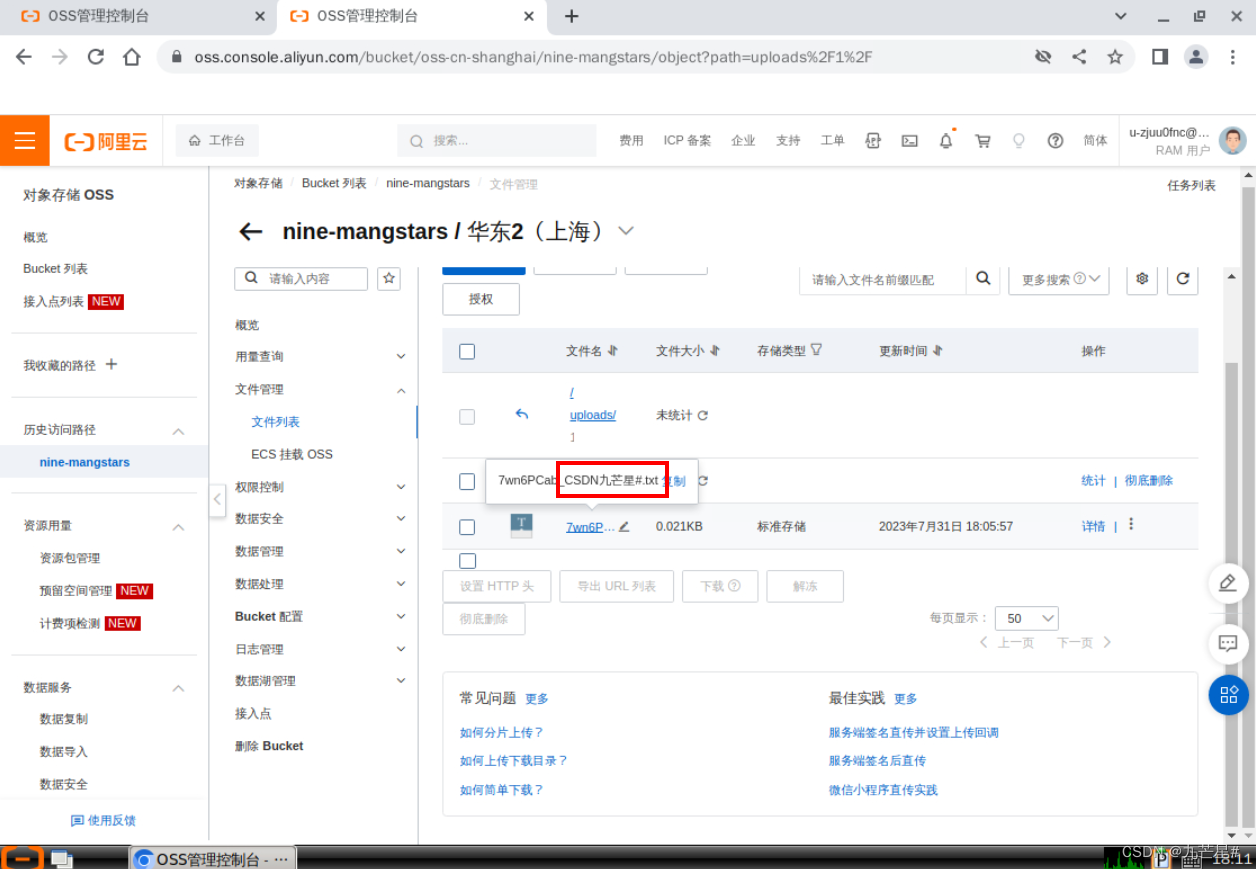
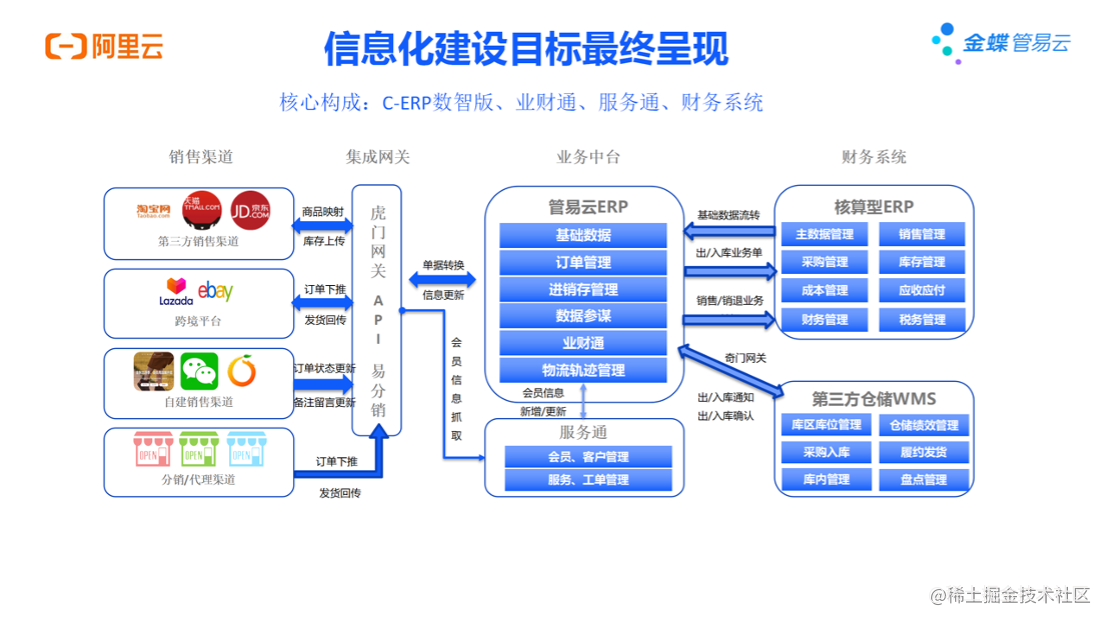
YOLOv8公布了自己每个模型的速度和参数量
那么如果我们自己对YOLOv8做了一些修改,又怎么样自己写代码统计一下修改后的模型的参数量和速度呢?
其实评估这些东西,大多数情况下不需要我们从头自己写一个函数来评估
一般来说,只要是作者公布的这些分数。作者都会把这些分数的实现代码放在它的代码中。你所需要的仅仅是找到这段代码所在的位置,然后直接调用作者的代码,计算即可。
上述计算要求的diam被放在了了下面这个位置(ultralytircs8.0.40这个版本是这样,其他版本有可能会不同)
\ultralytics\yolo\utils\torch_utils.py line 165
计算参数量的函数
def model_info(model, verbose=False, imgsz=640):
# Model information. imgsz may be int or list, i.e. imgsz=640 or imgsz=[640, 320]
n_p = get_num_params(model)
n_g = get_num_gradients(model) # number gradients
if verbose:
print(f"{'layer':>5} {'name':>40} {'gradient':>9} {'parameters':>12} {'shape':>20} {'mu':>10} {'sigma':>10}")
for i, (name, p) in enumerate(model.named_parameters()):
name = name.replace('module_list.', '')
print('%5g %40s %9s %12g %20s %10.3g %10.3g' %
(i, name, p.requires_grad, p.numel(), list(p.shape), p.mean(), p.std()))
flops = get_flops(model, imgsz)
fused = ' (fused)' if model.is_fused() else ''
fs = f', {flops:.1f} GFLOPs' if flops else ''
m = Path(getattr(model, 'yaml_file', '') or model.yaml.get('yaml_file', '')).stem.replace('yolo', 'YOLO') or 'Model'
LOGGER.info(f"{m} summary{fused}: {len(list(model.modules()))} layers, {n_p} parameters, {n_g} gradients{fs}")
def get_num_params(model):
return sum(x.numel() for x in model.parameters())
def get_num_gradients(model):
return sum(x.numel() for x in model.parameters() if x.requires_grad)
def get_flops(model, imgsz=640):
try:
model = de_parallel(model)
p = next(model.parameters())
stride = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) if hasattr(model, 'stride') else 32 # max stride
im = torch.empty((1, p.shape[1], stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in BCHW format
flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=(im,), verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 # stride GFLOPs
imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
flops = flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride # 640x640 GFLOPs
return flops
except Exception:
return 0计算速度的函数
line354
def profile(input, ops, n=10, device=None):
""" YOLOv8 speed/memory/FLOPs profiler
Usage:
input = torch.randn(16, 3, 640, 640)
m1 = lambda x: x * torch.sigmoid(x)
m2 = nn.SiLU()
profile(input, [m1, m2], n=100) # profile over 100 iterations
"""
results = []
if not isinstance(device, torch.device):
device = select_device(device)
print(f"{'Params':>12s}{'GFLOPs':>12s}{'GPU_mem (GB)':>14s}{'forward (ms)':>14s}{'backward (ms)':>14s}"
f"{'input':>24s}{'output':>24s}")
for x in input if isinstance(input, list) else [input]:
x = x.to(device)
x.requires_grad = True
for m in ops if isinstance(ops, list) else [ops]:
m = m.to(device) if hasattr(m, 'to') else m # device
m = m.half() if hasattr(m, 'half') and isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) and x.dtype is torch.float16 else m
tf, tb, t = 0, 0, [0, 0, 0] # dt forward, backward
try:
flops = thop.profile(m, inputs=(x,), verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 # GFLOPs
except Exception:
flops = 0
try:
for _ in range(n):
t[0] = time_sync()
y = m(x)
t[1] = time_sync()
try:
_ = (sum(yi.sum() for yi in y) if isinstance(y, list) else y).sum().backward()
t[2] = time_sync()
except Exception: # no backward method
# print(e) # for debug
t[2] = float('nan')
tf += (t[1] - t[0]) * 1000 / n # ms per op forward
tb += (t[2] - t[1]) * 1000 / n # ms per op backward
mem = torch.cuda.memory_reserved() / 1E9 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0 # (GB)
s_in, s_out = (tuple(x.shape) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else 'list' for x in (x, y)) # shapes
p = sum(x.numel() for x in m.parameters()) if isinstance(m, nn.Module) else 0 # parameters
print(f'{p:12}{flops:12.4g}{mem:>14.3f}{tf:14.4g}{tb:14.4g}{str(s_in):>24s}{str(s_out):>24s}')
results.append([p, flops, mem, tf, tb, s_in, s_out])
except Exception as e:
print(e)
results.append(None)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
return results