基于YOLOv5的S弯识别
目录
- 基于YOLOv5的S弯识别
- 技术背景
- 算法介绍
- 具体实现
- 1、下载仓库
- 2、配置环境
- 3、数据处理
- 4、转成engine文件
- 5、使用代码实现识别
- 技术总结
技术背景
S弯识别是一个在自动驾驶和机器人领域中很常见的任务,它需要识别道路上的弯道,特别是S形弯道,以便车辆或机器人能够相应地控制速度和方向。为了实现航天智慧物流比赛中的难点:识别S弯,在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用YOLOv5,一种基于深度学习的目标检测算法,来实现S弯识别。
算法介绍
YOLOv5是一种基于深度学习的目标检测算法,它是YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列算法的最新版本。与之前的版本相比,YOLOv5采用了一些新的技术来提高检测精度和速度。
YOLOv5算法的核心思想是将目标检测问题转化为一个回归问题。具体来说,它将输入图像划分为一个固定大小的网格,并在每个网格中预测多个目标的位置和类别。每个目标由一个边界框(bounding box)和一个置信度分数(confidence score)表示。边界框是一个矩形,它框住了目标的位置,而置信度分数则表示目标在该边界框内的概率。
YOLOv5采用了一种基于锚框(anchor box)的方法来处理不同大小和比例的目标。锚框是一些预定义的矩形框,它们具有不同的宽度和高度,并与输入图像中的每个网格相关联。YOLOv5使用这些锚框来预测目标的位置和大小,从而提高了检测精度。
为了进一步提高检测精度,YOLOv5还采用了一种新的训练策略,称为AutoML。AutoML是一种自动化机器学习技术,它可以自动地优化模型的超参数,从而提高模型的性能。在YOLOv5中,AutoML用于优化模型的网络结构、损失函数和数据增强等方面。
除了精度之外,速度也是YOLOv5的一个关键优势。YOLOv5采用了一种新的网络结构,称为CSPNet(Cross Stage Partial Network),它可以提高网络的计算效率。此外,YOLOv5还采用了一些优化技术,例如混合精度训练和模型剪枝,以进一步提高速度和效率。
具体实现
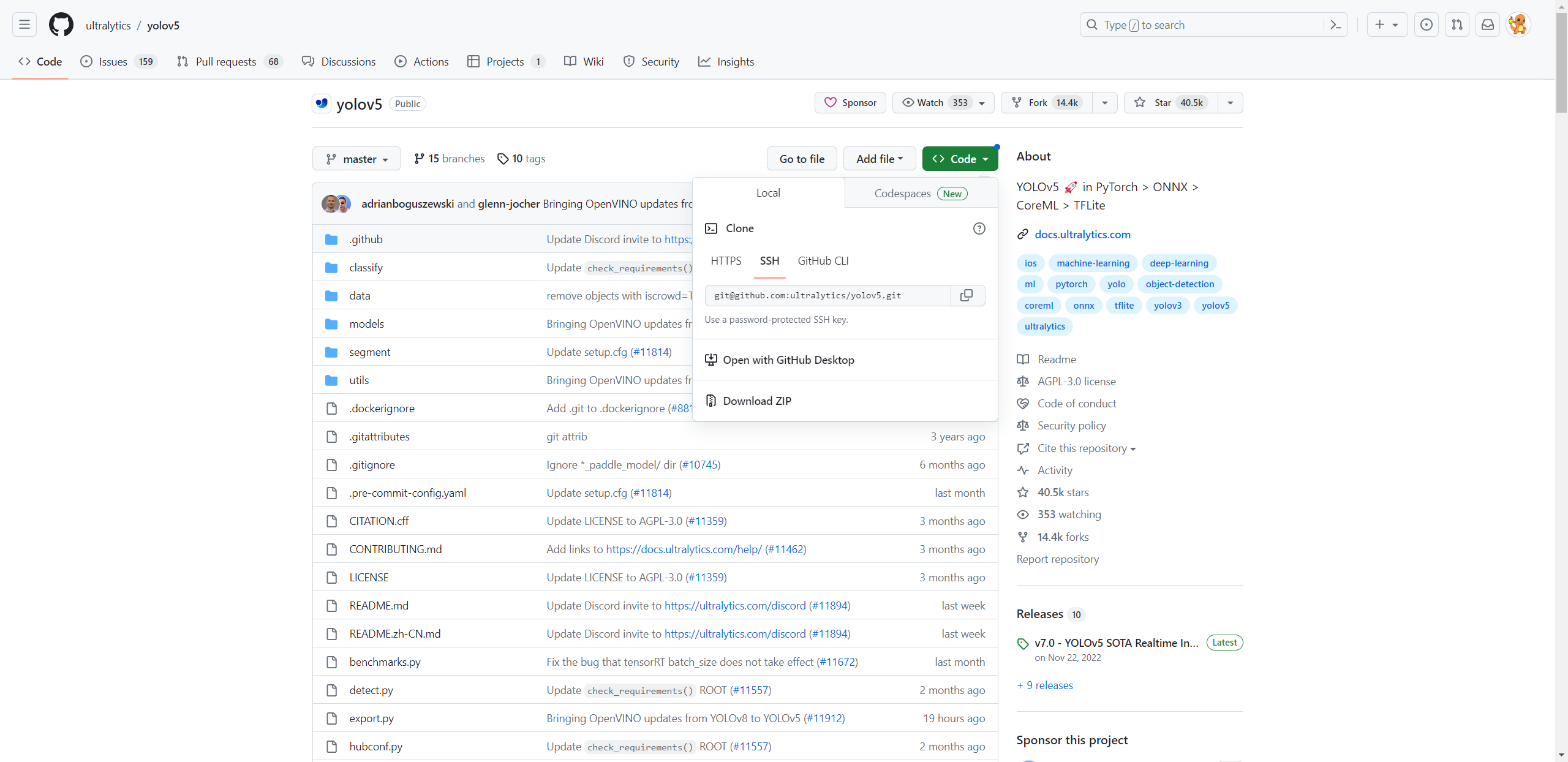
1、下载仓库
官网地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
点击download zip下载压缩包到本地
2、配置环境
使⽤ anaconda 创建虚拟环境,安装仓库中 requirements.txt ⽂件中的第三⽅库,或者
直接使⽤命令 pip install -r requirements.txt
注意:如果下载依赖较慢,可以考虑更换镜像源,搜索python镜像源即可,这里提供一些常见的。
常见国内镜像源
http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ 豆瓣
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ 阿里
http://pypi.hustunique.com/simple/ 华中理工大学
http://pypi.sdutlinux.org/simple/ 山东理工大学
http://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/ 中国科学技术大学
3、数据处理
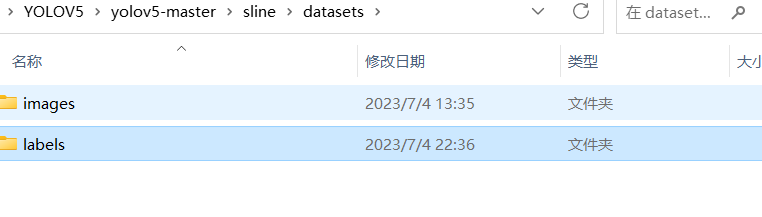
使用 labelimg 工具,对图片进行标注,S弯车道线标注为s
将对应的图片以及标注后的txt文件放入数据集中:images存放原图,labels存放标注后的文件
修改两个yaml文件关于模型类别的参数配置
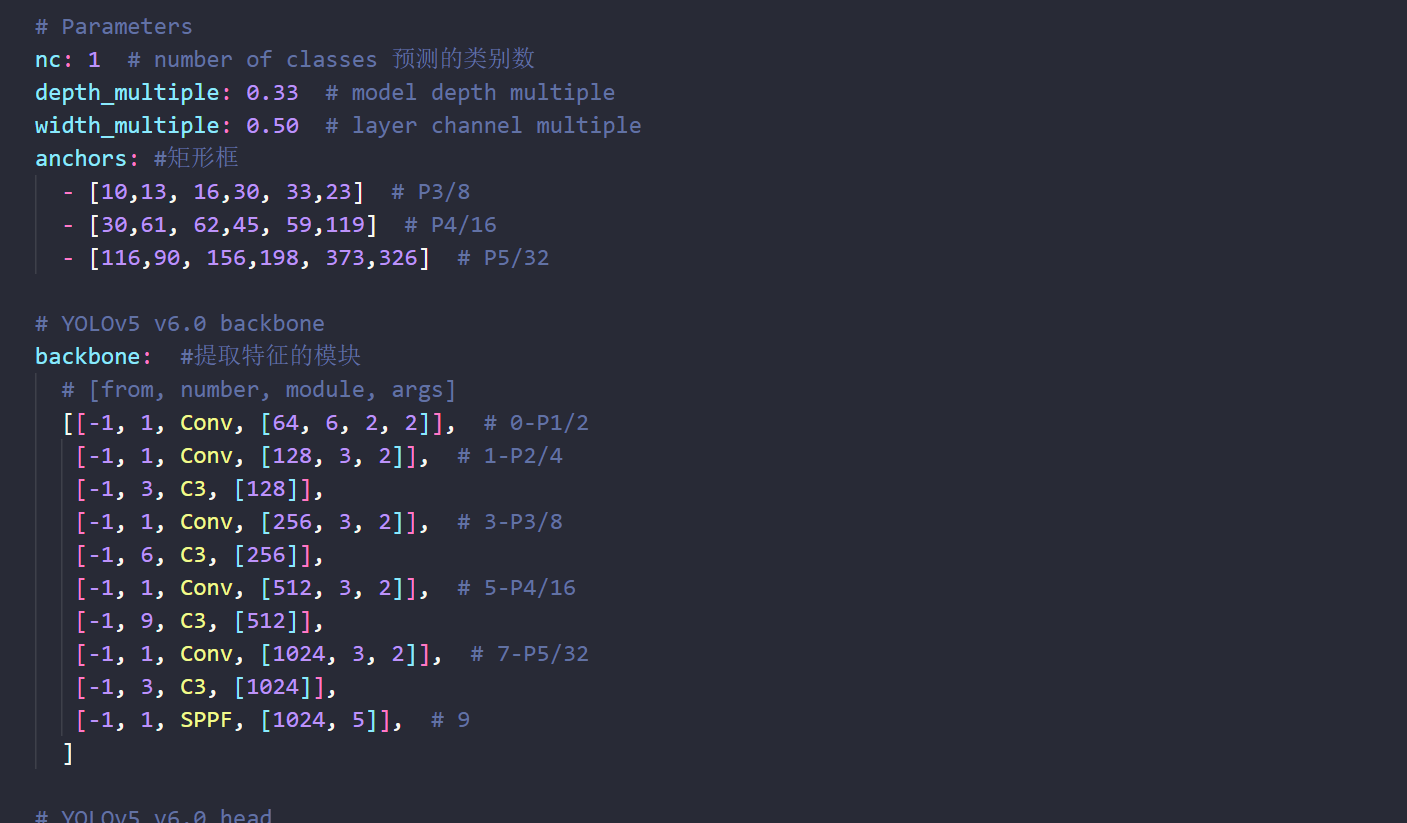
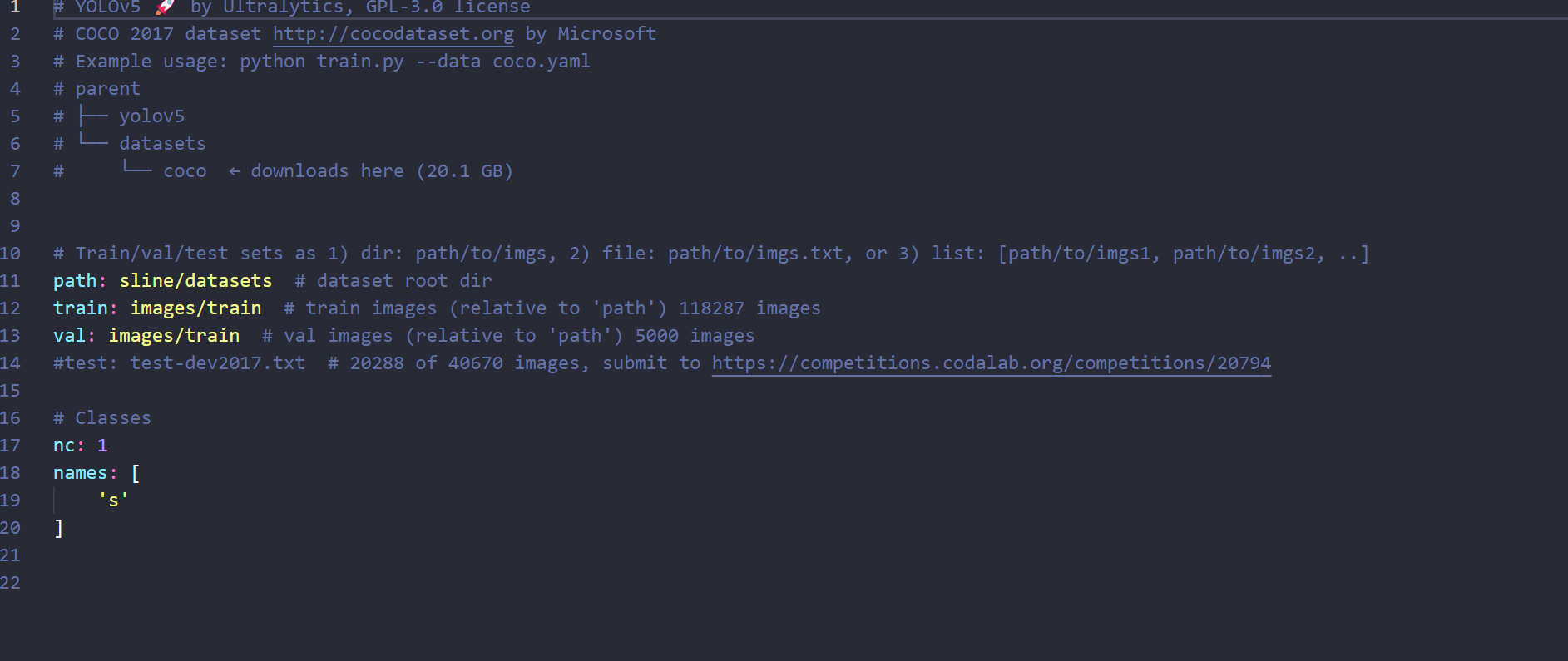
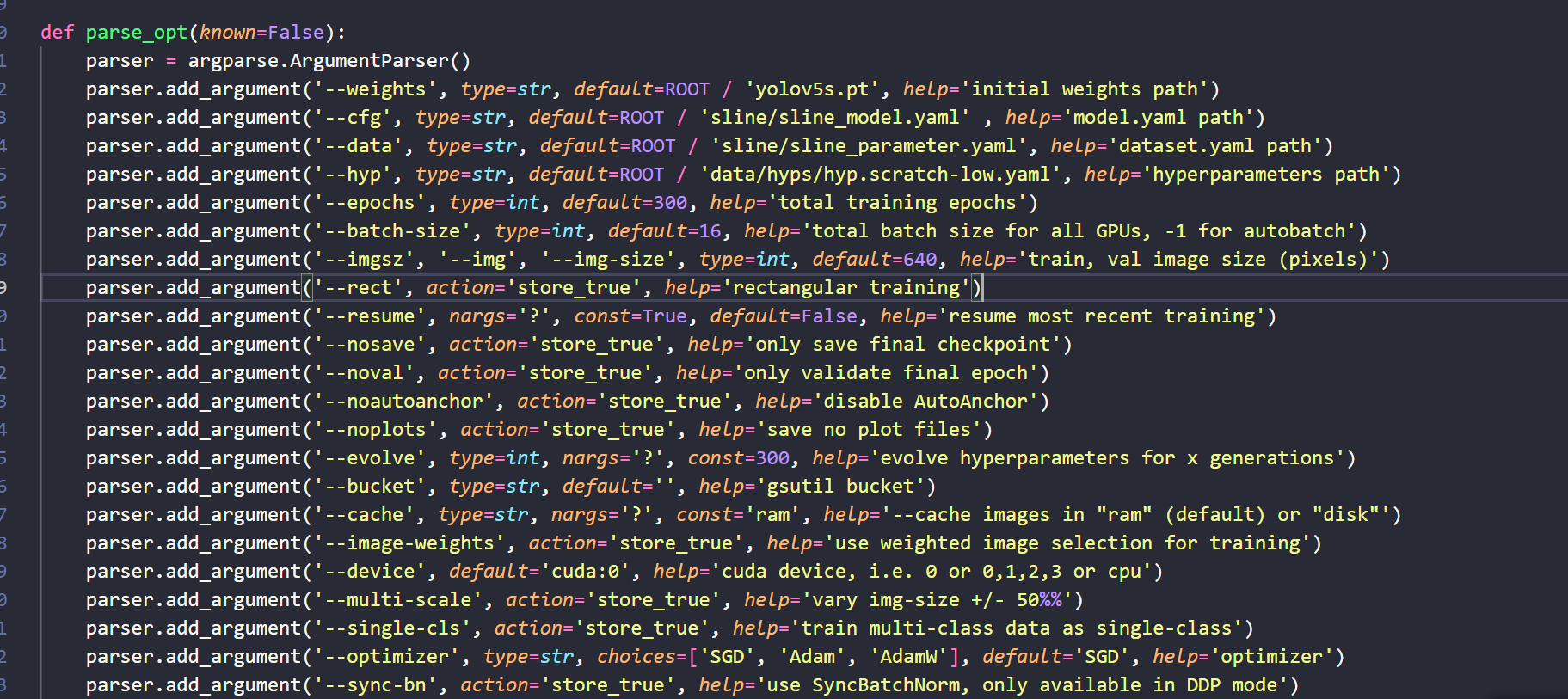
将train.py中的参数改成数据集的路径,如图所示,运行训练即可。
这里的轮次以及输入图片的大小都可以更具自己的需求更改参数,按照实际情况与电脑GPU算法能力微调即可。
4、转成engine文件
为了提高模型的性能和效率,我们可以将训练引擎文件转换为TensorRT格式,并将其应用于小车的硬件加速中。TensorRT是一种高性能的推理引擎,它可以优化深度学习模型的推理速度和内存使用,并将其部署到GPU和其他硬件设备上。
官网地址:tensorrtx/yolov5 at yolov5-v6.2 · wang-xinyu/tensorrtx (github.com)
将pt文件通过ftp协议远程传输到小车上,再使用以下命令完成模型的转化。
- generate .wts from pytorch with .pt, or download .wts from model zoo
// clone code according to above #Different versions of yolov5
// download https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.2/yolov5s.pt
cp {tensorrtx}/yolov5/gen_wts.py {ultralytics}/yolov5
cd {ultralytics}/yolov5
python gen_wts.py -w yolov5s.pt -o yolov5s.wts
// a file 'yolov5s.wts' will be generated.
- build tensorrtx/yolov5 and run
cd {tensorrtx}/yolov5/
// update CLASS_NUM in yololayer.h if your model is trained on custom dataset
mkdir build
cd build
cp {ultralytics}/yolov5/yolov5s.wts {tensorrtx}/yolov5/build
cmake ..
make
sudo ./yolov5 -s [.wts] [.engine] [n/s/m/l/x/n6/s6/m6/l6/x6 or c/c6 gd gw] // serialize model to plan file
sudo ./yolov5 -d [.engine] [image folder] // deserialize and run inference, the images in [image folder] will be processed.
// For example yolov5s
sudo ./yolov5 -s yolov5s.wts yolov5s.engine s
sudo ./yolov5 -d yolov5s.engine ../samples
// For example Custom model with depth_multiple=0.17, width_multiple=0.25 in yolov5.yaml
sudo ./yolov5 -s yolov5_custom.wts yolov5.engine c 0.17 0.25
sudo ./yolov5 -d yolov5.engine ../samples
5、使用代码实现识别
使用官方的python_trt代码即可识别
"""
An example that uses TensorRT's Python api to make inferences.
"""
import ctypes
import os
import shutil
import random
import sys
import threading
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
cuda.Context.pop()
CONF_THRESH = 0.5
IOU_THRESHOLD = 0.4
def gstreamer_pipeline(
capture_width=1280,
capture_height=720,
display_width=1280,
display_height=720,
framerate=120,
flip_method=0,
):
return (
"nvarguscamerasrc ! "
"video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), width=(int)%d, height=(int)%d, format=(string)NV12, framerate=(fraction)%d/1! "
"nvvidconv flip-method=%d ! "
"video/x-raw, width=(int)%d, height=(int)%d, format=(string)BGRx ! "
"videoconvert ! "
"video/x-raw, format=(string)BGR ! "
"appsink"
% (
capture_width,
capture_height,
framerate,
flip_method,
display_width,
display_height,
)
)
def get_img_path_batches(batch_size, img_dir):
ret = []
batch = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(img_dir):
for name in files:
if len(batch) == batch_size:
ret.append(batch)
batch = []
batch.append(os.path.join(root, name))
if len(batch) > 0:
ret.append(batch)
return ret
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=None):
"""
description: Plots one bounding box on image img,
this function comes from YoLov5 project.
param:
x: a box likes [x1,y1,x2,y2]
img: a opencv image object
color: color to draw rectangle, such as (0,255,0)
label: str
line_thickness: int
return:
no return
"""
tl = (
line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1
) # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(
img,
label,
(c1[0], c1[1] - 2),
0,
tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255],
thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)
class YoLov5TRT(object):
"""
description: A YOLOv5 class that warps TensorRT ops, preprocess and postprocess ops.
"""
def __init__(self, engine_file_path):
# Create a Context on this device,
self.ctx = cuda.Device(0).make_context()
stream = cuda.Stream()
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
runtime = trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER)
# Deserialize the engine from file
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
context = engine.create_execution_context()
host_inputs = []
cuda_inputs = []
host_outputs = []
cuda_outputs = []
bindings = []
for binding in engine:
print('bingding:', binding, engine.get_binding_shape(binding))
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# Allocate host and device buffers
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
cuda_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
# Append the device buffer to device bindings.
bindings.append(int(cuda_mem))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
self.input_w = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-1]
self.input_h = engine.get_binding_shape(binding)[-2]
host_inputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_inputs.append(cuda_mem)
else:
host_outputs.append(host_mem)
cuda_outputs.append(cuda_mem)
# Store
self.stream = stream
self.context = context
self.engine = engine
self.host_inputs = host_inputs
self.cuda_inputs = cuda_inputs
self.host_outputs = host_outputs
self.cuda_outputs = cuda_outputs
self.bindings = bindings
self.batch_size = engine.max_batch_size
def infer(self, raw_image_generator):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
# Make self the active context, pushing it on top of the context stack.
self.ctx.push()
# Restore
stream = self.stream
context = self.context
engine = self.engine
host_inputs = self.host_inputs
cuda_inputs = self.cuda_inputs
host_outputs = self.host_outputs
cuda_outputs = self.cuda_outputs
bindings = self.bindings
# Do image preprocess
batch_image_raw = []
batch_origin_h = []
batch_origin_w = []
batch_input_image = np.empty(shape=[self.batch_size, 3, self.input_h, self.input_w])
for i, image_raw in enumerate(raw_image_generator):
input_image, image_raw, origin_h, origin_w = self.preprocess_image(image_raw)
batch_image_raw.append(image_raw)
batch_origin_h.append(origin_h)
batch_origin_w.append(origin_w)
np.copyto(batch_input_image[i], input_image)
batch_input_image = np.ascontiguousarray(batch_input_image)
# Copy input image to host buffer
np.copyto(host_inputs[0], batch_input_image.ravel())
start = time.time()
# Transfer input data to the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(cuda_inputs[0], host_inputs[0], stream)
# Run inference.
context.execute_async(batch_size=self.batch_size, bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(host_outputs[0], cuda_outputs[0], stream)
# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()
end = time.time()
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
# Here we use the first row of output in that batch_size = 1
output = host_outputs[0]
# Do postprocess
for i in range(self.batch_size):
result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid = self.post_process(
output[i * 6001: (i + 1) * 6001], batch_origin_h[i], batch_origin_w[i]
)
# Draw rectangles and labels on the original image
for j in range(len(result_boxes)):
box = result_boxes[j]
plot_one_box(
box,
batch_image_raw[i],
label="{}:{:.2f}".format(
categories[int(result_classid[j])], result_scores[j]
),
)
return batch_image_raw, end - start
def destroy(self):
# Remove any context from the top of the context stack, deactivating it.
self.ctx.pop()
def get_raw_image(self, image_path_batch):
"""
description: Read an image from image path
"""
for img_path in image_path_batch:
yield cv2.imread(img_path)
def get_raw_image_zeros(self, image_path_batch=None):
"""
description: Ready data for warmup
"""
for _ in range(self.batch_size):
yield np.zeros([self.input_h, self.input_w, 3], dtype=np.uint8)
def preprocess_image(self, raw_bgr_image):
"""
description: Convert BGR image to RGB,
resize and pad it to target size, normalize to [0,1],
transform to NCHW format.
param:
input_image_path: str, image path
return:
image: the processed image
image_raw: the original image
h: original height
w: original width
"""
image_raw = raw_bgr_image
h, w, c = image_raw.shape
image = cv2.cvtColor(image_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Calculate widht and height and paddings
r_w = self.input_w / w
r_h = self.input_h / h
if r_h > r_w:
tw = self.input_w
th = int(r_w * h)
tx1 = tx2 = 0
ty1 = int((self.input_h - th) / 2)
ty2 = self.input_h - th - ty1
else:
tw = int(r_h * w)
th = self.input_h
tx1 = int((self.input_w - tw) / 2)
tx2 = self.input_w - tw - tx1
ty1 = ty2 = 0
# Resize the image with long side while maintaining ratio
image = cv2.resize(image, (tw, th))
# Pad the short side with (128,128,128)
image = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
image, ty1, ty2, tx1, tx2, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, None, (128, 128, 128)
)
image = image.astype(np.float32)
# Normalize to [0,1]
image /= 255.0
# HWC to CHW format:
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
# CHW to NCHW format
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
# Convert the image to row-major order, also known as "C order":
image = np.ascontiguousarray(image)
return image, image_raw, h, w
def xywh2xyxy(self, origin_h, origin_w, x):
"""
description: Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
param:
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
x: A boxes numpy, each row is a box [center_x, center_y, w, h]
return:
y: A boxes numpy, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
"""
y = np.zeros_like(x)
r_w = self.input_w / origin_w
r_h = self.input_h / origin_h
if r_h > r_w:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 - (self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 - (self.input_h - r_w * origin_h) / 2
y /= r_w
else:
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 - (self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 - (self.input_w - r_h * origin_w) / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
y /= r_h
return y
def post_process(self, output, origin_h, origin_w):
"""
description: postprocess the prediction
param:
output: A numpy likes [num_boxes,cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, cx,cy,w,h,conf,cls_id, ...]
origin_h: height of original image
origin_w: width of original image
return:
result_boxes: finally boxes, a boxes numpy, each row is a box [x1, y1, x2, y2]
result_scores: finally scores, a numpy, each element is the score correspoing to box
result_classid: finally classid, a numpy, each element is the classid correspoing to box
"""
# Get the num of boxes detected
num = int(output[0])
# Reshape to a two dimentional ndarray
pred = np.reshape(output[1:], (-1, 6))[:num, :]
# Do nms
boxes = self.non_max_suppression(pred, origin_h, origin_w, conf_thres=CONF_THRESH, nms_thres=IOU_THRESHOLD)
result_boxes = boxes[:, :4] if len(boxes) else np.array([])
result_scores = boxes[:, 4] if len(boxes) else np.array([])
result_classid = boxes[:, 5] if len(boxes) else np.array([])
return result_boxes, result_scores, result_classid
def bbox_iou(self, box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True):
"""
description: compute the IoU of two bounding boxes
param:
box1: A box coordinate (can be (x1, y1, x2, y2) or (x, y, w, h))
box2: A box coordinate (can be (x1, y1, x2, y2) or (x, y, w, h))
x1y1x2y2: select the coordinate format
return:
iou: computed iou
"""
if not x1y1x2y2:
# Transform from center and width to exact coordinates
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2
else:
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1], box1[:, 2], box1[:, 3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1], box2[:, 2], box2[:, 3]
# Get the coordinates of the intersection rectangle
inter_rect_x1 = np.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)
inter_rect_y1 = np.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)
inter_rect_x2 = np.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2)
inter_rect_y2 = np.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2)
# Intersection area
inter_area = np.clip(inter_rect_x2 - inter_rect_x1 + 1, 0, None) * \
np.clip(inter_rect_y2 - inter_rect_y1 + 1, 0, None)
# Union Area
b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1 + 1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1 + 1)
b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1 + 1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1 + 1)
iou = inter_area / (b1_area + b2_area - inter_area + 1e-16)
return iou
def non_max_suppression(self, prediction, origin_h, origin_w, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
"""
description: Removes detections with lower object confidence score than 'conf_thres' and performs
Non-Maximum Suppression to further filter detections.
param:
prediction: detections, (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls_id)
origin_h: original image height
origin_w: original image width
conf_thres: a confidence threshold to filter detections
nms_thres: a iou threshold to filter detections
return:
boxes: output after nms with the shape (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls_id)
"""
# Get the boxes that score > CONF_THRESH
boxes = prediction[prediction[:, 4] >= conf_thres]
# Trandform bbox from [center_x, center_y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
boxes[:, :4] = self.xywh2xyxy(origin_h, origin_w, boxes[:, :4])
# clip the coordinates
boxes[:, 0] = np.clip(boxes[:, 0], 0, origin_w -1)
boxes[:, 2] = np.clip(boxes[:, 2], 0, origin_w -1)
boxes[:, 1] = np.clip(boxes[:, 1], 0, origin_h -1)
boxes[:, 3] = np.clip(boxes[:, 3], 0, origin_h -1)
# Object confidence
confs = boxes[:, 4]
# Sort by the confs
boxes = boxes[np.argsort(-confs)]
# Perform non-maximum suppression
keep_boxes = []
while boxes.shape[0]:
large_overlap = self.bbox_iou(np.expand_dims(boxes[0, :4], 0), boxes[:, :4]) > nms_thres
label_match = boxes[0, -1] == boxes[:, -1]
# Indices of boxes with lower confidence scores, large IOUs and matching labels
invalid = large_overlap & label_match
keep_boxes += [boxes[0]]
boxes = boxes[~invalid]
boxes = np.stack(keep_boxes, 0) if len(keep_boxes) else np.array([])
return boxes
class inferThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper, image_path_batch):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
self.image_path_batch = image_path_batch
def run(self):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(self.yolov5_wrapper.get_raw_image(self.image_path_batch))
for i, img_path in enumerate(self.image_path_batch):
parent, filename = os.path.split(img_path)
save_name = os.path.join('output', filename)
# Save image
cv2.imwrite(save_name, batch_image_raw[i])
print('input->{}, time->{:.2f}ms, saving into output/'.format(self.image_path_batch, use_time * 1000))
class warmUpThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, yolov5_wrapper):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.yolov5_wrapper = yolov5_wrapper
def run(self):
batch_image_raw, use_time = self.yolov5_wrapper.infer(self.yolov5_wrapper.get_raw_image_zeros())
print('warm_up->{}, time->{:.2f}ms'.format(batch_image_raw[0].shape, use_time * 1000))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# load custom plugin and engine
PLUGIN_LIBRARY = "build/libmyplugins.so"
engine_file_path = "build/lv.engine"
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
engine_file_path = sys.argv[1]
if len(sys.argv) > 2:
PLUGIN_LIBRARY = sys.argv[2]
ctypes.CDLL(PLUGIN_LIBRARY)
# load coco labels
categories = ["r","g","s","1","2","3","4"]
if os.path.exists('output/'):
shutil.rmtree('output/')
os.makedirs('output/')
# a YoLov5TRT instance
yolov5_wrapper = YoLov5TRT(engine_file_path)
try:
print('batch size is', yolov5_wrapper.batch_size)
image_dir = "images/"
image_path_batches = get_img_path_batches(yolov5_wrapper.batch_size, image_dir)
for i in range(10):
# create a new thread to do warm_up
thread1 = warmUpThread(yolov5_wrapper)
thread1.start()
thread1.join()
for batch in image_path_batches:
# create a new thread to do inference
thread1 = inferThread(yolov5_wrapper, batch)
thread1.start()
thread1.join()
finally:
# destroy the instance
yolov5_wrapper.destroy()
技术总结
使用YOLOv5算法识别S弯,并将模型转换为TensorRT格式以实现硬件加速,可以显著提高模型的性能和效率,从而更好地适应实际场景中的应用需求。这种方法可以应用于各种机器人和智能小车等应用场景中,帮助开发者快速构建高性能和高效率的智能车辆系统。同时,这种方法也可以为深度学习在嵌入式系统中的应用提供参考和思路。