目录
十六、Spring对事务的支持
16.1事务概述
16.2引入事务场景
16.3Spring对事务的支持
Spring实现事务的两种方式
Spring事务管理API
声明式事务之注解实现方式
事务属性
事务的全注解式开发
声明式事务之XML实现方式
十六、Spring对事务的支持
16.1事务概述
-
什么是事务
-
在一个业务流程当中,通常需要多条DML语句共同联合才能完成,这多条DML语句必须同时成功或者同时失败,这样才能保证数据的安全。
-
多条DML要么同时成功,要么同时失败,这叫做事务。
-
事务:Transaction(tx)
-
-
事务的四个处理过程:
-
第一步:开启事务
-
第二步:执行核心业务代码
-
第三步:提交事务(如果核心业务处理过程中没有出现异常)
-
第四步:回滚事务(如果核心业务处理过程中出现异常)
-
-
事务的四个特性:
-
A 原子性:事务是最小的工作单元,不可再分。
-
C 一致性:事务要求要么同时成功,要么同时失败。事务前和事务后的总量不变。
-
I 隔离性:事务和事务之间因为有隔离性,才可以保证互不干扰。
-
D 持久性:持久性是事务结束的标志。
-
16.2引入事务场景
-
以银行账户转账为例。两个账户act001和act002,act001账户向act002账户转账10000,必须同时成功或者同时失败。
-
连接数据库的技术采用Spring框架的JdbcTemplate。
-
采用三层架构搭建:

pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring013-tx-bank</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!--spring-context-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--德鲁伊连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>
<!--@Resource注解-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--log4j2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.19.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>20</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>20</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
</project>第一步:准备数据库表

第二步:准备POJO类
package com.hhb.bank.pojo;
public class Account {
private String actno;
private Double balance;
public Account(String actno, Double balance) {
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
public Account() {
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
}
第三步:编写持久层
package com.hhb.bank.dao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 根据账号查询账户信息
*
* @param actno
* @return
*/
Account selectByActno(String actno);
/**
* 更新账户信息
*
* @param act
* @return
*/
int update(Account act);
}package com.hhb.bank.dao.impl;
import com.hhb.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Resource(name = "jdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public Account selectByActno(String actno) {
String sql = "select actno,balance from t_act where actno=?";
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int update(Account act) {
String sql = "update t_act set balance=? where actno=?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, act.getBalance(), act.getActno());
return count;
}
}第四步:编写业务类
package com.hhb.bank.service;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账业务方法
*
* @param fromActno
* @param toActno
* @param money
*/
void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money);
}
package com.hhb.bank.service.impl;
import com.hhb.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.hhb.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
//控制事务,因为在这个方法中要完成所有的转账业务
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
//第一步:开启事务
//第二步:执行核心业务逻辑
//查询转出账户的余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
//余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
//将内存中两个对象的余额先修改
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
//数据库更新
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
//模拟异常
/*String s = null;
s.toString();*/
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("转账失败,联系银行!");
}
//第三步:如果执行业务流程过程中,没有异常,提交事务。
//第四步:如果执行业务流程过程中,有异常,回滚事务。
}
}第五步:编写Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hhb.bank"/>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="030522"/>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>第六步:编写表示层(测试程序)
@Test
public void testSpringTx() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act001", "act002", 10000);
System.out.println("转账成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}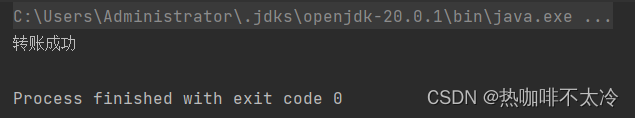
-
数据库中丢失一万

16.3Spring对事务的支持
Spring实现事务的两种方式
-
编程式事务
-
通过编写代码的方式来实现事务的管理。
-
-
声明式事务
-
基于注解方式
-
基于XML配置方式
-
Spring事务管理API
-
Spring对事务的管理底层实现方式是基于AOP实现的,采用AOP的方式进行了封装。所以Spring专门针对事务开发了一套API。
-
PlatformTransactionManager接口:spring事务管理器的核心接口。在Spring6中它有两个实现:
-
DataSourceTransactionManager:支持JdbcTemplate、MyBatis、Hibernate等事务管理。
-
JtaTransactionManager:支持分布式事务管理。
-
-
如果要在Spring6中使用JdbcTemplate,就要使用DataSourceTransactionManager来管理事务。
声明式事务之注解实现方式
第一步:在spring配置文件中配置事务管理器、事务注解驱动器
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--开启事务注解驱动器,开启事务注解,告诉Spring框架,采用注解的方式去控制事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>第二步:在spring配置文件中引入tx命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">第三步:在service类上或方法上添加@Transactional注解
-
在类上添加该注解,该类中所有的方法都有事务。在某个方法上添加该注解,表示只有这个方法使用事务。
package com.hhb.bank.service.impl;
import com.hhb.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.hhb.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("accountService")
//@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
//控制事务,因为在这个方法中要完成所有的转账业务
@Override
@Transactional
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
//查询转出账户的余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
//余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
//将内存中两个对象的余额先修改
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
//数据库更新
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
//模拟异常
/*String s = null;
s.toString();*/
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("转账失败,联系银行!");
}
}
}-
通过测试,出现异常发现数据没有变化,事务起作用了。
事务属性
事务属性包括哪些

-
事务中的重点属性:
-
事务传播行为
-
事务隔离级别
-
事务超时
-
只读事务
-
设置出现哪些异常回滚事务
-
设置出现哪些异常不回滚事务
-
事务传播行为
-
什么是事务的传播行为?
-
在service类中有a()方法和b()方法,a()方法上有事务,b()方法上也有事务,当a()方法执行过程中调用了b()方法,事务是如何传递的?这就是事务传播行为。
-
-
一共有七种传播行为:
-
REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个(默认)。
-
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
-
MANDATORY:必须运行在一个事务中,如果当前没有事务正在发生,将抛出一个异常。
-
REQUIRES_NEW:开启一个新的事务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起。(不管有没有事务,直接开启一个新事务,开启的新事务和之前的事务不存在嵌套关系,之前事务被挂起)
-
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务。(不支持事务,存在就挂起)
-
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常。(不支持事务,存在就抛异常)
-
NESTED:如果当前正有一个事务在进行中,则该方法应当运行在一个嵌套式事务中。被嵌套
的事务可以独⽴于外层事务进⾏提交或回滚。如果外层事务不存在,⾏为就像REQUIRED⼀
样。
-
-
在代码中设置事务的传播行为:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)-
测试
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void save(Account act) {
// 这⾥调⽤dao的insert⽅法。
accountDao.insert(act); // 保存act-003账户
// 创建账户对象
Account act2 = new Account("act-004", 1000.0);
try {
accountService.save(act2); // 保存act-004账户
} catch (Exception e) {
}
// 继续往后进⾏我当前1号事务⾃⼰的事⼉。
}@Override
//@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void save(Account act) {
accountDao.insert(act);
// 模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
// 事⼉没有处理完,这个⼤括号当中的后续也许还有其他的DML语句。
}-
一定要集成Log4j2日志框架,在日志信息中可以看到更加详细的信息。
事务隔离级别
-
事务隔离级别类似于教室A和教室B之间的那道墙,隔离级别越高表示墙体越厚,隔音效果越好。
-
数据库中读取数据存在的三大读问题:
-
脏读:读取到没有提交到数据库的数据,叫做脏读。
-
不可重复读:在同一事务当中,第一次和第二次读取的数据不一样。
-
幻读:读到的数据是假的。
-
-
事务隔离级别包括四个级别:
-
读未提交:READ_UNCOMMITTED
-
这种隔离级别,存在脏读问题,所谓的脏读表示能够读取到其它事务未提交的数据。
-
-
读提交:READ_COMMITTED
-
解决了脏读问题,其它事务提交之后才能读到,但存在不可重复读问题。
-
-
可重复读:REPEATABLE_READ
-
解决了不可重复读问题,可以达到可重复读效果,只要当前事务不结束,读取到的数据一直都是一样的。但存在幻读问题。
-
-
序列化:SERIALIZABLE
-
解决了幻读问题,事务排队执行。不支持并发。
-
-
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交 | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| 读提交 | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| 可重复读 | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| 序列化 | 无 | 无 | 无 |
-
在Spring代码中如何设置隔离级别?
-
隔离级别在spring中以枚举类型存在:
-

-
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
-
-
测试事务隔离级别:READ_UNCOMMITTED 和 READ_COMMITTED
package com.hhb.bank.service.impl;
import com.hhb.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("i1")
public class IsolationService1 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
//负责查询
//当前事务可以读取到别的事务没有提交的数据
//@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
//对方事务提交之后的数据才能读到
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
public void getByActno(String actno) {
Account account = accountDao.selectByActno(actno);
System.out.println("查询到的账户信息是:" + account);
}
}package com.hhb.bank.service.impl;
import com.hhb.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.hhb.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("i2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
public void save(Account act){
accountDao.insert(act);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}@Test
public void testIsolation2() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService2 i2 = applicationContext.getBean("i2", IsolationService2.class);
Account act = new Account("act005", 100000.0);
i2.save(act);
}
@Test
public void testIsolation1() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService1 i1 = applicationContext.getBean("i1", IsolationService1.class);
i1.getByActno("act005");
}-
通过执行结果可以看出隔离级别不同,执行效果不同。
事务超时
-
代码如下:
-
@Transactional(timeout=10)
-
-
以上代码表示事务的超时时间为10s,超过10s如果该事务中所有的DML语句还没有执行的话,最终会选择回滚。
-
默认值是-1,表示没有时间限制。
-
在当前事务中,最后一条DML语句执行之前的时间为超时时间。如果最后一条DML语句后面还有很多业务逻辑,这些业务代码执行的时间不被计入超时时间。
@Service("i2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
//设置事务超时时间为10s
@Transactional(timeout = 10)
public void save(Account act){
accountDao.insert(act);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*12);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}-
如果想让整个方法的所有代码都计入超时时间的话,可以在方法最后一行添加一行无关紧要的DML语句。
只读事务
-
代码如下:
-
Transactional(readOnly=true)
-
-
将当前事务设置为只读事务,在该事务执行过程中只允许select语句,delete insert update均不执行。
-
该特性的作用是:启动spring的优化策略,提高selecct语句执行效率。
-
如果该事务中确实没有增删改操作,建议设置为只读事务。
@Service("i2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void save(Account act){
accountDao.insert(act);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*12);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}设置哪些异常回滚事务
-
代码如下:
-
Transactional(rollbackFor=RuntimeException.class)
-
-
表示只有发生RuntimeException异常或该异常的子类异常才回滚。
@Service("i2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class)
public void save(Account act) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(act);
//模拟异常
if (1 == 1) {
//throw new RuntimeException();
throw new IOException();
}
}
}设置哪些异常不回滚事务
-
代码如下:
-
Transactional(noRollbackFor=NullPointerException.class)
-
-
表示发生NullPointerException或该异常的子类异常不回滚,其它异常则回滚。
@Service("i2")
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class)
public void save(Account act) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(act);
//模拟异常
if (1 == 1) {
//throw new RuntimeException();
//throw new IOException();
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
}事务的全注解式开发
-
编写一个类来代替配置文件:
Spring6Config
package com.hhb.bank;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration//代替spring.xml配置文件,在这个类当中完成配置
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启事务注解
@ComponentScan("com.hhb.bank")//组件扫描
public class Spring6Config {
//Spring框架,看到这个@Bean注解后,会调用这个被标注的方法,这个方法的返回值是一个java对象,这个java对象会自动纳入IoC容器管理
//返回对象就是Spring容器当中的一个Bean,并且这个bean的名字是dataSource
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DruidDataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("030522");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {//Spring在调用这个方法的时候会自动给我们传递过来一个dataSource对象。
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean(name = "txManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager txManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
txManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return txManager;
}
}测试
@Test
public void testNoXML(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
accountService.transfer("act001","act002",10000.0);
System.out.println("转账成功");
}声明式事务之XML实现方式
-
配置步骤:
-
第一步:配置事务管理器
-
第二步:配置通知
-
第三步:配置切面
-
-
记得添加aspectj的依赖:
<!--aspectj依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>-
Spring配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hhb.bank"/>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="030522"/>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置通知,具体的增强代码-->
<!--注意:在通知当中要关联事务管理器-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<!--配置通知的相关属性-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--之前所讲的所有事务属性都可以在以下标签中配置-->
<tx:method name="transfer" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Throwable"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--切点-->
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* com.hhb.bank.service..*(..))"/>
<!--切面=切点+通知-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
-
将AccountServiceImpl类上的@Transactional注解删除。
-
测试