本文将基于PyTorch源码重新审视MultiheadAttention与Transformer。事实上,早在一年前博主就已经分别介绍了两者:各种注意力机制的PyTorch实现、从零开始手写一个Transformer,但当时的实现大部分是基于d2l教程的,这次将基于PyTorch源码重新实现一遍。
目录
- 1. MultiheadAttention
- 1.1 思路
- 1.2 源码
- 1.3 极简版MHA(面试用)
- 2. Transformer
- 3. Q&A
- 1. MHA的参数量?复杂度?FLOPs?
1. MultiheadAttention
1.1 思路
回顾多头注意力,其公式如下:
MHA ( Q , K , V ) = Concat ( head 1 , ⋯ , head h ) W O head i = Attn ( Q W i Q , K W i K , V W i V ) \text{MHA}(Q,K,V)=\text{Concat}(\text{head}_1,\cdots,\text{head}_h)W^O \\ \text{head}_i=\text{Attn}(QW_i^Q,KW_i^K,VW_i^V) MHA(Q,K,V)=Concat(head1,⋯,headh)WOheadi=Attn(QWiQ,KWiK,VWiV)
其中 W i Q ∈ R d m o d e l × d k W_i^Q\in \mathbb{R}^{d_{model}\times d_k} WiQ∈Rdmodel×dk, W i K ∈ R d m o d e l × d k W_i^K\in \mathbb{R}^{d_{model}\times d_k} WiK∈Rdmodel×dk, W i V ∈ R d m o d e l × d v W_i^V\in \mathbb{R}^{d_{model}\times d_v} WiV∈Rdmodel×dv, W O ∈ R h d v × d m o d e l W^O\in \mathbb{R}^{hd_v\times d_{model}} WO∈Rhdv×dmodel,且 d k = d v = d m o d e l / h d_k=d_v=d_{model}/h dk=dv=dmodel/h。
如果记 d h e a d = d m o d e l / h d_{head}=d_{model}/h dhead=dmodel/h,则 W i Q , W i K , W i V W_i^Q,W_i^K,W_i^V WiQ,WiK,WiV 的形状均为 ( d m o d e l , d h e a d ) (d_{model},d_{head}) (dmodel,dhead), W O W^O WO 的形状为 ( d m o d e l , d m o d e l ) (d_{model},d_{model}) (dmodel,dmodel)。
先不考虑batch和mask的情形,在只有一个头的情况下( h = 1 h=1 h=1),MHA的计算方式为
class MHA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model):
super().__init__()
self.w_q = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model))
self.w_k = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model))
self.w_v = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model))
self.w_o = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model))
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
for p in self.parameters():
if p.dim() > 1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
def forward(self, query, key, value):
"""
Args:
query: (n, d_model),n是query的个数,m是key-value的个数
key: (m, d_model)
value: (m, d_model)
"""
q = query @ self.w_q
k = key @ self.w_k
v = value @ self.w_v
attn_logits = q @ k.transpose(0, 1) / math.sqrt(q.size(1)) # attn_logits: (n, m)
attn_probs = F.softmax(attn_logits, dim=-1)
attn_output = attn_probs @ v # attn_output: (n, d_model)
return attn_output, attn_probs
现在考虑 h = 2 h=2 h=2 的情形,此时一共需要 3 ⋅ 2 + 1 = 7 3\cdot2+1=7 3⋅2+1=7 个参数矩阵
class MHA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model):
super().__init__()
self.w_q_1 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_k_1 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_v_1 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_q_2 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_k_2 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_v_2 = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model // 2))
self.w_o = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(d_model, d_model))
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
for p in self.parameters():
if p.dim() > 1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
def forward(self, query, key, value):
"""
Args:
query: (n, d_model),n是query的个数,m是key-value的个数
key: (m, d_model)
value: (m, d_model)
"""
q_1 = query @ self.w_q_1
k_1 = key @ self.w_k_1
v_1 = value @ self.w_v_1
q_2 = query @ self.w_q_2
k_2 = key @ self.w_k_2
v_2 = value @ self.w_v_2
attn_logits_1 = q_1 @ k_1.transpose(0, 1) / math.sqrt(q_1.size(1))
attn_probs_1 = F.softmax(attn_logits_1, dim=-1)
attn_output_1 = attn_probs_1 @ v_1
attn_logits_2 = q_2 @ k_2.transpose(0, 1) / math.sqrt(q_2.size(1))
attn_probs_2 = F.softmax(attn_logits_2, dim=-1)
attn_output_2 = attn_probs_2 @ v_2
attn_output = torch.cat([attn_output_1, attn_output_2], dim=-1) @ self.w_o # attn_output: (n, d_model)
attn_probs = torch.stack([attn_probs_1, attn_probs_2], dim=0) # attn_probs: (2, n, m),其中2是头数
return attn_output, attn_probs
可以看到代码量已经增加了不少,如果扩展到 h h h 个头的情形,则需要 3 h + 1 3h+1 3h+1 个参数矩阵。手动去一个个声明显然不现实,因为 h h h 是动态变化的,而用for循环创建又略显笨拙,有没有更简便的方法呢?
在上面的代码中,我们用小写 q q q 来代表查询 Q Q Q 经过投影后的结果( k , v k,v k,v 同理),即
q i = Q W i Q , i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , h q_i=QW_i^Q,\quad i =1,2,\cdots,h qi=QWiQ,i=1,2,⋯,h
其中 Q Q Q 的形状为 ( n , d m o d e l ) (n,d_{model}) (n,dmodel), q i q_i qi 的形状为 ( n , d h e a d ) (n,d_{head}) (n,dhead),且有
h e a d i = softmax ( q i k i T d h e a d ) v i head_i=\text{softmax}\left(\frac{q_ik_i^{T}}{\sqrt{d_{head}}}\right)v_i headi=softmax(dheadqikiT)vi
注意到
[ q 1 , q 2 , ⋯ , q h ] = Q [ W 1 Q , W 2 Q , ⋯ , W h Q ] (1) [q_1,q_2,\cdots,q_h]=Q[W_1^Q,W_2^Q,\cdots,W_h^Q]\tag{1} [q1,q2,⋯,qh]=Q[W1Q,W2Q,⋯,WhQ](1)
如果记 q ≜ [ q 1 , q 2 , ⋯ , q h ] q\triangleq [q_1,q_2,\cdots,q_h] q≜[q1,q2,⋯,qh], W Q ≜ [ W 1 Q , W 2 Q , ⋯ , W h Q ] W^Q\triangleq [W_1^Q,W_2^Q,\cdots,W_h^Q] WQ≜[W1Q,W2Q,⋯,WhQ],则 W Q W^Q WQ 的形状为 ( d m o d e l , d m o d e l ) (d_{model},d_{model}) (dmodel,dmodel),与 h h h 无关, q q q 的形状为 ( n , d m o d e l ) (n,d_{model}) (n,dmodel)。这样一来,我们就不需要一个个声明 W i Q W_i^Q WiQ 了,并且可以一次性存储所有的 q i q_i qi。
要计算 h e a d 1 head_1 head1,我们需要能够从 q q q 中取出 q 1 q_1 q1( k , v k,v k,v 同理),所以我们期望 q q q 的形状是 ( h , n , d h e a d ) (h,n,d_{head}) (h,n,dhead),从而 q [ 1 ] q[1] q[1] 就是 q 1 q_1 q1(这里下标从 1 1 1 开始)。
📝 当然也可以是 ( n , h , d h e a d ) (n,h,d_{head}) (n,h,dhead) 等形状,但必须要确保形状里含且只含这三个数字。之所以把 h h h 放在第一个维度是为了方便索引和后续计算。
同理可知
k
,
v
k,v
k,v 的形状均为
(
h
,
m
,
d
h
e
a
d
)
(h,m,d_{head})
(h,m,dhead)。我们可以视
h
h
h 所在的维度为批量维,从而可以执行批量乘法 torch.bmm 来一次性算出
h
h
h 个头的结果。
q = torch.randn(h, n, d_head)
k = torch.randn(h, m, d_head)
v = torch.randn(h, m, d_head)
# @和torch.bmm的效果相同,但写法更简洁
attn_logits = q @ k.transpose(1, 2) / math.sqrt(q.size(2))
attn_probs = F.softmax(attn_logits, dim=-1)
attn_output = attn_probs @ v # attn_output: (h, n, d_head)
h h h 个头的结果存储在形状为 ( h , n , d h e a d ) (h,n,d_{head}) (h,n,dhead) 的张量中,那我们如何把这 h h h 个结果concat在一起呢?注意到我们实际上是将 h h h 个形状为 ( n , d h e a d ) (n,d_{head}) (n,dhead) 的张量横向concat为一个形状为 ( n , d m o d e l ) (n,d_{model}) (n,dmodel) 的张量,因此只需执行如下的形状变换:
( h , n , d h e a d ) → ( n , h , d h e a d ) → ( n , h ⋅ d h e a d ) = ( n , d m o d e l ) (2) (h,n,d_{head})\to(n,h,d_{head})\to(n,h\cdot d_{head})=(n,d_{model}) \tag{2} (h,n,dhead)→(n,h,dhead)→(n,h⋅dhead)=(n,dmodel)(2)
n = attn_output.size(1)
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(0, 1).reshape(n, -1)
⚠️ 注意,切勿直接将 ( h , n , d h e a d ) (h,n,d_{head}) (h,n,dhead) reshape成 ( n , d m o d e l ) (n,d_{model}) (n,dmodel)。
之前我们只讨论了 q q q 的形状应当是 ( h , n , d h e a d ) (h,n,d_{head}) (h,n,dhead),但并没有讨论它是如何变换得来的。这是因为, Q Q Q 在经过投影后得到的 q q q 只具有 ( n , d m o d e l ) (n,d_{model}) (n,dmodel) 的形状,要进行形状变换,一种做法是对 q q q 沿纵向切 h h h 刀再堆叠起来,这样从直观上来看也比较符合公式 ( 1 ) (1) (1)
q = torch.randn(n, d_model)
q = torch.stack(torch.split(q, d_head, dim=-1), dim=0)
但由于 W Q W^Q WQ 初始时是随机的,所以我们不需要严格按照公式 ( 1 ) (1) (1) 那样操作,直接执行 ( 2 ) (2) (2) 的逆变换即可
( n , d m o d e l ) = ( n , h ⋅ d h e a d ) → ( n , h , d h e a d ) → ( h , n , d h e a d ) (n,d_{model})=(n,h\cdot d_{head})\to(n,h,d_{head})\to(h,n,d_{head}) (n,dmodel)=(n,h⋅dhead)→(n,h,dhead)→(h,n,dhead)
现考虑有batch的情形,设批量大小为
b
b
b,则
Q
Q
Q 的形状为
(
b
,
n
,
d
m
o
d
e
l
)
(b,n,d_{model})
(b,n,dmodel) 或
(
n
,
b
,
d
m
o
d
e
l
)
(n,b,d_{model})
(n,b,dmodel),具体是哪一个要看 batch_first 是否为 True。接下来均假设 batch_first = False。
在以上的假设下, q q q 的形状也为 ( n , b , d m o d e l ) (n,b,d_{model}) (n,b,dmodel),我们将 b b b 和 h h h 看成同一维度(都是批量维),从而 ( 2 ) (2) (2) 式改写为
( n , b , d m o d e l ) → ( n , b , h , d h e a d ) → ( n , b ⋅ h , d h e a d ) → ( b ⋅ h , n , d h e a d ) (n,b,d_{model})\to(n,b,h,d_{head})\to(n,b\cdot h,d_{head})\to(b\cdot h,n,d_{head}) (n,b,dmodel)→(n,b,h,dhead)→(n,b⋅h,dhead)→(b⋅h,n,dhead)
关于 key_padding_mask 和 attn_mask 这里不再介绍,如有需要可阅读博主之前的文章,这里主要讲解如何合并两种mask。
前者的形状为
(
b
,
m
)
(b,m)
(b,m),用来mask掉key中的 [PAD],防止query注意到它。而后者的形状可以是
(
n
,
m
)
(n,m)
(n,m) 也可以是
(
b
⋅
h
,
n
,
m
)
(b\cdot h,n,m)
(b⋅h,n,m)。在实际合并两种mask的时候,我们均需要按照
(
b
⋅
h
,
n
,
m
)
(b\cdot h,n,m)
(b⋅h,n,m) 这个形状去计算。也就是说,如果是 key_padding_mask,我们需要进行形状变换
(
b
,
m
)
→
(
b
,
1
,
1
,
m
)
→
(
b
,
h
,
1
,
m
)
→
(
b
⋅
h
,
1
,
m
)
(b,m)\to(b,1,1,m)\to(b,h,1,m)\to(b\cdot h,1,m)
(b,m)→(b,1,1,m)→(b,h,1,m)→(b⋅h,1,m);如果是 attn_mask,我们需要进行形状变换
(
n
,
m
)
→
(
1
,
n
,
m
)
(n,m)\to(1,n,m)
(n,m)→(1,n,m)。
1.2 源码
本节将遵循以下记号:
| 记号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| b b b | batch size |
| h h h | num heads |
| d d d | head dim |
| n n n | num queries |
| m m m | num key-value pairs |
首先实现一个MHA的基类:
class MultiheadAttentionBase_(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_dim, num_heads, dropout=0., bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.dropout = dropout
self.head_dim = embed_dim // num_heads
assert self.head_dim * num_heads == embed_dim
self.in_proj_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim, embed_dim))
if bias:
self.in_proj_bias = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim))
else:
self.register_parameter('in_proj_bias', None)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=bias)
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.in_proj_weight)
if self.in_proj_bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(self.in_proj_bias, 0.)
nn.init.constant_(self.out_proj.bias, 0.)
def forward(
self,
query,
key,
value,
key_padding_mask,
attn_mask,
need_weights=True,
):
"""
Args:
query: (n, b, h * d)
key: (m, b, h * d)
value: (m, b, h * d)
key_padding_mask: (b, m), bool type
attn_mask: (n, m) or (b * h, n, m), bool type
Returns:
attn_output: (n, b, h * d)
attn_weights: (b, h, n, m)
"""
w_q, w_k, w_v = self.in_proj_weight.chunk(3)
if self.in_proj_bias is not None:
b_q, b_k, b_v = self.in_proj_bias.chunk(3)
else:
b_q = b_k = b_v = None
q = F.linear(query, w_q, b_q)
k = F.linear(key, w_k, b_k)
v = F.linear(value, w_v, b_v)
b, h, d = q.size(1), self.num_heads, self.head_dim
q, k, v = map(lambda x: x.reshape(-1, b, h, d), [q, k, v])
attn_mask = self.merge_masks(key_padding_mask, attn_mask, q)
attn_output, attn_weights = self.attention(q, k, v, attn_mask, out_proj=self.out_proj, dropout=self.dropout, training=self.training)
if not need_weights:
attn_weights = None
return attn_output, attn_weights
def merge_masks(self, key_padding_mask, attn_mask, q):
"""
Args:
key_padding_mask: (b, m), bool type
attn_mask: (n, m) or (b * h, n, m), bool type
q: only used to confirm the dtype of attn_mask
Returns:
attn_mask: (b * h, n, m), float type
"""
assert key_padding_mask is not None and key_padding_mask.dtype == torch.bool
b, m = key_padding_mask.size()
key_padding_mask = key_padding_mask.view(b, 1, 1, m).expand(-1, self.num_heads, -1, -1).reshape(b * self.num_heads, 1, m)
if attn_mask is not None:
assert attn_mask.dtype == torch.bool
if attn_mask.dim() == 2:
attn_mask = attn_mask.unsqueeze(0)
attn_mask = attn_mask.logical_or(key_padding_mask)
else:
attn_mask = key_padding_mask
attn_mask = torch.zeros_like(attn_mask, dtype=q.dtype).masked_fill_(attn_mask, -1e28)
return attn_mask
def attention(self, q, k, v, attn_mask, out_proj, dropout, training):
"""
Args:
q: (n, b, h, d)
k: (m, b, h, d)
v: (m, b, h, d)
attn_mask: (b * h, n, m), float type
out_proj: nn.Linear(h * d, h * d)
Returns:
attn_output: (n, b, h * d), is the result of concating h heads.
attn_weights: (b, h, n, m)
"""
raise NotImplementedError
接下来,只需要重写 attention 方法就可以实现普通版的MHA了
class MultiheadAttention(MultiheadAttentionBase_):
def attention(self, q, k, v, attn_mask, out_proj, dropout, training):
if not training:
dropout = 0
n, b, h, d = q.size()
q, k, v = map(lambda x: x.reshape(-1, b * h, d).transpose(0, 1), [q, k, v])
attn_logits = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1) / math.sqrt(d) + attn_mask
attn_probs = F.softmax(attn_logits, dim=-1)
attn_weights = F.dropout(attn_probs, p=dropout)
attn_output = attn_weights @ v
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(0, 1).reshape(n, b, h * d)
attn_output = out_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights
1.3 极简版MHA(面试用)
不少面试会让现场手写MHA,这里提供了一份模版,略去了很多细节。
相比原版,极简版做了如下改动:
- 略去了参数初始化。
- 去掉了mask
class MultiheadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_dim, num_heads, dropout=0., bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.head_dim = embed_dim // num_heads
assert self.head_dim * num_heads == embed_dim
self.in_proj_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim, embed_dim))
if bias:
self.in_proj_bias = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(3 * embed_dim))
else:
self.register_parameter('in_proj_bias', None)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=bias)
def forward(self, query, key, value):
"""
Args:
query: (n, b, h * d)
key: (m, b, h * d)
value: (m, b, h * d)
"""
w_q, w_k, w_v = self.in_proj_weight.chunk(3)
if self.in_proj_bias is not None:
b_q, b_k, b_v = self.in_proj_bias.chunk(3)
else:
b_q = b_k = b_v = None
q, k, v = F.linear(query, w_q, b_q), F.linear(key, w_k, b_k), F.linear(value, w_v, b_v)
b, h, d = q.size(1), self.num_heads, self.head_dim
q, k, v = map(lambda x: x.reshape(-1, b * h, d).transpose(0, 1), [q, k, v])
attn_logits = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1) / math.sqrt(d)
attn_probs = F.softmax(attn_logits, dim=-1)
attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_probs)
attn_output = attn_weights @ v
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(0, 1).reshape(-1, b, h * d)
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights
注意,如果尝试直接输出的话,会得到一堆 nan,这是因为没有xavier初始化,需要 _reset_parameters() 一下。
具体需要哪种mask可根据面试官的要求去实现。
2. Transformer
接下来基于PyTorch官方的MHA来实现Transformer。
首先需要实现一个基础函数,它可以用来复制一个 Module N次。
def _get_clones(module, n):
return nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(module) for _ in range(n)])
EncoderLayer的实现
class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
d_model,
n_head,
d_ffn,
dropout=0.1,
activation=F.relu,
norm_first=False,
):
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=d_model, num_heads=n_head, dropout=dropout)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(d_model, d_ffn)
self.activation = activation
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(d_ffn, d_model)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm_first = norm_first
def forward(self, src, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask):
x = src
if self.norm_first:
x = x + self._sa_block(self.norm1(x), src_mask, src_key_padding_mask)
x = x + self._ff_block(self.norm2(x))
else:
x = self.norm1(x + self._sa_block(x, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask))
x = self.norm2(x + self._ff_block(x))
return x
def _sa_block(self, x, attn_mask, key_padding_mask):
x = self.self_attn(x, x, x, attn_mask=attn_mask, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, need_weights=False)[0]
return self.dropout1(x)
def _ff_block(self, x):
x = self.linear2(self.dropout2(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
return self.dropout3(x)
这里的 norm_first 用来决定是Pre-LN还是Post-LN,如下图所示
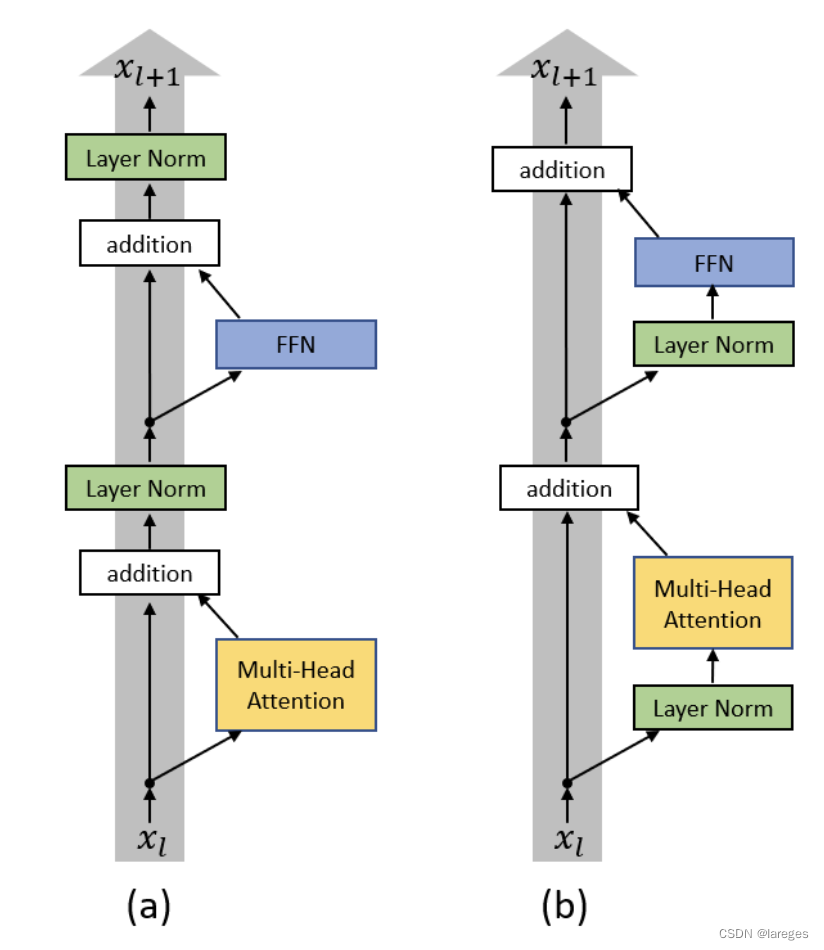
DecoderLayer的实现
class TransformerDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
d_model,
n_head,
d_ffn,
dropout=0.1,
activation=F.relu,
norm_first=False,
):
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=d_model, num_heads=n_head, dropout=dropout)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.cross_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=d_model, num_heads=n_head, dropout=dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(d_model, d_ffn)
self.activation = activation
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(d_ffn, d_model)
self.dropout4 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm3 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm_first = norm_first
def forward(self, tgt, memory, tgt_mask, memory_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, memory_key_padding_mask):
x = tgt
if self.norm_first:
x = x + self._sa_block(self.norm1(x), tgt_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask)
x = x + self._ca_block(self.norm2(x), memory, memory_mask, memory_key_padding_mask)
x = x + self._ff_block(self.norm3(x))
else:
x = self.norm1(x + self._sa_block(x, tgt_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask))
x = self.norm2(x + self._ca_block(x, memory, memory_mask, memory_key_padding_mask))
x = self.norm3(x + self._ff_block(x))
return x
def _sa_block(self, x, attn_mask, key_padding_mask):
x = self.self_attn(x, x, x, attn_mask=attn_mask, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, need_weights=False)[0]
return self.dropout1(x)
def _ca_block(self, x, mem, attn_mask, key_padding_mask):
x = self.cross_attn(x, mem, mem, attn_mask=attn_mask, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, need_weights=False)[0]
return self.dropout2(x)
def _ff_block(self, x):
x = self.linear2(self.dropout3(self.activation(self.linear1(x))))
return self.dropout4(x)
根据EncoderLayer搭建Encoder。需要注意的是,PyTorch源码中还提供了 encoder_norm 这一参数,即决定是否在Encoder最后放一个LN。
class TransformerEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder_layer, num_layers, encoder_norm=None):
super().__init__()
self.layers = _get_clones(encoder_layer, num_layers)
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.encoder_norm = encoder_norm
def forward(self, src, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask):
output = src
for mod in self.layers:
output = mod(output, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask)
if self.encoder_norm is not None:
output = self.encoder_norm(output)
return output
DecoderLayer同理
class TransformerDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, decoder_layer, num_layers, decoder_norm=None):
super().__init__()
self.layers = _get_clones(decoder_layer, num_layers)
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.decoder_norm = decoder_norm
def forward(self, tgt, memory, tgt_mask, memory_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, memory_key_padding_mask):
output = tgt
for mod in self.layers:
output = mod(output, memory, tgt_mask, memory_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, memory_key_padding_mask)
if self.decoder_norm is not None:
output = self.decoder_norm(output)
return output
PyTorch官方的Transformer默认添加 encoder_norm 和 decoder_norm,然而这对于Post-LN的情形,无疑是多余的,所以这里我们做个简单修改,即如果是Post-LN情形,就不在最后添加LN了。
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
d_model=512,
n_head=8,
num_encoder_layers=6,
num_decoder_layers=6,
d_ffn=2048,
dropout=0.1,
activation=F.relu,
norm_first=False,
):
super().__init__()
if norm_first:
encoder_norm, decoder_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_model), nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
else:
encoder_norm = decoder_norm = None
encoder_layer = TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model, n_head, d_ffn, dropout, activation, norm_first)
self.encoder = TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_encoder_layers, encoder_norm)
decoder_layer = TransformerDecoderLayer(d_model, n_head, d_ffn, dropout, activation, norm_first)
self.decoder = TransformerDecoder(decoder_layer, num_decoder_layers, decoder_norm)
self._reset_parameters()
def _reset_parameters(self):
for p in self.parameters():
if p.dim() > 1:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(p)
def forward(
self,
src,
tgt,
src_mask=None,
tgt_mask=None,
memory_mask=None,
src_key_padding_mask=None,
tgt_key_padding_mask=None,
memory_key_padding_mask=None,
):
memory = self.encoder(src, src_mask, src_key_padding_mask)
output = self.decoder(tgt, memory, tgt_mask, memory_mask, tgt_key_padding_mask, memory_key_padding_mask)
return output
截止到目前,我们实现的Transfomer并不是完整的,还缺少embedding层和Decoder后面的Linear层,这里只介绍前者,因为后者仅仅是简单的 nn.Linear(d_model, tgt_vocab_size)。
Transformer的embedding层分为token embedding和Positional Encoding,前者是可学习的 nn.Embedding,后者是固定的Sinusoidal编码。
PE的公式为
P [ i , 2 j ] = sin ( i 1000 0 2 j / d m o d e l ) P [ i , 2 j + 1 ] = cos ( i 1000 0 2 j / d m o d e l ) 0 ≤ i < m a x _ l e n , 0 ≤ j < d m o d e l P[i,2j]=\sin\left(\frac{i}{10000^{2j/d_{model}}}\right)\\ P[i,2j+1]=\cos\left(\frac{i}{10000^{2j/d_{model}}}\right) \\ 0\leq i < max\_len,\;0\leq j<d_{model} P[i,2j]=sin(100002j/dmodeli)P[i,2j+1]=cos(100002j/dmodeli)0≤i<max_len,0≤j<dmodel
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout=0.1, max_len=5000):
super().__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
position = torch.arange(max_len).unsqueeze(1)
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2) * (-math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe = torch.zeros(max_len, 1, d_model) # 1是batch size维度
pe[:, 0, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 0, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.pe[:x.size(0)]
return self.dropout(x)
3. Q&A
1. MHA的参数量?复杂度?FLOPs?
只考虑自注意力情形。
MHA模块一共包含四个参数矩阵: W Q , W K , W V , W O W^Q,W^K,W^V,W^O WQ,WK,WV,WO,形状均为 ( d m o d e l , d m o d e l ) (d_{model},d_{model}) (dmodel,dmodel),因此weight部分的参数量是 4 ⋅ d m o d e l 2 4\cdot d_{model}^2 4⋅dmodel2。每个参数矩阵都会带有一个长度为 d m o d e l d_{model} dmodel 的bias,因此总共的参数量为 4 ⋅ d m o d e l 2 + 4 ⋅ d m o d e l 4\cdot d_{model}^2+4\cdot d_{model} 4⋅dmodel2+4⋅dmodel。
设序列长度为 l l l,则注意力矩阵的形状为 ( l , l ) (l,l) (l,l),将这个矩阵填满所需要的复杂度为 O ( l 2 ) O(l^2) O(l2)。每填一个数字都要计算两个 d d d 维向量的内积,计算内积的复杂度是 O ( d ) O(d) O(d),所以总复杂度是 O ( l 2 d ) O(l^2d) O(l2d)。
📝 注意FLOPs和FLOPS的含义不同。前者是floating point operations,指浮点运算数,可以理解为计算量,用来衡量模型/算法的复杂度;后者是floating point operations per second,指每秒浮点运算次数,可以理解为计算速度,用来衡量衡量硬件的性能。
FLOPs(floating point operations)