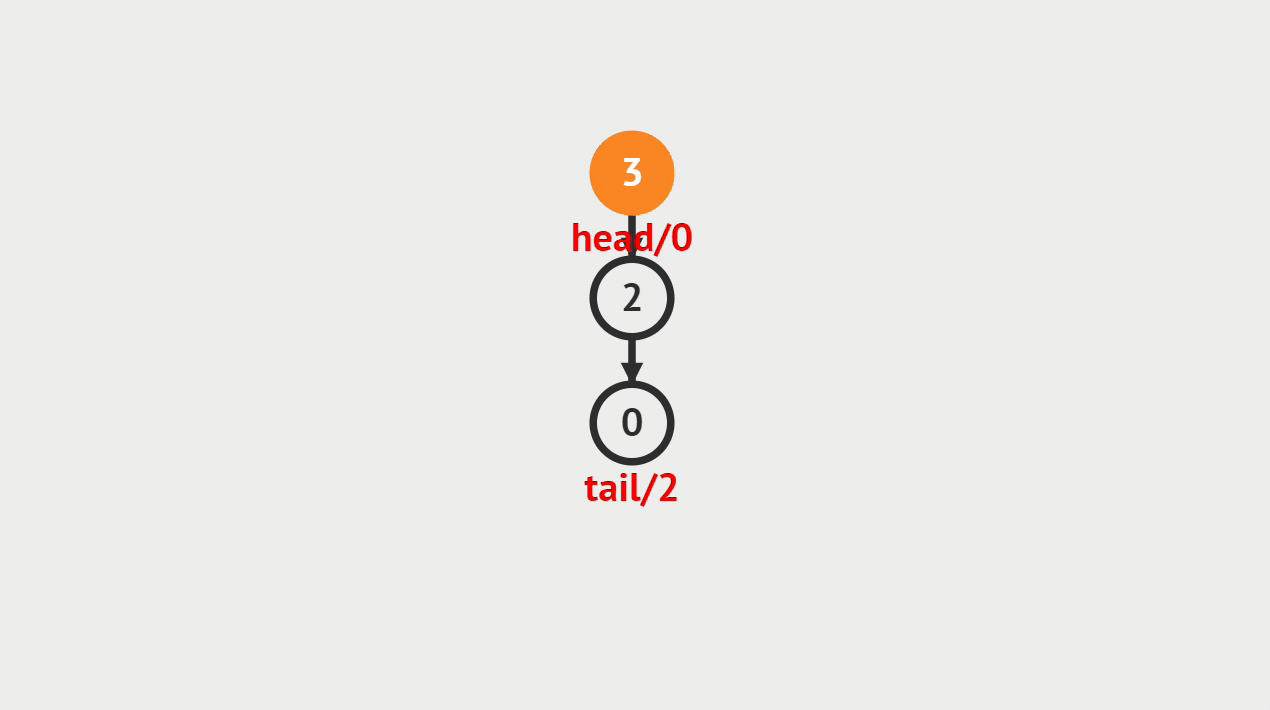
3.代码演示
public T peek(T val) {
return data.getEnByIndex(this.size() - 1);
}
//获得指定索引的元素
public T getEnByIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
return this.data[index];
}基本的栈能用到的就这些基本的方法,接下来给大家一个完整的代码,供大家学习参考
public class StackDemo<T> implements Stack<T> {
//以我们封装的数组作为栈的底层数据结构
private arrSub<T>data;
public StackDemo() {
data=new arrSub<>();
}
public StackDemo(int capacity) {
data=new arrSub<>(capacity);
}
@Override//弹栈
public T pop() {
return data.removeTail();
}
@Override//往栈中添加元素
public void push(T val) {
data.addTail(val);
}
@Override//查看元素个数
public int size() {
return data.getSize();//获得数组元素个数
}
@Override//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return data.isEmpty();
}
@Override//查看栈顶元素
public T peek(T val) {
return data.getEnByIndex(this.size() - 1);
}
@Override
public T peek() {
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("栈顶[");
T[] arr = data.getData();
for (int i = size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
sb.append(arr[i]);
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("]栈底");
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> stack = new StackDemo<>(10);
String[] fruits
= {"apple", "banana", "peach", "watermelon", "strawberry", "pear", "orange", "grape"};
for (int i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {
stack.push(fruits[i]);
}
System.out.println(stack);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("ele-->" + stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack + "栈中元素的个数:" + stack.size());
}
}
}public class arrSub<T> {
//数据容器
private T[] data;
//容积
private int capacity;
//实际存放的元素个数
private int size;
public arrSub(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.data = (T[]) new Object[this.capacity];
this.size = 0;
}
public arrSub() {
this.capacity = 10;
}
// 判断数据容器是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
public T[] getData(){
return this.data;
}
//获得数组的容积
public int getCapacity() {
return this.capacity;
}
//获取元素的个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
//首行添加元素
public void addTop(T val) {
// for (int i = size-1; i >=0 ; i--) {
// this.data[i+1]=this.data[i];
// }
// this.data[0]=val;
this.add(0, val);
}
//在末尾添加元素
public void addTail(T val) {
//this.data[size]=val;
this.add(this.size, val);
}
//在中间插入元素
public void add(int index, T val) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
//判断数组是否满
if(this.size==this.capacity){
//数组满的话扩容原来数组的两倍
int newCapacity=this.capacity*2;
T[] newDate=(T[]) new Object[newCapacity];//创建一个新的数组
//进行数组迁移
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newDate[i]=this.data[i];
}
this.capacity=newCapacity;
this.data=newDate;
}
for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
this.data[i + 1] = this.data[i];
}
this.data[index] = val;
this.size += 1;
}
//获得指定索引的元素
public T getEnByIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
return this.data[index];
}
//获得指定元素的索引
public int getEnByVal(int index, T val) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (this.data[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//判断是否包含某种布局
public boolean contains(T val) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (this.data[i] == val) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//修改指定索引的元素
public void upLoad(T var, int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
this.data[index] = var;
}
//重写toString的方法
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(10);
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
stringBuilder.append(this.data[i] + ",");
}
return stringBuilder.substring(0, stringBuilder.lastIndexOf(",") == -1 ? 0 : stringBuilder.lastIndexOf(","));
}
//移出末尾
public T removeTail() {
// T val=this.data[size-1];
// this.size-=1;
// return val;
return this.remove(this.size);
}
//移出首部
public T removeTop() {
// T val=this.data[0];
// for (int i = 1; i <this.size; i++) {
// this.data[i-1]=this.data[i];
// }
// this.size-=1;
// return val;
return this.remove(0);
}
//中部移出
public T remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is invalid!");
}
T val = this.data[index];
for (int i = index; i < this.size; i++) {
this.data[i] = this.data[i+1];
}
this.size -= 1;
if(this.size<=this.capacity/4&&this.capacity/2>1){
int newCapacity=this.capacity/2;
T[] newDate=(T[])new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newDate[i]=this.data[i];
}
this.capacity=newCapacity;
this.data=newDate;
}
return val;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
arrSub myArr = new arrSub(50);
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
myArr.addTail(i + 10);
}
System.out.println(myArr);
// System.out.println("20?" + myArr.contains(20));
// System.out.println("50?" + myArr.contains(50));
while (!myArr.isEmpty()) {
myArr.removeTail();
System.out.println(myArr);
}
}
leetcode题单:
从尾到头打印链表
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while(head != null) {
stack.addLast(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = stack.removeLast();
return res;
}括号的最大嵌套深度
public int maxDepth(String s) {
int ans = 0, size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') {
++size;
ans = Math.max(ans, size);
} else if (ch == ')') {
--size;
}
}
return ans;
}回文链表
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return false;
}
StringBuilder s1=new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder s2=new StringBuilder();
while(head!=null){
s1.append(head.val);
s2.append(head.val);
head=head.next;
}
s2.reverse();
return s1.toString().equals(s2.toString());}这里以数组为底层结构的队列代码供大家参考
import java.util.Optional;
public class ArrQueue<T> implements Queue<T> {
// 队列的容器
CycleArray<T> data;
// 构造函数
public ArrQueue() {
data = new CycleArray<>();
}
public ArrQueue(int capacity) {
this.data = new CycleArray<>(capacity);
}
@Override
public void offer(T ele) {
data.addTail(ele);
}
@Override
public T poll() {
return data.removeHead();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return data.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return data.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public T peek() {
Optional<T> optional = data.getFront();
if (optional.isPresent()) {
return optional.get();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data.toString();
}
}
import java.util.Optional;
/*解决了队列删除时的时间复杂度O(n),循环队列删除时的时间复杂度为O(1)
* 假设有两个索引,front-->始终指该数组的第一个元素 tail-->始终指向元素插入位置
* 如果front==tail时,该循环数组为空
* 如果(tail+1)%capacity=front时,该数组为满状态
*
* */
/**
* 循环队列的底层容器
*/
public class CycleArray<T> {
// 数据容器
private T[] data;
// 容积
private int capacity;
// 实际存放元素的个数
private int size;
// 声明两个索引 front--队首 tail--队尾
int front = 0;
int tail = 0;
// front === tail 队列是空的 (tail+1)/capacity == front 队列是满的
public CycleArray() {
this(10);
}
public CycleArray(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;//因为要浪费一个空间,所以在这里要多加一个空间
this.data = (T[]) new Object[this.capacity];// 浪费一个空间
this.size = 0;
}
public T[] getData() {
return this.data;
}
// 1、队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.front == this.tail;
}
// 2、获取数组的容积
public int getCapacity() {
return this.capacity;
}
//3、获取实际存放元素的个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 在队列的尾部添加元素(tail指向待插入元素的位置)
public void addTail(T val) {
// 当队列已满,要进行扩容
if ((this.tail + 1) % this.capacity == this.front) {
// 新的容积
int newCapacity = 2 * (this.capacity - 1);
resize(newCapacity);
}
// 将val插入到队列的尾部
this.data[this.tail] = val;
// tail向后移动
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % capacity;
// 更新size的值
this.size += 1;
}
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
T[] newData = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity + 1];
// 迁移数据 this.front
int cur = this.front;
int index = 0;
while (cur != this.tail) {
newData[index++] = this.data[cur];
cur = (cur + 1) % this.capacity;
}
// 修改属性
this.capacity = newCapacity + 1;
this.data = newData;
this.front = 0;
this.tail = this.size;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int cur = this.front;
while (cur != this.tail) {
sb.append(this.data[cur]);
if ((cur + 1) % this.capacity != this.tail) {
sb.append(",");
}
cur = (cur + 1) % this.capacity;
}
sb.append("[" + this.front + "<-->" + this.tail + "]");
return sb.toString();
}
//从队列中移除元素
public T removeHead() {
// 1、队列是否为空
if (this.front == this.tail) {
return null;
}
T val = this.data[this.front];
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.capacity;
this.size--;
// 缩容
if (this.size <= this.capacity / 4 && this.capacity / 2 > 1) {
resize(this.capacity / 2);
}
return val;
}
public Optional<T> getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.of(this.data[this.front]);
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
CycleArray<Integer> myArr = new CycleArray<>(5);
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {
myArr.addTail(i + 25);
System.out.println("添加:" + myArr);
if (i % 3 == 0) {
int val = myArr.removeHead();
System.out.println("删除: Header是:" + val);
}
}
}