模拟退火算法
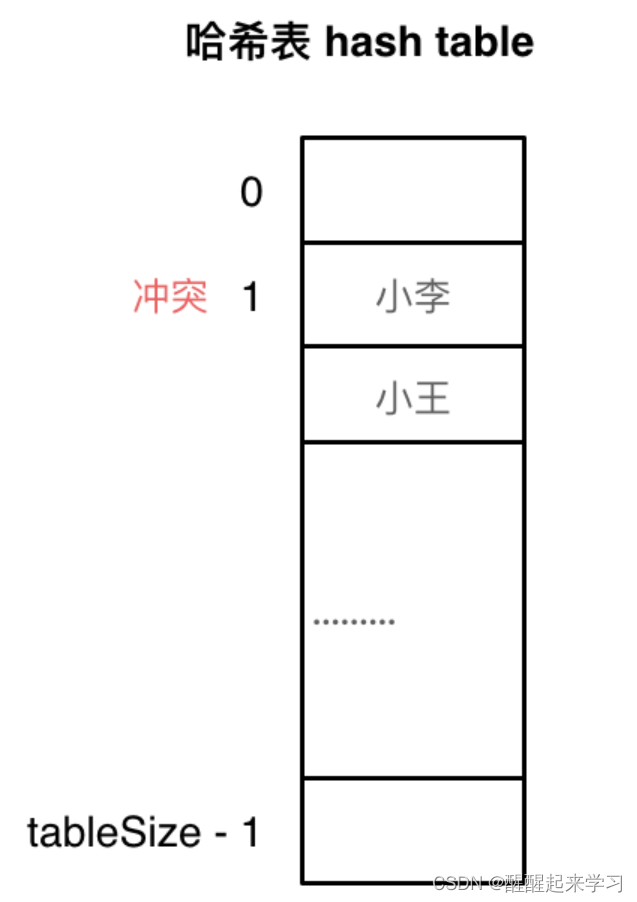
模拟退火算法流程图
- 初始温度
- 新温度值
- 进入循环
- 生成新的解
- 按照 bound
- 按照 constraint
- 计算新解与当前解的目标差异
- 判断是否接受解
- 判断是否更新解
- 生成新的解
- 循环结束
- 进入循环
- 按照温度降低率降低温度
- 新温度值
- 温度小于最低温度
- 输出结果
模拟退火算法示例代码1
import numpy as np
def objective_function(x):
return x[0]**2 + 2*x[0] - 15 + 4*4*2*x[1] + 4*x[1]**2
def simulated_annealing(objective_func, initial_solution = np.array([0, 0]), \
temperature = 100, min_temperature = 0.1, \
cooling_rate = 0.90, iter_max = 100, seed = 0):
np.random.seed(seed)
current_solution = initial_solution
best_solution = current_solution
while temperature > min_temperature:
for j in range(iter_max):
# 生成新的解
new_solution = current_solution + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(current_solution))
# 计算新解与当前解之间的目标函数值差异
current_cost = objective_func(current_solution)
new_cost = objective_func(new_solution)
cost_diff = new_cost - current_cost
# 判断是否接受新解
if cost_diff < 0 or np.exp(-cost_diff / temperature) > np.random.random():
current_solution = new_solution
# 更新最优解
if objective_func(current_solution) < objective_func(best_solution):
best_solution = current_solution
# 降低温度
temperature *= cooling_rate
return best_solution
# 调用退火算法求解最小值
best_solution = simulated_annealing(objective_function)
print(f"函数最小值: {objective_function(best_solution)} 自变量取值:{best_solution}")
- 运行结果

模拟退火算法示例代码2
import numpy as np
global x_bound
global x_up
x_bound = 3
x_up = 10
def fun1(p0, p1):
return (x_up**2 - x_bound**2)/3 - p0 - p1
def fun2(p2):
return p2 + (x_up**2 + x_bound**2 + x_bound**3)/3
def fun3(p2):
return (x_up**2 * x_bound**2)*p2
def cons(try_solution):
return 5 < np.sum(try_solution) < 10
def objective_function(params):
return params[0]*fun1(params[0], params[1]) + fun2(params[2])*(params[1] + params[2]) - fun3(params[2])*(params[0] + params[2])
def simulated_annealing(objective_func, initial_solution = np.array([0, 0, 9]), \
temperature = 100, min_temperature = 0.1, \
cooling_rate = 0.90, iter_max = 100, seed = 0):
np.random.seed(seed)
current_solution = initial_solution
best_solution = current_solution
while temperature > min_temperature:
for j in range(iter_max):
# 生成新的解
FLAG = True
for k in range(iter_max):
try_solution = current_solution + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(current_solution))
if cons(try_solution):
new_solution = try_solution
FLAG = False
break
if FLAG:
print(f"找不到满足约束的解 在温度{temperature}")
break
# 计算新解与当前解之间的目标函数值差异
current_cost = objective_func(current_solution)
new_cost = objective_func(new_solution)
cost_diff = new_cost - current_cost
# 判断是否接受新解
if cost_diff < 0 or np.exp(-cost_diff / temperature) > np.random.random():
current_solution = new_solution
# 更新最优解
if objective_func(current_solution) < objective_func(best_solution):
best_solution = current_solution
# 降低温度
temperature *= cooling_rate
return best_solution
# 调用退火算法求解最小值
best_solution = simulated_annealing(objective_function)
print(f"函数最小值: {objective_function(best_solution)} 自变量取值:{best_solution}")
模拟退火算法的可视化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
global x_bound
global x_up
x_bound = 3
x_up = 10
def fun1(p0, p1):
return (x_up**2 - x_bound**2)/3 - p0 - p1
def fun2(p0, p1):
return p1 + (p0**2 + x_bound**(p1-p0))/3
def cons(try_solution):
return 5 < np.sum(try_solution) < 10
def objective_function(params):
return params[0]*fun1(params[0], params[1]) + (params[0] + params[1])*fun2(params[0], params[1])
def simulated_annealing(objective_func, initial_solution = np.array([4, 4]), \
temperature = 100, min_temperature = 0.1, \
cooling_rate = 0.90, iter_max = 100, seed = 0):
np.random.seed(seed)
current_solution = initial_solution
best_solution = current_solution
RECODE_temp,RECODE_sol = [],[]
raw_temperature = temperature
while temperature > min_temperature:
RECODE_temp.append(temperature)
for j in range(iter_max):
# 生成新的解
FLAG = True
for k in range(iter_max):
try_solution = current_solution + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(current_solution))
if cons(try_solution):
new_solution = try_solution
FLAG = False
break
if FLAG:
print(f"找不到满足约束的解 在温度{temperature}")
break
# 计算新解与当前解之间的目标函数值差异
current_cost = objective_func(current_solution)
new_cost = objective_func(new_solution)
cost_diff = new_cost - current_cost
# 判断是否接受新解
if cost_diff < 0 or np.exp(-cost_diff / temperature) > np.random.random():
current_solution = new_solution
# 更新最优解
if objective_func(current_solution) < objective_func(best_solution):
best_solution = current_solution
# 降低温度
temperature *= cooling_rate
RECODE_sol.append(best_solution)
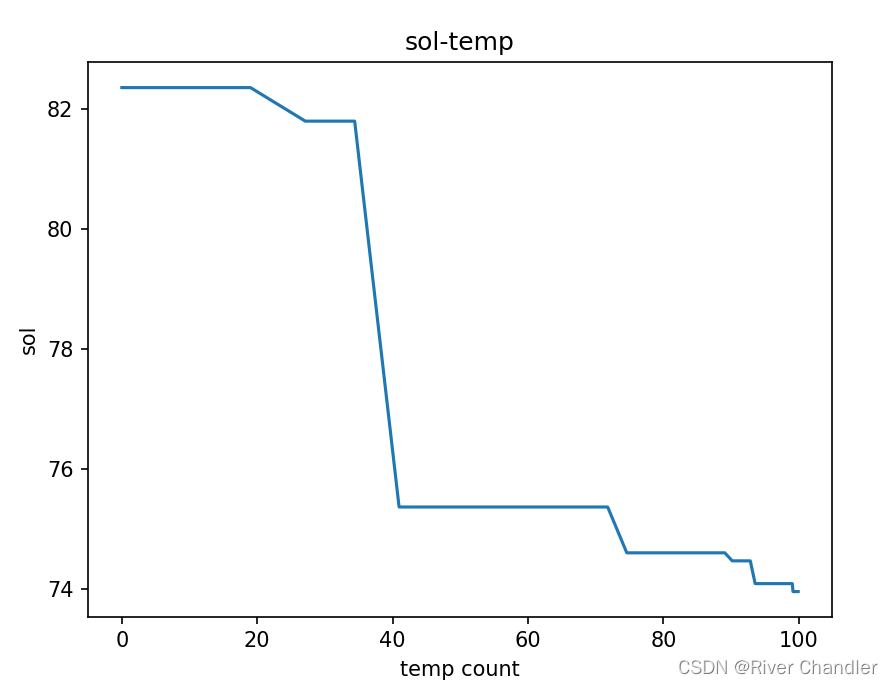
RECODE_temp = [raw_temperature - i for i in RECODE_temp]
RECODE_sol = [objective_function(i) for i in RECODE_sol]
plt.plot(RECODE_temp, RECODE_sol)
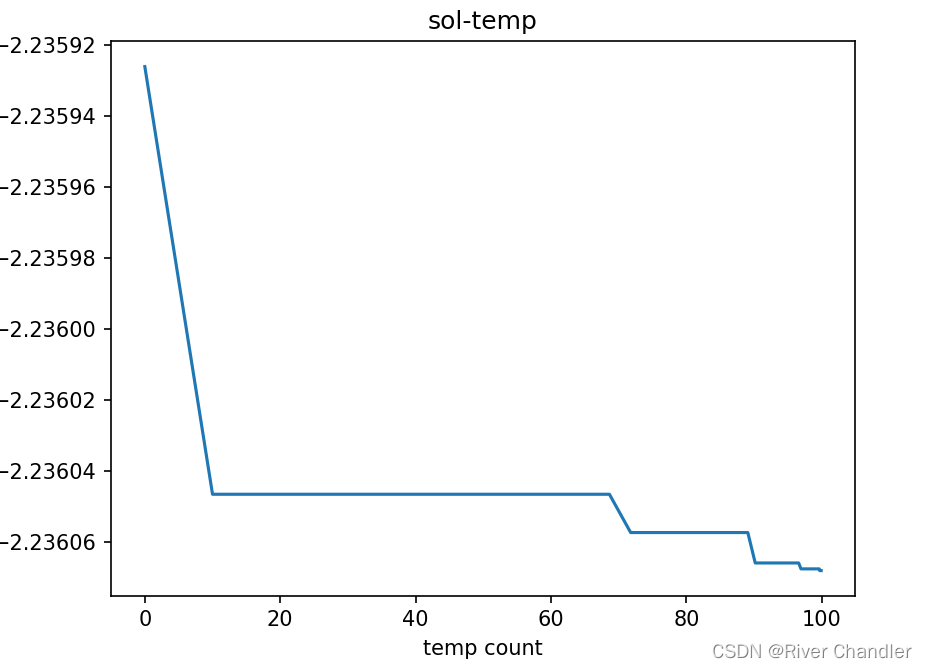
plt.title("sol-temp")
plt.xlabel("temp count")
plt.ylabel("sol")
plt.pause(0.01)
return best_solution
# 调用退火算法求解最小值
best_solution = simulated_annealing(objective_function)
print(f"函数最小值: {objective_function(best_solution)} 自变量取值:{best_solution}")
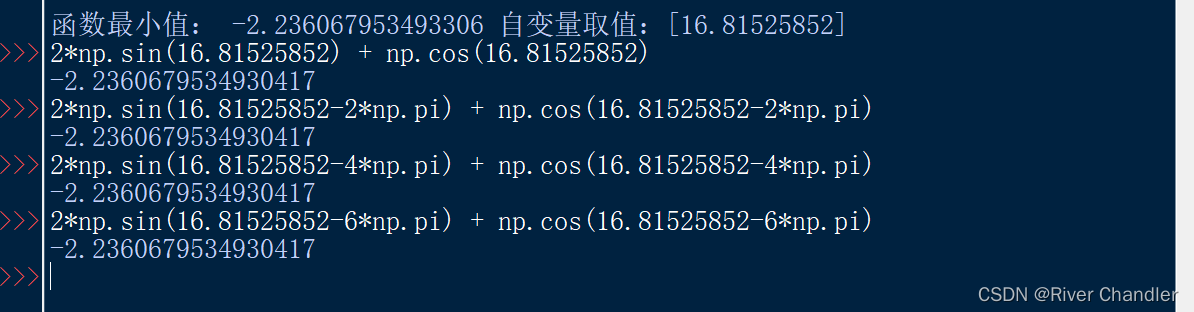
example 2sin(x)+cos(x)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def objective_function(params):
return 2*np.sin(params[0]) + np.cos(params[0])
def cons(try_solution):
return True
def simulated_annealing(objective_func, initial_solution = np.array([4, ]), \
temperature = 100, min_temperature = 0.1, \
cooling_rate = 0.90, iter_max = 100, seed = 0):
np.random.seed(seed)
current_solution = initial_solution
best_solution = current_solution
RECODE_temp,RECODE_sol = [],[]
raw_temperature = temperature
while temperature > min_temperature:
RECODE_temp.append(temperature)
for j in range(iter_max):
# 生成新的解
FLAG = True
for k in range(iter_max):
try_solution = current_solution + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(current_solution))
if cons(try_solution):
new_solution = try_solution
FLAG = False
break
if FLAG:
print(f"找不到满足约束的解 在温度{temperature}")
break
# 计算新解与当前解之间的目标函数值差异
current_cost = objective_func(current_solution)
new_cost = objective_func(new_solution)
cost_diff = new_cost - current_cost
# 判断是否接受新解
if cost_diff < 0 or np.exp(-cost_diff / temperature) > np.random.random():
current_solution = new_solution
# 更新最优解
if objective_func(current_solution) < objective_func(best_solution):
best_solution = current_solution
# 降低温度
temperature *= cooling_rate
RECODE_sol.append(best_solution)
RECODE_temp = [raw_temperature - i for i in RECODE_temp]
RECODE_sol = [objective_function(i) for i in RECODE_sol]
plt.plot(RECODE_temp, RECODE_sol)
plt.title("sol-temp")
plt.xlabel("temp count")
plt.ylabel("sol")
plt.pause(0.01)
return best_solution
# 调用退火算法求解最小值
best_solution = simulated_annealing(objective_function)
print(f"函数最小值: {objective_function(best_solution)} 自变量取值:{best_solution}")