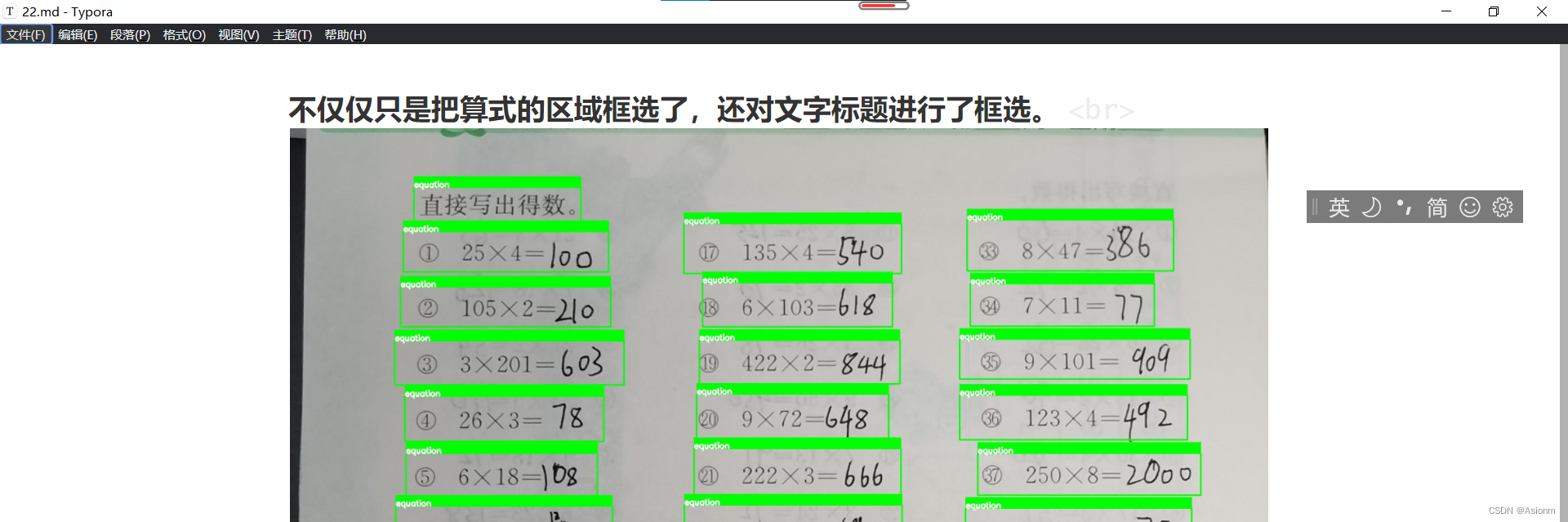
目录
一,日期类
二,运算符重载
运算符重载1(比较)
1.<
2. ==
复用
3.>
4.!=
5.<=
6.>=
运算符重载2(日期加减)
0.准备条件------计算每月的日期函数
1.+=
2.+
3.-=
4.-
5.前置++
6.后置++
7前置--
6.后置--
7.计算两个日期的相差天数
三,改进优化
四,源代码
一,日期类
写日期类的第一步是啥?当然是构建一个日期类啦。那这个类里面有啥啊?
1.成员变量:_year,_month,_day。
2.构造函数。
3.#include<iostream>。
4.using namespace std;
现在基本上就写这些。代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};此时,我们的类对象就创建好了。我们便可以定义一个日期类对象了。在另一个cpp源文件里。
#include"Date.h"
int main()
{
Date d1(2023, 8, 29);
Date d2(2023, 8, 31);
}运行发现没有问题。
二,运算符重载
接下来我们来探索新功能吧。如果现在我们想要比较这两个日期的大小我们该如何比较呢?
答案是写个函数,但是纠结的点就来了:
1.不会英文,那就写个拼音来作函数名吧!但是如果你的同事是个老外怎么办?
2.会英文,那就起个英文名吧compare1,compare2,compare3,compare4。哈哈,这就难为死看的人了。
那到底要怎么办啊?直接用大于,小于号?但是这明显是不行的,因为类比较不了啊!此时一个叫做运算符重载的靓仔走过。
运算符重载1(比较)
运算符重载是啥呢?运算符重载其实就是Cpp增加的一个新语法。通过一个叫做operator的关键字将一些符号重载,从而扩展该符号的功能。比如<号想要扩展功能的话便可以写成operator<函数。比如要比较上面的日期类,便可以写成如下代码:
1.<
//思想:先比较年,再比较月,再比较天
bool Date:: operator<(const Date& d)
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month&&_day<d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}这样便实现了<的函数重载。当我们定义:Date d1(3023, 8, 29); Date d2(2023, 8, 31);
时调用<比较时,编译器会把d1<d2解释为:d1.operator<(d2) 因为有this指针的原因再进一步剖析的话其实就是:operator<(&d1,d2)。
2. ==
在理解了上面的<运算符重载以后,便可以再趁热打铁写一个==运算符重载。代码如下:
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}等于便写出来了。
复用
其实在写完上面的两个运算符以后,其它的运算符便很好写了。比如大于,不就是!<嘛!
比如!=不就是!==嘛!比如大于等于不就是>或者==中的一个条件成立即可,小于等于不就是<和==中的一个条件成立即可。知道了这些以后,便可以着手写代码了:
3.>
bool Date:: operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this < d);
}4.!=
bool Date:: operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}5.<=
bool Date:: operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this < d);
}6.>=
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}运算符重载2(日期加减)
在搞定了比较的运算符以后便可以来搞+,+=,-,-=,++,--;以及计算日期之间的差值的运算符重载了。
0.准备条件------计算每月的日期函数
其实在加减日期时最关键的便是计算出每个月的天数。日期天数计算代码如下:
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//按平年写数组数据
if (month == 2 && ((year % 400 == 0) || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)))//如果是闰年便可以将二月的天数++
{
MonthDay[2]++;
}
return MonthDay[month];
}1.+=
Date& Date:: operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}2.+
+与+=的区别就是,+不改变自身,+=改变自身。所以复用+=实现+的运算符重载代码如下:
Date Date::operator+(int day)//此时的返回值就不能是Date&了,
//因为tmp是这个运算符重载函数里的临时变量。
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}补充说明:
为什么不先实现+而先实现+=呢?因为先实现+会比+=多几次拷贝。这样虽然不会对计算机的运行效率有太多的影响,但是为了发扬中国人民勤俭节约的美好品德还是先实现+=为好!
3.-=
Date& Date:: operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}4.-
和前面的+一样,复用就完事了。
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}5.前置++
再实现前置++与后置++时可能大家会很好奇,这两个长得一摸一样的东西到底需要怎么区分呢?在这里可以这样区分:前置++是:operator ++(),后置++是:operator ++(int)。这个好像是祖师爷自己定义的,我们知道就可以了。所以代码如下:
Date& Date:: operator++()//因为前置++是先++后使用的所以直接改变*this
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}6.后置++
Date Date:: operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
++*this;
return tmp;
}7前置--
前置--和后置--的声明也和前置++与后置++的声明类似,所以--的代码如下:
Date&Date:: operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}6.后置--
Date Date:: operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
--*this;
return tmp;
}7.计算两个日期的相差天数
这个函数算是比较有意思的函数了,一开始我还不会写。但是在实现了前面的运算符重载以后这个函数代码的书写也就水到渠成了。具体代码如下:
int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (max < min)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
}
int count = 0;
while (min != max)
{
min+=1;
count++;
}
return count;
}三,改进优化
大家能看出这里还有什么需要优化的地方吗?
1.判断日期是否合法,这该在那里判断呢?这是不是应该就要在传入日期的时候就判断啊?
所以判断日期是否合法就应该在构造函数里判断。
Date(int year, int month, int day) { if (day > GetMonthDay(year, month) || month >= 13) { cout << "日期非法" << endl; } _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; }2.我们有没有可能想要计算一个日期+=负数的情况呢?以此来计算前面几天是什么日子呢?
答案是当然有,那我们该如何实现呢?还是复用。加等一个负数其实就是减等一个负的负数。减等一个负数其实就是+=一个负的负数。所以改进代码如下:
+=:
Date& Date:: operator+=(int day) { if (day < 0) { *this -= (-day); return *this; } _day += day; while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { _month++; _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); if (_month == 13) { _year++; _month = 1; } } return *this; }-=:
Date& Date:: operator-=(int day) { if (day < 0) { *this += (-day); return *this; } _day -= day; while (_day <= 0) { _month--; if (_month == 0) { _year--; _month = 12; } _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } return *this; }3.打印日期,我们都知道自定义类型的变量都可以用cout打印出来。那我们是否可以将日期也用cout打印出来呢?答案是不能,那我们有没有办法打印出来呢?答案是有的,那就是运算符重载。代码如下:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Date& d) { out << d.Getyear() << "/" << d.Getmonth() << "/" << d.Getday() << endl; return out; } 记得要将声明与定义分离!!!
四,源代码
1,Date.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (day > GetMonthDay(year, month) || month >= 13)
{
cout << "日期非法" << endl;
}
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//按平年写数组数据
if (month == 2 && ((year % 400 == 0) || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)))//如果是闰年便可以将二月的天数++
{
MonthDay[2]++;
}
return MonthDay[month];
}
int Getyear()
{
return _year;
}
int Getmonth()
{
return _month;
}
int Getday()
{
return _day;
}
bool operator<(const Date& d);
bool operator==(const Date& d);
bool operator>(const Date& d);
bool operator!=(const Date& d);
bool operator<=(const Date& d);
bool operator>=(const Date& d);
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator-(int day);
Date& operator++();
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
int operator-(Date& d1);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& istream, Date& d);2,Date.c:
#include"Date.h"
bool Date:: operator<(const Date& d)
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month&&_day<d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
bool Date:: operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this < d);
}
bool Date:: operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date:: operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this < d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
Date& Date:: operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this -= (-day);
return *this;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_month++;
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
*this += (-day);
return *this;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date:: operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
++*this;
return tmp;
}
Date&Date:: operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date:: operator--(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
--*this;
return tmp;
}
int Date::operator-(Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (max < min)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
}
int count = 0;
while (min != max)
{
min+=1;
count++;
}
return count;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Date& d)
{
out << d.Getyear() << "/" << d.Getmonth() << "/" << d.Getday() << endl;
return out;
}


![[SSM]Spring对事务的支持](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d57847d30c594389823e32a63cd4b417.png)